Home / CHILDREN'S BENEFITS AND BENEFITS
Back
Published: March 27, 2020
Reading time: 2 min
0
634
Deduction of income tax is the direct responsibility of every employed citizen of the Russian Federation. Tax is charged on almost all payments made to an employee. The only exception is the payment of a number of benefits carried out by government agencies. These include the payment due to women when they go on maternity leave (Maternity leave ). We are looking into whether personal income tax is deducted from benefits for employment and other payments related to the birth and care of a child.
- 1 Social guarantees for expectant mothers: the concept of maternity payments
- 2 Payment for maternity leave
- 3 Are maternity benefits subject to personal income tax?
- 4 Tax withholding from child care benefits up to 1.5 years old
What is maternity leave
According to labor law, a pregnant employee has the right not to go to work seventy days before giving birth and another seventy days after it.
During her stay at home, she will receive an allowance, and this period of time is called maternity leave or maternity leave, in official terms. It goes without saying that when making calculations, enterprise managers are interested in whether personal income tax is withheld from maternity leave, as well as other taxes and contributions.
The same question, of course, worries employees who are going on vacation - after all, it is much more pleasant to receive the entire accrued amount in your hands in full, without any deductions.
Nuances of personal income tax payments
What nuances should you know in order to accurately calculate and make personal income tax payments? Experts advise paying attention to the following points:
- The tax reporting period is 1 year - Tax Code, Article No. 216 and Article No. 55, paragraph 1.
- After the end of the reporting period, to calculate personal income tax, it is necessary to determine:
- tax base;
- the amount of tax to be paid.
- Payers have every right to apply tax deductions - Tax Code, articles No. 218-221.
- For those who carry out calculations on their own, it is mandatory to submit declaration documentation to the local tax service - Tax Code, articles No. 227-229.
- For tax agents, special document forms have been developed in which all the necessary information about workers and their income is entered - Tax Code, Articles No. 24 (clause 4) and No. 230 (clause 2).
What is income tax?
Income tax is a tax that is levied on amounts of money received by individuals and recognized as their income. All payments under an employment contract in the form of wages are subject to mandatory personal income tax.
How to calculate maternity leave for pregnancy and childbirth can be found here.
The personal income tax rate that applies to wages and related payments is 13 percent.
When calculating wages, the accountant calculates 13% of the accrued amount, subtracts the resulting tax amount, and the employee is given earnings minus personal income tax.
In addition to personal income tax, wage payments are also subject to insurance contributions . But unlike personal income tax, contributions are calculated in excess of the amount of income and are paid from the employer’s funds. Income tax falls on the shoulders of the individual; the employer only performs the function of a tax agent - an intermediary who withholds and transfers funds to the budget.
This type of tax is levied on wages, vacation pay, bonuses, vacation compensation, and sick leave payments. As for payments for maternity leave (maternity leave and child care), different rules apply.
Do I need to withhold maternity benefits or not?
Whether or not sick leave benefits for pregnancy and childbirth are taxable is specified in clause 1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This article lists non-taxable income of individuals, including maternity payments.
The accountant calculates maternity benefits after receiving an application for leave and sick leave from a pregnant employee. The period for calculating and assigning payment is 10 calendar days. About the procedure and deadline for paying maternity benefits
What taxes are paid on sick leave?
A sick leave certificate is a document of strict accountability. Issued in case of serious violations in human health. The reason for issuing the disability document directly affects the amount of the benefit.
These accruals do not constitute payment there, since professional activities were not carried out.
Based on sick leave, the following are carried out:
- calculations for temporary disability;
- benefits for pregnant women and women who have given birth.
When issuing a document due to injury, illness, or caring for a needy family member, the accrued monetary compensation is subject to personal income tax. It is withheld from the entire accrued amount.
Before the benefit is issued, personal income tax is withheld from it, and the employee receives compensation minus it. No other deductions are made from sick leave. No deductions are deducted from the amount of compensation for pregnancy and childbirth, as this is stipulated by law
. All disability payments are not subject to insurance premiums.
Maternity leave and taxes
By law, any monetary income is taxed. Is the income of individuals (abbreviated as personal income tax) paid as maternity leave taxed? Employees and their employers are certainly interested in the question: will certain tax levies be made on maternity benefits?
Of course, no one wants this money to be deducted by the authorities. Women want to receive all payments without any deductions that reduce the total amount of vacation pay. In this regard, the question arises: “If tax levies cannot be circumvented, how can they be reduced?”
Such questions are best answered by a qualified lawyer, but in this case you can delve into some of the subtleties on your own, especially since the legislative norms quite clearly state what happens to vacation pay, whether they are taxed or not. In any case, the answer to the question of whether they are taxed is clear - withholding personal income tax from maternity leave is unacceptable. Maternity benefits are not taxed because it is against the law.
Despite the fact that it is illegal to collect personal income tax from maternity leave, there are cases when taxation of cash payments received on maternity leave still occurs. If, despite all this, the accountant at the enterprise withheld a certain amount as tax, it must subsequently be returned to the employee. To return the money, an employee or employee of the organization must write a written statement addressed to the head of the company or accountant, after which the woman will be returned the money due.
The issue of tax withholding from the benefits in question is directly linked to the issue of calculating these payments accrued to a pregnant woman taking maternity leave. According to the existing law, all benefits provided by the state itself are actually exempt from personal income tax.
The only exception is taxes aimed at subsidies for temporary inability to carry out labor activities. That is, the exception is when you are on forced sick leave with a sick child. Unlike other payments, maternity benefits are not subject to any taxes also because these benefits are fully provided by the state.
Assignment of maternity benefits
When calculating benefits related to pregnancy and upcoming childbirth, the employer must focus on the following regulatory documents:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 255);
- Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance for illnesses and maternity”;
- order of the authorship of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated December 23, 2009, No. 1012n with the Rules for issuing child benefits.
The employer calculates the amount of the benefit in question based on average daily earnings over the last 2 years. In this case, the two-year period is counted back not from the month the certificate of incapacity for work was opened, but from the year in which the employee goes on maternity leave. If there is no information about earnings in previous periods, a certificate of income from previous employers is required.
If the employee is unable to provide a certificate, all days will be taken into account in the calculation, but there will be no income in some intervals. Due to this, the amount of the benefit will be underestimated.
If a certificate of income is submitted late, the employer recalculates the benefits and pays the difference between the initial and adjustment calculations. After the payment has been made to the maternity leave, the business entity can reduce its obligations for social insurance contributions by the amount of the transferred funds.
Let's name some features of calculating the benefit amount:
- when calculating benefits, it is necessary to compare the average daily income with the minimum and maximum limits established for the years used in the calculations;
- the basis for calculations can be taken as earnings that do not exceed the income limit on which insurance premiums are calculated in the corresponding calendar year;
- if there is a significant difference between the average monthly benefit and the average earnings in the last year (not in favor of the benefit), the employer has the right to make an additional charge: the source of financing the main amount for sick leave will be funds from the Social Insurance Fund, and the employer will make the additional payment from its own resources.
Are maternity payments income?
Payment of maternity benefits relates to the income of an individual based on the general meaning of Articles 208 and 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. From an accounting point of view, such a payment is a type of sick leave.
When calculating maternity benefits, average daily earnings are used. Due to this, the amount of payment depends on the duration of sick leave. So, if it is less than 140 days at the initiative of the employee, then she will receive less maternity leave for sick leave (but more salary at the current rate).
How is daily earnings determined:
- Add up all the employee’s income for the last 2 calendar years. This includes payments from which insurance premiums were paid for temporary disability and in connection with maternity.
- Calculate the sum of calendar days for 2 years. The number of exception days must be subtracted from it.
- Divide the indicator from the first point by the indicator from the second.
Which days are deducted:
- regular sick leave, sick leave for BIR, child care leave;
- days of release from work while maintaining earnings without paying contributions to extra-budgetary funds.
Let's look at an example:
Svetlana Shcherbakova works in and goes on sick leave from February 1 for 140 days. In 2021, her salary was 20,000 rubles. In 2021, indexation was carried out and from January 1, the salary was 25,000 rubles. In 2021, she received a promotion and her salary increased to 35,000 in January. Over the past 2 years, Shcherbakova took sick leave 5 times - 7, 4, 10, 3 and 9 days.
Calculation:
- Total income: 20,000 × 12 + 25,000 × 12 = 540,000.
- Period: 365 × 2 – (7 + 4 + 10 + 3 + 9) = 697.
- Daily earnings: 540,000 / 697 = 775.
- Amount of payment for sick leave: 775 × 140 = 108,500 rubles.
Important! When calculating benefits under the BIR, take into account the minimum and maximum amount of payment, as well as the calculation based on the minimum wage for employees who have not had any income over the last 2 years.
Social guarantees of the state
Having children is always associated with considerable material and physical costs. No matter how desirable a child is, parents are not always able to plan everything in advance and adequately prepare for this significant event. Obviously, additional help will never be superfluous.
In the Russian Federation, pregnancy and motherhood are under special attention from the state. As part of social security, the following payments are provided:
- maternity benefit (MPB);
- a one-time benefit for women who registered with medical organizations in the early stages of pregnancy;
- lump sum benefit for the birth of a child;
- monthly child care allowance.
Regulatory and legal regulation of relations regarding the appointment of maternity benefits
Employees of the organization (insured persons) receive insurance coverage in the form of maternity benefits (clause 2, part 1, article 1.4, clause 1, part 1, part 2, article 2 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” (Law No. 255-FZ)).
The appointment and payment are carried out by the policyholder (employer) at the place of work of the insured person (employee) (Part 1, Article 13 of Law No. 255-FZ).
To do this, the employee provides a certificate of incapacity for work issued by a medical organization in the appropriate manner and in the prescribed form (Part 5, Article 13 of Law No. 255-FZ).
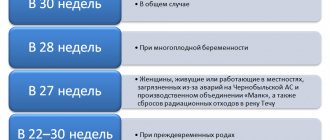
In general, women, upon their application and on the basis of the provided certificate of incapacity for work, are granted leave of 140 calendar days (70 days before childbirth, 70 days after). State social insurance benefits are paid in the amount established by federal laws. Maternity leave is calculated in total and is provided to a woman completely regardless of the number of days actually used by her before giving birth (Article 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Part 1, Article 10 of Law No. 255-FZ, Article 7 of the Federal Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ “On state benefits for citizens with children”).
The benefit is assigned within 10 calendar days from the date the insured person applies for it with the necessary documents (certificate of incapacity for work), and its payment is made by the employer on the next day after the grant is assigned, established for the payment of wages (Part 1, Article 15 of Law No. 255 -FZ, clause 14, 18, paragraph “a” clause 16 of the Procedure and conditions for the appointment and payment of state benefits to citizens with children, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 23, 2009 No. 1012n (Procedure)).
The entire maternity leave amount, calculated in accordance with the law, is paid from the budget of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation (as follows from Part 1, Article 3 of Law No. 255-FZ, paragraph “a”, paragraph 17 of the Procedure).
The amount of insurance contributions paid by the organization for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity is reduced by the amount of funds paid (clause 2 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, part 2 of Article 4.6 of Law No. 255-FZ).
In addition, women who register with medical organizations in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 12 weeks) have the right to receive a one-time payment (in addition to the calculated one), which is one of the types of insurance coverage for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with motherhood (Article 9, paragraph 3, part 1, article 3 of the Federal Law of May 19, 1995 No. 81-FZ, clause 19 of the Procedure, paragraph 3, part 1, article 1.4 of Law No. 255-FZ).
A one-time payment to women who register with medical organizations in the early stages is assigned and paid at the place of destination and payment of maternity benefits. To do this, the employee must provide the organization with an application for appointment, a certificate from the antenatal clinic or another medical organization that registered the woman early (clauses 5, 21, 22 of the Procedure).
IMPORTANT!
From 02/01/2021, the amount of a one-time payment to women who have registered in advance with medical organizations is 675.15 rubles.
The payment is also made at the expense of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation (paragraph 2, part 1, article 4 of law No. 81-FZ, part 1, article 3 of law No. 255-FZ, clause 23 of the Procedure).
In general, by the amount of the lump-sum maternity benefit paid to the employee, the organization reduces the amount of insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity. If the insurance premiums accrued by the policyholder are not enough to pay the amounts in full, he has the right to apply for the necessary funds to the territorial body of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation (Part 2, Article 4.6 of Law No. 255-FZ, Clauses 2, 9, Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the calculation of insurance premiums, maternity benefits are reflected in full in the calculation of insurance premiums 2021, with the corresponding payment; Section 3 should be completed even for employees who are on maternity leave and do not receive payments in the reporting period, excluding subsection 3.2, since employees of the organization who are on maternity leave are insured persons (Article 7 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ “On compulsory pension insurance in the Russian Federation”, Article 2 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ, Article 10 of the Federal Law of November 29, 2010 No. 326-FZ “On Compulsory Medical Insurance in the Russian Federation”) .
A one-time benefit for women who registered with medical organizations early is assigned and paid simultaneously with the main maternity benefit, if a certificate of early registration is provided simultaneously with the documents necessary for the appointment and payment of maternity benefits , which are specified in clause 16 of the Procedure. If the certificate is provided later, the amount is paid no later than 10 days from the date of receipt (registration) of the registration certificate (clause 24, clause “a”, clause 9 of the Procedure).
Payment for temporary disability due to pregnancy and childbirth
Before wondering whether maternity leave is subject to personal income tax in 2021, it would be good to know exactly how maternity leave payments are calculated and calculated in 2021. In total, payment for this period is made in the same way as payment for the most ordinary annual calendar leave, only it is called an allowance and is issued from the Social Insurance Fund.
This happens because, although maternity leave is a vacation, it is documented as a period of temporary disability - and this is the sphere of activity and responsibility of the Social Insurance Fund. Calculations, as having complete information, are made by employers and provide only the final result to the Fund. Therefore, they are obliged to figure out whether maternity leave is taxed, even despite the fact that, according to the new legal requirements, along with the final figure, a calculation sheet is provided, on which all calculations are fully described
Payment order
Just like regular calendar paid rest from work, the period of release from work duties for pregnancy and childbirth is paid according to the average daily earnings - you need to know this before calculating taxes on maternity leave.
In the same way, all payments subject to taxes and contributions during the billing period are summed up and divided by the number of days worked over the last two years. The calculation period does not include all time periods when the employee received partial earnings or full earnings, but not subject to taxes and insurance contributions.
If in the previous two years the employee worked at a different company from which she is going on maternity leave, she must bring a certificate of income for calculations. By the way, if an employee is registered and works at several enterprises, she can apply for benefits at all places of her work. Of course, the question of whether personal income tax is charged on maternity leave will then have to be decided by all its employers.
Taxation of maternity payments
The list of types of income of individuals that are not subject to taxation (according to Article 217 of the Tax Code) includes benefits for temporary disability due to pregnancy and childbirth. According to the Ministry of Finance's explanation of how maternity benefits are taxed, it also turns out that this type of government benefit is not subject to taxation. Of course, such benefits are not included in the enterprise's expenses.
Taxation of maternity leave in 2021–2021: is personal income tax withheld from these payments?
In paragraph 1 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains an unambiguous answer to the question of whether income tax is withheld from maternity leave. The text of this article states that maternity benefits are not subject to personal income tax. This makes maternity benefits different from regular sick leave, from which personal income tax must be withheld.
Whether it is necessary to show the B&R allowance in the 6-NDFL report, find out in the ConsultantPlus Ready Solution. Get trial access to the system and study expert materials for free.
Unemployed women are not entitled to maternity leave, with the exception of those who were dismissed due to the liquidation of the organization. Like women who go on regular maternity leave, they receive all the required payments without having to reduce them by the amount of income tax.
In addition, all pregnant women have the right to 2 more benefits:
- A one-time payment for those who registered at the antenatal clinic before the 12th week of pregnancy. Its basic amount established by law is 300 rubles. Taking into account indexation from 02/01/2021, it is equal to 675.15 rubles.
- A lump sum payment for the birth of a child. Its basic value, established by law, is 8,000 rubles. Taking into account indexation, this benefit from 02/01/2021 is equal to 18,004.12 rubles.
Income tax is not deducted from the amounts of these payments, as well as from maternity payments.
Are maternity payments subject to income tax?
In addition to maternity benefits, regardless of length of insurance and type of employment, all pregnant women are entitled to the following benefits:
- a one-time benefit for women who registered before 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- benefits in connection with the birth of a child.
Taxation of personal income tax for pregnancy benefits
The list of payments subject to personal income tax is listed in Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, even if the payment is not mentioned in this article, but it is expressed in cash and entails a material benefit for the employee, tax is paid on it. Also, funds issued to the worker must be mentioned in the 2-NDFL certificate.
So what about maternity benefits (M&B)? Previously, it was believed that it should be subject to personal income tax, since it is a woman’s income. However, a significant amendment has now been made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which state compensation (which includes benefits) is exempt from taxation. Legislators claim that the development of the amendment was due to discrepancies and contradictions in the reading of the law. It was not clear whether the benefits counted towards the employee's income. The amendment clarified this point. Now all entrepreneurs are required to comply with the same standard.
Even before the adoption of the amendment, Letter No. 03-04-06/3-127 of the Ministry of Finance dated June 1, 2011 was issued, according to which all state benefits should not be subject to personal income tax. The purpose of its publication was also to clarify an ambiguous issue.
Taxation of personal income tax for child care benefits up to 1.5 years old
The benefit is paid not only to the mother of the child, but also to any person caring for him. Begins to accrue from the date of birth of children. The payment end date is:
- The day a woman goes to work.
- The baby reaches 1.5 years old.
When calculating this type of benefit, you need to take into account its minimum and maximum level:
- The minimum is the minimum wage adopted for the year of calculation of payments.
- The maximum is the maximum average earnings of a worker per day.
Childcare benefits for children under 1.5 years of age are payments exempt from personal income tax. This rule is contained in paragraph 1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. That is, the employer, when making payments, does not have to pay anything to the state budget.
IMPORTANT! If an employer pays an employee an amount above the established benefit level, this money will be subject to personal income tax.
Non-taxable certificates of incapacity for work
According to the current legislation, the Government has identified a list of income acquired through sick leave, which is not subject to income tax:
- BC of an unemployed person registered with the Employment Center;
- compensation for injury;
- reimbursement by the employer of the cost of a voucher for sanatorium treatment;
- reimbursement by the employer of expenses for medical services, medicines for employees and members of their families.
In each case, the execution of a document requires strict adherence to the provisions of the law - errors and inaccuracies are unacceptable.