What is the tariff system of remuneration. Differences from the tariff-free system
The tariff system includes a number of provisions, norms, rules and regulations that make up a unified method of calculation, as well as the calculation of employee wages. The form of remuneration under consideration differs significantly from the non-tariff form.
The tariff system takes into account the complexity of the work, its intensity, working conditions, qualifications of certain categories of personnel; only if the specified components are available and analyzed, the employee will be paid a salary.
The non-tariff system has fundamental differences: the wages of all employees of the enterprise depend on the results of the work of the entire enterprise and on the amount of money allocated by the employer to pay for the labor process.
A fundamentally important element of the non-tariff system is the coefficient that takes into account the individual contribution of each employee to the overall final result. The tariff-free system is distinguished by the fact that the salary of each member of the work team is part of the general wage fund.
The tariff system of remuneration includes the main elements:
- tariff schedules;
- tariff directories;
- tariff rates.
Do you need help from a labor lawyer?
We will analyze your prospects for free!
+7
The tariff schedule is a scale of tariff categories and corresponding tariff coefficients, establishing the ratio of wages for workers of various qualifications.
In organizations transporting and storing oil, petroleum products and gas, six-bit grids are used. Payment ratios between categories are expressed by tariff coefficients. The tariff coefficient of category I is usually taken equal to one. The tariff coefficient of each subsequent category shows the level of increase in the wages of a worker of this category compared to the wages of a worker of the first category. The ratio of the tariff coefficient of the last (VI) category to the tariff coefficient of the first category is called the range of the tariff schedule. [p.93] At enterprises transporting and storing oil, petroleum products and gas, a tariff schedule with the following tariff coefficients is applied [p.93] Increase in the tariff coefficient of the next category to the previous one, %. ……… [p.93]
The tariff schedule is used to determine the wage ratios for workers of different skill levels. The tariff schedule is a set of categories, each of which has its own tariff coefficient. The tariff coefficient shows how many times the tariff rate of a given category is higher than the rate of the first category. The tariff coefficient of the first category is assumed to be equal to one. Tariff coefficients of subsequent categories show the degree of correlation between labor of various skill levels and unskilled labor. Tariff coefficients usually increase progressively, i.e., as the rank increases, the wage gap increases. This construction of the tariff schedule creates a material interest among workers in improving their qualifications (grade). [p.230]
The tariff schedule in force at enterprises in the oil and gas production and oil refining industries contains six categories with the ratio of tariff coefficients of the extreme categories being 1 1.86 and 1 1.72, respectively (Table 21). [p.230]
Tariff rates of the first category are established for all industries. Differences in wages are reflected in the differentiation of tariff rates. Differentiation of tariff rates provides for the allocation of wages to leading industries. Knowing the tariff rate of the first category and tariff coefficients, you can calculate the tariff rate of a worker of any category. [p.231]
I la oil refining industry enterprises operate a six-digit tariff schedule with the ratio of tariff coefficients of the extreme categories 1 1.72. [p.167]
From the indicators in table. 4.5, you can establish the changes that occurred in the qualification composition of workers during the reporting period, for which we calculate the average tariff coefficient of workers according to the plan and according to the report. [p.80]
Average tariff coefficient of workers [p.80]
From the above calculations, it is established that the average tariff coefficient of workers at the analyzed enterprise is lower in comparison with the plan, which indicates a decrease in the qualifications of workers at the enterprise under consideration. In order to answer the question of what determined the decrease in the average tariff coefficient of workers, it is necessary to establish the enterprise’s implementation of the planned measures to improve the professional skills and qualifications of workers, using for these purposes the data of Form No. 4-k of the annual report and Form No. 10-of periodic statistical reporting . [p.80]
Categories of workers Tariff coefficient Number of people Deviation, people [p.81]
ABSOLUTE INCREASE IN TARIFF COEFFICIENTS - the difference between tariff coefficients of adjacent categories. For example, A.v.t.k. between the first and second category is 0.3 (at the rate of 1.3-1.0), between the second and third it is 0.39, and between the third and fourth it is only 0.28. By the end of the grid, this difference reaches 1.0. If we abstract from some violations of the principle of constructing the tariff schedule (this can be seen from a comparison of the absolute difference in tariff coefficients of adjacent 3rd and 4th categories), in general the tariff schedule is built on the principle of a progressive increase in the absolute difference in tariff coefficients, which implies a sufficient level of incentives for advanced training . [p.1]
RANGE OF THE TARIFF SCHEDULE - the ratio of wages for workers of categories. The range of the adopted grid is defined as 1.0 10.07, where the numerical values are indicated by the tariff coefficients of the extreme digits. [p.67]
UNIFIED TARIFF SCHEDULE is a set of standards intended to regulate the remuneration of public sector workers. E.t.s. — the basis of the tariff system in this field of activity is a scale of tariffs and remuneration for all categories of workers from the lowest level worker to the managers of the organization. When developing the tariff schedule, the following principles of its construction were taken as a basis: determination of the initial base at a level not lower than the minimum wage established by law; increase in tariff rates by category, ensuring material interest in work as its complexity increases, taking into account the qualifications of the employee based on the corresponding tariff coefficients E.t.s. is based on a comparison of the complexity of labor functions of various groups and categories of personnel, specific job responsibilities of employees and their educational level, taking into account the content and nature of the work performed, the diversity (complexity) of the work of managing subordinates, the degree of independence and level of responsibility. The conditions, severity, intensity of labor, the significance of the scope of its application, regional characteristics, quantitative and qualitative parameters of collective and individual labor results must be taken into account through other elements of wages, in relation to which the tariff rate (salary), as payment for labor standards, is the basis formation of all earnings. E.t.s. covers all categories of workers in all industries - from workers to managers at various levels, incl. those who were previously charged according to ranks, classes, categories, qualification groups or for which monthly salaries were established. The grouping of blue-collar professions and office positions is based on the commonality of the work (functions) performed. Categories of workers from the perspective of the commonality of functions performed in the labor process are presented in the E.T.S. one group. Categories of employees in production and non-production industries are divided into blocks [p.79]
Ti - tariff rate (or tariff coefficient) corresponding to the qualification level i-ro of the employee [p.172]
RELATIVE INCREASE OF TARIFF COEFFICIENTS - the ratio of the tariff coefficient corresponding to a larger category to the tariff coefficient of an adjacent smaller category minus one, expressed as a percentage. For example, the relative increase between the second and third ranks is 30% at the rate of (1.69/1.3 - - 1) 100, from the 4th to the 15th ranks inclusive it is only 13%, and for subsequent ranks it decreases up to 11%. This indicates the regressive nature of the construction of the tariff schedule and the low level of incentives for workers, because Sociologists have determined the “threshold of perception” of a wage increase at the level of 10%. Consequently, almost the lowest level of incentives for improving qualifications is involved. [p.233]
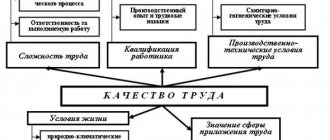
TARIFF SYSTEM - a set of standards with the help of which the wages of workers are regulated depending on the complexity of the work (qualifications), working conditions and its intensity, the importance of the areas of labor application, natural and climatic conditions of work and accommodation of workers. Those. includes tariff rates, tariff coefficients, tariff-qualification reference books, regional coefficients for wages, compensatory (compensatory) and incentive allowances and additional payments of a tariff nature. [p.376]
FIRST GRADE TARIFF RATE - the minimum rate of the tariff schedule, which corresponds to a tariff coefficient equal to 1.0. Tariff rates can be set in the form of fixed single-digit values or in the form of “forks” that determine the maximum (minimum and maximum) values. If the first principle is characteristic of all ta- [p.376]
The tariff schedule serves to determine the wage ratios for workers of various qualifications. It consists of tariff coefficients that determine the difference in wages for workers of different qualifications. Tariff coefficients of the grid determine how many times the rate of a worker of a given category is higher than the rate of a worker of the first category. The tariff coefficient of category I is assumed to be equal to one. [p.168]
The tariff coefficient shows the ratio of the hourly tariff rate of the corresponding category to the hourly rate of the first category. The ratio of the extreme tariff coefficients in the tariff schedule establishes the so-called range of the tariff schedule. [p.126]
The tariff schedule is a scale that includes the tariff categories established in a given industry, characterizing the qualifications of the worker, and the tariff coefficients assigned to this category. [p.81]
The second element of the tariff system is the tariff schedule, which reflects the ratio of wages for workers of various qualifications and consists of tariff categories and tariff coefficients. [p.38]
The tariff schedule, or otherwise the grid of tariff categories, operating at oil and gas industry enterprises, contains six categories with the ratio of tariff coefficients of the extreme categories 1 1.86 (Table 2). The tariff coefficient shows how many times the tariff level [p.38]
Tariff schedules are structured in such a way as to create a material interest among workers in improving their skills, so the gap in the absolute value of the tariff coefficient grows from rank to rank. [p.39]
Payment ratios between categories are expressed by tariff coefficients. The tariff coefficient of category I is usually taken equal to one. The tariff coefficient of each subsequent category shows the level of increase in the pay of a worker of this category compared to the payment of a worker of category I. The ratio of the tariff coefficient of the last (VI) category to the tariff coefficient of category I is called the range of the tariff schedule. [p.240]
The tariff rate is the amount of wages per unit of time (hour, shift, month). Tariff rates are set by the government for each industry. The basis is the tariff rate of category I. The rates of the remaining categories are determined by multiplying the rate of category I by the tariff coefficient according to the tariff schedule. [p.241]
The tariff schedule is a scale that determines the ratio of tariff rates depending on the qualifications (complexity) of labor, and consists of tariff coefficients showing how many times the tariff rate of a worker of a given category is higher than the tariff rate of a worker of the first category. [p.180]
Tariff settlement is used to determine the ratios in payment for a group of workers of various qualifications. It represents a COLLECTION of categories, each of which has its own tariff coefficient. The tariff coefficient shows how many times the tariff rate of a given category is higher than the rate of the first category, the tariff coefficient of the first ra (the series is taken equal to one. Tariff coefficients increase progressively, i.e., as the category increases, paipUB in wages increases. [p.167]
The tariff village does not establish the amount of wages. Tariff warblers are used for this. They determine the level of workers' wages per hour or day. They are approved by the government for workers of the first class in each branch of industry. Knowing the tariff rate of the first category and tariff coefficients, it is possible to calculate the worker’s tariff rate. any category. [p.167]
Indicators characterizing the actual labor contribution for each category of employees are differentiated, the average value of the indicator is established, which is adjusted by a certain amount depending on the performance of each employee and his main characteristics (for example, length of service in a given position). As a result, each person is assigned his “point” within the “fork”. When distributing the wage fund of an enterprise among employees, the share principle of wage calculation is used, ensuring a flexible dependence of the amount of an employee’s salary on the actual performance of his work and the final results of the organization as a whole. VSOTeRK is used at a number of enterprises in Russia and other CIS countries. A modification of such a model in the form of tariff coefficients for each job (functional) group, but without a “plug”, is used, for example, at the Veshkinsky experimental production plant for commercial equipment. BEKHTEREV VLADIMIR MIKHAILOVICH (1857-1927) - an outstanding Russian and Soviet neuropathologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, physiologist. In 1910, he was the first in Russian psychological science to formulate the subject and tasks of social psychology. He paid considerable attention to issues of scientific organization of labor. In 1921, in Leningrad, B. organized and headed the Central Laboratory for the Study of Labor at the Institute of Mental Health and Mental Activity, a team of co- [p.22]
TARIFF COEFFICIENT is an element of the tariff system that characterizes the tariff schedule. Expresses the ratio of tariff rates of the second and subsequent categories to the tariff rate of the first category. Value T.k. shows how many times the level of payment for work (workers) classified in this category exceeds the level of payment for the most basic work and low-skilled workers. Because used to determine the degree of complexity of work or operations when assigning them to the appropriate categories. System T.K. by rank forms inter-category pay ratios, which are characterized by an absolute and relative (in percentage) increase in coefficients from rank to rank. Based on the tariff rate of the first category and T.k. corresponding category OP- [p.377]
Tariff coefficients show how many times the rate of each tariff category is greater than the rate of the first category, which is always equal to one. With the help of tariff coefficients, the necessary differences in the payment of workers are established according to the quality of their work, creating the interest of workers in improving their skills. [p.81]
Unified tariff and qualification reference books
These reference books are necessary to regulate the work of representatives of the main working professions, management positions, employees and specialists within the enterprise. Using the provisions of a single directory, you can determine the suitability of an employee for the position held.
The document contains requirements for personnel categories, descriptions for each type of activity, a listing of the employee’s skills and knowledge, and a list of professions related to each type of work.
The unified directory of positions for managers, employees, and specialists contains requirements for the qualifications, knowledge and education of these categories of workers and explains their main job responsibilities.
Using the provisions of the directory, various types of professional activities are compared according to the complexity of their components. In addition, categories and qualifications are determined. This process is generalized into the concept of “tariffication”.
Hourly Tariff Rates for Housing and Communal Services Workers for 2021
It may also depend on the norm performed per unit of time, with a corresponding premium for productive work. On the river The second stage of the Ministry of Economic Development proposes to be carried out from July 1. The general rate of insurance contributions to state extra-budgetary funds in the city.
Minimum Tariff Rate for Worker in Housing and Utilities Calculation
Civil law. Commercial law. Medical law. Insurance law. Economic law. The minimum tariff rate is one year. Legal assistance! Moscow and region Add a comment Cancel reply Your e-mail will not be published. St. Petersburg and region Federal number - ext
The document that fixes the conditions of remuneration developed at the enterprise is a collective agreement or regulation on remuneration. Local regulation of wages is essential for linking earnings with the results of one’s work activity.
Tariffing procedure
Tariffication occurs by comparing the work performed at the enterprise with the list and examples of work contained in a single directory. For pricing purposes, an enterprise can develop and introduce internal lists of work, and use them along with the main ones.
Depending on the rank, the salary of an employee of an enterprise varies. To transfer an employee from rank to rank, in accordance with the internal regulations of the organization, a qualification commission is formed and convened, and its chairman is elected.
The employee, in the presence of members of the commission, passes a qualification exam, which includes testing theoretical knowledge and, in some cases, practical skills. If the exam is passed successfully, the employee receives a certain rank or moves from one to another, which is recorded in his work book. To rate the salaries of managers, as well as employees and specialists, a single directory of the specified positions is used.
What does the tariff coefficient show?
The tariff coefficient shows that the remuneration of two workers performing work in the same specialty (profession) at the same enterprise can differ significantly. And the reason for this is the different skill levels of workers and the complexity of the work they perform. Depending on their qualifications and complexity, workers are assigned ranks and tariff coefficients are established (hereinafter in the article - TC).
Let's give some examples.
- 1st, the lowest, is assigned to such workers as a watch glass cleaner, a bathhouse maintenance worker, a stoker, a nanny and others;
- 2-6th—the most numerous category of a wide variety of working professions;
- Adjusters of various equipment (technological, printing, testing, etc.) “reach” the 8th level.
A list of all professions and categories is given in the All-Russian Classifier of Worker Professions and Clerk Positions. In addition, starting from July 1, 2021, professional standards are used to determine qualifications. They use the concept of “skill level” (from 1 to 8).
Tariff rates
The tariff rate is understood as a payment to an employee measured in monetary terms, taking into account his qualifications, nature and standards of work performed. Calculation of tariffs occurs both for time-based and piecework wages.
The tariff rate is a guarantee that the employee will receive money for work, provided that it is performed in good faith. Additional payments, bonuses, compensations are not included in the concept of “tariff rate”. Consequently, the tariff rate is the minimum wage for an employee, to which, in the process of wage formation and calculations, other components of wages are added.
Features and main elements
The tariff wage system is the most common wage system. It includes components such as tariff rates, grids, salaries and tariff coefficients.
The tariff rate determines the amount of monetary remuneration to an employee for a certain temporary standard or standard in remuneration. It corresponds to the level of complexity of the job functions performed or the specific qualifications of the employee.
The specified rate does not include various incentives, compensation and social payments, which may also be provided for employees.
Salaries and tariff rates must reflect the minimum wage , i.e., without additional payments or allowances. The difference between a rate and a salary is that the salary is set for persons for whom standards cannot be established (for example, for accountants, lawyers, engineers, etc.). Rates are usually set for workers such as construction workers, representatives of the manufacturing sector, etc.
The tariff schedule is a system of tariff categories that determines the ratio of the complexity of labor functions and the size of wages based on the tariff coefficient. An employee’s rank is an indicator that reflects the complexity of the functions performed or the level of qualifications. The coefficient is a value that reflects how the tariff rate relates to the rate for the first category.
Based on the qualification category, an increase in the employee’s salary is allowed and the level of training for working citizens is determined.
The process of correlating types of activities and a certain category is called tariffication. For example, for state employees, 18 tariff categories are established, based on the qualifications of employees and the complexity of work. The basis for calculating the salary tariff is the rate for 1st category. Subsequently, one of the coefficients is applied to it depending on the assigned rank.
Thus, personnel who are assigned basic duties are assigned rank 1. In the future, it increases as the employee’s professional level grows.
Various elements of the tariff system are determined by profession and position.
Let's give an example of determining a tariff for an industrial worker . For example, a worker performs particularly complex work and has extensive knowledge of chemistry and physics and has taken professional courses. The employee was assigned the highest 5th category.
For first-class workers, the tariff rate is 8,500 rubles. For employees of the 5th category, a coefficient of 2.5 is applied. Accordingly, his salary excluding bonuses and allowances will be 21,250 rubles. (the rate for a 1st category employee is multiplied by the coefficient for his specialty).
Tariff schedule and tariff category
The tariff schedule represents the ratio of tariff rates in accordance with the category. Designed in the form of a table for entering data. For different categories of work, tariff scales with different numbers of categories are provided.
Enterprises, as a rule, use a six-digit grid, where the first digit is the lowest and the sixth is the highest.
An enterprise, in accordance with its internal situation, can change the tariff scale towards increasing or decreasing its range. The instrument in question is used not only in relation to blue-collar professions. The tariff schedule is typical for calculating wages of public sector workers.
The tariff category shows the level of qualifications and skills of the employee and characterizes the complexity of the work he performs. The composition and size of an employee’s salary largely depends on the tariff category.
How to calculate
In the Soviet Union, there was a unified tariff schedule, which established minimum wages (for the lowest qualification category for a specific profession) and Labor Codes. Currently, there is no such grid and the question arises: what does the tariff coefficient show in practice and why is it needed.
It shows the following: the higher the worker’s qualifications and the labor intensity of the work, the greater the labor cost by which the minimum rate is multiplied. It is needed to differentiate wages for workers in the same profession, but performing work of varying degrees of complexity.
Today, the state regulates minimum wages and labor standards only in relation to public sector employees (the basic document is the so-called New Wage System and industry agreements). Other enterprises have the right to create grids and calculate TC independently. To do this, define:
- how many categories of one profession (specialty) you will enter;
- what is the planned gap between the lowest and highest levels of qualifications;
- how the TC increases - uniformly (1; 1.2; 1.4; 1.6...) or progressively (1; 1.2; 1.5; 1.9...).
To calculate the coefficient with a uniform increase, we use the formula:
(max. coefficient – min. coefficient) / (number of digits – 1).
Example:
It was decided to introduce 5 categories for turners: from 2nd to 6th. The gap in the TC is 2 (the lowest is coefficient 1, the highest is coefficient 2).
Solution: (2 – 1) / (5 – 1) = 0.25.
This means that the TC for the categories will be:
2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 1 1,25 1,5 1,75 2
The use of tariff systems for time-based and piecework wages
The main types of payroll calculation include:
- time payment;
- piece-work payment.
When calculating wages, the employer takes into account the following elements:
- grade of work;
- its characteristics;
- the standard time allotted for its implementation;
- tariff rate.
Calculation of piecework payment is made on the basis of the provisions of the unified tariff and qualification reference books. The most important component of work with piecework payment is production. One of the main disadvantages of piecework payment is the high probability that, in an effort to produce more products, the employee will not pay due attention to the quality of the finished product.
When calculating time wages, the amount of money an employee receives monthly depends on his rank. Also, when calculating time-based wages, the amount of time worked plays a significant role, which fundamentally distinguishes this form of payment from piecework.
Time-based payment requires mandatory staff pricing and clear timekeeping of the time spent by the employee on work. Today, most enterprises produce time-based wages, recognizing it as a more convenient type of payment for the parties to labor relations than piecework wages.
Answers to pressing questions
Question No. 1. How are vacations and sick leave paid under the tariff system?
Organizations using this system “keep up” with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and provide employees with the entire social package.
Question No. 2. What does equality between the rate of a 1st category employee and the minimum wage lead to?
At the same time, the organization must change the tariff schedule when the minimum wage increases. This leads to an increase in staff salaries. As a result, employees form the opinion that wages depend not on the results of work, but on the rate of inflation and policies regarding the size of the minimum wage. Therefore, the first category rate should be set higher than the minimum wage. Only then will employees have an incentive to increase the productivity of the production process.
Question No. 3. Where is the tariff system applied?
This form is used mainly by large organizations. Regardless of the number of departments at such enterprises, it is necessary to establish a uniform salary payment template. Tariffs are less commonly used by small companies.
Question No. 4. What guarantees are provided to employees working under the tariff?
The law only protects salary. Management can even deprive pregnant and young mothers of bonus payments. The main thing is that the accrued earnings are greater than or equal to the minimum wage.
Question No. 5. What are the disadvantages of tariff payment?
This payment system also has negative aspects:
- The employer must have a good understanding of the laws and monitor their changes.
- The priority is the qualifications of the staff, not the quality of work.
- Management forms the salary fund based on tariffs and laws, without taking into account profits and work results.
- An employee’s contribution to the work process depends little on the amount of incentives.
The tariff system is a full-fledged opportunity to work according to the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, without depriving staff of wages. To prevent possible problems with the labor inspectorate, the administration should be guided by the law, and employees should carefully read the contract and ask questions to avoid disagreements.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to become better for you: If you have not found the answer to your question, then you can get an answer to your question by calling the numbers ⇓ Free legal advice Moscow, Moscow region call
One-click call St. Petersburg, Leningrad region call: +7 (812) 317-60-16
Call in one click From other regions of the Russian Federation, call
One-click call
>Tariff system of remuneration in the commercial and public sector
Procedure for establishing tariff systems
Russian labor law in its provisions determines the procedure for establishing tariff systems. Regardless of the legal form of the organization and the type of its activity, the tariff payment system is established by local regulations, provisions of collective agreements, and agreements.
Also, when establishing tariff systems, the data of the unified tariff and qualification reference book are fundamentally taken into account, taking into account all the requirements of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and other regulations mandatory for execution on the territory of the Russian Federation. The employer, when introducing tariff systems to the enterprise, must respect the rights of the employee and create decent working conditions.
Author of the article
Scope of application
The tariff system of remuneration is quite popular in Russian practice. It can be used in almost every enterprise, but in state companies and budgetary organizations the tariff system of remuneration is mandatory for use. In this area, special regulations have been approved, which approve tariff rates and schedules, as well as the amount of allowances for civil servants.
A unified tariff schedule has been developed for industries such as education, medicine and forestry. If an organization operates in one of these areas, then it must be guided by the tariffs approved by law. If wages are set at a lower level than required, the budgetary organization may be held accountable.
Assessing the possibility of using the tariff system and making a decision on its implementation at the enterprise is made by the employer independently on a voluntary basis. It is not permitted by law to force an enterprise to use the tariff system.
It is allowed for tariff and non-tariff payment systems to be used within one enterprise in different branches, departments and divisions.
When an employer uses a tariff payment system at an enterprise, he must specify the conditions for calculating wages and the rules for calculating them through the publication of the corresponding local regulatory act. The employment contract signed with the employee must contain his salary rate.
To implement a tariff system of remuneration at an enterprise, the employer must initiate a tariffication procedure or assign categories or grades to certain types of labor.
When hiring an employee, he must be familiarized with the current tariff schedule in the organization or his salary.
When an employer applies a tariff system, this does not relieve him of the need to follow established government standards in the field of remuneration. In particular, an employee’s earnings cannot be less than the minimum wage.