Tariff rate and tariff category are the main elements of tariff remuneration. We will tell you how they affect the salary and how the minimum wage relates to them. Article 143 of the Labor Code establishes the basic concepts that characterize the tariff system of remuneration. It assumes that workers are paid differently depending on their category.
The tariff rate is one of the basic components of this system. It determines the amount of payment for the designated amount of work. Depending on the category, it increases by the corresponding coefficient.
A qualification category is a parameter reflecting the level of professional training. Their combination, together with increasing coefficients, forms a tariff schedule.
How the tariff scale by category is used in organizations
In each organization, at the local level, it is fixed which remuneration system it uses.
If this is a tariff system, the rules of use of which in 2020-2021 are regulated by the current norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then a local regulatory act, for example a regulation on wages or a collective agreement, prescribes all the components of this system and the principles of their application. Thus, the employer must describe the tariff schedule that will be used when calculating salaries to employees. Within the framework of the tariff schedule, a link to tariff categories is fixed, that is, all positions in the enterprise are divided into certain groups - categories. Typically, the 1st rank is assigned to the least qualified positions, and as the level of complexity of the work increases, the rank also increases.
Note! Naturally, higher wages are set for more complex work that requires certain knowledge and skills. In order not to set separate amounts for each group of positions, tariff coefficients are used. With their help, the salary assigned for positions of the 1st category is automatically increased by the established coefficient for the 2nd, 3rd, etc. categories.
Thus, a tariff schedule is formed, where each category is assigned its own coefficient. The tariff system is used by many enterprises, but their tariff schedules may vary. In private companies, HR employees independently develop salary schedules taking into account the specifics of their activities, and the number of ranks in such schedules varies.
There is more unity in the budget system, since in this case the issues of remuneration are regulated at the state level, including the application of the Unified Tariff Schedule, approved earlier.
What is a tariff coefficient and what does it depend on?
The tariff coefficient is a multiplier that is applied to the wages of a first-class worker. This is an indicator that increases the employee’s salary, taking into account such indicators as tariff category, tariff coefficient. Enterprises usually apply a rank tariff rate consisting of six ranks. Thus, a worker of the first category has the lowest salary, and the sixth, accordingly, the highest. The tariff coefficient of the 1st category corresponds to the minimum wage and is equal to 1.0.
To apply the tariff system of remuneration, you need to have a table with tariff coefficients. At different enterprises they may differ; the tariff coefficient of working grades is determined in the Order on the accounting policy of the enterprise. This is if we talk about a single enterprise. The state has developed a unified tariff schedule for public sector workers. She has 18 ranks. If we talk about specific figures, it is worth noting that compared to the first, lowest, rank 18 has a tariff coefficient of 4.5.
Unified tariff schedule for public sector employees
From the end of 1992 to December 1, 2008, a Unified Tariff Schedule was in force in Russia, according to which salaries for public sector employees were calculated. The main issues were resolved in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On differentiation in the levels of remuneration of public sector workers based on the Unified Tariff Schedule” dated October 14, 1992 No. 785. This act approved the UTS itself, and also recognized it as mandatory for use in all budgetary institutions.
Initially, the Unified Tariff Schedule consisted of 18 categories, it included coefficients from 1 to 10.7. To calculate the tariff rate, for example, for the 5th category, it was necessary to multiply the rate of the 1st category by the coefficient of the 5th category. The only question was what rate to apply for the 1st category. And it was decided in the following way: it was accepted by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Tariff categories were established depending on the complexity of the work. In order to unify the distribution of workers by tariff categories, 2 qualification directories were used:
- Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Works and Blue-collar Professions (UTKS);
- Unified qualification directory of positions of managers, specialists and employees (USC).
Both directories are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. They are constantly updated as the level of technology development increases and new work standards are introduced.
As it was before
Until 2011, the tariff system of remuneration was in effect in all budgetary institutions. The country had a Unified Tariff Schedule of the Russian Federation. It indicated categories for all specialties of public sector workers. The only exceptions were the country's top leaders (ministers and their deputies). The single grid contained 18 bits.
- the profession of a worker belonged to categories 1-4;
- technicians for 2-4 categories;
- engineers for grades 6-13;
- guide to 14-18 categories.
In addition to the salaries indicated in the grid, various allowances were applied. For example, for long working hours, for long service, for working in hazardous conditions, etc. This system has been in effect in the country since 1992. But in 2008, changes occurred. The remuneration scheme for public sector employees has changed. However, it was not immediately possible to completely move away from the Unified Grid. It existed until June 1, 2011.
Commercial enterprises have never been forced by law to apply tariff wages. The decision was up to management. Large factories and large organizations often used such a system. This is convenient when there are several hundred employees. Allows for a fairly fair distribution of the wage fund among people.
The tariff schedule is convenient when the number of employees is several hundred people
This method of calculating wages can only be used by organizations with so-called “white” wages. Unfortunately, salaries in envelopes flourish among commercial organizations. The employer pays employees a certain small amount, from which they deduct taxes and make contributions to funds. The employee receives the rest of the amount in his hands. With such a system, it may turn out that the director officially receives 18,000 rubles. per month, and the cleaning lady also receives 18,000 rubles. per month. And this is a direct violation of Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It states that a person’s salary depends on the working conditions, its complexity, the qualifications of the worker himself, as well as the quality and quantity of labor. Perhaps the actual “gray” salary meets these requirements, but based on the size of the official salary, there is no need to talk about compliance with the norms of Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
197-FZ
One can only guess how much extra they pay out of pocket. The amount of such additional payment depends solely on the will and desire of the owner or manager of the company. And in this case, it is not always possible to talk about fair remuneration for workers.
It is precisely these types of schemes that tariff wages could combat. When using it, it is simply impossible for the official salaries of the director and the cleaning lady to be the same. The employee himself can easily figure out how his salary was calculated, and therefore, if necessary, defend his rights.
Unfortunately, instead of legislating tariff wages for commercial organizations, the authorities went the opposite way and abolished the Unified Grid for public sector employees. Therefore, today private companies also practice remuneration in violation of laws.
Undoubtedly, consolidating the tariff system of remuneration at the legislative level would be a step towards strengthening measures to protect the rights of workers.
New remuneration systems in budgetary organizations
From 12/01/2008, the Unified Tariff Schedule was replaced by a slightly different method of tariffication of public sector employees’ salaries. This happened after the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the introduction of new remuneration systems for employees of federal budgetary, autonomous and government institutions” dated August 5, 2008 No. 583 came into force.
Important! Qualification directories are still in use, but instead of tariff categories, the categories “professional qualification groups” and “qualification levels” are now used. In addition, systems of compensation and incentive payments have been developed and implemented.
Now the salary and rate are set by the head of the institution itself, for which he must take into account the complexity of the work performed and the level of qualifications of the employee. And the salary of the manager himself directly depends on the average earnings of the institution’s employees. This relationship should help to correctly distribute the wage fund among all employees, without bias towards the management level.
Determination of the tariff category and its features
What is a tariff category? The tariff coefficient is a component of the category based on qualification characteristics. It characterizes the level of complexity of the work. The tariff category (tariff coefficient) is one of the most important components of the tariff schedule. How is it determined? It can be found in a special reference book of worker characteristics by skill level.
In the tariff schedule, the countdown always starts with first-class workers. They tend to have the lowest salaries and skill levels. Typically, the salary level for first-class workers corresponds to the minimum wage level determined at the state level.
Classification of simple working professions
In order to maintain the unity of tariffication of work and determination of the qualification level of blue-collar professions, the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations recommends that managers apply the ETKS, which was also in effect during the use of the Unified Tariff Schedule.
This guide contains the following information:
- characteristics of the main types of work;
- the complexity of these works;
- compliance of each type of work with the tariff category;
- requirements that must be applied to the employee’s level of knowledge and skills within the qualification level;
- examples of specific work or professional standards that apply to a particular type of work.
The reference book itself is not a single document, but is divided into sections. Each section is dedicated to a specific field of activity, for example, clothing production or advertising and design work. Each section is fixed by order of the ministry regulating labor relations in this area at the time the order is issued. Since many orders were issued back in the USSR, the reference book also contains orders of the USSR State Committee for Labor. Then orders were issued by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
The tariff and qualification characteristics of each type of work contain 2 sections:
- Characteristics of the work. It describes what the employee must be able to do.
- Must know. This section lists the requirements for the level of knowledge of the specifics of the profession, as well as instructions and regulations regulating work activities.
Issues of the directory are periodically updated, but there are still many types of work left, the standards for which were developed back in the USSR.
The importance of the tariff system
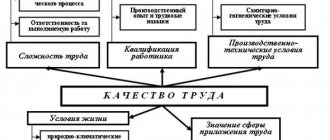
The tariff category, tariff coefficient and tariff rate are used when planning the wage fund at the enterprise. This allows you to determine the level of earnings of certain categories of workers. Let's consider situations where it is important to know the level of tariff rates for certain categories of workers:
- when planning the budget for the basic salary of employees by category;
- during the distribution of the wage fund among categories of workers;
- when planning increases in tariff rates.
An example of a tariff schedule is given in the table.
| Index | Meaning | |||||
| Tariff category | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| tariff coefficient | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,4 | 1,6 | 1,8 | 2,0 |
The tariff system of remuneration has advantages and disadvantages. But its use is currently the best option not only in the budget sector.
Classification of management employees
The CAS was approved by Decree of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated August 21, 1998 No. 37. This reference book is designed to simplify the delimitation of functions and powers of employees, for which the qualification characteristics of individual positions are used. And this, in turn, will help to uniformly apply tariff schedules in organizations.
The directory mentions only mass positions that have become widespread in various fields of activity. Job titles are determined by job responsibilities. The employees themselves are divided into 3 categories:
- managers;
- specialists;
- other employees, such as technical executives.
The directory has 2 sections:
- 1st contains positions that have become widespread in the production sector;
- in the 2nd - in research, design, and design areas.
The qualification characteristics of each position consist of 3 parts:
- Job responsibilities. The main job functions of the employee are listed here.
- Must know. This part reveals the requirements for the level of special knowledge, as well as knowledge of regulations and standards governing activities in the workplace.
- Qualification requirements. This part includes requirements for the level of professional training and work experience.
These qualification characteristics and division of positions can be used when setting wages and forming a tariff schedule. To do this, the remuneration system must be fixed at the local level using elements of the directory.
Does the tariff schedule have a future?
Calculating salaries for employees according to the tariff schedule is quite transparent and simple. This method has been used in our country for several decades. It is worth noting that its simplicity was also due to the technical capabilities of that time. Salaries were calculated manually.
Today, an accountant does not need to carry out payroll calculations independently. A special program does this for him. Therefore, there is no longer any urgent need for a simple wage system - the machine will calculate anything.
Tariff scale example
However, this affected the workers themselves. Previously, a person could count his earnings. Or, using the tariff schedule, determine how much he will receive after mastering a particular profession or reaching a higher rank. Today, many workers, having received a pay slip in their hands, do not understand at all where these or those numbers came from.
However, the tariff schedule continues to exist. Let it be only on voluntary terms. There are still organizations and enterprises that have retained this form of remuneration. What awaits the tariff schedule in the future depends on the decision of the authorities. Most likely, its use will remain advisory in nature.
Definition and Objectives
Soviet legislators developed remuneration according to a certain system back in the first half of the last century. According to the developers, the salary of any employee (from a simple worker to a manager) should depend on:
- from the position held;
- on the complexity and significance of the work.
To determine the difference in salaries, tariff scales (TS) are developed. The basis of the Customs Union is a unified tariff schedule (UTS), compiled in the form of a table. The table elements are:
- wage grades (18 in total);
- tariff coefficients.
The coefficient increases with each rank.
In addition to the ETS, grids are being developed by category, indicating positions and qualifications. Such vehicles are divided into industries. In the public sector, for example, the industries are:
- healthcare;
- education;
- forestry, etc.
In addition, each industry is divided into sub-industries. For example, education is divided into elements:
- Universities;
- public education;
- leaders.
In turn, each sub-sector may contain its own components. Using education as an example, the manager sub-sector contains the following grids:
- general education;
- higher education.
The vehicles themselves are also tables that consist of columns with values:
- position or qualification;
- range of applied coefficients.
For clarity, let's look at an example:
According to the tariff schedule, the salary of a university rector should be in the range of the ETS category from 17 to 18, and that of a school teacher - from 7 to 14.
Rank coefficients: for the rector - from 9.07 to 10.07, and for teachers - from 2.76 to 6.51.
That is, the minimum wage for the first category is multiplied by the specified coefficients.
Which category coefficient to apply is indicated in the reference books:
- ETKS (contains types of work according to the categories of working professions and positions);
- EKS (applies to managers, specialists and employees).
From the above summary: the Customs Union establishes by what coefficient the minimum wage must be multiplied in order to obtain the salary amount.
Tariff rates for workers by category 2021
1.2. This Agreement is a legal act regulating social and labor relations and establishing general principles for regulating related economic relations between authorized representatives of workers and employers of Organizations covered by the Agreement, regardless of the form of ownership of the Organizations, general conditions of remuneration, labor guarantees and benefits for employees, as well as defining the rights, obligations and responsibilities of the parties to the social partnership. The agreement is aimed at improving the system of relationships and coordination of interests between employees, government bodies, local governments, employers on the regulation of social, labor and other related economic relations in the housing and communal spheres, as well as increasing the efficiency of work of housing and communal organizations economy (hereinafter referred to as the Organization), for the implementation of socio-economic, labor rights and legitimate interests of workers in this industry.
Occupational Safety and Health
4.1.6. Issuing certified work clothing, safety footwear and other personal protective equipment to employees in accordance with established standards. A specific list of mandatory special clothing, safety footwear, including warm footwear, and other personal protective equipment, as well as standards for their issuance, are established in the collective agreement. Work without appropriate protective clothing, safety shoes and other personal protective equipment is prohibited.
ORDER of April 4, 2021 N 67 In accordance with the Methodology for determining the cost of construction products on the territory of the Russian Federation, approved, with the Methodological guidelines for determining the amount of overhead costs in construction, approved, with the Methodology for determining estimated prices for labor costs in construction, approved, I order: To establish the amount of funds for workers' compensation for the first quarter of 2021 as part of direct costs in estimates and contract prices for construction by types and complexes of work, structural elements and the facility as a whole in accordance with the appendix to this order. Minister V. KUNIZHEV Appendix to the order of the Ministry of Construction and road infrastructure of the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic from April 4, 2021
We recommend reading: Bonus for 1st category teacher
The Union of Estimating Engineers proposes to establish in the FSIS CS of the Ministry of Construction of Russia from March 25, 2021 BASIC HOURLY TARIFF RATES for wages of workers in construction with normal working conditions and a regional coefficient of 1.0. As the President of the Union Pavel Goryachkin explained, the indicators of hourly tariff rates take into account additional payments and allowances, bonuses and incentive payments that are systematic in nature (length of service, additional
Nuances and rules for using the tariff schedule by category
Related articles Table of contents If you find an error in the text, please let us know by highlighting it and pressing Ctrl+Enter For budget organizations of the lowest rank, increasing coefficients are established at the state level (industry agreements, regional regulations). A commercial organization can develop its own tariff schedule independently, taking into account the collective, trade union opinion.
And many of our compatriots sacrifice their lives for a salary that sometimes does not even reach the average. July 29, 2021 at 11:09 am June 25, 2021 March 02, 2021 February 05, 2021 August 29, 2021 August 13, 2021 FAVORITES This feature is only available to registered users NO THANK YOU
DEVELOPMENT OF A TARIFF SCHEDULE BY COMMERCIAL STRUCTURES
When developing a tariff schedule, the option of increasing (from category to category) inter-category coefficients is used. There are the following options for constructing a tariff scale:
- progressive absolute and progressive relative (in percent) growth of tariff coefficients (Table 1). In this case, with increasing rank, the absolute and relative values of the coefficients increase;
- progressive absolute and constant relative (in percent) growth of tariff coefficients (Table 2), where the value of the relative growth of tariff coefficients is constant;
- constant absolute and regressive relative (in percent) growth of tariff coefficients (Table 3), at which the growth rate of the absolute coefficient is constant;
- regressive absolute and regressive relative growth of tariff coefficients (Table 4). Here, the magnitude of the coefficient and the relative value of tariff coefficients decrease with increasing rank.
The most economical and widely used is the progressive absolute and relative growth of tariff coefficients.
Table 1. Example of a scale of progressive absolute and relative growth of tariff coefficients
ETS of state employees
The payment system in the public sector according to a single grid was used until the end of 2008; today it is not used . To calculate salaries of public sector employees in 2021, the rules of Resolution No. 583 are applied.
This legal act introduced new systems for calculating salaries of employees of municipal, federal or government organizations.
In the new system, the use of the ETKS and EKS directories is mandatory, but the rates or salaries are approved by the head of the organization.
When setting a rate or salary, the head of a budget-funded enterprise must take into account:
- complexity and significance of the work;
- employee qualifications;
- complexity of the work.
Meanwhile, the salary of a public sector employee is not only a bare salary, but also:
- allowances (for length of service, rank, class, etc.);
- bonuses (sizes and grounds are indicated in local regulations);
- compensation (for harmfulness, for example, or “northern”).
According to Resolution 583, the system for setting employee salaries must be recorded in the local act of the organization:
- in the collective agreement;
- in the regulations on wages and bonuses;
- in other agreements.
How exactly to develop a remuneration system is described in the recommendations of the Russian Commission dated December 25, 2015. (Record of decision No. 12).
The commission decided that the salary of the head of an enterprise directly depends on the average salary of his subordinates. In addition, when forming a remuneration system, the following conditions must apply:
- the salary for the lowest category cannot be less than the legal minimum wage;
- the work of workers of the same position and qualifications should be paid equally;
- salary reduction is unacceptable;
- fixed salaries and rates are set taking into account membership in a professional qualified group;
- all salaries, rates, allowances and bonuses are included in the staffing table.
As a result, what we get: the amount of salary (salary + bonuses and allowances) can be found out from local acts:
- staffing schedule;
- collective agreement (if any);
- regulations on wages, bonuses, allowances, etc.
Employees have the right to familiarize themselves with all documents and acts of the organization that relate to salaries.
Classification of working professions
According to the norm of Article 143 of the Labor Code, an employee’s payment must be proportionate to his efficiency. That is, the higher the rank or qualification of an employee, the more expensive his work. And the category directly depends on the type of work. All types of work inherent in a particular category (by profession) are listed in the ETKS.
The directory defines:
- industries (construction, foundry, forging, etc.);
- professions;
- ranks.
The directory is regularly updated; the current version of ETKS is located here.
For each category of any working profession, the directory describes:
- what education should the employee have;
- experience;
- what he should know and be able to do;
- what work to do.
Based on the data from the directory, you can set a category or tariff coefficient.
Classification of managers
The management team (managers) is the administration of the organization, whose tasks include ensuring the activities of the enterprise in accordance with:
- with the goals of the enterprise;
- with current legislation.
That is, the administration is obliged to organize its work in such a way that the enterprise works for the result outlined in the charter, and at the same time the legal rights of workers and the state are respected.
For this purpose, Soviet developers created the EKS reference book. It is still in effect, but changes regularly. Its latest edition was approved in 2014. The directory contains information:
- titles of management positions;
- requirements for knowledge and skills for each position;
- education and experience requirements;
- main functions.
All data can be viewed via the link.
The directory describes the requirements for positions in all departments of the management apparatus:
- to managers (directors, managers, heads of departments, etc.);
- specialists (engineers, technicians);
- employees (agents, secretaries, operators).
The directory data is required for the development of a remuneration system in the organization.
Continuous work experience is maintained if the break was no more than...? You can find out the answer in our article. You can find out how to receive maternity payments in the amount you need here.
The correct algorithm for obtaining and processing your sick leave is here!