Is it necessary to issue an order?
The need to fulfill or exceed the production plan does not always fit into the framework of working hours. In this case, there is a need to organize work beyond the normal duration of the shift, but overtime work according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has restrictions on attracting personnel to work outside the limits of the normal working day. In addition to its own restrictions established by Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, involvement in such work requires additional payment for overtime hours, which is established by Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not indicate that registration of overtime work requires the issuance of a separate order from the manager. The main requirement is the employee’s written consent to work beyond the norm.
An exception is the cases listed in Part 3 of Art. 99 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employee’s consent may not be asked if:
- there is a need to prevent an accident or natural disaster;
- engage an employee to eliminate a breakdown that interferes with the enterprise’s water supply, lighting, communications, transport and other communications;
- An emergency arose, martial law was introduced, etc.
Despite the fact that in the above cases the employee’s written consent to overtime work is not necessary, overtime must be formalized and paid for.
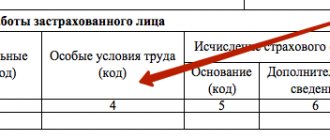
For payment, overtime time in the time sheet is indicated by the code “C” or “04”. The basis for paying overtime hours is the timesheet.
The following categories of employees have the right to refuse overtime work:
- disabled people;
- women raising children under three years of age;
- a parent raising a child under five years of age alone;
- citizens raising disabled children;
- employees caring for a sick relative.
Such employees must be informed in writing of the possibility of refusing overtime work. This information can be indicated in the order. Managers of organizations should be aware that it is prohibited to involve pregnant employees and minors in extracurricular work.
How is an employee’s overtime work recorded and processed?
The time that an employee worked overtime must be reflected in the time sheet (according to forms T-12, T-13, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of 2004 No. 1).
It is the employer's responsibility to ensure that hours of overtime work are accurately recorded. Overtime hours from the time sheet must be indicated with the digital value “04” and next to it the number of overtime hours.
For some categories of workers, there is a special procedure for attracting overtime work. In relation to these employees, the employer is obliged to :
- initially obtain the employee’s written consent;
- make sure there are no contraindications;
- inform the employee, against signature, of the possibility of refusing to perform overtime tasks.
Based on Art. 259, 264 Labor Code such employees include :
- disabled people;
- women with children under 3 years of age;
- fathers and mothers who raise children alone under the age of 5;
- workers with disabled children;
- workers who care for sick family members;
- guardians and trustees of minors.
In most cases, the employer must obtain consent from the employee to work overtime . By order of the employer, an employee without consent may be involved in overtime work on the basis of Art. 99 TK:
- to prevent a disaster or in case of a production accident;
- to eliminate the consequences of an industrial accident;
- to eliminate circumstances when centralized systems, water, heat, and gas supply systems ceased to function;
- when introducing a state of emergency or martial law in emergency cases, if this poses a threat to the population (fires, floods, etc.).
To engage in work on the specified grounds, the consent of the employee and the trade union is not required, and if he refuses to perform the work, a corresponding act is drawn up.
In other situations, involvement in overtime work is allowed in the following situations (also on the basis of Article 99 of the Labor Code):
- If it is necessary to complete work that has begun, which, due to an unexpected delay due to technical conditions, cannot be completed during the normal duration of the working day.
- When performing temporary work on the repair and restoration of mechanisms or structures in cases where their malfunction can cause the cessation of work for many employees.
- When performing work in the absence of a replacement employee, if such work does not allow breaks.
Also, for some employees, an additional stage is provided : the employer must familiarize certain categories of employees with the opportunity to refuse such work. Decisions regarding overtime work must take into account the views of the union.
After receiving consent from the employee to engage him in overtime work, the employer issues a corresponding order. This order does not have a unified format and must contain an indication of the reason for engaging the employee overtime, the start date of work, the employee’s full name, his position and details of the document with the employee’s consent to be hired to work.
If there is an amount of additional overtime pay in a collective agreement or local document, this amount must be specified in the order. The amount is determined by agreement of the parties.
If the employee has decided on the form of compensation, then this fact must be stated in the order. Such compensation may be: increased wages or additional rest time at the request of the employee under Art. 152 TK.
The employee’s order must be familiarized with a personal signature . The law does not oblige the employer to provide rest to the employee at a time that is preferable to him, but the parties usually resolve this issue by agreement.
Violation of the procedure for involving an employee in overtime work threatens the employer with liability, according to Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO).
The fine under this article is 30-50 thousand rubles, otherwise the official who committed the violation will be fined 1-5 thousand rubles.
How much and how are overtime hours paid?
Organizational managers are often interested in how much to pay for overtime worked by an employee? For greater clarity, we have placed a table:
| Period of extracurricular work | Overtime pay |
| First 2 hours | Must be paid at least one and a half times the amount |
| Subsequent hours | At least double the size |
The amount of payment for overtime work indicated in the table is considered minimal, that is, the employer does not have the right to pay less. But the amount of payment for work above the norm can be increased by the head of the enterprise. Information about this should be indicated in the company’s local act or employment contract with the employee.
If the employee does not mind, the organization can compensate him for the time worked above the norm, not in cash, but with additional days off. The duration of the non-working period cannot be less than the time spent on work. But such overtime work is paid at a single rate.
If processing is the employee’s own initiative, then such work is not extracurricular and is not paid.
Payment order
The manager must record a certain payment in the internal documents of the enterprise. Overtime work is subject to greater payment:
- One and a half accruals are typical for the initial two hours.
- All other times are subject to double payment.
The employer may be confused with the definitions as accruals progress. But, according to the law, you just need to adhere to the following rules:
- Piece workers are required to be paid time and a half for the first hours, and all others are paid double.
- If an employee works at daily rates, then payment is made by calculating one and a half daily rate for the initial hours, and the rest of the time at double the daily rate.
- If the worker works on a salary, then he is paid one and a half times the rate in addition to the salary for the initial hours. All other time is paid at double hourly rate.
Whether overtime work can be compensated by additional rest , see the video:
What methods of recording working hours exist?
Choosing a method for recording working time is a concern for managers. Much in this matter depends on the scope of the organization. The chosen type of accounting must be specified by the director of the company in the internal regulations. The following types of accounting are distinguished:
- daily;
- Monday;
- summarized.
With summarized accounting, there may be a deviation in the duration of working hours during the day, week or month. The main requirement: at the end of the accounting period, the employee must have worked a number of hours in accordance with the approved norm.
The standard working day is 8 hours. With a five-day working week, the working time limit reaches 40 hours. But there are exceptions. If a person works a shift, his working day can last 12 hours. For some categories of employees, a shortened working day may be established. In this case, their working week is 24-36 hours. You can find out how much time a worker with a normal or reduced working day must work per month, quarter and year using the production calendar. Using a regular calculator, it will not be difficult to calculate recycling.
In the case of daily accounting, overtime or shortfalls are recorded within one day. Labor payment is calculated for each day of processing separately. And overtime (payment) is given at the end of the month.
Overtime pay: example
Let's look at a specific example of how to calculate overtime (2020). Manager Barulin V.M. worked 3 hours after hours on 03/03/2019 and 4 hours on 03/10/2019. His hourly earnings are 140 rubles. The first two hours of each overtime must be paid at one and a half times the rate. The rest of the time is double time. The amount will be:
March 3 = (140 rub. × 1.5 × 2 hours) + (140 rub. × 2 × 1 hour) = 700 rub.
March 10 = (140 rubles × 1.5 × 2 hours) + (140 rubles × 2 × 2 hours) = 980 rubles.
Barulin V.M. 1680 rubles will be credited. for extra work.
When recording working hours in aggregate, overtime work (payment) should be assessed as follows: time worked outside of normal hours is calculated based on the results of the accounting period. The first two hours of work are paid at least time and a half. The rest of the time is double time.
Overtime concept
– Overtime work allows the employee to count on additional guarantees and compensation. The main distinctive features of overtime work are contained in Part 1 of Art. 99 Labor Code (LC) :
- It is carried out at the initiative of the employer.
- It goes beyond the length of the working day and the daily work (shift) of the employee.
If an employee is late at work on his own initiative, then such work is not paid overtime. This position is contained, for example, in the Letter of Rostrud of 2008 No. 658-6-0. Also, work that was performed during the working day is not considered overtime.
When accounting for working hours in aggregate, overtime is considered to be work that is set in excess of the normal number of hours during the working period. The employer needs to define the accounting period in the internal regulations. This period can be a month, a quarter or another period of up to a year. This is necessary for correct calculations of hours worked overtime under Art. 104 TK.
Involvement in overtime work should not be systematic : it should be exceptional, occurring sporadically in certain cases (based on Rostrud letter No. 1316-6-1 of 2008).
The normal working week is 40 hours (based on Article 91 of the Labor Code). The duration of overtime work cannot exceed 4 hours for an employee for 2 consecutive days or 120 hours annually (based on Article 99 of the Labor Code).
For example, a sales manager works 5 days a week from 9.00 to 18.00. The employer asked him to stay late and urgently make a report. The employee had to stay until 21.00. In this case, the time from 18.00 to 21.00 will be considered overtime work.
For some employees, reduced working hours are provided , which is normal (based on Article 92 of the Labor Code). These include, for example:
- For minor workers – 24-35 hours weekly depending on age.
- Disabled people of groups 1-2 – no more than 35 hours.
- Workers with hazardous working conditions of 3-4 degrees or dangerous conditions - no more than 36 hours.
- Women working in the Far North (under Article 320 of the Labor Code).
- Teachers (based on Article 333 of the Labor Code).
- Health workers (Article 350 of the Labor Code).
For the categories listed above, overtime may be considered work that exceeds reduced working hours (daily work or shift).
The rules regarding overtime work apply to both employees at the main place of work and part-time workers.
Work on a weekend will not be considered overtime . This is a special case of processing and it is regulated by Art. 153 TK. If an employee has worked a monthly standard of working time, then his work on a day off is paid at least double the rate above the salary (based on Part 1 of Article 153 of the Labor Code). Work that is performed on non-working days is not overtime.
Working on non-working holidays also does not apply to overtime.
In some cases, it is illegal to work overtime. Pregnant women and persons under 18 years of age are not allowed to work overtime (based on Article 99 of the Labor Code).
But there are exceptions to these categories: creative workers, athletes, employees during the period of a student agreement, and other employees.
So, remember that the key distinguishing features of overtime work are:
- leader's initiative;
- employee consent to processing;
- the urgent nature of such work.
How is overtime paid on a salary basis?
In Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation there is no information about what amount should be taken into account. Therefore, many employers are wondering whether to take into account only salary or average income along with bonuses and allowances. When calculating overtime, managers often take double the tariff as a minimum. Incentive and compensation payments are not taken into account. Overtime work is paid inclusive of bonus payments only if the employer has established such a procedure.
If such a procedure is not established, then the cost of an hour is equal to the salary divided by the number of standard hours in the accounting month according to the production calendar. If the period of summarized accounting is more than one month, it is necessary to determine the average cost of an hour for the entire period (for example, salary income for a quarter divided by the standard time for the specified quarter). Overtime calculations must be made from the resulting cost per hour.
Can't attract
As a general rule, involvement in overtime work is possible only with the consent of the employee. Part 1 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes some exceptional cases when such consent is not required - disaster prevention, state of emergency, etc. But even in these cases, some categories of workers have the right to refuse (disabled people, single parents and a number of others).
Furthermore, in accordance with Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it is prohibited to engage in overtime work even with their consent:
- pregnant women;
- employees who have medical conditions that prevent them from working overtime;
- minor employees (with some exceptions).
For these categories of workers, work beyond the established working hours is prohibited, and, accordingly, compensation for it is not established.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace legal advice. If you have any questions, please contact an attorney.
What are the rules for paying overtime on a shift schedule?
Let's look at how overtime is paid during a shift work schedule. If a worker works in shifts, his salary can be calculated using both hourly tariff rates and on a salary basis.
In the first case, overtime is calculated as follows: the number of hours worked during a certain period is multiplied by the established rate.
If the organization uses a salary system, then every month the employee is transferred the same amount of remuneration.
How is overtime pay for piece workers calculated?
Citizens who work piecework are paid for each part produced. Overtime pay for piece workers depends on how many parts they produce outside of normal working hours, as well as on the length of overtime work. Cash is paid without taking into account one and a half or double premium.
Example: Kurochkina A.N. works at the factory. She works piecework. For each part made, she is paid 400 rubles. On 03/09/2019 she worked 4 hours outside of school hours, producing 5 parts during this time: 2 pcs. - for the first 2 hours and 3 pcs. — for the remaining 2 hours. Payment depends on the number of parts produced and on the time worked above the norm. Therefore the calculation is:
(400 rub. × 1.5 × 2 pcs.) + (400 rub. × 2 × 3 pcs.) = 1200 rubles + 2400 rubles = 3600 rubles.