When terminating an employment contract, it is important to comply with Russian legislation. Dismissal at the initiative of the employer is a case that requires special attention from both parties. If the procedure is performed incorrectly, all participants risk ending up in court, which is an unfavorable outcome of cooperation. What reasons can serve as grounds for dismissal at the initiative of the employer and how to dismiss an employee legally?
Latest changes to Article 81 of the Labor Code of Russia
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the dismissal of an employee at the initiative of the employer.
It is she who determines the exhaustive list of grounds on which employment relations are terminated. To correctly interpret the law when terminating an employment relationship at the request of the employer, you should study Art.
81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in a new edition with comments.
Special cases
People with disabilities are one of the categories of workers who require additional state protection, therefore the management of the enterprise, when dismissing them, must be prepared for legislative restrictions.
An employee who has become disabled while working at an enterprise can be fired immediately only if the medical board has established disability group 1, for which work is contraindicated. If the employee remains able to work, the administration is obliged to offer him another place that meets his health in terms of working conditions. Management may dismiss an employee if, after establishing the group, he requires long-term rehabilitation - more than 4 months. Dismissal of a disabled person is permissible for violation of labor discipline or in the event of liquidation, staff reduction, refusal of an offered position, or transfer for medical reasons. The administration's decision must be justified by reference to the medical report.
Read more: Objections to the act of identifying a violation of the Pension Fund
Dismissal of a pregnant woman is permissible if continuation of work is impossible (liquidation of the company, refusal to move with the enterprise, etc.). There are also restrictions on the dismissal of single mothers (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is permissible to fire a single mother (that is, a woman raising a child alone due to divorce or death of a spouse, as well as if the father is not identified or the child is adopted without a husband) in the following cases:
- upon liquidation of a legal entity or termination of the activities of a citizen-employer in the status of an individual entrepreneur;
- in the event of a violation of labor discipline established by the Labor Regulations (if, in addition, there are already penalties for similar offenses - clause 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), or a one-time gross violation of discipline;
- for immoral behavior;
- in the event of a crime being committed at the place of duty: theft, embezzlement, etc.
As part of the pension reform, a law was adopted according to which it is impossible to dismiss people who have less than 5 years left until retirement (pre-retirees) without sufficient grounds established by law, under pain of criminal prosecution.
List of legal grounds
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation describes why you can fire a negligent employee without his consent and other cases that do not imply the obligation to obtain the employee’s approval:
- appearing at the workplace or other area where work activities are carried out in a state of intoxication;
- repeated failure to fulfill job duties, disciplinary sanctions, a single but gross violation of the production process;
- liquidation of the enterprise;
- staff reduction;
- inadequacy for the position held, which must be proven by certification;
- loss of trust of the employer due to the commission of certain actions that caused the waste of material assets;
- submission of invalid or forged documents;
- immoral behavior if the position involves educational activities.
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer must be carried out if one of the listed grounds exists.
Sometimes, even if there are significant grounds and misconduct on the part of the employee, the employer does not always have the right to terminate the employment relationship on its own initiative.
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer.
Management can dismiss an employee only for the reasons specified in the law. Dismissal must be justified and motivated. The reasons for dismissal must be confirmed.
The grounds for dismissal at the request of management include:
- Termination of its activities (liquidation);
- Abbreviations;
- Insufficient qualifications of the employee;
- Gross violation by the employee of his obligations;
- Repeated violation of labor obligations;
- Loss of trust in an employee working with money or goods;
- An immoral act on the part of an employee-educator;
- Other cases established by law.
When is it impossible to fire an unwanted employee from work if he himself does not want it?
There are certain categories of workers who are under enhanced protection in the field of labor relations. These are the most vulnerable and unprotected groups, for whom employment, having a regular income and maintaining a job are especially important.
Categories of workers protected from dismissal include:
- pregnant women or on maternity leave, with the exception of liquidation of the enterprise;
- an employee who is on sick leave or on vacation;
- a single mother with a child under 3 years old, a disabled child under 18 years old, the sole breadwinner of a minor, a parent with many children and the sole breadwinner.
The categories of employees listed in the last paragraph can be dismissed at the request of the employer, but for a limited number of reasons. Dismissal of such employees on grounds not permitted by law threatens the employer with legal proceedings.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call: +7 Moscow and region.
+7 St. Petersburg and region. 8 Other regions of the Russian Federation You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of all your problems!
What to do if you get fired
If, however, the employee does not agree with the dismissal or the reasons for the dismissal, he can go to court to protect his rights. He is given a month to do this from the moment he learned of the fact of his illegal dismissal. You can also contact the labor commission, but, as practice shows, a more effective way would be to contact the judicial authorities.
If the court considers the employer’s actions illegal, the employee may be reinstated at work. Unfortunately, this does not guarantee the absence of similar situations at work in the future.
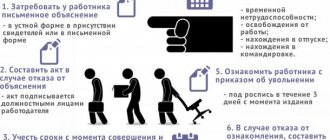
Step-by-step instructions for terminating an employment contract by decision of the employer
How to fire an employee without his desire according to the law, in order to avoid problems in the future associated with challenging the decision?
To do this, you will need to follow a sequence of actions that are somewhat different depending on the basis for termination of cooperation. The general scheme for dismissing an employee is as follows:
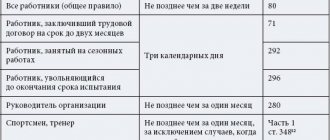
- notifying the employee of the upcoming termination of the employment contract. The timing and procedure for reporting depends on the basis and status of the employee;
- drawing up a dismissal order and familiarizing the employee with it against signature;
- finalization of the remaining period, if provided;
- making an entry in the work book and personal file;
- final settlement.
In some cases, each stage has its own characteristics, which cannot be ignored.
Liquidation of the enterprise
A special procedure for dismissal is provided for during the liquidation of an enterprise; in this regard, the following stages of the process can be distinguished:
- making a decision on liquidation;
- appointment of a liquidation commission;
- determining a plan for dismissing employees if there are many of them in the organization;
- notifying the person being dismissed 2 months in advance by sending a notice;
- issuance of a dismissal order. It is possible to create a single order to terminate relations with several employees at once;
- registration of dismissal and settlement with employees, making entries in the work book and personal file.
After completing the above stages, the employer still needs to transfer information on registering those liable for military service and issue all employees upon dismissal with a certificate in form 2-NDFL.
Staff reduction
The employer's actions when reducing staff are similar to the procedure for dismissing an employee during liquidation. The employer is obliged to warn the employee who is being laid off in advance and in writing. Before dismissal, an order is drawn up indicating the relevant grounds and article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition to standard payments, a laid-off employee is entitled to compensation.
Under the article for violations
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer, if the employee committed violations systematically or once, is carried out according to the standard scenario, but has features depending on the grounds.
It will be necessary to prepare an evidence base confirming the presence of an offense and the absence of valid reasons for its commission. An important step is drawing up an act that reflects the essence of the violation.
Witnesses of the precedent and specialists responsible for ensuring order at the enterprise must sign it.
Recording a violation
The employee can write an explanatory note.
To dismiss an employee for the reasons listed above, you need to document the fact of the event and prove the employee’s guilt in the committed act.
Confirmation of the fact of a violation can be acts, testimonies of witnesses to the violation, reports and official notes, and recordings from CCTV cameras.
Each basis may have its own set of supporting facts. For example, the procedure for dismissal for absenteeism, according to the law, requires the presence of witnesses to the violation or readings from the control system devices.
It is also impossible to fire a person just like that due to inadequacy for the position held. The discrepancy must be confirmed by a special commission.
The fact of theft must be confirmed by the results of an inventory or a resolution of a law enforcement agency.
Arriving at work drunk is recorded and confirmed by the commission.
The manager draws up a report on the detected fact of violation. The employee must review it and sign for it. If the employee has not been familiar with the documents, this may give rise to a dispute in the courts or in the CCC.
If a violation occurs, the employee must be asked to provide a written explanation of the reasons for the action.
The employer considers the case, taking into account all the nuances and factual circumstances. If, as a result, the employee is fired, then an order is drawn up, to which all the collected evidence and documents are attached. The employee’s refusal to familiarize himself with the order is reflected in it.
As a result, the reason for dismissal is recorded in the work book with reference to the clause and article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How to write an order correctly?
When drawing up an order, it is advisable to adhere to the standard T-8 form:
- FULL NAME. employee;
- name of the employer, full name of the manager;
- Date of preparation;
- reason and basis for termination of employment relations;
- manager's signature and seal.
The T-8 form is not required to be used; the employer can draw up an order in a different form. However, working with a standard form and, if necessary, using a sample order will help you avoid mistakes.
Employer mistakes
- Execution of documentation in an improper manner. This item includes incorrect formulation of reasons, untimely notification, and incorrectly drawn up order.
- There are no reasons to terminate the employment relationship. Often the employer does not apply administrative penalties, deciding to fire the employee immediately. In this case, the employee who appeals to the Labor Inspectorate or the court will definitely win the claim.
Each party to the employment agreement has the right to terminate it.
An employee must understand that failure to comply with labor discipline, non-compliance with work schedules, and careless attitude towards work and performance of official duties is fraught with dismissal.
ATTENTION! Every employee who values his job and knows that he has been fired without good reason can be reinstated in his job by going to court or the Labor Inspectorate.
Final settlement and payment of compensation
On the last working day, regardless of the reason for dismissal, the employee should be paid off.
The following monetary amounts are due as payments:
- salary;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- bonuses;
- other payments due due to dismissal or in accordance with the contract.
Payments are usually made to the employee's bank card. The main thing for an accountant is to make the transfer no later than the last working day.
Payments
Upon dismissal, the employee receives wages for all days worked, as well as compensation for unused vacation. In addition, if he was laid off or liquidated, he should be paid a benefit in the amount of one average monthly salary. He also retains his salary for two months, provided that he does not find employment elsewhere.
More details: “Payments and benefits upon layoff” and “Payments upon dismissal due to liquidation of the enterprise.”
Features of the process of dismissal of certain categories of workers
When dismissing certain categories of citizens at the initiative of the employer, it is necessary to take into account some features. There are categories of persons who cannot be laid off or cooperation with them cannot be terminated at the initiative of the employer.
Disabled people
There are no significant benefits for disabled people when dismissal at the initiative of the employer. If an employee is hired with an existing illness and degree of disability, then the work he performs and the position he holds corresponds to his capabilities.
In this case, in case of staff reduction or other circumstances, the employee does not have any advantages over others.
If the disability is acquired as a result of work activity, the employer is obliged to consider the possibility of transferring to another position that corresponds to the employee’s physical capabilities. If there is none, dismissal is carried out due to loss of health if the commission determines that the employee cannot work.
Pensioners
If a pensioner is dismissed at the request of the employer, there are also no additional benefits. In case of violation of labor discipline, inconsistency with the position or other circumstances, the pensioner will be dismissed along with other employees. However, the law does not allow the dismissal of an employee solely because of retirement.
Pregnant women and women on maternity leave
The most protected category of workers are pregnant women, as well as employees on maternity leave. They cannot be fired even if there are significant grounds, such as absenteeism.
The only reason for termination of cooperation is the liquidation of the enterprise. The employer can influence employees who abuse their position in other ways.
For example, issue a disciplinary sanction, and when the period of maternity leave expires, apply other types of sanctions, up to and including dismissal.
Whom an employer cannot fire?
The law prohibits a manager from dismissing an employee on his own initiative if he:
- absent due to being on vacation;
- issued a sick leave due to illness.
Special requirements are imposed upon the dismissal of citizens under the following circumstances:
- if the employee is a woman who is pregnant;
- if she is a single mother with a child under 14 years of age;
- if she is caring for a child who has not reached the age of three;
- when a working citizen takes care of a disabled child who has not reached the age of majority.
To dismiss this category of workers under state protection, dismissal is provided in a special manner.
What are the consequences for a manager for violating labor laws?
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer is the most frequently contested. If the parties have entered into an agreement or the employee independently decides to leave the workplace, significantly fewer problems and conflicts arise.
In case of violation of labor legislation and infringement of the employee’s interests, the injured person may appeal to the following authorities:
- trade union;
- labor inspection;
- court;
- prosecutor's office
Most often they go to court and the labor inspectorate.
As a result of such statements, the following consequences are possible for the employer:
- unscheduled inspections;
- reinstatement of a dismissed employee;
- compensation for moral damage;
- payment of average earnings during the employee’s forced suspension;
- deprivation of the right to engage in activities and disqualification for repeated violations of the law.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
All measures are applied individually and in different combinations. It all depends on the specifics of the case, the nature of the claim and the amount of evidence presented by the parties.
Due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties
These cases are specified in Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- conscription into the Armed Forces;
- reinstatement of the former worker by court decision;
- establishment of punishment by court verdict in the form of imprisonment;
- the employee’s inability to perform duties for medical reasons;
- expiration of the contract;
- force majeure;
- establishing a ban on work or holding a certain position;
- denial of access to state secrets if it is necessary for work;
- cancellation of the decision on reinstatement.
When should the money be disbursed?
If, on the day the dismissal occurred, the employee did not carry out his work activity, all payments must be made no later than the next day after the dismissed person requested a full settlement with him. If there is a dispute between the employee and the employer about exactly what funds should be paid, the employer must pay the minimum amount about which there is no dispute within the deadlines indicated above. The rest is paid if the dispute is won by the employee.
Additional funds
In some cases, upon termination of an employment contract with an employee at the initiative of the organization’s management, he may be provided with additional funds.
Bonuses due
The payment regulations in force at the enterprise may provide for regular bonuses. In the same case, when an employee resigns, and the results he has achieved under the terms of the provision allow him to qualify for a bonus, it must be paid to him. The exact amount of such bonuses is determined by local regulations in force in the organization.
Other payments
Labor legislation in some cases provides for the need for additional payments to an employee who is dismissed by decision of the employer. These include:
- Average earnings for two weeks. It is paid, for example, if the organization is liquidated.
- Average payment for the time spent on new employment, but not more than 2 months. This payment occurs if an employee is dismissed due to staff or headcount reduction.
- Three average salaries. These payments are due to the manager (general director), his deputy or chief accountant if they resign due to a change of ownership.