Some enterprises, taking into account the specifics of their activities, organize their work on schedules different from the usual ones (five days with two days off), and work during the working week, providing employees with days off on a sliding schedule.
When introducing such an option into an organization, an employer must clearly understand: what is a staggered schedule? How to calculate a sliding schedule and, in turn, what is the difference between a shift schedule and a flexible one? When determining a sliding work schedule for an enterprise according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (we will give an example a little later), the employer is obliged to strictly observe many nuances to prevent violations of the law.
What is a sliding work schedule according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation practically does not give a direct answer to the question of what a sliding work schedule means. He only mentions in the text of Art. 100, which defines a number of working modes, the need for the employer to provide (as one of the options) working hours on a staggered schedule and days off on a staggered schedule.
Organization of activities in this format also includes:
- Art. 101 - regarding irregular days of work;
- Art. 102 - regarding the organization of flexible working hours;
- Art. 103 - regarding the shift schedule;
- Art. 104 - in terms of recording employee working hours;
- Art. 105 - regarding information about the permissible redistribution of work time.
However, the ability to work on a flexible schedule is a popular way of organizing work among employers. Weekends with a staggered work schedule are not fixed; the situation is similar with work shifts.
The number of days off for a staggered schedule varies, but the most popular work schedule for a staggered schedule (sample below) is a staggered work week in the 2/2 format (alternating two working days with two days off).
Thus, labor legislation, answering the question of what a sliding work schedule means, is actually based on the summarized accounting of work time, which is regulated by Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with a number of restrictions.
Sample of filling out an employment contract with a flexible work schedule
- Period of transition to flexible working hours, start date and end date, if known.
- List of positions (full name) of employees for whom a flexible time regime will be established.
- A full description of the established flexible working time regime(s).
Please note => For individual maternity benefits
An example of a flexible work schedule: an employee is given a five-day work week with two fixed days off, but he must always be present at work only from 10-00 to 17-00, and can work the remaining two hours either from 8-00 to 10-00, either from 17-00 to 19-00 hours, or divide them between these two periods.
Why is it needed?
What is a flexible work schedule for an employer and what are its advantages? In what cases is a sliding schedule established? Working according to a schedule, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, allows you to optimize the use of the organization’s personnel potential in conditions of its insufficiency and the lack of economic feasibility to use a shift and flexible schedule (what is the difference between these modes - we will consider further).
Answers to the questions of how to understand a staggered schedule, whether it is allowed to refuse a staggered schedule, how days off are provided on a staggered schedule, and how days off are paid on a staggered schedule, appear after realizing that a staggered work schedule is how and what its feasibility is.
This mode is applied if the enterprise is unable (or is not practical for it) to establish a standard 5/2 mode or work in a shift format. Let us consider, as an example, areas of activity in which such a regime is regularly used:
- Sales network. For most stores, it doesn't make sense to set a shift schedule, but it makes sense to not set days off when the work schedule is staggered. The length of the working day, as well as the standard hours, with a 2/2 sliding schedule, as a rule, exceeds 8 hours (as with normal work in the five days and two days off schedule). The schedule is most suitable for this type of activity. You just need to decide how to create a rotating work schedule for a specific institution.
- Security systems. The algorithm for organizing the activities of such enterprises is identical to sales networks. In the process of work, the institution is obliged to ensure security, but security during the day is not always impractical.
- Communication organizations, consultants. The company's activities are structured in such a way that during the day it is necessary to maintain the uninterrupted operation of the consultation line and the presence of an employee to answer phone calls. The work schedule seven days a week is most optimal.
Thus, the advisability of using a sliding format is determined by the inability to apply other labor algorithms in the institution. But organizing work in a similar form for the “manager” category is often not relevant.
The correct algorithm for calculating wages for a shift work schedule - formulas, example
The scope of activity of some institutions has features in which it is possible to ensure the smooth operation of the enterprise only by establishing a shift schedule.
The use of this mode will improve the efficiency of operation of technical equipment and ensure uninterrupted operation of the company.
How should staff salaries be calculated?
The article describes typical situations. To solve your problem , write to our consultant or call for free:
+7 — Moscow — CALL
+7 — St. Petersburg — CALL
+8 ext.849 — Other regions — CALL
It's fast and free!
Definition
A shift work schedule is the implementation of professional activities in 2 or more shifts. The definition of this concept is present in Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with the information specified in the regulatory act, this technology is used in cases where the total length of the working day exceeds the norm.
Features of the labor process and wage calculation technology must be reflected in the collective and labor agreement.
The shift schedule can be of several types:
- day and night shifts. After working at night, the employee is given a day to rest and 1 more day off;
- a shift consisting of 2 working days (two after two). The duration of each of them is 11 hours. Night work is not provided;
- three days later. During the day, the employee performs his job duties. At the end of 24 working hours, he is given a day off, which lasts 3 days.
The first type is most often used in organizations whose work does not involve production stops. These include various factories, factories and other enterprises of a similar type.
The second type of shift schedule is used in cases where there is no need to work at night. At the same time, it must be ensured that there is no break in work shifts.
Dispatchers, salespeople, administrators, etc. often work according to this schedule. Throughout the day, mostly employees of security companies and the Ministry of Emergency Situations work.
How to calculate salary?
When calculating wages for employees working in shifts, rules are applied that are unusual for a 5-day work week.
In this case, Saturday and Sunday can be considered both weekends and working days.
With a shift method, the total number of hours worked may exceed the maximum allowable value.
[2]
In this situation, planned overtime arises, for which it is necessary to calculate the salary at an increased rate.
It is important to take into account that when using the summarized working time recording technology, the number of hours worked overtime should not exceed 120. This rule is regulated by Article 120 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
To avoid misunderstandings and irregularities in salary calculations, at the end of the accounting period established by the company, it is necessary to reconcile the following indicators:
- the number of hours actually worked in accordance with the work schedule;
- number of working hours in the accounting period.
If, based on the results of calculations, the first indicator turns out to be higher than the second, the employer is obliged to make a recalculation, during which the employee must be paid for overtime work.
Example when working in two-by-two shifts
You can finally understand the technology of calculating wages during a shift schedule by considering an example.
The dispatcher of the Quadra company works on a shift schedule - 2/2 (two after two). Each working day has 11 working hours. Hourly rate - 250 rub. A month is used as an accounting period for calculating wages.
According to the schedule, the employee worked 165 hours during the month.
Salary at the tariff rate = 165 x 150 = 24,000.
At the same time there was processing, the duration of which was 5 hours. To calculate the number of working days in a month, you need to do the following:
Shifts worked = 165 / 11 = 15.
The resulting indicator is less than 2, therefore, overtime is paid at 1.5 times the rate.
Payment for processing = 250 x 5 x (1.5 - 1) = 625.
Final salary amount = 24,000 + 625 = 24,625 rubles.
How are weekends and holidays paid?
If an employee’s shift falls on a non-working holiday, payment for such time is carried out using the procedure established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
The tariff rate for wages should be increased at least 2 times.
This norm is regulated by Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If an employee works on Saturday or Sunday according to the shift schedule, wages for these days are calculated in the standard way.
[1]
The only exceptions are weekends established by the state.
The technology for using a shift work schedule is reflected in the Labor Legislation of the Russian Federation. A feature of this technique is the high probability of overwork.
All of them must be paid accordingly. At the same time, the amount of total annual overtime work should not exceed a certain indicator.
This technology for arranging working hours is used in situations where it is necessary to ensure the uninterrupted operation of the enterprise. Almost employees of all factories and other organizations of a similar nature work in shifts.
The procedure for calculating wages when working in shifts depends on the established wage system. Calculation rules must be documented - in a local act, an employment contract.
The article describes typical situations. To solve your problem , write to our consultant or call for free:
+7 — Moscow — CALL
+7 — St. Petersburg — CALL
+8 ext.849 — Other regions — CALL
Overtime calculation: calculator
Calculation of overtime hours based on salary is a special algorithm provided for by current labor legislation.
What work is considered performed in excess of the established norm is written in Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It also indicates in what cases personnel can be involved in such work, and who cannot be involved.
The calculation scheme is described in Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and our calculator was developed on its basis.
How to install
More detailed information about the staggered work schedule, including the employer’s algorithm for the schedule, for example, 2/2 for 12 hours, is given below.
The employer takes the following steps:
- Selects the period for recording work time (month, quarter, year), clarifies the hours of work (standards for using the 2/2 mode on a 12-hour scheme entail overtime for the employee due to the fact that a week of work will account for 42 working hours with the permitted maximum at 40. During the reporting period, additional days off should be provided for a specific employee).
- Sets the number of employees at one workplace.
- Determines the order of weekends and working days.
- Checks whether the category of employees belongs to one that has special requirements of the legislator (for example, indicating the start and end times of the work day, rest and meal breaks, alternating days of work and rest).
- Issues a local act regulating the operation of the enterprise (there is no prescribed form of the document, all employees should be familiarized with it, and the accounting period should be indicated - no more than a year and no less than a week).
- Provides for work and rest time in the PVTR or employment contract (in this version, the schedule reflects the employee’s full name and the change of weekends and working days) in the absence of special requirements.
- Signs an employment agreement with the employee indicating the fact that the mentioned regime has been determined in relation to him (introduces information about the schedule into the relevant part of the document - work and rest schedule) upon hiring or signs an additional agreement if the need arose during the work process.
- Develops a schedule (you need to take a month and distribute working days and weekends in a 2/2 format).
- Assigns weekends as scheduled.
Summarized working time tracking
The schedule is drawn up by the personnel officer or manager, taking into account the wishes of the employee. Set the following parameters:
- The period of time during which an employee is required to remain at the workplace. For example, from 11.00 to 15.00.
- Variable time when the employee determines the beginning and end of the working day at his own discretion. For example, the day starts at 9.00. until 11.00. The employee must report to work before 11 am. Missed hours must be worked within the established accounting period.
- Time for rest/lunch. According to Art. 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee has the right to a snack for 30–60 minutes.
To record time worked, the T-13 form (timesheet) is used. This document is filled out by the personnel officer or department head. If an employee is transferred to a flexible schedule, then a summary record of his working hours is kept.
The unified form of document T-13 allows you to take into account the working time of all employees
How to keep records when working in shifts:
- The employee must work a specified number of hours during the accounting period. If there was overtime during the current week, then it can be compensated by the weekend next week.
- It is recommended to set the longest accounting period so as not to infringe/take away working hours from workers and not to create a large number of overtime hours. The accounting time can be assigned from a month to a year.
- Employee overtime is paid at an increased rate in accordance with the Labor Code.
- For some types of work, restrictions on the accounting period are established. For example, 1 month for drivers.
In order to avoid violating the legal requirements when drawing up a work schedule regarding compliance with working hours for the accounting period, the duration of inter-shift and weekly continuous rest, and also so that the number of working hours provided for in the schedule does not lead to a decrease in the employee’s earnings due to shortcomings, it is better to establish as much as possible long accounting period.
SHKLOVETS Ivan Ivanovich, Rostrud
To understand how many employees are required per workplace, consider the following rules:
- For each category, the norm of working hours for the accounting period is established (24, 35, 36 or 40 hours per week). These standards are displayed in the production calendar. The standard cannot be exceeded.
- Time tracking for newly hired workers begins from the current date, i.e. the calculation is carried out for part of the accounting period.
- The production calendar already takes into account holidays and non-working days. There is no need to reduce the standard hours if a holiday falls on an employee’s working day.
- If annual leave falls within the accounting period, then the standard hours should be reduced by its duration.
The number of working days for the current period, the duration of the working day, and the norms of the production calendar are taken into account
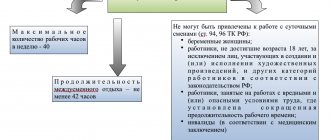
When allocating days off, it is important to take into account that each employee has the right to rest for 42 hours continuously each week. Employees are notified of the schedule in advance. The familiarization period is fixed in the local regulatory act of the enterprise.
Features of charts
The employer needs to understand the difference between a shift schedule and a sliding schedule.
Since employers clarify how a shift schedule differs from a flexible one, and how a sliding schedule differs from a flexible one, it is necessary to distinguish all these forms, although they also have common features:
| Sliding | Removable |
| General Features | |
| The use of summarized accounting of work time, that is, remuneration for a sliding work schedule, as well as the answer to the question of how a sliding work schedule is paid, presupposes the use of an identical regulatory framework. | |
| Identical restrictions (the principle of prohibition of establishing work volumes above the standards). | |
| Ability to define a work schedule in a non-standard format. | |
| Differences | |
| One-sidedness in decision making. | |
| The employee’s agreement with the conditions stipulated in the employment agreement, and in the future the possibility of changing them by the employer within the framework of legally established methods (for example, issuing an order on a staggered work schedule). | The existence of an agreement between the employee and the employer in the event of a need to change the schedule (either party initiates the change). |
| Using the mode | |
| To establish a different regime from the usual for line employees. | When ensuring work activity in a continuous or round-the-clock format, the introduction of a different type of regime is complicated by the type of activity and the nature of production. |
| There is no obligation to report to work on a previously determined shift. | Returning to work on a previously determined shift. |
| Shifts assigned at night are not necessarily shortened by one hour (for example, an employee is hired exclusively to work at night). | Shifts assigned at night are necessarily shorter by one hour. |
| Employees are not required to be notified of the fact of introduction no later than a month before the introduction. | Employees are required to be notified of the fact of introduction no later than a month before introduction. |
| Fixation method | |
| Allows you to plan in advance the employee’s work algorithm during the accounting period. | Allows you to record work time as a fait accompli, since this format is subject to frequent adjustments (compared to sliding). Often it does not involve the use of summarized accounting of work time (as a rule, the calculation comes from the shifts actually worked). |
Flexible work schedule
If, when applying for a job, the applicant’s working hours differ from the general rules in force at the employer, then this condition is fixed in the employment contract and is also reflected in the employment order. In the line “Conditions, nature of work” it is indicated: “Flexible working hours, accounting period.” In addition, remember the maximum total working time per day (no more than 10 hours) and the time spent in the institution from the beginning to the end of work (shift), including unpaid breaks in it (no more than 12 hours) (clause 3.1 of the Resolution ).
21 Dec 2021 marketur 170
Share this post
Related Posts
Limitations of using a rolling schedule
The legislator has defined a number of restrictions on the use of operating modes, which also apply to a staggered schedule. It means that:
- the employee cannot be overworked beyond a certain standard (for example, more than 40 working hours per week);
- weekends and holidays established by the legislator are subject to accounting for a staggered work schedule;
- when the legislator determines for a certain category of employees or types of activities restrictions in the form of a shorter duration in hours, this feature is taken into account when creating and maintaining records, and accordingly, payment is adjusted for a sliding work schedule;
- You should respect the right of employees to rest, that is, understand what a weekend schedule is and whether it is possible to provide time off for a sliding schedule. An employee has the right to work within the established limits and have at least one break for continuous rest of 42 hours during the working week on a rotating schedule, and if the duration of one shift exceeds an interval of 4 hours, have a lunch break.
Additional agreement to the employment contract work schedule 2 through 2
Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If, due to the presence of vacancies in the organization, the employer needs additional labor, then labor legislation allows the use of workers on a part-time basis. In this case, one should be guided by the provisions provided for in Art. 98 and ch. 44 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Part-time work is understood as the performance by an employee of other regular paid work under the terms of an employment contract during free time from the main job with payment in proportion to the time worked with restrictions established by labor legislation. The introduction of summarized recording of working hours in the absence of a sufficient number of employees is unlikely to help solve the problem filling vacant places. This is due, for example, to the fact that shift schedules will have to be developed and approved taking into account normal working hours (i.e.
Financial issues The new provision will be in effect from the moment the additional agreement is signed. Accordingly, all calculations under the amended rule will be made from this date. Important nuances Remember that p Reflection in the time sheet The relevant changes must also be reflected in the work period sheet in order to determine how to correctly calculate wages.
Sample order to transfer an employee to a shift work schedule
The document is signed by the head of the company. It is also necessary to familiarize employees with its provisions. Based on the order, new labor regulations (or additional agreements to employment contracts) are subsequently drawn up, which fix the changed work schedule.
5. Provide employees with annual paid leave of _________________ calendar days, consisting of a basic leave of _____________________ (at least 28) calendar days; additionally _________ calendar days.