There are many indicators characterizing the development of a state’s economic system. The well-being of specific citizens depends on what level the entire country has achieved.
The minimum wage is also an indicator that requires consideration. What is the minimum wage, how the concept is deciphered, what features are associated with it, will be described in detail in this article.
Minimum wage: what is it?
The abbreviation MROT stands for minimum wage. This is the lower threshold of the amount that an employer is required to pay an employee for a full month worked. This indicator is approved by law and is mandatory for all employers, regardless of the form of ownership of the organization. Failure to fulfill the employer's obligation to set a salary not lower than the minimum wage entails administrative liability.
For almost the entire post-Soviet history, Russia was characterized by a significant lag between the minimum wage and the subsistence level, and only since 2016 the situation began to change. From May 1, 2018, the minimum wage is equal to the average subsistence level in the country.
Changes in the federal minimum wage in the Russian Federation over the past 10 years
Data are presented in reverse order.
| Date of establishment of the new minimum wage | Minimum wage amount |
| from January 1, 2021 to the current moment | 12130 rubles |
| from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2019 | 11280 rubles |
| from May 1, 2021 to December 31, 2018 | 11163 rubles |
| from January 1, 2021 | 9489 rubles |
| from July 1, 2021 | 7800 rubles |
| from July 1, 2021 | 7500 rubles |
| from January 1, 2021 | 6204 rubles |
| from January 1, 2015 | 5965 rubles |
| from January 1, 2014 | 5554 rubles |
| from January 1, 2013 | 5205 rubles |
| from June 1, 2011 | 4611 rubles |
| from January 1, 2009 | 4330 rubles |
Watch a foreign video, designed in a cartoon format with Russian subtitles, which clearly reveals the essence of the concept of minimum wage (minimum wage) and how it affects unemployment:
Video: How the minimum wage creates unemployment
What does a promotion give?
The minimum wage is the lower limit of earnings. In Russian regions there are still employees who receive salaries comparable to the minimum wage in the country. These citizens benefit from increasing the minimum wage.
The rest of the working population does not experience any changes due to its increase. Social compensation, including calculations for sick leave, increases with the increase in the minimum wage in the country, since it is taken into account when calculating these benefits.
Low-income families receiving government support benefit the most from increasing the minimum wage.
Why and who needs a minimum wage?
First of all, the minimum wage is used to regulate labor relations. Employers of any form of ownership do not have the right to pay wages below the minimum level established by law. Exceptions are specifically stated in the law; they will be discussed below.
In addition, social benefits (maternity benefits, sick leave), and in some cases unemployment benefits are calculated based on the minimum wage.
The size of the minimum wage in the Russian Federation has not only economic, but also political significance. Some political forces have long called for an increase in the minimum wage to a living wage. Others argued that such actions would fuel inflation by causing wage increases that were not matched by increases in labor productivity and, as a consequence, higher prices. As a result, the principle of political expediency prevailed: against the background of a series of election campaigns over 2 years, the amount of the minimum wage increased by more than 80%. A mitigating circumstance was the record low level of inflation in the country.
In total, according to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, an increase in the minimum wage directly affects payments to approximately four million working residents of the country. Another 12 million have salaries and benefits tied to the minimum wage.
Why is a minimum wage needed at all?
The minimum wage is one of the regulators in the labor market. This is how the state influences employers so that they gradually increase wages. At least minimal, to the level of inflation in the country. This is necessary in order to gradually increase the level of well-being of citizens and increase tax revenues in nominal terms.
In nominal terms - in rubles. In reality, the ruble becomes cheaper every year due to inflation, so the actual amount of taxes and the minimum wage in most cases remains unchanged.
The minimum wage is also a political instrument. This is how factions in economically and socially developed countries influence ordinary citizens. Some call for increasing the minimum wage constantly, while others, on the contrary, keep it at the same level and index it only to inflation. Regardless of the course, parties will change each other, and, accordingly, the politics in the country. After all, if someone does a bad job, they replace him.
Such political influence is relevant for Western Europe and the USA. There are several strong parties that balance with each other, changing periodically. Some pursue a policy of increasing the minimum wage and improving the social situation, others focus on the economy. As soon as one course fails, the second one is connected.
In our country, the political influence of the minimum wage is practically minimal. All politicians understand that if the minimum wage is now sharply raised to the conditional 20,000 rubles, then small and medium-sized businesses will suffer greatly. Some firms will close, the number of jobs will decrease, taxes will be cut and opportunities for social improvement will decrease. But in the future, under a different political system, the minimum wage will have a stronger influence on votes in elections.
The minimum wage is also used by some employers to evade taxes. In any business, with the exception of a small individual entrepreneur, the biggest expense is employee wages. The employer pays from the salary:
- 22% to the pension insurance fund;
- 2.9% to the social insurance fund;
- 5.1% to the health insurance fund.
Essentially, the employer must pay 30% of the employees' salary in the form of contributions. If you leave only the minimum wage, and pay all the remaining money on top, you can save significantly. And increase your salary accordingly. But there is a small problem for the workers themselves: sick leave will be paid according to the official salary; The pension will also be calculated based on the official salary. Therefore, for employees with average and high salaries, it is more profitable to work in a white position.
Who sets the minimum wage
The minimum wage according to Russian legislation is established both at the level of the entire country and for each region. Moreover, the regional minimum wage cannot be less than the federal one.
The all-Russian level is proposed by the government of the Russian Federation, adopted in the form of a law by the State Duma, approved by the Federation Council and signed by the president. The regional size of the minimum wage is established by an agreement concluded for 3 years between the government of the region, territory or republic, the regional association of trade unions and the regional association of industrialists and entrepreneurs.
Regional levels of indicators
Municipal authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to set a minimum wage level that differs from the national one. As of 2015, similar changes were made in 27 regions of our country. The Labor Code describes specific requirements that must be observed:
- The minimum wage is formed only taking into account the subsistence level.
- We must also rely on the current level of unemployment, prices for goods and products, and wages.
- The regional minimum is usually higher than the federal one.
Most often, regions where the economy is sufficiently developed strive to increase the indicator. For example, in the Far North, where prices fully compensate for any costs. Residents of such territories cannot survive on the minimum wage at the federal level. In Moscow, this figure is also one of the highest.
What is a regional minimum wage
To establish the minimum wage in a subject, an appropriate regional agreement must be in force. Most regions of the country did not take advantage of the opportunity to set their own indicator. But, for example, in the capital, the Moscow region and some other regions there is a regional agreement. It uses the cost of living in the region as a “reference point”. In accordance with the document, the minimum salary in Moscow in 2021, from January 1, 2021, is 20,195 rubles. After such an agreement is accepted, employers begin to implement it or write a reasoned refusal. 30 days are allocated for this from the date of official publication of the document. After this time, employers who have not provided a waiver are automatically considered parties to the agreement.
What laws regulate the minimum wage?
The minimum wage is regulated by several legal acts.
1 Federal Law “On the Minimum Wage” (No. 82-FZ of June 19, 2000).
A fairly outdated document, the main value of which is to determine the scope of the minimum wage: to regulate wages and determine the amount of benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth, as well as for other purposes of compulsory social insurance. This indicator cannot be used for other purposes.
2 Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It states that the minimum wage cannot be lower than the subsistence level. This point has not been implemented for a long time, but since May 2021, reality has been brought into line with the law. Also, Article 133 specifies how the minimum wage should be paid:
- private companies - at their own expense;
- budgetary companies - at the expense of funds from the relevant budgets (federal, regional or local, depending on the organization’s jurisdiction) and extra-budgetary money (for example, from income from paid services, voluntary donations, grants, etc.).
In addition, it is noted that the minimum wage is due to any employee who has fulfilled the monthly work standard established for his position.
3 Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
It regulates the setting of minimum wages in the regions. The text almost completely repeats Article 133 with the difference that in regions, territories and republics, workers’ wages cannot be lower than the regional minimum wage. The regional minimum wage does not apply to employees of organizations financed from the federal treasury.
4 Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Here it is defined that wages are salary, compensation and incentive payments. In relation to the minimum wage, this formulation is important because theoretically, an employee’s salary may be less than the minimum if he does not fulfill the requirements that entail receiving a bonus. This is in conflict with Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (“The monthly wage of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours during this period and fulfilled labor standards (labor duties) cannot be lower than the minimum wage”). A way out of such a legal conflict was found in increasing the compensation part: even if an employee is not entitled to a bonus in a given month for some reason, he is given an additional payment up to the minimum wage level.
5 Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2017 N 38-P
A document with the dry title “On the case of verifying the constitutionality of the provisions of Article 129, parts one and three of Article 133, parts one, two, three, four and eleven of Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” is extremely important for millions of Russians. In it, the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation put an end to discussions of whether regional coefficients (RC) are included in the minimum wage. The fact is that in Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation until 2007 there was a clause that the minimum wage is the minimum wage for unskilled labor under normal conditions (accordingly, any allowances for qualifications and special conditions must go above the “minimum wage”). There are still many articles circulating on the Internet that cite this point as valid. However, back in April 2007, State Duma deputies excluded it from the law. They did not fail to take advantage of this in regions where increasing coefficients were established for difficult working conditions - in the Far North, for example.
As a result, it turned out that the region set the minimum wage slightly higher than the federal one, but allowed “northern” allowances to be included in it. The Constitutional Court explained that the minimum wage must be provided to all workers, regardless of working conditions. This means that the “northerns” have nothing to do with it. Accordingly, employers are obliged to pay employees not “minimum wages, including the Republic of Kazakhstan”, but “minimum wages plus the Republic of Kazakhstan”.
6 Federal laws No. 41-FZ of March 7, 2018 and No. 421-FZ of December 28, 2017.
These legal acts establish the amount of the minimum wage as of May 1, 2021 and the rules for changing the minimum wage subsequently (more on this in the FAQ section).
Definition and role of the minimum wage
The minimum wage in the Russian Federation, or minimum wage, is determined at the legislative level.
The basic value of this value in the country today is 12,130 rubles (in 2021 it was 11,280 rubles.) Every citizen of Russia needs to know this information in order to prevent violation of their rights by their employer or government officials. On the one hand, the minimum wage in the Russian Federation is the minimum amount of earnings established at the legislative level for a person that can be paid for a certain period. This period can be a month, a year, a week or several days. The main condition is that the employee fulfills the terms of the employment contract. In this case, the employer has no right to pay less than 12,130 rubles. However, this rule can only be applied if the person is officially employed in the organization.
On the other hand, the minimum wage in Russia is a measure of regulation of the amount of state benefits for the non-working population, taxes, fines and fees for legal entities and individuals conducting business activities.
Minimum wage and living wage - what's the difference?
The living wage is a social indicator. It shows how much money you need to live at a sufficient level. The living wage is formed from the following indicators:
- Consumer basket. For the most part, all indicators of the living wage are based on the minimum basket, which is developed by the Government together with Rosstat.
- Formal statistics on rising food prices. For example, there was recently a good article on Pikabu, where the author compared product prices now and 5 years ago. Directly with checks. And the real inflation rate has been about 10% per year or 50% over the last 5 years. But statistically, in our country, inflation during this time was slightly more than 20%, so this is the indicator that is used when compiling the cost of living.
- Price growth index. This is inflation, only the indicator is slightly different. As in the previous case, the nominal rather than the actual indicator is taken into account.
- The amount of all mandatory payments. Utility bills, payment for rented housing and similar mandatory things that no citizen can do without.
The cost of living indicator is compared with the income of different population groups. Thanks to this indicator, additional payments are formed:
- Benefits.
- Tax deductions.
- Government subsidies.
- Grants, etc.
The difference is also in the significance of these indicators. The minimum wage is rather an economic figure. It shows how much money employees should receive, how much taxes will be paid and how the business will develop. But the living wage is a social norm. It shows the overall welfare of the population and how much the average worker should spend per month.
What new minimum wage is in effect now?
Here I will show you a free tool with updated information on the minimum wage.
To easily use the tool you need to distinguish between 2 concepts:
- Minimum wage - minimum wage,
- MW – minimum wage.
What is the difference between them?
The minimum wage is set at the federal level.
It operates throughout the Russian Federation.
However, regional authorities can set their own minimum wage, which is valid on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Is it planned to increase the minimum wage?
The minimum wage is increased every year. In most cases, it is indexed for inflation + a couple of % are added to the final amount. This is done in order to maintain the same level of taxation and report to higher authorities about the increase in real salaries of citizens.
In 2021, it is also planned to increase the minimum wage. From January 1, the minimum wage will be 12,130 rubles.
The cost of living for pensioners, the most vulnerable segments of the population, in 2021 is projected to be 9,311 rubles. This is indicated in the 2021 federal budget.
What is included in the minimum wage
Based on the above legal acts, the minimum wage includes:
- An official salary or other remuneration for work based on the employee’s skill level.
- Compensatory payments (in particular, additional payment to the minimum wage level for employees whose salaries are lower, as well as a regional coefficient in territories where they are in no hurry to implement the decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, given above).
- Premium payments.
About additional payment to the minimum wage
To process such additional payments, the management of the enterprise must issue a separate order. This should happen immediately after it becomes clear that the salary is below the established minimum.
Such orders can be issued only once and then not be duplicated separately for each employee. After the document is issued, the accounting department must carry out the appropriate recalculations.
The main thing is to register the actions taken officially, using the appropriate logs.
Minimum wage when working on weekends and holidays
The Labor Code includes special articles devoted to work on holidays, weekends, and at night. This time is calculated and paid in excess of the labor standards established for this position. Accordingly, overtime is not included in the minimum wage. Payments for additional time worked are not included in the minimum wage (if a junior teacher works at one and a half times the rate, the “minimum wage” is calculated based on one rate).
For overtime hours, payment is 1.5-2 times more expensive than usual (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and for work on holidays or weekends - double the amount of payment. Night work is paid in accordance with the standards at each enterprise, but always at an increased rate (by at least 20%) compared to daytime work. The difference is also not taken into account in the minimum wage.
What does the minimum wage consist of?
The minimum wage in Russia is the lowest payment for the work of an unskilled employee. And this means full-time work. It is necessary to carry out the work process under normal conditions.
Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines the components of the minimum:
- the work itself, taking into account the employee’s qualifications;
- volume produced;
- various surcharges.
So according to Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum wage includes the following transfers to the employee:
- salary determined based on the specialist’s qualifications, complexity and characteristics of the work;
- compensation payments (for example, due for harmful or dangerous working conditions);
- incentive payments (annual, quarterly, monthly bonuses, etc.);
- other additional payments received from the hiring company.
If an employee works as an internal part-time worker, i.e. In addition to the main duties, he performs additional ones, the latter are paid separately.
The income of an external part-time worker depends on the agreements reached between him and the company. If a person worked at 1.5 times the rate instead of one, he cannot receive a salary of one “minimum wage”. His income will be calculated in proportion to the time worked.
What is the minimum wage made up of?
The minimum wage for an employee in 2021 is calculated in the amount of 12,130 rubles. What is included in the minimum wage in 2021, and are compensation and incentive payments included in the minimum wage?
Let's find out what payments are included in the minimum wage:
- the main part of the “minimum wage” is the salary, which is assigned to the employee according to his position and qualifications;
- allowances and additional payments that compensate for unfavorable and harmful to health and life-threatening working conditions, as well as other types of compensation that are included in the employment agreement;
- monetary rewards that stimulate employee motivation. These include incentive bonuses, additional allowances and additional payments. Bonuses are paid for achievements and production results in an employee’s work. Bonuses are given to holders of academic degrees, for length of service, etc.
If the salary is calculated only from the salary amount without accruing additional payments, then the salary cannot be set less than the minimum wage. If the salary is still below the “minimum wage,” what is included in the minimum wage when calculating wages in 2021? In this situation, the employer will have to use additional payments to bring the salary rate to the mandatory minimum wage level
In situations where compensation and incentive payments are established for the employee in addition to the base salary, it is possible that the salary is less than the minimum wage. But the final salary, taking into account all payments, has no right to be set below the minimum payment (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In both cases, from an accrued salary of at least 12,130 rubles, a personal income tax of 13% is withheld from the mercenary. Therefore, in fact, the employee will receive: 12,130 x 13% = 10,553 rubles, which, in fact, contradicts the principle of social protection for workers. In most countries, the minimum wage indicator is removed from the tax field.
It is worth noting that the interpretation of the minimum wage, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, allows employers to manipulate when setting salaries for employees. For employees, even with specific qualifications, a rate is set below the minimum, and then, with the help of additional payments and compensations, they are brought into compliance with the minimum wage. This practice not only distorts the real state of affairs in determining the actual level of the minimum wage, but also the principle of protecting the social and labor rights of workers.
What accruals are not included in the “minimum wage”
When calculating the minimum wage, those payments that are not related to the payment of the main job, in accordance with established labor standards and working hours, are not taken into account.
Part-time work refers to work performed during free time from primary job responsibilities. The payment will be added beyond the minimum wage if the number of labor hours established by the standard is exceeded (Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1/OOG-7353). The same principle applies to overtime premiums.
Regional coefficient. This indicator is established for areas with unfavorable and severe climatic conditions (Article 148 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and implies an increased salary. Resolution of the Constitutional Court No. 38 of December 7, 2017 established that regional coefficients and additional payment for each year of work in the Far North and areas equivalent to it are not included in the “minimum wage” component.
This rule applies not only to the minimum wage indicator, but also to the minimum wage. If the minimum wage is already set above the federal minimum wage, northern additional payments are made based on the minimum wage, if it does not include them.
The ratio of minimum wage and salary
If the employee’s salary includes only the salary, and the variable part is not provided, then the salary must be no less than the minimum wage. But when the salary includes bonuses, allowances and other incentive components, the salary may be lower than the minimum wage. As mentioned above, Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation only requires that the total amount of remuneration for work not be lower than the minimum wage.
An important question: what amount is considered the minimum amount - including personal income tax or “net”, received by the employee in person? The legislation views this issue as follows: the employer is an intermediary between the employee and the tax service. It is not he who collects the tax. This means that the employer’s task is to charge an amount no less than the minimum wage. And paying income tax on this money is the employee’s business; the employer has nothing to do with him (except for technical transfers). Accordingly, from May 1, 2021, the employer is obliged to charge an amount not less than 11,163 rubles. In fact, taking into account the payment of personal income tax, the employee receives 9,711.8 rubles.
Here are two more cases when wages can be legally lower than the minimum wage:
1Part-time job. Article 285 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for remuneration for part-time work based on the volume of output or in proportion to the time worked.
2Part-time work. Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the employer to pay below the minimum wage for part-time work. This can be either ordinary work in a reduced volume, or the activities of certain categories of workers who are allowed by the Labor Code to use part-time work (minors; pregnant women; caring for sick family members; parents of a disabled child under the age of 14).
How is the minimum wage deciphered?
This concept is necessary in order to correctly calculate the amount of tax fees, penalties, penalties and other payments. What is the minimum wage? In simple words, this is the minimum adopted by the government of the Russian Federation, which each enterprise is obliged to pay to its employee for the month worked.
Each employee should know the amount of his salary, since this is a kind of evidence that he will not receive less than this amount for the period worked. According to the law, an employer cannot pay a salary lower than this indicator. If an enterprise nevertheless pays less than the minimum wage, then it faces both administrative and criminal liability.
What are the consequences of a salary below the minimum wage?
Despite the fact that remuneration for a full month of any work cannot be lower than the minimum wage, there are quite a lot of organizations in Russia where even the minimum wage is not paid. Due to the peculiarities of tax legislation, the main reason for violating the requirements of the Labor Code is an attempt to reduce the fiscal burden on business. The lower the salary, the less accrual on it (amounts going to the Pension Fund and Social Security Fund). Therefore, many entrepreneurs prefer to pay a meager salary officially, and the rest of the salary goes “in an envelope” and is not subject to state accounting and taxation. In many cases, it turns out that formally the monthly payment is below the minimum wage.
For employers paying wages below the minimum established level, a fine of 10 to 20 thousand rubles is provided for officials, and from 30 to 50 thousand rubles for legal entities. Individual entrepreneurs can be punished with a fine of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles.
For a repeated violation, the fine for officials increases to 20-30 thousand rubles, for legal entities - up to 50-100 thousand, for individual entrepreneurs - up to 10-30 thousand rubles. In this case, the guilty official (for example, the director of a company) may be disqualified for up to three years.
What to do if your salary is below the minimum wage?
If you really want to officially receive at least the minimum level of wages (this is not always rational for the employee, since by increasing the official part of the salary, the employer reduces the total amount paid, subtracting taxes and charges from it), the procedure is as follows:
1Make a free-form demand to the employer to review your salary and pay the difference between your official salary and the minimum wage for the entire period of work.
2If the employer refuses to revise the official part of the salary, a copy of the request along with the application can be sent to the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office.
Pros and cons of increasing the minimum wage
The positive aspects of increasing the minimum wage are obvious: rising wages improve the standard of living of the population.
The negative aspects are well disguised. Let's analyze the disadvantages of increasing the minimum wage:
- not all employers are able to pay their employees wages increased to the minimum wage. This leads to job losses and increased unemployment;
- a decrease in the difference between the average salary and the minimum wage reduces the motivation of low-wage workers to acquire new skills and knowledge;
- reduction of investments in economically weak regions. It becomes less profitable for investors to invest their funds due to the fact that they will have to pay more to hired workers. This leads to an outflow of investment to countries with lower labor costs;
- an increase in prices for manufactured goods, since the calculation of the selling price includes wages of workers.
Minimum wage and living wage
Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly states: the minimum wage should not be lower than the subsistence level. Since the beginning of the 90s, this standard has not been met due to a lack of budgetary funds (most of the positions that are paid below the minimum are in the public sector). Since 2021, the gap between the minimum wage and the living wage has begun to narrow. And on both sides: in many regions, decisions were made to reduce the cost of living.
In order to avoid such manipulations and due to the low level of inflation, as well as for the political reasons that have already been mentioned, a decision was made from May 1, 2021 to set the minimum wage at the level of the average subsistence level in the country. However, in reality, due to the collection of personal income tax, the income of an employee receiving the minimum wage will still be below the subsistence level.
Increasing performance
Based on all of the above, you can understand the difference between the minimum wage and the subsistence level. What are the forecasts? When will people be provided with a decent salary on which they can live fully?
Now it is 2021, and it is the last one in the Action Plan of the Ministry of Social Protection and Labor. There is growth, but it is very slight. Not only citizens of the country, but also trade unions think so.
If we compare the Russian minimum wage with indicators in other countries, a sad picture emerges. The Russian Federation, considered a developed state, one of the strongest in the world, is in the third ten. Of course, someone may argue that other countries have higher prices and taxes, but all this is taken into account when compiling the rating. So citizens of other countries, even with a minimum salary, still have “free” funds.
Minimum wage and sick leave
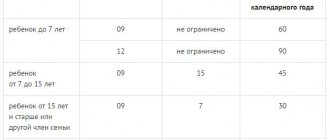
Temporary disability benefits are calculated based on the minimum wage in several cases:
- If the employee's work experience is less than 6 months.
- When the average employee's earnings are below the minimum wage.
- If the sick person has had no income in the last 2 years.
- If an employee, being admitted to a hospital, violated the hospital regime (for example, went home without permission, interrupting the course of treatment).
- If an employee missed a regular medical examination (at jobs where it is mandatory) and then went on sick leave.
The amount of sick pay depends on length of service. The calculation algorithm is as follows:
1Calculation of the minimum average daily earnings (MSW):
MSZ = minimum wage * 24 months / 730 days
2If sick leave has been issued over the past two years, then the number of days of temporary disability is subtracted from 730 days.
Minimum wage and benefits
“Maternity” benefits are calculated based on the minimum wage in several cases:
- If the employee has not worked within the last 2 years
- If the employee’s average salary was lower than the current minimum wage
- If the employee's length of service is less than six months
Child care benefits up to 1.5 years old cannot be lower than the minimum wage.
Unemployment benefits depend on the minimum wage when the unemployed person has minor children or other persons with limited legal capacity as dependents. In this case, the benefit amount increases by ½ minimum wage for each dependent.
The maximum unemployment benefit cannot exceed the “minimum wage” by more than 1.5 times.
Payments that no longer depend on the minimum wage
Until recently, entrepreneurs made insurance contributions based on the minimum wage, but from January 1, 2021, they were replaced by fixed amounts.
Until mid-2007 (before amendments were made to the Code of Administrative Offenses by Federal Law No. 116-FZ dated June 22, 2007), fines depended on the minimum wage. The minimum wage for calculating fines was considered equal to 100 rubles.
Until July 2009, the minimum wage was used to calculate the size of the authorized capital of joint-stock and unitary enterprises.
New minimum wage
Let's look at the highest and lowest cash payments in Russian regions for 2021. From January 1, the minimum wage increased to seven thousand eight hundred rubles. Most urban districts adhere to the same amount.
There are regions with a minimum wage higher than seven thousand eight hundred rubles, for example:
- Bryansk and Vladimir regions increased the figure to eight thousand five hundred rubles.
- Kursk region - nine thousand eight hundred rubles.
- Moscow - seventeen thousand five hundred rubles.
- Moscow region - thirteen thousand seven hundred rubles.
- Ryazan and Tambov region - eight thousand three hundred rubles.
- Yaroslavl region - ten thousand rubles.
- Krasnoyarsk Territory - from ten thousand five hundred rubles to twenty seven thousand seven hundred rubles.
In the Oryol region, the minimum wage has increased to ten thousand rubles. And in the Tula region, the minimum wage increased by five thousand two hundred rubles.
It is worth noting that in the entire Siberian region the minimum wage is higher than the standard established by the state.
Minimum wages in the regions
In accordance with Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, any region of Russia has the right to establish its own minimum wage. The only condition is that it should not be lower than the federal one. In the northern regions, in addition to the national minimum wage level, bonuses and coefficients are awarded. In Moscow and St. Petersburg, the minimum wage has historically been higher than the national average. The minimum level of wages varied significantly in cities with special working conditions (Norilsk and other industrial areas). Before May 1, 2018, almost three dozen regions of the country had a minimum wage that differed from the national minimum wage. After raising the minimum level to 11,163 rubles, the number of such federal subjects decreased.
Regions in which the minimum wage differs from the national average
| Region | Regional minimum wage (rub.) |
| Moscow | 18742 |
| Saint Petersburg | 17,000 (11,163 for public sector employees) |
| Magadan Region | 19500 – 21060 (depending on territory) |
| Kamchatka Krai | 18360 – 21180 (depending on territory) |
| Irkutsk region | 11163 – 27908 (depending on territory) |
| Krasnoyarsk region | 11163 – 26376 (depending on territory) |
| The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 17388 (11163 – for public sector employees) |
| Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 16299 (including allowances and bonuses) |
| Murmansk region | 15185 (11163 – for public sector employees) |
| Moscow region | 13750 (11163 – for public sector employees) |
| Tula region | 13,000 (11,163 for public sector employees) |
| Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 18567 (11163 – for public sector employees) |
| Tomsk region | 11163 – 16500 (depending on territory) |
| Khabarovsk region | 11163 – 15510 (depending on territory) |
| Republic of Karelia | 11163 – 12100 (depending on territory) |
| Kemerovo region | Cost of living in the region for the previous quarter * 1.5 |
| Volgograd region | Cost of living in the region for the previous quarter * 1.2 |
| Bashkortostan | Federal minimum wage + bonuses, allowances and coefficients (the minimum wage includes only salary) |
| KHMAO-Yugra | Federal minimum wage + regional coefficient |
As mentioned above, the regional minimum wage is irrelevant for employees of budgetary institutions receiving salaries from the federal budget. In addition, in order to avoid a sharp increase in regional budget expenditures, many federal subjects establish an all-Russian minimum wage for all budgetary organizations - both federal, regional and local.
Purpose and rules of use
In Russia, the minimum wage is used to solve such main problems as:
- monitoring and adjusting wage levels;
- establishing the amount of cash benefits (social benefits and benefits);
- assessment of the rights of those groups of citizens who are insured with pensions.
In addition, individual entrepreneurs who carry out their activities make certain insurance contributions based on the minimum wage. This means that when the cost of living in a country increases, not only the size of wages increases, but also the amount of deductions increases, which leads to higher prices.
The minimum wage stands for a certain indicator that affects the amount of fines and taxes. In addition, the minimum subsistence level is applied in the following codes:
- Tax.
- Civil.
- Administrative.
In all legislative acts it is used at the initial level, in relation to which all monetary fines are formed.
FAQ
The minimum wage has been legally increased to the subsistence level. But the latter is set every quarter and often downwards. Does this mean that the minimum wage may be higher than the subsistence level?
On May 1, the legislator introduced a flexible system for determining the minimum wage. Federal Law No. 41-FZ of March 7, 2018 established the minimum wage at 11,163 rubles. This minimum wage will be in effect until January 1, 2021, after which Article 3 of Federal Law No. 421-FZ of December 28, 2017 will come into force. It states: the minimum wage is set once a year from January 1 at the level of the subsistence level for the second quarter of the previous year. Moreover, the current level of the minimum wage cannot be reduced: if it turns out that the cost of living has fallen, the minimum wage will still be 11,163 rubles. So, in theory, the minimum wage may be higher than the subsistence level.
I am an employer, I opened a branch in a region where the local minimum wage is higher than the federal one. Established by tripartite agreement. If I refuse to join this agreement, can I calculate the salaries of branch employees based on the federal minimum wage?
Formally, the employer has the right to refuse to join the agreement on the regional minimum wage. To do this, he must, within a month from the date of publication of the agreement or opening of the enterprise, send an official refusal to the commission that concluded the agreement. The document must be motivated. In your case, this may be the start of a business; difficult economic circumstances are also taken into account: a fall in the stock market, the bankruptcy of the bank in which your funds were located, a refusal of a loan, emergencies, etc. Each argument must be supported by documentation: an extract from the balance sheet, a report from the insurance company, and so on. But even in this case, the chances of a positive solution to your question are almost zero. At least in the Russian Federation, there are no precedents when companies were allowed to apply the federal minimum wage in regions where a higher regional one applies.
Over the past 2 years, the minimum wage has been increased 4 times. From what minimum wage are sick pay calculated (when calculating them, a period of 2 years is taken) - from the current one, or are all 4 amounts taken into account, broken down by the periods in which they were valid?
All benefits (for temporary disability, for pregnancy and childbirth, for child care up to 1.5 years) are calculated only on the basis of the minimum wage in force at the time of calculation.
How is it calculated and by whom is it installed?
We have so far been talking about a salary amount set by someone without naming it. I'm correcting myself. From January 1, 2021, the minimum salary was 11,280 rubles. Let's look at where exactly this figure came from.
Article 133 of the Labor Code establishes that the minimum wage cannot be lower than the subsistence level. Until May 2021, this condition was not met in the Russian Federation. Discussions about rectifying the situation have been going on for several years. Finally, from May 1, 2018, the minimum wage was equalized with the subsistence level, and it became equal to 11,280 rubles.
The subsistence level is a set of food and non-food goods and services that a person needs for existence.
This amount is calculated for different categories of citizens: the working population, pensioners, children. The minimum wage is equal to the subsistence level of the working population. This is done as follows:
- The minimum wage is set annually, and the subsistence minimum is set quarterly. Therefore, for the current year, the minimum wage level is equal to the cost of living for the 2nd quarter of the previous year, i.e. 2021. And this is 11,280 rubles. For 2021 it will be set according to the 2nd quarter of 2021, etc.
- If the cost of living changes downward during the year, this will not affect the minimum wage in any way. In this case, it will remain at the same level. If the cost of living increases, then the minimum wage will also increase.
The minimum wage is set at the federal and regional levels. In the first case, it applies throughout the entire country, in the second, throughout the entire region. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the regional minimum wage cannot be lower than the federal level. Any entity sets its minimum wage on the basis of a signed agreement between:
- trade union organizations,
- employers' associations,
- executive authorities.
Within 30 days, an employer who does not want to join the agreement submits a reasoned refusal. In other words, he must prove why he cannot comply with the terms of the document. If such a refusal is not received, it is considered that the employer agrees to fulfill the conditions and pay a salary not lower than the regional minimum wage.
The agreements apply to employees working in the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, with the exception of people who receive salaries from the federal budget.
The size of the regional salary is not taken from heaven, but is set depending on the socio-economic situation of the region and the cost of living. The latter is very different from region to region. For example, in the 2nd quarter of 2021 (the quarter for which the minimum wage is set), the cost of living in the Ivanovo region was 11,003 rubles. for the working population, in Moscow – 18,781 rubles.
I will not provide a table by region with the minimum wage level today, i.e. 2021, in the article. It will take up too much space. Her analysis showed that in most subjects of the Russian Federation the federal amount is established, because the regions have not yet adopted agreements on the regional minimum wage.
In Kamchatka it amounted to 29,024 rubles, in the Kemerovo region - 18,313 rubles. In some regions, especially northern ones, the minimum wage also depends on the region. For example, in the Magadan region it is equal to 33,150 rubles, and in the separate North Evensky district - 35,802 rubles.