Labor relations, regardless of their duration, must be documented between the parties to cooperation. Registration of labor relations in the Russian Federation is regulated by the Labor Code and consists of the signing of an agreement by the parties. The agreement contains mandatory and additional conditions that the parties must adhere to in their working interaction.
Labor relationships must be formalized in strict accordance with the legislative norms in force on the territory of the Russian Federation. And their violation threatens the parties with administrative, civil or even criminal penalties.
The procedure for registering labor relations
The state guarantees freedom of labor and protects the rights of working citizens.
Legal guarantees are established by law, one of which is the formalization of labor relations. Documenting the rules in the field of permanent work is a way of monitoring compliance with law and order. A ban on unofficial hired labor, compliance by commercial enterprises with social guarantees and labor protection rules, a special dismissal procedure - such benefits cannot be obtained without consolidating relationships in the field of employment, so it is worth knowing the conditions for legally concluding transactions with the employer.
Working according to the labor code, your working hours will not be more than you agreed upon when applying.
Special cases
It is worth noting that for some categories of subordinates the procedure for formalizing labor relations with the employer will differ from the standard procedure. In particular this applies to:
- Minors. This group includes persons aged 14 to 18 years. For them, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for a reduced shift schedule, as well as additional leave for studying or taking exams. If a teenager cannot combine attending an educational institution and work, then the authorities should refuse him further cooperation. Persons under 15 years of age will not be able to find employment without the written consent of their parents;
- Foreigners. Before concluding an agreement with a person who has foreign registration, the manager must make sure that he has the right to work in Russia (this can be obtained from the migration service). This is the only restriction under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applied to foreign subordinates. Otherwise, they receive the same social guarantees as citizens of the Russian Federation.
Also, when employing minors, management must make sure that the teenager can cope with the task. To do this, he needs to undergo an in-depth medical examination.
Legal aspects of relationships in the field of employment
The law (Article No. 15, Russian Labor Code) gives the concept of working relations as an agreement on the performance by an employee of labor functions in the interests and under the control of the employer. They are formalized using an agreement, the conclusion of which occurs by establishing official, professional, and qualification responsibilities for a specific type of action according to the organization’s staffing table.
Legal norms (Article No. 56.1, Russian Labor Code) establish a ban on agency labor (performed under the control of an individual or legal entity that does not act as an employer) labor.
If we are talking about sending a citizen for temporary employment to another organization, then the procedure for transfer is regulated by law.
In addition, according to the law (Article No. 60, Russian Labor Code), an employee has the right to refuse to perform duties not provided for in the contract without formalizing additional functions and corresponding additional payment.
Infringement of the right to employment is prohibited by law:
- By refusing employment without specifying the reason for such action.
- Based on gender, nationality, age limit, place of registration.
- Women due to pregnancy.
- If the employee was invited by letter to transfer to another company, and thirty days have not passed since his dismissal.
Refusal to draw up a contract at the request of an unhired employee must be made in writing. A paper with reasons for non-acceptance is issued within a period not exceeding a week from the moment the organization receives such a request. Its contents can be appealed in court.
Proper registration of labor relations with the employee guarantees compliance with the employee’s labor rights
From the numerous appeals from citizens received by the prosecutor's office, it is clear that employers often violate labor legislation when registering labor relations with employees, which in turn infringes on the rights of employees guaranteed by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts. In this regard, when formalizing an employment relationship with an employer, an employee should know, firstly, that in accordance with Art.
As history shows, the relations of mankind, which arose on the basis of the performance of certain works, are the most ancient principles of communication that have developed in the social order. Without certain relationships, no activity to produce a material or intellectual product is possible. In general, the concept of labor relations characterizes them as the interaction of the parties, which acts as a structural basis in relation to the performance of certain types of work.
Thanks to the development of the social institution of labor relations, they acquired a clear order and hierarchy established by law. In the modern world, labor relations in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are similar to the concept of industrial relations, which were determined by the superstructure of the entire economic system of society. In order for labor relations to have a strong systemic basis, they are universally based on legally binding provisions established by labor legislation.
Types Labor relations are divided into types, each of which differs in the nature of the work involved. These include the following: Main work in an enterprise, company, or organization. Part-time work. Temporary work (for a period of no more than two months). Seasonal work. Employment for an individual. Work from home. Contract job. In accordance with the listed types of work, certain types of employment contracts (agreements) are drawn up, providing for special relations between the parties to the employment contract. Parties The concept of parties to an employment relationship is determined by the employment contract and is based on the functional purpose of the person in relation to working conditions.
The parties to the labor relationship are those who sign the employment contract. One of the parties is the employer, who can be an individual or legal entity.
Other ways to formalize working relationships with employees
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes the mandatory registration of labor relations in accordance with the Russian Labor Code. In principle, it is allowed to attract labor in other ways, but only with certain reservations:
- Formalization of cooperation with individual entrepreneurs. This option is beneficial to both parties - the employer does not pay social insurance, the employee receives a profit. These transactions allow you to formalize one-time work and long-term commercial interaction.
- Conclusion of civil law transactions. Commercial enterprises can sign contracts for the provision of services for a fee with individuals, and in this way attract workers to carry out one-time short-term work (sewage cleaning, air conditioner repair). But if the supervisory authorities determine that the citizens who signed the agreement are performing a work function. They will force the employer to enter into a legally required agreement and restructure the relationship with employees. Additionally, the state labor inspectorate has the right to impose administrative penalties on a company that does not employ its workers.
- Distant work. At its core, this is a normal relationship between employer and employee, formalized by an appropriate contract. This option differs from the usual method of employment only in the location of the employee’s place of work (he works at home) and in the way he communicates with the employer (the Internet or telephone is used for this purpose).
- Outsourcing. This method of attracting labor should not be confused with outstaffing. The first option means sending an employee to perform actions in another organization on the basis of a civil agreement between commercial enterprises. In this case, the person works in the interests and under the control of the company with which he has an employment contract, but performs his duties outside its location. The second term means placing employees under complete subordination to a third-party organization. In this situation, work duties are performed in the interests of a company that did not enter into a contract with the employee. This method of employment is recognized by law as agency labor and has been prohibited by the Labor Code since May 2014.
Civil contract with an employee - an individual
A civil law agreement (CLA) is a good opportunity for an employer to order a service (work) from a third-party contractor that cannot be performed by its full-time employees. Such an agreement is also suitable in cases where the volume of work is small and hiring an employee on staff would be unreasonable.
This could be repairing something, performing a translation, attracting a certain number of clients, developing technical documentation, etc. Such an agreement is drawn up not as an employment agreement, but in the form of a contract or service agreement. In addition, civil law contracts, on the basis of which an individual can be involved in execution, include contracts of carriage, transport expedition, assignment, agency, commission.
The subject of the GPC agreement will be the implementation of a specific task that has a measurable result. It is this result that will be paid for by the employer, who in this case acts as the customer. Labor legislation does not apply to persons performing work or providing services on the basis of GPC agreements.
In this type of work, the customer does not make entries in the contractor’s work book, but the period of work under a civil contract is included in the contractor’s length of service. Why? The fact is that although the GPC agreement is not an employment contract, the customer must, at his own expense, transfer insurance contributions to the Pension Fund for the contractor , based on the remuneration amounts paid. Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases are not mandatory and can be provided on a voluntary basis. In addition, the customer, under a civil contract with the contractor - an individual, must fulfill the duty of a tax agent, that is, withhold and transfer personal income tax from the remuneration amount.
Let's compare the features of two types of contracts with an employee: labor and civil law.
| Employment contract | GPC agreement with an individual | |
| Subject of the agreement | Personal performance of a labor function by an employee | Measurable final result of work (service), accepted according to the act. The Contractor may involve third parties to complete the task, unless otherwise provided by the contract |
| Documenting | An employment contract is concluded, a hiring order is issued, a personal card is issued, and an entry is made in the employee’s work book. | A civil law contract is concluded and a task is agreed upon in the form of achieving a specific result of a service or work; an entry is not made in the work book. |
| Salary | The employee receives a monthly salary specified in the employment contract. Salaries are paid twice a month; for violation of payment deadlines, the employee is paid a penalty | The customer pays remuneration to the contractor after completing the scope of work or services. The customer is not obliged to make monthly payments, but stage-by-stage delivery of work or advance payments may be provided |
| Insurance premiums | Contributions to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are required | Only contributions to the Pension Fund are required |
| Personal income tax | Held | Held |
| Social guarantees | The employee is provided with vacation, maternity leave, child care benefits, sick leave, and dismissal benefits at the employer's expense. | Social guarantees are not provided |
| Internal labor regulations | The employee must comply with the work schedule, obey officials, work occurs under the control of the employer | The contractor is not subject to the PVTR, the customer can check the progress of tasks, but does not have the right to give mandatory instructions |
| Work time | Recorded in the time sheet; work on weekends, non-working holidays and overtime work is paid additionally | The customer pays not for the time spent, but for the result. Working hours are not recorded, and no additional payment is made for overtime or work on weekends (non-working days). |
| Working conditions | The employer must equip the workplace, create material conditions for performing the work function, and provide safety instructions | The customer is not responsible for the creation and equipment of the workplace, safety precautions and labor protection. The contractor may use his own materials and tools (as determined by the terms of the contract) |
| Refusal to conclude a contract | Unreasonable refusal when concluding an employment contract is prohibited. Discrimination based on age, nationality, gender, language, etc. is not allowed | There is freedom of civil contract, so the customer can refuse to enter into a contract with a specific contractor |
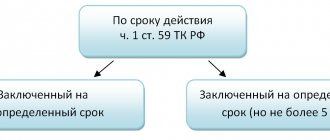
| Contract time | The default is for an indefinite period. The conclusion of an employment contract indicating the term is permitted if there are grounds specified in Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example, when temporarily replacing an absent employee) | The contract is concluded for the period of performance of work or provision of services |
| Prosecution | It is possible to bring the employee to disciplinary liability (reprimand, reprimand, dismissal for certain reasons). An employee's normal financial liability is limited to his monthly salary. An agreement on full financial liability can be concluded only with some employees | For violation of deadlines for completing work (services), the contractor may be required to pay a penalty. Causing material damage to the customer is compensated by the contractor in full. The contractor also bears the risk of accidental death or damage to the result of the work performed before its acceptance by the customer |
Differences between labor relations and civil transactions
The law (Article No. 15, Russian Labor Code) prohibits formalizing actual labor relations in a civil contract. To protect your interests during employment, knowledge of the differences between labor and civil contracts will be useful.
- Target. When officially employed, she performs the duties that are performed in a specific position. They are established by the staffing schedule and internal local acts of the enterprise. In the case of concluding a transaction for the provision of services or performance of work, this is the result of the actions of the contractor. The range of responsibilities of counterparties in such a formalized relationship is narrower and is limited by deadlines, the required level of quality and quantity, and payment for the means to achieve the goal (materials). All these aspects are not established by third-party documents, but are written directly in the text of the civil contract itself.
- Deadlines. Contracts (if they are not temporary) do not specify a validity period, but civil law activities are limited in time and penalties are imposed for late fulfillment of obligations.
- Responsibility. When officially employed, an employee receives punishments under the Labor Code (disciplinary sanctions), the severity of which is not measured in monetary terms. The penalty for improper execution of a civil transaction is expressed in a specific amount or percentage of the payment for services.
- Salary. The legal registration of labor relations with an enterprise provides for the frequency of payments for labor (wages). In a civil transaction, it is not the actions that are paid for, but their results.
- Social guarantees. In the case of a legal employment procedure, a citizen receives the right to payment in case of missed work days due to illness, paid leave, time off or additional payments for overtime. When concluding a transaction for the provision of services, receiving additional benefits from the state when the contractor does not show up. He has the right to demand only payment for the result of his actions as agreed.
In a situation of looking for a new job, it is worth remembering that registering labor relations with a work book implies more rights for the citizen and hassle for the employer, so you should carefully consider the provisions for applying for a job established in each specific organization. Contractual regulation of labor relations is the best option to avoid conflicts between employer and employee.
Introduction
Personnel management is a continuous process aimed at creating means of stimulating personnel, as well as monitoring their activities in order to achieve effective results in their work.
The relevance of the chosen topic is due to the importance of this stage of employment, since the future of each individual employee and his position in the personnel structure depend on this stage. The correctness of the formalization of labor relations and knowledge of the basics of labor legislation largely guarantee the occurrence of forceful circumstances.
At the present stage of development, there is a need for a type of labor law that would consolidate the principles of humanism and fairness in the sphere of labor relations, maximally facilitating their transition to a market nature, both in form and content.
This direction is constrained due to a decrease in the share of production activities in the gross volume of the national economy and imperfections in the management system in organizations.
The purpose of this work is a theoretical study of the procedure for registering labor relations.
Based on the set goal, the following tasks were solved:
1 – the concept and characteristics of labor relations have been studied;
2 – analyzed the legal regulation of labor relations;
3 – the procedure for formalizing labor relations in an organization has been studied.
The object of research in this work is labor relations.
The subject of the study is the procedure for formalizing labor relations in an organization.
The study of the internal functions of the state is reflected in the works of many domestic economists: Bereslavskaya V.A., Korolkova T.A., Nurtdinova A., Savvinova Yu.A. and etc.
The research methods used in this work include methods of analysis and synthesis, hypothesis building, logical assessment of events, graphical and other methods of collecting and processing information. The research is also based on general scientific methodology, which involves the use of systemic and institutional approaches.
Documents used to consolidate the relationship between the employee and the organization
The law (Article No. 65, Russian Labor Code) establishes a list of papers that are provided by a person when joining a commercial company:
- Passport or paper identifying the citizen’s personal data.
- Employment history.
- Document on registration with the Pension Fund.
- Documentation on military registration.
- Papers proving the level of education and qualifications.
- Documents confirming no criminal record or completion of criminal prosecution (if the organization’s activities do not allow the employment of convicted or criminally prosecuted citizens).
A work record book and SNILS are not provided for first-time employment. In this situation, they are issued by the employer.
Legislative provisions allow for the requirement of additional documents if the conditions of employment at a particular enterprise require it. It is prohibited to force citizens to provide papers in cases where such provision is not established by law.
Rules for office work when registering labor relations between an employee and an employer
Legislation (Article No. 67 of the Russian Labor Code) establishes a written form of a transaction aimed at getting a person a job. An employment contract is drawn up by drawing up two original documents, one is given to the employee (against signature), and the second remains at the enterprise.
If the papers are not signed, the relationship is considered to have arisen if the person is allowed to actually perform work duties. In such a situation, the paperwork must be completed within three working days. It is worth meeting the same deadline if the relationship that was initially formalized in a civil law transaction is recognized as working.
A concluded contract is considered legal if the following mandatory information is indicated in it (Article No. 57 of the Russian Labor Code):
- Personal information about the employee (full name).
- Full name (title, organizational form, location) of the employer.
- Information about the identity document of the future employee or employer-citizen.
- TIN of the enterprise (or individual entrepreneur) hiring a new person.
- Data of the person authorized by the organization to sign employment contracts.
- Name of the locality and day of the transaction.
- Place of performance of work duties.
- Labor function (indication of job and professional responsibilities for a specific job according to the organization’s staffing table).
- The day on which the citizen starts work.
- The procedure for payment for work (salary, tariff, allowances or additional payments).
- Periods of work and rest.
- Conditions for additional payment for harmfulness if the work is considered harmful.
- Nature of actions (mobile, traveling work).
- Conditions on workplace equipment.
- Regulations on social insurance of employed citizens.
In a situation where the employer, having fulfilled the requirements for formalizing the employment relationship, did not indicate the required information, this does not entail the nullity of the contract - they simply add to the signed document. If the terms of the performance of work duties are not indicated in the text of the transaction, they are drawn up in an additional document. The employment contract must spell out all the specific features of your specific work process.
Employment contract with the employee
Under an employment contract, the employer undertakes to provide the employee with work for a certain labor function, provide working conditions, pay wages on time and in full, and the employee undertakes to personally perform the labor function determined by this agreement and comply with the internal labor regulations of this employer (Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
An employment contract maximally protects the rights of the employee and, at the same time, places on the employer the maximum responsibility of all possible options for formalizing the employment relationship. We discussed how to conclude an employment contract and what conditions should be included in it in a separate article, because when concluding such an agreement, many nuances must be taken into account.
What else, besides concluding an employment contract, should an employer do when hiring and further interaction with an employee? The rights and obligations of the employee and the employer are prescribed in Articles 21 and 22 of the Labor Code. Let's briefly go through the points that an employer must provide to its employee:
- familiarize yourself with local regulations, such as internal labor regulations, regulations on remuneration, regulations on the protection of personal data;
- ensure safety and working conditions, as well as equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform labor duties;
- pay the employee wages in full, and payments must be made at least twice a month;
- pay monthly insurance premiums for the employee to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund at your own expense;
- provide for the everyday needs of employees related to the performance of their job duties;
- pay for non-working holidays and annual leave;
- compensate for harm caused to employees in connection with the performance of their labor duties;
- pay for maternity leave and child care benefits for up to one and a half years;
- pay for days of incapacity.
Dismissal of an employee without his actual consent is possible only for a number of reasons, and can sometimes create difficulties for the employer.
Drawing up an order for acceptance to a position
After signing the contract and specifying all the requirements, an order or order is issued to hire the person for the position. It is issued to the citizen within a period not exceeding three days from the signing of the agreement. Additionally, upon employment, an employee, against receipt, familiarizes himself with the internal regulations and discipline of the organization.
The contract comes into force after it is signed. The employee begins to perform work duties from the moment specified in the contract. If the time is not documented, the employee begins actions from the next day after registration of employment.
Registration of employment
Enrollment at the place of duty is formalized by an order of the employer, issued on the basis of a concluded employment contract. The hiring order is announced to the employee against signature within three days from the date of signing the employment agreement. At the request of the applicant, the employer is obliged to issue him a certified copy of the specified order, familiarize him with the internal labor regulations in force in the organization, other local regulations related to his labor function, as well as with the collective agreement.