An important point: if an employee voluntarily works longer than expected, such overtime work is not recognized and is not paid additionally. The employer must involve the employee in working beyond the norm, having received written consent. And in this case, management is obliged to calculate overtime work. In addition, if an employee’s employment contract establishes an irregular working day, working beyond the allotted time is also not considered overtime. Workers with irregular schedules are entitled to another benefit - additional leave.
How are overtime hours calculated?
HR and accounting department employees are required to correctly take into account the duration of work for each employee.
According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the normal length of working time is 40 hours per week. It is important to remember that an employee should not work beyond the norm for more than 4 hours, 2 days in a row and longer than 120 hours a year (Part 6 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For some categories of citizens, a shortened day (24-35 or 36 hours a week) is the norm, and working beyond this time is overtime for them. The time worked must be reflected in the working time sheet, form T-12 or T-13. Overtime hours o or code 04. There is a timesheet program for calculating overtime hours, which automates filling out the timesheet and calculates payment for overtime using formulas.
Overtime work is paid at an increased rate (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for the first 2 hours at one and a half times;
- for the following hours - double.
Instead of increased pay, the employee can choose another option - get additional time for rest (no less than he worked overtime). In this case, processing is still paid, but at a single rate.
What is the minimum amount an employer must pay for working after hours?
Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain an answer to this question, and officials of the Ministry of Health in a letter dated 07/02/14 N 16-4/2059436 explain the situation as follows: to pay overtime you can use the rule of Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to the norm of this article, the minimum amount of double payment is a double tariff without taking into account compensation and incentive payments. According to the logic of this norm, the least that an employer must pay is the employee’s average hourly earnings without bonuses and allowances, multiplied by 1.5 or 2 and multiplied by the number of hours worked in excess of the norm. Local regulations of a particular company, labor and collective agreement may establish higher payment for overtime: allowances and additional payments are included in the calculation in whole or in part, if the employer is ready for this.
Formula for calculating overtime:
What work is considered overtime?
The provisions of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation spell out the conditions under which periods worked in excess of the established standards are taken into account. They are presented:
- the initiative of the company's management has been demonstrated;
- if the activity exceeds the applicable boundaries of the working time of a particular citizen.
This means that work performed by an employee at his own request cannot be considered as overtime.
In addition, you should take into account the working hours that are established for each of the company’s employees. If the organization has decided to record the periods worked in a summarized form, then a separate indicator is provided by hours for a specific period.
If the specified standard is exceeded, the work should be considered as exceeding the standard. Legislative acts reflect restrictions on how long work activity used in excess of the norm must last.
Calculation of overtime hours based on salary
To calculate additional payments, you need to calculate the hourly part of the salary - how much the employee earns per hour. Then pay one and a half or two times more for each hour of overtime (depending on the time worked above the norm). The formula for calculating the amount earned per hour is given in the letter of the Ministry of Health dated 07/02/14 N 16-4/2059436:
To calculate this formula, the average monthly number of working hours per year is taken - the average value for the whole year is displayed, and not the actual number of hours worked in a month.
But this is not the only method for calculating hourly earnings. There is also an option taking into account the actual working hours in a particular month. To do this, there is no need to divide the hours by 12 months; it is enough to divide the salary by the hourly work rate for a separate month:
Since there are different options, the method for calculating the hourly tariff rate must be fixed in the local acts of the company or in an agreement with the employee (collective or labor).
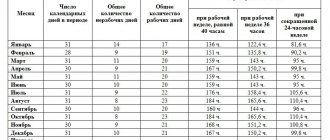
The norm of working time in a year or month is determined according to the production calendar (see production calendar) depending on which category the employee belongs to (whether he is entitled to a shortened working week).
Everything about overtime pay in 2021
At the request of the employee, overtime work can be compensated by providing additional rest time, but not less than the time worked overtime, while overtime hours worked are subject to payment at an increased rate, when the provided rest time is not subject to payment. Example. Let's remember the condition of the previous example. At the request of the employee, he was provided with additional rest time - 9 hours (3 hours + 2 hours + 4 hours). All overtime hours are paid in accordance with the generally established procedure. Additional rest time is not subject to payment. The accountant calculates the employee's wages based on the timesheet data, which reflects the hours worked overtime. Let's calculate the employee's monthly salary:
- payment for time worked according to schedule: RUB 15,000. : 176 h. x(176 h.
An example of calculating overtime hours with a salary
Salary of employee Malofeeva L.G. is 25,000 rubles per month. In September 2021, the employer delayed him twice: on September 1 for 3 hours, on September 8 for 1 hour. We will calculate overtime if the norm is for Malofeev L.G. 40-hour, five-day work week.
The first method (based on the average monthly number of working hours in 2016):
In 2021, the average annual working time for a 40-hour week is 1974 hours (see production calendar). Let’s calculate the hourly part of Malofeev’s salary in average form:
For overtime work on September 1, Malofeev L.G. will receive:
For September 8:
In total, the employee was credited 759.85 + 227.95 = 987.80 rubles in September 2021. for working overtime.
Second method (based on the actual number of working hours per month):
In September 2021, the average monthly working time for a 40-hour week is 176 hours (see production calendar). Let us calculate the hourly part of L.G. Malofeev’s salary. based on the actual (not average) number of working days in September:
We see that the result is a completely different amount of hourly earnings than when calculating using the first method (almost 10 rubles less). But at the same time, in another calendar month - in which the number of labor hours is less than in September - the amount obtained, on the contrary, will be greater than with the average annual calculation.
For September 1, Malofeev will receive:
For September 8:
Total for September 2021 Malofeeva L.G. overtime accrued: 710.20 + 213.06 = 923.26 rubles.
The amount turned out to be less than in the first case, which is unprofitable for the employee. The Ministry of Labor in letter No. 1202-21 dated 08/09/2002 recommends using the first method of calculating overtime if this improves the employee’s financial situation.
We pay overtime correctly
Info
If the organization uses a salary system, then every month the employee is transferred the same amount of remuneration. How is the payment for after-hours work calculated for piece workers? Citizens who work piecework are paid for each part produced.
Overtime pay for piece workers depends on how many parts they produce outside of normal working hours and also on the number of overtime hours worked.
Cash is paid without taking into account one and a half or double premium. Example: Kurochkina A.N. works at the factory. She works piecework. For each part made, she is paid 400 rubles. On March 9, 2021, she worked 4 hours outside of class hours, producing 5 parts during this time: 2 pcs. for the first 2 hours and 3 pcs. — for the remaining 2 hours. Payment depends on the number of parts produced and on the time worked above the norm. Therefore: (400 rub. * 1.5 * 2 pcs.) + (400 rub.
Calculation of overtime hours on a shift schedule
According to Art. 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a shift schedule implies work in two, three or four shifts, the need for which is determined by the continuity of the production process. Shift work must be fixed in the employment contract with the employee, since it is its essential condition. If a shift worker, at the request of the employer, goes out of his shift, then the payment for that day is doubled, or the employee is given a day off on his working day. If the scheduled shift falls on a holiday, non-working day, the work is paid twice as per Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the shift or part of it may fall at night, work during which is paid at an increased rate (at least 20%) according to Art. 96 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When an employer delays a shift worker at work beyond the scheduled hours, he is obliged to pay the employee additionally. Let's figure out how to calculate overtime hours on a shift schedule. And also if work beyond the norm occurs at night. The formula for calculating the amount of overtime does not change: the first two hours are paid at one and a half times the hourly portion of earnings, subsequent hours at double. As an example, let’s take the calculation of overtime and night shifts in a medical institution.
The specific nature of the work of doctors requires the presence of staff in the institution around the clock; the work schedule in the hospital is rotating. Moreover, in case of delay of doctors and other medical workers beyond the shift, management is obliged to pay for overtime. Let's figure out how to calculate night and overtime pay for doctors.
Payment for processing according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. What to expect and how to achieve it?
Recycling is a universally encouraged “good” tradition. And it’s okay if employees don’t have to stay at work longer too often and for really serious reasons. Especially if work above the norm is paid in the appropriate amount. But it is important that it be this way, because otherwise employees will begin to burn out, lose productivity and motivation. It cannot be otherwise, because any normal person wants to receive exactly what he has earned, in 100% volume. Moreover, there are enough workers who are willing to work happily after the end of the working day due to the increased hourly rate. But they must be sure that they will get what they deserve!
By the way, a company that welcomes, but does not properly take into account overtime work, can easily become interested in “people in uniform.” And if one of the employees contacts the labor inspectorate, the police or the prosecutor’s office, for a single statement the manager faces only administrative liability in the form of a small fine. But responsibility for group or systematic appeals is already criminal liability, with the possibility of restriction of freedom for up to 3 years.
Therefore, it is very important to accurately account for processing, register, document and adequately pay for it, following current legislation. And what it says on this topic, we will tell you below.
What exactly qualifies as overtime work?
To begin with, it should be noted that we can talk about overtime hours only with a fixed work schedule. First of all, we mean the standard 40-hour work week. For employees who signed a contract on an irregular work schedule, this opportunity is not provided. The reason is his instability, involvement in the performance of his official duties only as needed. But with such a schedule, the employee has the right to count on increased financial remuneration within the hourly rate. However, it all depends on the company and its policies.
Payment for overtime in the Russian Federation is regulated by Article 152 of the Labor Code, as well as a number of laws and regulations. Within the framework of current legislation, overtime hours are considered to be the following periods of work:
- after completing a standard 8-hour work shift on weekdays;
- after completing a standard 8-hour work shift on holidays or weekends;
- subject to working part-time on your day off.
Increased pay per hour is not awarded to employees who work part-time or part-time. By the way, this must be taken into account when applying for a job and agreeing on an employment contract. According to recent changes in legislation, even if a person works an incomplete week with 7-hour Mondays and Fridays, he is no longer entitled to accruals for overtime hours.
When can an employee be required to work overtime?
Opinions of employees and their managers regarding who, when and how much extra work can be involved vary. And this is natural. According to Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees (all, with the exception of a number of categories of specialists) can be involved in performing work at their enterprise/organization for a time exceeding the schedule specified in the employment agreement. But not at the whim of the boss, but only in case of urgent production necessity. In addition, management can use this right quite limitedly, since the total annual overtime per person should not exceed 120 hours.
To avoid possible problems with the accrual of increased pay for additional working hours, it is necessary to document each such case. You can do this in two ways:
- by signing the corresponding order of the boss, thereby expressing consent;
- by writing a free-form application indicating consent to work beyond the norm.
An employee has the right to refuse any proposed processing, with the exception of just a few situations:
- natural disaster, accident or catastrophe, but only when the involvement of an employee will help to quickly resolve the situation and minimize damage;
- when martial law or a state of emergency is introduced in the country;
- if the employee’s work is necessary to ensure social and public benefits (urgent repairs of water supply systems, power supply, etc.).
In any other case, the employee is not obliged to agree to the offer/demand for overtime. It is completely prohibited by law to involve pregnant women, officially employed minors and those working under an apprenticeship contract in compulsory overtime.
By the way, it is important to remember: increased pay for additional working hours is accrued only if it is the initiative of the employer. If an employee stays longer at work at his own request, the additional time by default is not paid at all. Exceptions exist, but they are individual, and are not regulated by law, but by clauses in the employment agreement/contract between the manager and the employee.
How to calculate payment for processing?
This issue is regulated by Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. And it states that:
- the first two hours after the end of an 8-hour day on a weekday are paid with a coefficient of 1.5, each subsequent hour is calculated at a double rate;
- An 8-hour working day that falls on an employee’s day off is paid at double the rate;
- all overtime on weekends and holidays is paid at a double rate;
- Part-time hours that fall on a weekend are paid at double the rate.
The tariff schedule to which the coefficient is applied is not standardized - it is specified in the employment agreement. Additional payments and coefficients, if specified in the contract, are not taken into account when calculating accruals for additional working hours.
It turns out that if an employee is “pushed” to work on his legal day off, each hour of work will be paid double, regardless of the length of the shift.
As for payment for overtime on weekdays, the situation is as follows. If an employee’s rate is 400 rubles per hour, and he worked 8 hours of the working day + 4 additional hours, he will earn:
- 8 x 400 = 3200 rubles per working day.
- 2 x 400 x 1.5 = 1200 rubles for the first two hours of processing.
- 2 x 400 x 2 = 1600 rubles for the next two hours of processing.
In total, earnings per day will be 6,000 rubles.
It should be noted that the minimum coefficients established by law are indicated above. The employer has the right to offer and stipulate higher values in the employment contract.
How to get money paid for overtime?
If the overtime is not documented, the employer can pay for it only of his own free will. So you need to keep an eye on this. Cases when management seeks to minimize the volume of payments occur every day in Russia. Unfortunately, this is a normal phenomenon for our country.
Workers can fight this trend only legally. The first step is always to notify the intention to contact the labor inspectorate. The second is the appeal itself. An employee can also file an application with the prosecutor’s office and try to defend his interests in court. These are effective methods, but you need to be prepared for the fact that months will pass between the start of the process and receipt of payment.
We automate monitoring of overtime hours
In most organizations, employee time tracking is done the old fashioned way - mostly visually, and not at all accurately. This approach is an anachronism, because there are automated systems for recording working hours. For example, Kickidler is an automated time tracking system.
It is installed on employees’ computers and analyzes their activities using a whole set of criteria, including counting actual working hours. Thanks to its extensive control capabilities, the program will absolutely accurately note who came to work on time and who was late, who worked conscientiously all day, and who spent more time in the canteen, smoking room or other places than at their desk. Also, Kickidler’s functionality allows you to find out whether an employee did something important during his overtime hours, or stayed at work to quietly play on the computer...
Recording of working time, including overtime, must be perfectly accurate - this is important for creating a normal atmosphere in the team. And the capabilities of the Kickidler system are very useful here!
Kickidler time tracking system
Did you like the article? Follow us on social networks.
An example of calculating overtime and night pay on a shift schedule
Medical worker I.P. Trifonov has a work schedule of two 12-hour shifts (day shift from 8:00 to 20:00, night shift from 20:00 to 8:00). The employee's salary is 16,000 rubles. The norm for Trifonov I.P. is a 40-hour work week. In September 2016, he was required to work overtime for 4 hours on September 2 after the day shift, and for 2 hours on September 5 after the night shift. The local regulatory act of a medical institution establishes an additional payment for night work in the amount of 40% of the official salary (the minimum amount of such additional payment according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is 20%, but employers have the right to establish more favorable conditions for employees). We will calculate the additional payment for I.P. Trifonov for work outside of school hours.
According to the production calendar in September 2021, for a 40-hour work week, the standard working time is 176 hours. To calculate overtime, we will highlight the hourly part of I.P. Trifonov’s salary:
Night hours are the time from 22:00 to 6:00 (work at this time is paid at an increased rate). September 2 Trifonov I.P. was brought to work after the day shift for 4 hours, the shift ends at 20:00. The employee worked overtime from 20:00 to 24:00, 2 hours of this period were at night. For these 2 hours, he is entitled to an additional 40% of the salary, in addition, they are paid at double the rate, while the first 2 hours of overtime are paid at one and a half times. But when calculating overtime and night, there is no need to multiply the coefficients at the same time. You should add up the amount of extra pay for night hours and the amount of overtime.
For September 2, Trifonov is entitled to:
Of which 72.72 rubles are for work on the night shift.
After the night shift on September 5, Trifonov worked 2 hours - the work occurred during the day, did not exceed 2 hours and was paid at time and a half.
Overtime for September 5:
Total in September Trifonov I.P. accrued for additional work, partly at night, 709.02 + 272.70 = 981.72 rubles.
A visual explanation of recycling calculations
To understand the mechanism for paying for additional hours of work, it is necessary to analyze the situation using the example of calculating overtime.
Employee Nazarenko was left to work overtime twice in a month. On March 5, the employee was late for two hours, and on the fifteenth, for four. Nazarenko’s monthly salary is twenty thousand rubles. During the year, the employee works 1970 hours, in March - 159.
The man divides twenty thousand by the time worked during the month and receives his hourly rate - 125.79 rubles. The employee calculates the overtime rate, multiplies the calculated amount by one and a half (to determine earnings for two additional hours) and two (for four hours). It turns out 188.68 and 251.58. Having identified the hourly wage for work above the norm, Nazarenko finds out the amount of profit for the overtime. To do this, the employee adds up the resulting numbers. With a salary of twenty thousand rubles, the employee will receive overtime for March 5 in the amount of 377.36 and 880.52 for the 15th (the first two hours plus an additional two, i.e. 377.36 + 503.16).
Work beyond the norm is performed by the employee with written consent and is paid above normal. The rules for calculating overtime allow you to independently evaluate the labor invested and calculate the minimum amount of overtime.
Calculation of overtime with summarized recording of working time
According to Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in cases where it is impossible to comply with the daily (8 hours in the general case) or weekly (40 hours) standard working time, it is permissible to introduce a summarized recording of working time in the organization. Working hours are counted not for a week, but for the period established by the organization. This could be a month, a quarter or a year. Such accounting is introduced so that the duration of working hours does not exceed the normal number of working hours in the entire allotted period. In this case, one week an employee may work more than normal, and the next week, on the contrary, less. The employer will evaluate the time worked after the end of the accounting period - month, year or quarter.
Summarized accounting is convenient for companies with a shift schedule, in which employees work every other day, two to two, or several shifts a day. With such accounting, overtime may also arise, for which it is necessary to calculate payment.
Additional payment for extracurricular work in the case of cumulative recording of working hours is made after the end of the accounting period. Let's look at how overtime is calculated using an example.
Overtime pay: everything employers need to know about
Overtime pay is remuneration for work performed outside normal working hours. The maximum permissible amount of extracurricular time, in accordance with the law, is 120 hours per year. In this article we will tell you how overtime work is paid in 2021 under various work modes, and answer the questions that most often arise from employers.
Is it necessary to issue an order?
The need to fulfill or exceed the production plan does not always fit into the framework of working hours. In this case, there is a need to organize work beyond the normal duration of the shift, but overtime work according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has restrictions on attracting personnel to work outside the limits of the normal working day.
An example of calculating overtime with summarized recording of working hours
To employee Selivanov M.A. The hourly wage is set at 150 rubles per hour, the organization operates a summarized recording of working time, the accounting period is a quarter. The general working hours for this employee are 40 hours per week. Let's calculate overtime for Selivanov M.A for the 2nd quarter of 2021, if he worked 496 hours in this quarter according to the time sheet.
According to the production calendar, the standard working time for a 40-hour week in the 2nd quarter of 2021 is 488 hours.
According to the results of the quarter, Selivanov worked 496 - 488 = 8 hours of overtime. Of this time, 2 hours are paid at one and a half times, and the remaining 6 hours at double:
Payment for overtime work Selivanova M.A. will amount to 2,250 rubles based on the results of the accounting period - 2 quarters of 2021 with summarized accounting of working hours.
Legal restrictions
Information about overtime work should not be indicated in the employment contract concluded with the employee. HR employees, in turn, must keep records of their overtime hours. Usually they add up the number of hours at the end of the accounting period and subtract the time provided for by the work schedule from the resulting number. The difference in amounts is the calculation of overtime work.
The duration of overtime work is limited by law. For exceeding established legal norms, not only the organization, but also its leaders can be punished. Thus, the Labor Code establishes the total duration of the working regime - no more than 40 hours per week, that is, 8 hours per day. And the duration of processing should not exceed 4 hours for two days in a row. If we consider the period of possible processing per year - no more than 120 hours. In addition, pregnant women, employees with small children, minor workers, disabled people, and workers on the basis of an apprenticeship contract will not be able to work overtime.
Moreover, with a shift schedule, working two shifts in a row is prohibited. Employees who work irregular hours will not be able to claim overtime pay at all. But they have the opportunity to claim a bonus for working hours.