In the Labor Code there is no concept of “dismissal under an article,” since any of the dismissals occurs in accordance with the norms of a particular article of the Labor Code. This concept usually includes a dismissal that will have negative consequences for the employee and make it difficult for him to continue to be employed.
Typically, dismissal occurs at the initiative of the employee (formally) or by agreement of both parties. In such cases, the employee may receive some bonuses, guarantees, and compensation. The employer can be sure that a lawsuit will not be filed against him .
Article 81 of the Labor Code describes cases when an employer can dismiss an employee on his own initiative:
- Upon liquidation of an enterprise.
- When reducing numbers or staff.
- When the owner of the property changes, the new owner has the right to dismiss the director and his deputies, as well as the chief accountant.
- If the employee does not correspond to the position held based on the results of certification.
- For failure to fulfill official duties (repeatedly), if there is a disciplinary sanction.
- For a single gross violation.
Most often, it is the last three points that are called dismissal “under article”. Both employees and employers prefer to avoid this type of termination of employment.
At first, this may have a negative impact on future employment, and it is important for employers to comply with all formalities so that the employee cannot sue him for wrongful dismissal.
Reasons
Can they be fired under the article?
All grounds for termination of employment relations are listed in Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Among them, a special place is occupied by clause 4, which states that the initiator of dismissal is the employer.
The grounds for his adoption of such a decision are set out in Article 71 and Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Why you can be fired from your job:
- failure to pass the test;
- liquidation of an employer-legal entity or individual entrepreneur;
- staff reduction;
- unsatisfactory certification result, which revealed the employee’s inadequacy for his position;
- transfer of the company to another owner;
- systematic violation of labor discipline by an employee;
- a one-time gross disciplinary violation;
- loss of trust in the financially responsible employee;
- immoral offense of a teacher or educator;
- violation of discipline by the head of the organization;
- submission of false documents when applying for a job, etc.
Most of the reasons given for terminating an employment contract with an employee are related to the commission of unlawful acts.
Dismissal in this situation acts as the most severe type of disciplinary action.
Who can't be fired for reprimanding?
After reprimands, all beneficiaries, except pregnant women, can be fired without restrictions for subsequent violations. This category cannot be expelled under any circumstances (except for the liquidation of an organization), even if there are violations (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Important
A pregnant woman can be reprimanded and suspended from work, but she cannot be fired.
You cannot fire citizens while they are on vacation or sick leave. A reprimand cannot be given during these periods either. But some actions for an internal investigation can be carried out, for example, sending a letter with a proposal to provide an explanatory statement. The employee will then have the right to give an answer within 2 days not during sick leave, but after returning to work.
The legislative framework
Labor legislation provides for only three types of punishments for disciplinary offenses (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The mildest is a reprimand, then a reprimand and, finally, dismissal.
The main condition for the application of any penalty is a violation of labor discipline committed by an employee in the absence of good reasons.
For each offense there is only one punishment, commensurate with the consequences of the violation.
Dismissal as a disciplinary measure is possible only if there is one of the grounds listed in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is equally important to comply with the procedure for bringing to disciplinary liability prescribed by Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In case of violation of these requirements, dismissal will be considered illegal.
Myth No. 2. Failure to fulfill job duties
Grounds: clause 5 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: “Repeated failure by an employee to fulfill labor duties without good reason, if he has a disciplinary sanction.”
How this happens: failure to comply is repeated, without good reason, and if they threaten to dismiss you under the article, it means that at least one disciplinary sanction has already been imposed on the employee. Otherwise, this is a violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a disciplinary offense is the failure or improper performance by an employee, through his fault, of the labor duties assigned to him. Disciplinary action is allowed only in the form of:
- comments;
- reprimand;
- dismissal for appropriate reasons.
However, the penalty must correspond to the gravity of the offense. You cannot fire an employee for a minor offense. Before applying disciplinary action, in accordance with Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to request a written explanation from the employee. If after two working days the specified explanation is not provided, a report is drawn up. Disciplinary sanctions are applied no later than one month from the date of discovery of the misconduct, not counting the time:
- employee illness;
- being on vacation;
- necessary to take into account the opinion of the representative body of workers.
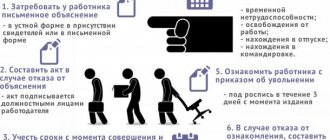
Thus, a disciplinary sanction may be imposed within a month after the discovery of the misconduct. A disciplinary sanction is formalized by an order (instruction). The citizen is required to sign, confirming that he has read the order, within three working days from the date of its publication, not counting the time of his absence from work. If he refuses to familiarize himself with the order (instruction), then an act is drawn up.
The disciplinary sanction is appealed by the employee to the state labor inspectorate and/or bodies for the consideration of individual labor disputes.
Let's summarize: in order to dismiss a citizen on the basis of clause 5 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, failure to fulfill his duties must be:
- repeated;
- without good reason.
If there are valid reasons, the employee must put them in writing. It is imperative to clarify whether he already has an appropriately formalized disciplinary sanction. Advice on how to avoid being dismissed under the article: do not commit violations of discipline.
Advice to the dismissing party
To avoid all sorts of troubles associated with the dismissal initiative, we recommend that you follow the following practice-tested rules.
- Accurately and strictly follow the dismissal procedure specific to each of the dismissal articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- comply with prior notice periods;
- do not neglect written confirmation of the facts of misconduct;
- take care in a timely manner to ensure that the employee signs for review of all types of dismissal documentation, and in case of refusal to sign, to sign the relevant document;
- pay on time and in full the funds due to the employee upon leaving;
- promptly return his work book with records of dismissal made in accordance with the protocol.
- If possible, use the wording “at your own request” when leaving. If the dismissed person committed an offense, such a reason indicated in the documents will not cast a shadow on his future reputation. For the employer, the advantage of this article is this. That it cannot be used to challenge the dismissal in court.
- If it is important for the employer to document the employee’s guilt upon dismissal, he should strictly follow the letter of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation when registering the dismissal.
- If we consider the judicial practice on challenging the grounds for termination of employment relations, the most problematic for the employer are the following articles of dismissal from work:
- for disclosing secrets protected by law (clause B, clause 6, article 81 of the Labor Code);
- for a decision made by a managerial employee without justification, which resulted in a loss, unlawful use or violation of the safety of assets (clause 9 of Article 81 of the Labor Code).
This is also important to know:
Dismissal of a financially responsible person at his own request
These grounds may be subject to ambiguity, making it easier for the employee to prove wrongful dismissal. This creates additional problems for the employer, since in the event of an ambiguous interpretation, the court usually gives preference to the “weaker” party, that is, the staff representative.
Other unpleasant reasons for dismissal
What other reasons should there be for dismissal?
- The appearance of an employee at work (at his workplace or on the territory of the employing organization or facility where, on behalf of the employer, the employee performs a labor function) in a state of alcohol, narcotic or other toxic intoxication (clause “b”, paragraph 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) ). But even if there is evidence, is it easy to fire an employee for drunkenness? It’s quite difficult: you need to find witnesses, draw up a report, invite the offender to undergo a medical examination, remove him from work and then prepare a traditional package of documents.
- Submission by an employee of forged documents when concluding an employment contract (Clause 11, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, commercial, official and other) that became known to an employee in connection with the performance of his job duties, including disclosure of personal data of another employee (clause “c” of paragraph 6 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A violation by an employee of labor safety requirements established by the labor safety commission or the labor safety commissioner, if this violation entailed serious consequences (work accident, breakdown, catastrophe) or knowingly created a real threat of such consequences (clause “e”, paragraph. 6, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Commitment by an employee performing educational functions of an immoral act incompatible with the continuation of work (clause 8 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Making an unfounded decision by the head of an organization (branch, representative office), his deputies and the chief accountant, which entailed a violation of the safety of property, its unlawful use or other damage to the property of the organization (clause 9 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A one-time gross violation by the head of an organization (branch, representative office) or his deputies of their labor duties (clause 10 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The Labor Code also stipulates that termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer occurs in other cases provided for in the agreement with the head of the organization and members of the company’s collegial executive body. It is no secret that sometimes there is no doubt whether it is profitable for an enterprise to fire an employee under an article - it is beneficial, and this happens to eliminate an objectionable person. Read the contract carefully before signing it!
Dismissal under article
Unfavorable consequences for the employee in the form of dismissal occur when one of the offenses listed in Part 1 of Art. 81 TK.
To apply punishment, a single violation of discipline or other offense is sufficient. Let's take a closer look at these reasons.
For absenteeism (absenteeism)
Most often, dismissal is used under the article for absenteeism. Such a basis is provided for in paragraphs. “a” clause 6, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Absenteeism is understood as a long-term, more than 4 hours, absence of an employee on site during working hours.
The law classifies such an offense as a gross violation of labor discipline and gives the employer the right to part with the employee who committed it.
However, if the absence is due to valid reasons, and the employee can confirm this, dismissal becomes impossible.
Failure to fulfill official duties
Failure to fulfill the duties prescribed by the employment contract can also lead to dismissal. But only if such a violation is systematic and has previously given rise to a more lenient disciplinary sanction against the employee.
The law does not establish a maximum number of violations of discipline followed by dismissal.
Therefore, the second offense may well be the last in this workplace.
Inconsistency with the position held
The certification results must prove that the employee occupies a position that does not correspond to his level of qualifications or professional and business qualities.
Its implementation is not regulated by labor legislation, therefore the procedure and timing are established by the employer himself.
This result may not be the employee’s fault, so an alternative solution is possible, for example, referral for advanced training.
Loss of trust
This basis for dismissal does not apply to all employees, but only to those who are directly related to the maintenance of material (monetary or physical) assets.
The reason for the loss of trust can only be culpable actions, that is, those committed with the clear intent to cause damage to the organization or due to negligence.
An internal investigation must prove the presence of guilt.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
For drunkenness
Alcohol intoxication, as well as that caused by other substances, can also be grounds for immediate dismissal. It is enough to appear on the territory of the organization drunk once. The time when this offense was committed does not matter; it may not be at work.
But for lawful dismissal, a medical examination of the employee must be carried out.
For theft
Theft or petty theft becomes a reason for parting with an employee if his guilt in committing such an offense is proven and there is a court verdict or a decision on administrative liability that has already entered into force.
Until such a procedural document is received, the employee is subject to the presumption of innocence.
Grounds for dismissal
Labor legislation protects the rights of employees very well, and sometimes, even if there are good reasons for dismissal, it is difficult to do this without getting a fine for it.
Therefore, employers are introducing a strict control system so that every violation is recorded and the employer has evidence of the legality of dismissal. It can be:
- system for marking the time of arrival at the workplace and departure. Usually the secretary or other responsible person has a journal in which the employee puts the date, time of arrival at work, and his signature. This can reveal both tardiness and absenteeism;
- system for setting task plans and reporting. The employee weekly or once a month submits to the manager a work plan for the upcoming period, and then, within the prescribed period, he must report on how much he managed to complete all the tasks.
- For each violation (absenteeism, tardiness) or failure to fulfill plans, an explanatory note is written. It is registered with the secretariat and stored. At the same time, the first time the manager can issue only a reprimand, and in case of repeated violations, dismiss.
- for gross violations, evidence may be a protocol or a doctor’s certificate (in case of alcohol intoxication), or a court decision (in case of embezzlement, theft).
All this will serve as written confirmation of the legality of the dismissal.
Procedure
Carrying out dismissal under this article requires the employer to perform a number of actions and draw up certain documents. Without this, termination of employment relations may be considered illegal and cancelled.
The general procedure for applying penalties and the timing of individual stages are given in Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Witnessing a fact
A written document – an act – is drawn up regarding an employee’s absence from the workplace, his appearance in a state of intoxication, an unsatisfactory result of certification, etc.
It records a certain fact, which is confirmed by the signatures of three witnesses. Usually this is the employee’s immediate supervisor, a personnel officer and one of the employees.
Warning
If the violation was committed for the first time, is minor, or the employee has valuable qualities for the organization, the employer may limit himself to an oral or written warning rather than a penalty.
The law does not require punishment.
However, in the future, this may become an obstacle to dismissal for a repeated violation that is not of a gross nature.
Explanatory
The employer is obliged to require the employee to explain in writing the reasons for the misconduct.
If, after two days, the explanatory note has not been received, then a report on the employee’s refusal is drawn up.
Without this, further application of the penalty becomes impossible. But the employee’s refusal to explain his behavior will not protect him from the application of penalties.
Order
A disciplinary sanction in the form of dismissal is formalized by order. It is published within three days from the date of receipt of the explanatory note or the drawing up of an act of refusal to write it. The employee gets acquainted with the order by signing it.
This is also important to know:
How to make calculations when dismissing an employee at his own request
Or another report is drawn up stating that the employee refused to do this. The absence of a signature does not prevent the application of the order.
Recording in labor
The reason for dismissal in the work book is stated in the same way as formulated in the Labor Code, indicating the specific paragraph of Part 1 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Like any record of dismissal, it is certified by the signature of a personnel officer and the seal of the organization.
The book is issued on the last working day and must be noted in a special journal.
How does dismissal occur at will and by agreement of the parties?
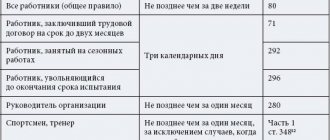
The employee's initiative in dismissal presupposes his free will to terminate the employment relationship. This occurs by submitting an application (see application for voluntary resignation) 2 weeks before the expected date of final separation from the employer. During the same period, he may change his mind and withdraw the application.
Often, company managers offer those at fault to resign of their own free will. The main argument in this case will be the preservation of his reputation in combination with threats if he refuses to dismiss the employee under the article for guilty actions. You need to understand that such actions carry serious risks of subsequent litigation for the employer. Subsequently, the employee may claim that psychological and moral pressure was exerted on him (see what to do if the employer forces you to resign).
If the employer wants to complete cooperation with the least risk, it is better to resort to dismissal by agreement of the parties. In this case, an additional agreement is concluded between the parties to the contract on the conditions for its termination, which, as a rule, provides for the payment of some monetary compensation to the employee (see dismissal by agreement of the parties with payment of compensation). This approach is considered the least risky in law enforcement practice.
What payments are due?
If an employee commits an offense for which he was fired, he is deprived of the right to part of the guarantees provided for by the Labor Code.
Thus, the employer is not obliged to pay severance pay and pay for the time necessary for further employment. Wages will not be accrued for absenteeism.
However, a number of payments are due upon dismissal to all employees, regardless of the reasons. This is a calculation, that is, a salary for the time actually worked, as well as compensation for vacation that was not used this year.
The employer is obliged to calculate and issue various types of compensation payments and allowances.
Which article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is supported by
Two articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulate the question of whether it is possible to apply dismissal as a disciplinary sanction.
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation mentions several reasons for dismissal on this occasion. It also indicates situations where removal from office for a single offense is possible.
Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that dismissal is a type of disciplinary sanction .
Consequences of such termination of employment
When an employee of an organization is fired for absenteeism, the most unpleasant thing is that an entry is made in his work book indicating:
- reason for dismissal - they write in plain text that there was absenteeism;
- basis - refer to the subparagraph and article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, a new employer can easily find out that an applicant for an open vacancy is a violator of discipline. Not every business owner would risk hiring a absentee because there is a common belief: people don't change. If a person has already violated labor discipline, then there is no guarantee that he will not do so in the future.
Advice: if the applicant’s work book says that he was fired for absenteeism, it is better to try to conduct your own check, to understand in detail the true reasons for the dismissal. The practice of labor relations in the Russian Federation is such that, often, dismissal for absenteeism is illegal, but has no consequences for the employer, due to the low level of legal literacy of the employee.
Employer's liability
If the termination of the employment contract was carried out legally, then the consequences can only be positive: the company gets rid of a careless employee who could have failed at any time and, in fact, failed. If dismissal for absenteeism was illegal, then the consequences may be different, but in both cases unpleasant:
- The employee has the right to be reinstated in his position based on a court decision. In this case, the employer will be obliged to pay compensation for forced absence and, depending on the requirements of the dismissed employee, some other money.
- An employer can be attracted under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for violation of legislation in the labor sphere. Finally, in some cases, criminal liability may apply. So, for example, if you fire a pregnant woman for absenteeism, then it is quite possible to become convicted under Art. 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, when dismissing a truant worker, the employer must be sure that he is doing absolutely legally. And to achieve such confidence it is necessary:
- so that the employee’s absence report is drawn up correctly and contains evidence that absenteeism occurred;
- so that the entire package of documents drawn up in the case in question is prepared;
- that there is no evidence of a valid reason for the employee’s absence from the workplace;
- so that the employee does not fall into the category of persons who cannot be fired for absenteeism or leaving the workplace during his shift.
You can go to court
You can protect your civil rights in court. In case of disagreement with your dismissal, the procedure for appeals is applied in accordance with Article 392 of the Civil Code. However, the former employee has 30 days to initiate proceedings.
Going to court
Within a month after the issuance of a work book with an “inconvenient” entry, it is necessary to file a claim against the former organization, in which it is necessary to indicate the demands for reinstatement and even payment of compensation for the period of forced non-fulfillment of labor duties. It is noted that the costs of paying for the proceedings are borne by the legal entity in which the dismissal was formalized.
During the trial, it will be established whether the administration of the enterprise really had grounds to dismiss the employee for guilty actions. If the contract was terminated under pressure from an employee or for other reasons that do not comply with the law, the company faces an administrative fine. In this case, the negligent organization will have to restore the citizen to his previous position and pay wages even if he was not actually engaged in labor activity.
The overwhelming majority of hearings end in a win for citizens, but at the same time, the employee, even if he is a former employee, should not lose his vigilance. HR departments of enterprises extremely rarely respect the rights of employees while protecting the economic interests of the administration.
In any case, each employee must keep with him a copy of the employment contract and all additional agreements. Often, in conversations with employees, personnel services use various tricks, provoking the wrong actions of citizens. This can happen even regardless of how right the employee is.
Step-by-step instructions: how to avoid contract termination
It is necessary to understand what the legislator means by this violation of labor discipline. Absenteeism occurs if:
- the employee was absent from the workplace for more than 4 hours in a row, or during the entire shift;
- it has not been proven that absence from work was caused by valid reasons.
Based on this, we can offer two options for getting out of an unpleasant situation:
- The employee under investigation must prove that he was not at work for less than 4 hours in a row. If this succeeds, then he will not be able to completely avoid disciplinary liability, but he will not be able to fire the person either.
- Prove that absence from work was caused by valid reasons.
Explanatory note form
How to write an explanatory note at work so as not to get fired? There is no set form, but the document should contain approximately the following information:
- FULL NAME. head of the organization, company name.
- FULL NAME. employee, his position.
- The word “explanatory” is approximately in the center of the page.
- A text that names and discloses valid reasons for absence from work.
- Date and signature of the person giving the explanation.
This is also important to know:
Characteristics from the place of work to the court: how to write correctly, document structure, sample
Such a document must be accompanied by documents confirming that there were valid reasons. For example, if an employee is involved in an accident, then you can attach a copy of the notification of the incident, a certificate prepared by the traffic police.
If the employee was summoned to court or, say, to the investigative authorities, then he must attach a summons, which indicates from what time to what time the person was in the specified authorities. This is all that concerns situations when there was, in fact, no absenteeism . But dismissal can also be avoided if the employee is guilty. Options:
- Contact the employer with a request to apply other disciplinary measures. How good is this option? It is relevant for those cases when you do not want to lose a convenient and profitable workplace. The reputation, in any case, will be damaged. But, on the other hand, you won’t need to look for another job. We emphasize that the application of other disciplinary measures is the right of the employer. He can leave a careless employee in the organization, or he can easily fire him.
- Ask to resign voluntarily. Here, too, everything depends on the manager’s view of the situation. Everyone understands that a record of absenteeism on a work record is a stain on one’s reputation. Therefore, if the employer is peaceful, then he may well accept the resignation letter at the employee’s initiative and prepare an appropriate order based on this paper. This will make it easier to find a new job. After all, there is nothing “criminal” about dismissal on your own.
From scratch or replacing the work book with a new form
One of the easiest ways to eliminate the problem with a negative record is to lose the work book. Its absence, of course, can confuse the administration of the enterprise. But be that as it may, the organization remains obligated to issue a new document upon employment. If the citizen is satisfied with the employer, then no problems with hiring will arise. The applicant will only have to pay for a new book, since it is a strict reporting form. But you can always purchase it yourself, since the book is on free sale.
The only thing that will make further work difficult is the inability to confirm your work experience. On the other hand, in modern enterprises the uniform length of service for calculating payments has been abolished. Each organization has its own profile period of work.
When there is an absolute need to confirm your work experience, you can always send a request to the places of work where the citizen had an employment relationship. In this way, you can always restore personal data, for example, before your upcoming retirement. Also, a duplicate work record book can be restored by contacting the employer who hired the citizen before the negligent organization.
What threatens
Dismissal “under article”, that is, for a fairly serious offense, can become a factor that negatively affects further employment.
Mention in the work book of such points of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, like 5 or 6, will cause natural caution among personnel officers. Most likely, he will be denied admission to a reputable position.
However, the employer should be extremely careful when dismissing an employee for a disciplinary offense.
The slightest deviation from the procedure prescribed by law is regarded as a violation of labor rights and may result in a fine from inspection bodies, for example, the State Labor Inspectorate.
The procedure for dismissing an employee under paragraph 3 of Article 81
Management can fire an employee if he is not suitable for his position, for example, he performs his duties improperly or does not have sufficient qualifications.
It is necessary to take into account the following pitfalls:
- prior to dismissal, other available vacancies must be offered}
- Most often, such termination of labor relations is carried out based on the results of certification}
- It is best if the necessary qualifications and other requirements for the position are set out in the job description.
Clause 3 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows you to dismiss an employee if he does not correspond to the position held
When offering other positions, it should be taken into account that they may be designed for lower qualifications, low salaries, and even involve moving to another area. Firstly, the boss is not obliged to offer a more qualified position; secondly, if the employee does not meet the lower qualifications, then what is the point of offering a higher one?
State-level certification is provided only for certain categories of workers, for example, for bosses, teachers, and Pension Fund employees. Of course, at the enterprise, on the initiative of the employer, certification can be carried out for other categories, but then it is necessary to draw up and approve the Regulations on certification. It is worth understanding that upon dismissal, if an employee wants to go to court, not only the results of certification will be considered - you need to be ready to provide other evidence of the employee’s inadequacy and, without fail, written evidence that he was offered a transfer to other positions.
Is it possible to challenge
Any decision of the employer, including dismissal under the article, can be challenged.
Due to the fact that the dismissed employee is no longer in an employment relationship with the employer, in order to protect his rights, he must go to court with an appropriate claim.
The consideration of labor disputes is adversarial in nature, which requires independent collection of evidence of one’s own innocence.
If it can be proven that there were violations on the part of the employer, the decision to dismiss will be cancelled.
This means that the employer is obliged:
- cancel the dismissal order;
- reinstate the employee to his previous position;
- make appropriate entries in the work book;
- pay for forced absence.
Is it possible to challenge dismissal for a reprimand?
Any types of disciplinary sanctions can be challenged by the state labor inspectorate and bodies authorized to consider individual labor disputes. There you need to write a statement in free form, where you outline the circumstances, your demands, evidence, and provide evidence of your innocence. The procedure is described in Chapter. 60 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Attention
The most fundamental way to appeal against an employer's actions is to file a lawsuit.
As a rule, this method is used after contacting the state labor inspectorate, if its order is not followed by the employer or if it does not satisfy the employee.
How to protect your rights in case of illegal dismissal? What to do and where to complain?
As a rule, the dismissal of an employee is formalized by order of the employer. The employer is obliged, on the basis of Part 2 of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, to familiarize the employee with the dismissal order against signature. If you need a copy of the order, then the employer, based on the same part of the law, is obliged to give you a copy of the dismissal order certified by his signature or seal. Based on Part 4 of Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on the day of dismissal, the employer is obliged to issue the employee a work book and, upon the employee’s written request, provide him with signed or sealed copies of work-related documents.
But what should an employee do after illegal dismissal?
Look, according to paragraph 1 of Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee has the right to go to court in disputes about dismissal within 1 month from the date of delivery of a copy of the dismissal order or work record book. Of course, you can limit yourself to a work book, but it’s still better to demand that they give you a certified copy of the dismissal order.
This is also important to know:
How to properly quit your job of your own free will: step-by-step instructions
As you can see, you have exactly 1 month, for this category of disputes the statute of limitations is only 1 month, this is due to the specifics of reinstatement at work. If you missed this deadline, it will be extremely difficult to restore it and only if you had valid reasons, for example, a serious illness or caring for a seriously ill loved one.
Many people make a mistake and file a complaint with the labor inspectorate; of course, after checking and identifying the fact of illegal dismissal, it will issue an order to eliminate the violation, and if the employer does not eliminate it, then he will be fined under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, but the matter may not come to that, although for legal entities the fine is quite substantial, from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles, which cannot be said about individual entrepreneurs; for such cases they are fined in amounts from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles. Therefore, for you, the labor inspectorate is a priority authority, since our statute of limitations is 30 days, and if you file a complaint with the labor inspectorate, then, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 12 of the law “On the procedure for considering appeals from citizens of the Russian Federation,” your appeal will be considered within a maximum 30 days, they may consider it on the 10th day, maybe on the 20th, or maybe on the 30th, and that you will sit and wait for the weather all this time, and then force the labor inspectorate to move, and in the meantime the statute of limitations will pass and it will not be possible to restore it.
We need to act immediately and the first thing we do is prepare a statement of claim to the court, demanding that you be reinstated in your job, since the dismissal was illegal. Even if the employer indicated the reason according to the Labor Code, this does not mean that your efforts are pointless; the employer will need to prove the fact of violation of labor discipline on your part. And since he will not have evidence, the court will be on your side.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
You, in turn, must also prepare well for the court, prepare your arguments, evidence, present your position, we indicate all this in the statement of claim, we also indicate which articles the employer violated.
Even if the employer fired you allegedly for absenteeism, he will have to prove that you were not at work without good reason for more than 4 hours in a row or throughout the entire working day; if he does not prove this, then the court will side with you.
It would be a good idea for you to bring witnesses who will confirm that you did not violate labor discipline, you were at the workplace. That is, the more evidence you have, the higher your chances in court. Witnesses can also confirm the fact of forced dismissal, that the employer put pressure on you and the decision to write a resignation letter of your own free will was not your initiative. If you are fired for absenteeism, then remember, perhaps on the day when you allegedly absented yourself, you signed some documents or did some kind of work documented with dates, all this can be claimed in court.
It is necessary to submit a statement of claim to the district court at your place of residence, that is, at the place of residence of the plaintiff in accordance with paragraph 6.3 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
When the court decides to reinstate the employee at work, it turns out that the court decision has now recognized that the employer violated the labor code and fired you illegally, which was the reason for forced absenteeism.
According to Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has an obligation to compensate the employee for the earnings he did not receive in all cases when the employee was illegally deprived of the opportunity to work due to the employer’s fault, and the employer has an obligation to compensate the employee for the earnings he did not receive as a result of forced absence in the event of the employee’s illegal removal from work. That is, if you were illegally fired and then reinstated, then the employer pays you for all the days of forced absence, about which a corresponding order is drawn up, which you and the employer must sign.
Also, if the court decision was in your favor and the court ordered the employer to reinstate you at work, then the employer issues an order to reinstate you at work and then makes an entry in your work book about reinstating you at work. Make sure that the employer indicates in the work book that the entry under such and such a serial number is not valid and indicates the number of the order by which he reinstated you at work.
This is also important to know:
Can an employer fire a disabled person and how to do it?
Please be aware that the court's decision to reinstate you at work must be executed immediately, no later than the next day after the decision is made.
Why can you be fired from your job at the initiative of the organization?
The list of grounds for termination of an employment contract by decision of the employer is strictly regulated by law and is confidential. One of the following events makes it possible to realize your desire to get rid of an employee:
- Failure to complete the probationary period;
- Completion of the activities of a business entity;
- Inconsistency between the employee’s qualifications and the work he performs;
- Repeated violation of labor discipline by an employee or failure to fulfill labor duties;
- Single gross disciplinary violation (truancy, alcohol or drug intoxication);
- Presence of circumstances for loss of trust;
- Reduction of staffing levels;
- Change of business owner (only for directors, chief accountants and their deputies).
For employees hired to work remotely, it is possible to establish in the employment contract other grounds for its termination at the initiative of the employer.
An important point if the manager or owner decides to leave an employee will be the mandatory correct documentation of the entire procedure. Any, even the most insignificant error or inaccuracy can become the reason for a subsequent lawsuit, which with a high degree of probability will be won by the dismissed person.
Dismissal for failure to complete the probationary period
The legislation has not established a mandatory list of evidence of an unsatisfactory test result. The following may be used as supporting documents:
- Order imposing disciplinary punishment;
- Acts and memos certifying unsatisfactory performance of duties;
- Written explanations from the subject;
- Complaints from partners or clients of the company.
In addition, the conditions for testing must be in the employee’s employment contract, and its functionality is described in the job description.
3 days before the expected date of dismissal, the employee is notified in writing, against signature. If he refuses to sign, then a corresponding act is drawn up. After this, on the specified day, a dismissal order is issued with reference to the basis for its implementation, entries are made in the work book and personal card, and a full settlement is made with the employee.
Dismissal for lack of qualifications
Inconsistency with the position held is confirmed by the results of certification. If it is not mandatory by law, its implementation should be provided for by the company’s local regulations. Before the start of the knowledge test, an appropriate order is issued, which also appoints the composition of the certification commission. It must include the following information:
- Identification data of the person being certified;
- Purpose of the event;
- Qualification test date.
Based on the results of the certification, a protocol is filled out in which its results are recorded. If it is determined that an employee is not suitable for the position held, he is notified of this in writing and also in a separate document, and other available vacancies (if any) are offered against signature. If there are no free rates or the employee refuses to switch to them, a dismissal order can be issued. If there is a trade union in the company, it should also be notified of the dismissal.
Dismissal for failure to perform official duties or violation of discipline
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for 2 grounds for dismissal for disciplinary offenses:
- In case of repeated violations;
- In case of a single gross violation:
- Absenteeism;
- Being at work under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- Violation of trade secrets;
- Committing an immoral act during educational work.
Such a penalty is the right of the company and can be replaced with a regular reprimand or reduction in bonus payments.
In any case, the employer needs:
- Document the misconduct through a memo from the employee’s supervisor or an act drawn up by the commission;
- Demand in writing from the perpetrator an explanation, which he must give within 2 days after receiving the request;
- In case of refusal of explanations, it is also necessary to draw up a report.
Dismissal for multiple violations is possible only if there is another outstanding or unresolved disciplinary penalty. Next, a dismissal order is also issued, which the employee is introduced to upon signature.
Dismissal due to loss of confidence
Only persons directly related to the storage and maintenance of monetary, material assets and property can be dismissed for actions incompatible with their position. In general, its procedure is similar to that used for disciplinary sanctions, except that the circumstances of the violation are additionally investigated by the commission. Based on the results of the investigation, a report is drawn up, which indicates the degree of guilt of all persons involved and makes recommendations on the application of punishment. It, together with other documents, serves as the basis for making a decision on dismissal and issuing an order (see dismissal due to loss of confidence).
What to do if you were fired under an article
First, you need to make sure that the termination of the employment contract was carried out legally. If this is not the case, you can file a complaint:
- to the prosecutor's office;
- to the labor inspectorate.
You can also contact the justice authorities with a claim to declare the dismissal illegal and reinstated at work. Even if there is no desire to return to the team, it is still necessary to get the record corrected, since dismissal under the article often entails negative consequences for the employee during subsequent employment.
Is it possible to join the labor exchange?
Any person who does not have a job can register with the employment center. In fact, the labor exchange, first of all, functions for this purpose, to help citizens find employment. Meanwhile, many who register are not interested in the opportunity to find a job with the assistance of the labor center, but in the emergence of the right to receive benefits. Unfortunately for truants, they should not count on a significant amount of benefits. Only the minimum wage will be paid, which in 2021 is slightly less than 1,000 rubles.
How to get a new job
Most employers, having seen a record of absenteeism in a job applicant’s work record, will not want to hire such a person to their organization. You will have to convince the potential employer that absenteeism was an unfortunate accident, and not a pattern, and prove your high professional level. How can this be done?
- Ask for a probationary period. According to Art. 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it can be 3 months, for some categories of workers – up to 6 months. It seems that the employer can agree to this option, because, if something happens, the employee will be easy to fire.
- Provide impeccable references and letters of recommendation from previous places of work. It happens: a person is a true professional, respects discipline, but then one day something happens, and a record of absenteeism appears in the work book. If there are characteristics and recommendations, then you can count on the fact that the potential employer, after weighing everything, will hire the absentee.
Thus, the success of employment depends on the person who advertises the availability of vacancies. This person makes the decision. The task of an applicant with a damaged work record is to convince him that absenteeism was an accident.
Summing up the topic, it can be noted that establishing the fact of absenteeism is not a sentence. Of course, the story is not pleasant, but, in a certain situation, it is quite possible to keep your previous job or find a new one.
Liability for illegal dismissal
The illegality of dismissal may be detected during a scheduled or unscheduled inspection by the labor inspectorate. An employee can also file a complaint with the prosecutor’s office, and it will consider his case itself, or forward the complaint to the inspectorate.
If violations are detected, a protocol is drawn up and the prosecutor issues a decision
to initiate proceedings on the fact of an administrative offense.
If the dismissal is declared illegal, the employee will have to be reinstated to his previous job. He may also be paid compensation in the amount of average earnings. The wording of the reason for dismissal and the date may also be changed. The employer faces a fine of up to 200 thousand rubles.
If this violation was committed against a pregnant woman or the mother of a child under 3 years of age, the employer may face criminal liability and a fine in the amount of income for up to 18 months or compulsory work for up to 180 hours.
Features of employment after dismissal
At a new place of work, they are always interested in the work record and carefully review the work record. This is why problems very often arise during subsequent employment.
In such situations, it is necessary to explain to the new employer the reason for such an entry and find a rational and convenient explanation.
The easiest way is to say that they could not find a common language with their former boss, and he thus decided to take revenge.
In most cases, this explanation is sufficient. Especially if the person applying for the job is a good specialist.
But you should still avoid dismissal for absenteeism - this entails many different problems. In addition, there are almost always various ways to avoid this type of entry in the work book.
How much time is given for punishment
If the punishment did not entail dismissal, then it will be considered fully repaid 1 year from the date of issue of the order . If the employer sees that the employee has realized his mistake, he can remove him ahead of schedule . To do this, he will need to issue 1 more order.
There are also time limits within which it will be impossible to punish an employee for an offense if it is discovered too late, that is, after 3 months from the date of occurrence .
The exception is penalties aimed at financially responsible employees. In this case, the employee can be punished within two years from the moment the offense was committed. The validity period is also 2 years.