The state guarantees a pregnant mother paid leave, which is divided into two parts. The first is maternity leave, which in turn is divided into periods before and after childbirth. Depending on the severity, both periods can last from 140 to 194 days. After the end of maternity leave, the second part begins, parental leave, lasting until the child reaches the third birthday.
Is it possible to work while on maternity leave?
Vacation for labor and employment is actually standardized sick leave. There are four timing options depending on the conditions of pregnancy.
| Vacation dates | Causes |
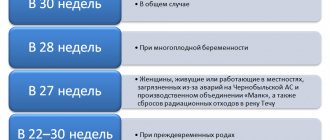
| 70 days before and after birth, total 140 days | Pregnancy proceeds without complications |
| 70/86, total 156 days | Complications, caesarean section and other obstetric operations |
| 90/70, total 160 days | Pregnancy in regions with increased radioactive or chemical background |
| 84/110, total 194 days | Multiple pregnancy |
Important! The duration does not depend on the specific date of birth. For example, if a mother used only 50 days of the 70 prenatal period, then the unused days are carried over to the postpartum period.
When adopting an infant and surrogacy options, a working woman is granted leave without the prenatal part. In this case, the time frame will be 70 days when taking one child and 110 days for two or more.
Legal basis for working during maternity leave
The features of women's labor during the duration of the decree are described in Chapter 41, Articles 255, 257 and 258 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The articles regulate the procedure for a woman going on maternity leave, methods of social protection, and the rights and obligations of the employer.
Peculiarities of women's labor during maternity leave
Article 260 specifies the possibility of combining regular annual leave with sick leave under the BiR. The decision cannot be challenged by the company; all that is needed is a statement at the initiative of the employee. The annual vacation period can be added both before and after Birth, depending on the wishes of the pregnant woman.
The birth of a disabled child does not provide additional preferences in terms of the duration of maternity leave. Article 262 of the code approves for parents of a disabled child 4 additional days off per month for two. Article 263 specifies the right of parents to receive an additional two-week unpaid leave. There are no improvements to the amount of payments or terms of maternity leave.
Important! Payment for sick leave according to BiR is made for the time that the employee does not actually work. If you leave early, the benefit will be cancelled.
Application for maternity leave
After the end of the B&R period, it smoothly flows into maternity leave. The maximum duration of paid child care time is 1.5 years, as stated in Article 256 of the Civil Code. Unlike leave under BiR, any legal guardian who actually cares for the child can go on maternity leave. In total, this type of leave can last up to 3 years, but for the last year and a half the guardian will be on it at his own expense.
Important! While on maternity leave, you are allowed to work part-time and have the right to change your status at any time without restrictions. This is due to the fact that maternity leave under BiR is actually sick leave, while nursing leave is social assistance from the state.
Sick leave for pregnant women before maternity leave
The reasons for registering sick leave before a vacation of the type in question can be very different. Most often they are the following:
- a disease directly related to pregnancy – a significant deterioration in well-being;
- loss of ability to work for a reason that is in no way related to pregnancy;
- desire to go on maternity leave early.
Today, a woman must be observed by a medical specialist and registered at the earliest stage of pregnancy. You will need to be checked periodically by a supervising healthcare professional. Sometimes it happens that pregnancy begins to progress with some complications and the supervision of a qualified specialist is required constantly, a hospital is required. Accordingly, the ability to work in this case is lost. It happens that during the period immediately before childbirth, a woman falls ill.
Options for maintaining benefits while working
It was already clarified above that benefits are paid only to mothers who are actually unemployed. The Labor Code directly states that maternity leave is provided at the request of the expectant mother, therefore, at the request of only the employer, it is impossible to send a woman on forced days off.
Maintaining benefits when working for pregnant women
It is necessary to understand that the division “70 days before, 70 after” is conditional. A woman can submit an application at any time, the accounting department will be required to pay for all 140 days (or more) in full. At the same time, returning to work before the end of the term is possible only if a vacation waiver is issued, which automatically deprives the employee of benefits.
In general, the situation is completely identical to registration of sick leave - for the duration of the illness, the employee receives help and payments, as soon as the sheet is closed, everything returns to normal. The choice is simple: either a salary or help from the Social Insurance Fund and the employer.
Sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth when going on maternity leave
Info
We also recommend reading: How many days can I take? The validity period of sick leave usually does not exceed 15 calendar days, but during pregnancy, the number of days can be increased. Important! It depends on the complexity of the case and the condition of the expectant mother.
The extension is carried out according to the conclusion of the medical commission for the period until complete recovery. For employees recognized by a medical commission as disabled, sick leave is provided for a period of 4 months during one continuous certificate of incapacity for work or 5 months during the year in total.
In addition to your own condition, you can apply for a paid sick leave certificate for the following reasons:
- Baby care. Up to 7 years of age, the entire period of the child’s illness is paid, from 7 to 15 years old - 15 days, from 15 to 18 years old - 7 days.
- Caring for a disabled child.
Applying for leave during maternity leave
Applying for leave during maternity leave
Combining planned and maternity leave is possible in three options:
- Planned leave is added to the start of maternity leave, allowing you to go on vacation earlier than 70 (90) days before the start of childbirth.
- Vacation pay is used immediately after the end of the B&R period.
- Unused days are applied at a convenient time after the end of the care period.
Important! Imposing maternity leave on other vacation periods is prohibited. Refusal of unused vacation days in exchange for monetary compensation is possible only upon dismissal.
Application for leave on the basis of Art. 260 TK
Continuity of term is not required. The employee has the right to use planned leave, then work a couple of days to clear the backlog of cases and then finally go on maternity leave.
You can apply for maternity leave here.
Do you receive salary and benefits at the same time?
The legislation on labor and social insurance does not provide for the simultaneous calculation of wages and disability benefits, since these are mutually exclusive concepts even in meaning. If a doctor determines that the person is incapacitated, the person should not continue working and is paid sick leave instead of salary.
Since pregnancy is not a disease in the classical sense, a woman can decide for herself when to write an application for leave under the BiR. But this also means that she voluntarily gives up benefits in favor of receiving payment for her work. Attempts to challenge this provision were frustrated by the Decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. AKPI12-1204 of November 14, 2012.
Registration for part-time and part-time work
Federal Law No. 255 regulates the amount of vacation pay and the rights of a young mother during a period of incapacity. The amount of payments throughout maternity leave is:
- average monthly earnings in the case of B&R benefits;
- 40% of monthly earnings when calculating care allowance.
To calculate the average income, the two previous years are taken into account minus official sick leave and vacations.
It turns out that in the 140-day period for pregnant women and young mothers, early return to work part-time is virtually meaningless. The salary will be approximately equal to the benefit received, and the child will be left without care during one of the most difficult periods of life.
Application for transfer to full-time work
Part-time employment makes sense when a parent goes on maternity leave. The law does not regulate free time sufficient to care for a child, so the benefit remains the same for freelancing or a 20-day work week. Article 93 of the Labor Code indicates that each specific case is individual, and sufficient work time is established by the parties to the employment agreement. At the same time, reducing working hours, for example, by an hour daily, cannot be considered a sufficient measure to continue payment of benefits. In this situation, an attempt to obtain additional income will be stopped by the Social Insurance Fund, which will recover money for the damage caused from the employer.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 93. Part-time work
To summarize, maternity benefits will be canceled when you return to work. The care allowance allows you to work part-time if this does not interfere with caring for the child.
Reducing the postpartum portion of leave
Will the employer face fines?
In this case, there are three different aspects to consider:
- fines under administrative law;
- fines under tax legislation and fines for late payment of insurance premiums;
- penalties under tax legislation and legislation on the payment of insurance premiums.
Early departure from maternity leave is actually a violation of the hospital regime. If the violation of the regime was committed on the initiative of the employee, and the employer did not force her to terminate her maternity leave early, there is no reason to bring the employer to administrative liability.
If early termination of maternity leave entails the need to recalculate taxes and insurance contributions, it is important for the employer to keep in mind the following:
- fines are assessed only if the employer is guilty of committing an offense;
- Penalties will be assessed regardless of the absence of guilt.
In light of this, the relevant question is whether an employer can refuse an employee who has submitted an application for early leave from maternity leave. In our opinion, this can be done, especially since the employer’s accounting department in this situation already has a sick leave certificate.
How to apply?
The basis for early termination of maternity leave is the employee’s application and the manager’s order based on the results of its consideration.
The legislation does not provide for standard forms of these documents. Therefore, they can be compiled in any form.
If the duties of a “maternity leaver” are performed by another employee, after the employee returns to work, the employment contract with him can be terminated.
The law does not provide for the obligation of an employee to warn the employer about going back to work early, much less, and does not set any deadline for such notification. Therefore, an employee can notify the employer of her desire to return to work immediately before the release date.
Moreover, after the dismissal of an employee hired for the period of maternity leave of an absent employee, the employer may find himself in an extremely unpleasant situation. After returning to work, the “maternity leaver” may change her decision. This is not prohibited by law. She can take advantage of parental leave until the child reaches the age of 1.5 years (with payment of child care benefits) or until the child reaches the age of 3 years (with payment of compensation in the amount of 50 rubles per month).
If a maternity leaver returns early, a number of other problems may arise, for example, the need to recalculate benefits and taxes.
How to recalculate benefits?
Financing of maternity benefits is provided by the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and is paid in total for the entire period of maternity leave. Maternity workers are already compensating the pregnant employee for her earnings. Therefore, it is impossible to accrue both wages and benefits at the same time. Accordingly, in this case the benefit is considered to be overpaid.
It is impossible to recover the amount of overpaid benefits at the initiative of the employer. In this situation, you will have to recalculate the amount of maternity benefits, and ask the employee to voluntarily return the excess.
Since when the postpartum part of maternity leave is reduced, benefits are actually overpaid, the accountant needs to recalculate taxes and salary contributions (see Table 2).
Table 2.
Tax consequences of early termination of maternity leave
| No. | Type of taxes (contributions) | A comment | |
| If the employee has returned the overpaid amount | If the employee does not return the overpaid amount | ||
| 1 | Personal income tax | There are no tax consequences. Maternity benefits are not subject to this tax. | Payments that have lost benefit status must be subject to personal income tax |
| 2 | Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, paid in accordance with Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009 (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 212-FZ) | There is a shortage. This is due to the fact that the amount of maternity benefit was offset against the payment of contributions. After the employee returns from vacation, amounts paid to her for the period from the date she returned to work lose their benefit status*. | |
| 3 | Contributions to the Pension Fund, FFOMS, paid in accordance with Law No. 212-FZ | There are no tax consequences. Maternity benefits are not subject to contributions. | Arrears arise because the payment that has lost its benefit status must be subject to salary contributions |
| 4 | Contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation for insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases | There are no tax consequences. Maternity benefits are not subject to contributions. | Arrears arise because the payment that has lost its benefit status must be subject to salary contributions |
| 5 | Income tax | Overpayment may occur. It is explained this way. | |
| The amount of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation is included in expenses when calculating income tax. After the benefit is recalculated, the amount of contributions may increase. | The amount of contributions to extra-budgetary funds is included in expenses when calculating income tax. After the benefit is recalculated, the amount of contributions may increase. | ||
| 6 | Single tax under the simplified tax system | Overpayment may occur. It is explained this way. | |
| The amount of contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation: - is included in expenses when paying a single tax on the difference between income and expenses; — reduces the amount of the single tax when paying a single tax on income (subject to the restrictions established by law). After the benefit is recalculated, the amount of contributions may increase. | The amount of contributions to extra-budgetary funds: - is included in expenses when paying a single tax on the difference between income and expenses, — reduces the amount of the single tax when paying a single tax on income (subject to the restrictions established by law). After the benefit is recalculated, the amount of contributions may increase. | ||
| 7 | UTII | Overpayment may occur. It is explained this way. | |
| The amount of contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation reduces the amount of the single tax (subject to the restrictions established by law). After the benefit is recalculated, the amount of contributions may increase. | The amount of contributions to extra-budgetary funds reduces the amount of the single tax (subject to the restrictions established by law). After recalculation of benefits, the amount of contributions may increase | ||
Should feeding breaks be provided?
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working women with children under the age of one and a half years are provided, in addition to breaks for rest and food, with additional breaks for feeding the child (children) at least every three hours of continuous work, lasting at least 30 minutes each .
If a working woman has two or more children under the age of one and a half years, the duration of the feeding break is set at least one hour.
In accordance with Part 3 of Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, at the request of a woman, breaks for feeding the child (children) are added to the break for rest and nutrition, or in aggregate form are transferred both to the beginning and to the end of the working day (work shift) with the corresponding ) abbreviation.
The legislation does not provide any exceptions for a woman who returned to work during maternity leave. She also has the right to breastfeeding breaks.
It is important to note that the employer is obliged to provide a woman with children under the age of one and a half years with paid breaks to feed the child, regardless of whether she is breastfeeding or not.
Part-time work and civil law agreements
When working in several companies on a part-time basis at the same time (often found among IT specialists and accountants), the employee has the right to receive benefits from all companies in which she has been employed for at least two years. This situation is described in detail in Article 287 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Certificate for appointment of payment of maternity benefits
To provide benefits for part-time work, each institution must provide a certificate of incapacity for work received at a medical institution and a standard application form. The issuance procedure is regulated in Order of the Ministry of Health No. 624n, specific features are prescribed in employment contracts.
Important! In places of work where the average monthly income of an employee is below the minimum wage, her benefit is equal to the minimum wage. Thanks to this, the benefit for part-time work can be higher than the woman’s usual monthly income.
Labor and employment leave is issued for each place of work individually. This means that a woman can work in one place and receive benefits in another. In the absence of a submitted application for one of the places of work, the employer is obliged to register the failure to appear as an absence for unknown reasons.
Working during pregnancy
Pregnancy is an exciting period for every woman. During this period, you need to treat yourself very carefully and avoid overwork and stress. A pregnant woman can work if it does not harm her health and the health of the child. After all, there are working conditions where a person experiences increased stress. For example, working at night or overtime. Therefore, the law protects pregnant women from such activities.
Thus, in accordance with Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), it is prohibited to engage pregnant women in the following work:
- overtime;
- on weekends and non-working holidays;
- going on business trips;
- on night shifts.
If a pregnant woman feels very tired, then she should write an application for another paid leave.
In accordance with Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a pregnant employee has the right to take the next paid leave at her request: it can be taken before or after maternity leave.
When working, you need to pay attention to a number of factors that can have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy:
- serious physical activity;
- strong vibration;
- more than three hours on your feet;
- conveyor production;
- prolonged monotony of movements;
- excessive noise;
- use of toxic or chemical agents;
- abnormal air humidity.
The presence of the above factors can negatively affect the health of the mother and child. If they occur at work, then you should contact management with a request to transfer to another workplace or reduce the working day.
Thus, according to Article 264 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on the basis of a medical report or a personal statement of a pregnant woman, production or service standards are reduced for her. And if there are unfavorable working conditions, she has the right to transfer to another workplace while maintaining the average earnings at the previous job.
Until the employer provides a new workplace that excludes exposure to harmful factors, the woman must be released from her previous job while maintaining her average monthly earnings.
According to the same norm, the employer is obliged to release a pregnant employee to undergo mandatory medical examinations, and the working time missed for this reason is paid.
The basis for maternity leave is the application of the pregnant employee and a certificate of incapacity for work from a medical institution. In accordance with Article 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of this leave in the general case (if the pregnancy is small and the birth was without complications) is one hundred and forty days (seventy days before childbirth and seventy after childbirth) with the payment of the corresponding benefit.
Changing jobs during maternity leave
Notice of upcoming dismissal
Direct dismissal of a pregnant woman is prohibited by Article 261 of the Labor Code. An exception is the dissolution of a company with the liquidation of its assets. Nevertheless, quite often cases of reorganization arise when conditional companies A and B are dissolved with the subsequent hiring of all valuable employees to company B. Sometimes a change of job is caused by the personal desire of the employee.
Liquidation of the organization leads to the fact that the pregnant woman loses all benefits paid from her. To receive assistance from the state, a woman needs to contact the social security authorities. In this case, the financial losses will be significant: in contrast to the full average salary during the BiR period and 40% during a year and a half of care, the state pays 1,500 rubles per month for the first child and 3,000 rubles for all subsequent ones. In fact, the dissolution of the company deprives the mother of a significant amount of assistance and increases the burden on the family.
Liquidation of the organization leads to the loss of paid benefits for the pregnant woman
If it is impossible to fire a woman during the labor and economic period, then during the period of leaving and working part-time, the employer has the right to expel the employee in case of serious violations of the Labor Code. The list of such violations includes:
- systematic lateness or absenteeism without a good reason;
- appearing at the workplace under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- theft of employer funds or property;
- gross violations of work duties.
If the mother is on maternity leave completely without going to work, then she cannot be expelled from the company’s staff or transferred to another place of work without her written consent.
Any employment in a new company during the B&R period attracts the close attention of the Social Insurance Fund. According to social services, very few employers are willing to pay a promising employee money and keep his job for a year and a half. According to Article 61 of the Labor Code, a contract can be declared invalid if a woman gets a job and immediately goes on maternity leave.
Entry into force of the employment contract
The transition to another company can be formalized either through voluntary dismissal and re-employment, or by direct transfer to another employer. The first option looks much better for the Social Insurance Fund, the second gives additional guarantees to the woman, since within a month the new company cannot refuse her to conclude an agreement.
Accounting difficulties, risks during substitution
A non-standard attitude towards maternity leave will create a lot of inconvenience for the accounting department of the enterprise. Before the actual start of the labor and labor leave, the woman is paid a salary, not a disability benefit, and then she is paid a benefit for 70 days of the postpartum period and the remainder of the prenatal days.
If a woman decides to refuse leave under the BiR altogether, then she may not count on disability benefits either.
She will be paid a salary for the days she works. It is more difficult to decide on those pregnant women who do not go to work and have not written a leave application. In this case, it is impossible to fire someone for absenteeism (Article 261 of the Labor Code), but such cases still need to be documented. This will allow you not to pay wages for missed days, and at least somehow influence the irresponsible employee.
Another difficulty concerns filling a maternity position. Until the employer has an application from the pregnant woman and her sick leave, he cannot hire a new employee in her place under a fixed-term contract.
Responsibility of the parties
If the employer approaches the issue in principle and records the date of actual receipt of sick leave from the pregnant woman, then it is impossible to hold him accountable for untimely provision of maternity leave.
In the same way , you need to carefully record the hours and days worked by the expectant mother in the report card, so that the employer is not accused of incomplete payment of wages.
In relation to the pregnant woman herself, the law is even more lenient. The law does not provide for any fines or disciplinary sanctions for late notification of maternity leave for such workers. In addition, it prohibited the application of dismissal to expectant mothers in the form of a disciplinary sanction, Art. 261 TK.
The procedure for recalculating payments and the obstacles associated with it
The BiR benefit is paid in full at the expense of the state and its size does not depend on the length of insurance coverage; no reduction factor is applied to the accrued amount. Problems with calculating benefits can only arise if the pregnant woman first went on leave under the Labor and Employment Regulations and then went back to work for a short period or before the end of her maternity leave.
If the benefit has already been paid for the entire period of maternity leave, then it must be re-read:
- Determine the periods of being on leave under the BiR and being at the workplace.
- Calculate wages for days worked.
- Re-calculate the amount of benefits for calendar days (the employee’s statement will help determine the periods).
- Calculate the overpayment for sick leave and reverse it from the previous amount.
- Reflect the recalculation in the reporting to the Social Insurance Fund and, if necessary, draw up an explanatory note for the fund.
Do they have the right to refuse entry into office after the issuance of an order on the timing?
Taking advantage of the right to maternity leave or refusing the period of preparation for childbirth proposed by law is a voluntary matter for every pregnant woman, Art. 255 TK.
A certificate of incapacity for work simply limits a certain period when a woman can not go to work. The employee can use it in full or reduce it; such a desire must be stated in writing.
But after the leave order is issued and the pregnant woman is familiar with it, the dates of leave can only be changed by mutual agreement with the employer.
It is quite understandable that management will be critical of the new mother’s desire to urgently return to work without waiting for the end of her sick leave. In this situation, the employer can completely legally refuse services offered in a timely manner. Moreover, another specialist can temporarily work in the place of a pregnant woman during her vacation.
How to leave maternity leave early
No part of maternity leave is mandatory for the employee. If you wish, you can not go on vacation at all, for example, when a child is born during the winter or May holidays. For those who prefer work to child care, there is a standard procedure for leaving maternity leave. Most often, this problem arises among single mothers on “black” wages, who do not have enough benefits in the amount of the minimum wage.
Application for interruption of maternity leave
To completely refuse leave, it is enough for a pregnant woman not to write an application. As mentioned above, rest time according to the BiR is not mandatory, and the employer cannot influence entry and exit from it. If the leave was nevertheless granted, to refuse it the employee must submit a free-form application at least two weeks before the day of leave.
For those who prefer work to childcare, there is a standard procedure for leaving maternity leave.
In addition to directly refusing leave, the employer may enter into an additional employment contract with the employee. This will give her the opportunity to work while on maternity leave and receiving benefits. It is worth remembering that in this case the working week should not be more than 20 hours, otherwise the Social Insurance Fund will intervene and cancel the benefit along with a company fine.
Resumption of work by a woman during maternity leave
Is it possible to work officially while on maternity leave? Yes. The employee chooses any of the acceptable options for carrying out work activities. Let's consider each of them separately.
Is it possible to work part-time?
The current legislation of the Russian Federation does not prohibit a mother from working in part-time workload mode. However, the contract concluded with the enterprise must contain additional clauses that relate to the modified output schedule.
Remote employment
Is it possible to work during maternity leave? Yes. Remote employment would be a good option. To do this, it is enough to have a computer with Internet access.
If a mother gets a remote job during maternity leave, then all documentation regulating labor obligations is completed electronically.
The advantage of remote employment is that you can independently plan your workday. This is especially true for the mother, since she will be able to care for the baby and earn extra money at the same time.
Is it allowed to work part-time?
Is it possible to work on maternity leave? According to Article No. 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, any employee can work part-time. A pregnant woman can also take advantage of this opportunity. The mother will work 4 hours a day and will be able to care for the baby the rest of the time.
Is it possible to get another job while on maternity leave? Yes. If a woman wants to work part-time, then she will not need to write an application for a reduced work schedule.
Pros and cons of not taking maternity leave
According to the law, payment under the BiR is carried out in a lump sum, at the request of the woman, within six months after the end of the period. With a salary “in envelopes”, both parties may benefit from a waiver of maternity leave: the employer will not need to look for a replacement for a valuable employee, the mother will receive a salary along with benefits. Of course, this is illegal and is an attempt to deceive the FSS. The employer will be punished, and the mother will have to return the money received back.
Application for permission to return to work early
With a “white” salary and the absence of significant bonuses and bonuses, refusing a vacation without paying in advance will not give a woman anything. In any case, her vacation pay will be equal to the average salary, so by refusing maternity leave, she will work these 140 days just like that, for money that actually belongs to her.
Management does not have the right to fire a pregnant woman; any pressure or attempts to evade granting maternity leave are illegal. The state has transferred almost all the rights in the situation to the woman, so she will be able to choose in what format her vacation will take place over the next three years.
Certificate of incapacity for work issued by a general practitioner
Poor health of a pregnant woman as a reason to go on sick leave
A pregnant woman can get a consultation with a general practitioner either at the clinic at her place of residence or at the antenatal clinic. A visit to such a specialist may be due to the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature;
- chills;
- pain in the throat area;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- presence of cough;
- presence of a runny nose
- ear pain or migraine.
All of the above symptoms are a direct sign of a cold or respiratory disease of viral etymology. If such symptoms are present, the general practitioner alone prescribes a sick leave for a period of 3 to 5 days. If, upon re-examination, the woman has not recovered, the doctor must extend the period of such a sheet for another 5 days.
If after 10 days the woman does not get better, the hospital therapist can add more only after an examination together with the head of the department, who certifies this document with his seal. To issue sick leave due to an acute respiratory illness for more than 10 days, there must be solid arguments.
If there are any, then the woman carrying the child is recommended to be hospitalized or receive inpatient treatment. What complaints do you most often see a general practitioner with? The most common complaints are pain in the back, lumbar region, and legs. The pain causes inconvenience to the expectant mother, hinders movement, and interferes with work. A sick leave certificate for such complaints can be issued by a neurologist.
The therapist may refuse to issue a sick leave certificate. This happens when there are deviations from the norm in test results, but without any clinical manifestations. For example, a slight decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood without accompanying dizziness, low blood pressure or fainting.
In such circumstances, the doctor's recommendation would be to take iron supplements. The hospital doctor will not be able to prescribe, since the results of the analysis do not interfere with the performance of official duties.
The therapist cannot issue a sick leave based on complaints of low blood pressure. Especially if this fact was not confirmed when measuring blood pressure in the doctor’s office.
Who provides?
As soon as a woman finds out about her situation, she needs to register with the antenatal clinic at her place of residence and periodically come for routine examinations to a gynecologist. If your health is not satisfactory or there is a threat to pregnancy, the gynecologist may issue a sick leave.
Reasons for issuing a certificate of incapacity for work:
- toxicosis;
- uterine tone;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- threat of miscarriage.
In this case, the specialist doctor will issue a sick leave if there are reasons for opening it.
To obtain a certificate of incapacity for work, you can contact a general practitioner. The therapist does not monitor the progress of pregnancy as carefully as a gynecologist does. But the therapist can issue a certificate if:
the pregnant woman has bad blood tests;- existing chronic diseases have worsened;
- ARVI or other infectious, colds.
The therapist usually suggests inpatient treatment, but the decision is up to the patient. You can carry out the necessary treatment without a 24-hour hospital - you just need to show up at a clinic or hospital to undergo procedures and take tests.
However, there are a number of dangers in which refusing hospitalization is very dangerous for both mother and child.
How to stay on sick leave throughout pregnancy
The first scenario is when a woman is really sick, and her work threatens her health. The second scenario is a simulation, i.e. you don’t have a real illness, but you don’t want to work. Each scenario has its own plan of action.
Scenario #1
The fact is that only a medical commission has the right to extend standard sick leave for a period of more than two weeks. The basis for such a decision is medical opinions, test data, examination results, and so on.
Read more: How to check whether a Russian citizen’s passport is valid
In the most difficult cases, the commission may issue a verdict to increase the duration of sick leave to ten months. It is clear that this period will automatically mean release from work for the entire period of pregnancy and even more.
Such an extension of sick leave may be followed by a referral to a hospital for conservation, sanatorium-resort treatment, etc. But as you understand, all this is only suitable for those who actually have complications. What should those who have no complications do, but don’t want to go to work?
Scenario #2
In this situation, you need to use more cunning tactics. It includes not only sick leave, but also a number of other mechanisms.
Firstly, despite the fact that one doctor cannot give you sick leave for more than 2 weeks, the law does not prohibit you from taking two (or more) sick days in a row (two weeks each), but from different doctors.
That is, you should alternately and as often as possible take sick leave from different doctors. Two weeks with a therapist, two weeks with a neurologist, two weeks with a gynecologist, etc. This is exactly what tactics should be based on.
The main thing is to be convincing! As we noted above, recently doctors have become “greedy” in issuing sick leaves to pregnant patients.
Know how to “put pressure” on the doctor, because by and large, he has no right to refuse you. And there may be a “heap” of reasons why you cannot go to work - toxicosis, vomiting, blood pressure. Use your imagination - it will become your main assistant in deciding how to spend your entire pregnancy on sick leave.
In addition, each woman may have her own characteristics in her relationship with her treating or supervising doctors. In some places you will actually have to invent non-existent syndromes, and in others you just need to directly ask for sick leave.
Secondly, since it will be difficult to continuously “jump” from one sick leave to another for several months in a row, use your other rights, namely:
- the right to the next paid leave (in this case it is granted “out of turn”, even if the woman has worked for less than 6 months);
- paid days for medical examination;
- the right to lighter work and shorter working hours.
All this together can provide the result you need and solve the issue of how to spend your entire pregnancy on sick leave.
Let's look at this in more detail.
From maternity leave to maternity leave. How is sick leave paid for pregnancy and childbirth?
- a medical organization registered with the expectant mother during pregnancy (antenatal clinic);
- obstetric care institution (perinatal center, maternity hospital or maternity ward in a hospital at the place of residence);
- employer (legal entity or individual entrepreneur providing a workplace to a woman during the prenatal and postnatal period);
- territorial branch of the Social Insurance Fund in which the employer is a member;
- a woman herself carrying out official labor activities in Russia.
To take into account the rights and interests of these parties in the context of the need to protect the rights and health of pregnant women and young mothers, a new form of a certificate of incapacity for work, introduced into circulation in Russia on July 1, 2011, by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of April 26, 2011 No. 347n, helps.
Instructions 1 Contact your therapist and complain about feeling unwell. Many doctors are sympathetic to pregnant women and issue them sick leave without delay.
If you have some kind of chronic disease, you can contact a specialist (for example, a neurologist or endocrinologist) so that he can issue you a sick leave. 2 If a doctor has written you a referral to a hospital, then regardless of whether you agree with his decision or refuse treatment in the hospital, he is obliged to issue you a sick leave, since the illness may threaten the health of your child. When prescribing outpatient treatment, follow all the doctor’s instructions and if your health worsens, be sure to go to the hospital.
Read more: Interest debt for using a loan
3 If your pregnancy threatens complications during childbirth, contact your gynecologist so that she can examine you and, if there is a threat of premature birth, refer you to the hospital.