What should you consider when concluding a contract for the purchase of workwear?
- The employer is obliged to purchase and issue workwear that has passed certification or declaration of conformity.
- Until December 31, 2013, workwear was purchased and issued based on the results of certification of workplaces for working conditions. From January 1, 2014, instead of certifying workplaces based on working conditions, a special assessment of working conditions is carried out. Therefore, if the organization additionally creates new jobs, which, according to the results of the special safety assessment, contain harmful or dangerous factors, and the necessary protective clothing is not available, a contract for its supply should be concluded again.
- Working clothes are purchased at the expense of the employer. This means that purchasing such clothing at the expense of employees is unacceptable. In practice, similar situations often arise.
- The protective clothing issued to employees must correspond to their gender, height and size, the nature and conditions of the work performed. Thus, the law obliges the employer to provide workwear of the required size. Therefore, when concluding an agreement with a supplier, you should indicate the entire size range in the application. When delivering materials, monitor its implementation.
How standards for wearing workwear depend on the type of production
Standards for issuing workwear by profession
The legislative framework provides for the issuance of protective clothing and personal protective equipment to 195 types of professions. In general, the service life of workwear, the standards of which are prescribed in Resolution of the Ministry of Labor No. 997n, depends on three factors - climatic conditions, type of production and work responsibilities of the subordinate. So, for an employee of one workshop where metal is melted, the wearing standards will be different from the norms for an employee of the next workshop where the same metal is processed.
Additional factors:
- type of pollution;
- there is a danger of electric shock;
- temperature indicators;
- presence of toxic substances;
- work associated with increased risk.
How it looks like in an example. Let's say we have a fleet driver and a battery technician. For them, the terms of use of workwear at the enterprise, the table of which is in the above-mentioned resolution, is:
- The driver, who additionally carries out car repairs in the company’s garage, is entitled to the usual cotton overalls, which are issued for up to two years, and gloves, one pair of which is required for 2 months of use;
- For a battery operator, the standards provide for the issuance of a suit with protection from acid burning for 1.5 years and 6 pairs of rubber gloves for 1 year, rubberized boots and an apron with a bib for up to 2 years, gloves made of dielectric material, glasses and galoshes “until worn out.”
An example of standards for the use of personal protective equipment by a repairman
Additional Information! The duration of wearing overalls is additionally established by a special commission during production certification.
What sources of financing can be used to purchase workwear?
This question most often interests accountants of budgetary institutions.
This type of expenditure can be financed both from budget subsidies allocated for the implementation of state (municipal) tasks, and from funds received from the provision of paid services. In addition, a budgetary institution has the right to purchase special clothing using insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases. The basis for the acquisition is the results of the SOUT.
The amount of funds allocated by the policyholder to finance preventive measures cannot exceed 20% of the amount of insurance premiums accrued for the previous calendar year, minus the costs of paying security for the specified type of insurance, made by the policyholder in the previous calendar year.
Let us note that in order to make expenses from insurance premiums for injuries, a budgetary organization must submit an application to the executive body of the Social Insurance Fund at the place of its registration before August 1 of the current calendar year.
Accounting for workwear and other personal protective equipment
From the article you will learn:
1. In what order should employers provide their employees with special clothing and other personal protective equipment.
2. How to reflect for tax purposes the costs of purchasing personal protective equipment.
3. What are the features of accounting for workwear and personal protective equipment.
Providing workers with special clothing, shoes and other personal protective equipment is not as uncommon as it might seem at first glance. For example, by law, an employer is required to provide PPE for employees whose work involves pollution. And this category includes, among other things, cleaners and drivers - positions that exist in almost every organization. In addition, PPE must be issued to employees engaged in work with harmful and dangerous working conditions, such as welders, laboratory technicians, mechanics, etc. With the introduction of a special assessment of working conditions mandatory for all employers, it is unlikely that it will be possible to “forget” to provide their employees with special clothing and PPE - a reminder will be the report of a specialized organization on the results of the special assessment. Therefore, employers need to be prepared to finance the purchase of personal protective equipment, and accountants need to reflect them in their accounts.
The procedure for providing workers with special clothing and other personal protective equipment
The employer is responsible for ensuring safe conditions and labor protection. For this purpose, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the issuance of personal protective equipment (PPE) to workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, as well as work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, personal protective equipment includes special clothing, special shoes and protective devices (overalls, suits, jackets, trousers, dressing gowns, sheepskin coats, sheepskin coats, various shoes, mittens, goggles, helmets, gas masks, respirators) used to prevent or reduce exposure to workers exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, as well as to protect against pollution.
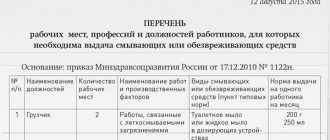
The procedure for providing workers with PPE is established by the Intersectoral Rules for Providing Workers with Special Clothing, Special Footwear and Other Personal Protective Equipment (approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n), according to which:
- The employer purchases personal protective equipment at his own expense; it is also possible to purchase personal protective equipment for temporary use under a lease agreement.
- PPE intended for issue to employees must have a valid certificate or declaration of conformity confirming compliance with the safety requirements established by law.
- Workwear and other personal protective equipment are issued to employees free of charge based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions and issuance standards.
Standard standards for issuing PPE to employees , universal for all sectors of the economy, are established by the following documents:
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated October 1, 2008 N 541n (valid until May 27, 2015), Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 9, 2014 N 997n (valid from May 28, 2015) - in relation to special clothing and footwear and other personal protective equipment for professions and positions;
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 1997 N 70 - in relation to warm special clothing and footwear according to climatic zones;
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 20, 2006 N 297 - regarding special high-visibility signal clothing.
In addition to industry-wide standards, there are standard standards for issuing PPE that are used in each specific industry, for example, in construction, transport, and healthcare. In addition, if there are financial opportunities, the employer has the right to establish increased issuance standards or otherwise improve the provision of workers with protective equipment. The established procedure for issuing PPE must be enshrined in the relevant local regulations.
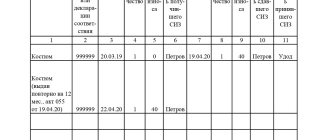
In order to comply with the standards for issuing PPE to employees and the timing of their use, the employer must organize a record of PPE in use . The issuance and return of protective clothing is reflected in the personal record card for the issuance of personal protective equipment, the form of which is established by the Intersectoral Rules (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n).
Download Personal record card for the issuance of personal protective equipment
Personal registration cards for the issuance of personal protective equipment can be filled out both in paper and electronic form. In the latter case, instead of the employee’s personal signature, the date and number of the accounting document, which contains the employee’s signature in receiving PPE (for example, a demand invoice), are affixed.
! Please note: Workwear and other personal protective equipment are issued to employees for use , while ownership remains with the employer. Therefore, upon dismissal or transfer to another job, the employee is obliged to return the PPE received, otherwise the cost of the PPE may be withheld from wages.
Tax accounting of workwear and personal protective equipment
Taxpayers have the right to include as expenses the costs of purchasing workwear and other personal protective equipment for employees both for calculating income tax and for the simplified tax system. However, it is possible to take into account the costs of personal protective equipment only within the current standard standards for issuing or increased standards, confirmed by the results of a special assessment of working conditions (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated November 25, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/59763, dated February 16, 2012 No. 03- 03-06/4/8).
The procedure for accepting expenses for the purchase of personal protective equipment for tax accounting depends on their cost and period of use. Depending on these factors, personal protective equipment can be taken into account either as part of material costs or as part of costs for the acquisition of fixed assets.
| Service life of PPE in accordance with standard standards | Cost of PPE | Accounting procedure for tax purposes |
| more than 12 months | more than 40,000 rub. | as fixed assets |
| 40,000 rub. or less | in material costs | |
| 12 months or less | any |
If personal protective equipment is accepted for tax accounting as fixed assets , then their cost is written off as expenses after commissioning (issuance to the employee):
- in the case of OSN - monthly during the established period of use by calculating depreciation;
- under the simplified tax system - a lump sum on the last day of the reporting (tax) period in the amount of amounts paid (clause 3 of article 346.16, clause 4 of clause 2 of article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
If personal protective equipment is taken into account as part of material costs , then their cost is taken into account for tax purposes:
- In the case of OSN - at a time during commissioning (issuance to an employee) or evenly, taking into account the period of use or other economically justified indicators (if the period of use of PPE exceeds one reporting period for income tax) (clause 3 of clause 1 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . The option of accounting for personal protective equipment chosen by the taxpayer must be fixed in the accounting policy for tax purposes;
- Under the simplified tax system - once after posting and payment.
! Please note: If the cost of purchased personal protective equipment is partially or fully reimbursed from the Social Insurance Fund, then the reimbursement amounts must be taken into account for tax purposes as non-operating income. The procedure for reimbursement of expenses for the purchase of special clothing and other personal protective equipment for employees is generally similar to the procedure for reimbursement of expenses for conducting a special assessment of working conditions, which is described in one of the previous articles.
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
Since special clothing and other personal protective equipment are issued to employees for use, without transfer of ownership, and are not remuneration for labor, their cost does not relate to employee income. In this regard, the cost of PPE transferred to employees is not taxed:
- Personal income tax (Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, FFOMS and Social Insurance Fund (Article 7 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 N 212-FZ, clause 1 of Article 20.1 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 N 125-FZ).
Accounting for workwear and personal protective equipment
For the purpose of accounting for special clothing and other personal protective equipment, organizations must be guided by the Guidelines for accounting of special tools, special devices, special equipment and special clothing (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 26, 2002 N 135n). In accordance with these instructions, personal protective equipment, regardless of their cost and period of use, are accounted for as inventories (on account 10). However, the organization has the right to provide for the accounting of personal protective equipment that meets the criteria of fixed assets as part of fixed assets (account 01) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 12, 2003 No. 16-00-14/159).
! Please note: Since accounting for personal protective equipment as fixed assets is the right of the organization, the choice of a specific accounting option must be fixed in the accounting policy for accounting purposes:
- Option 1. Special clothing and other personal protective equipment are taken into account as part of inventories, regardless of cost and service life.
or
- Option 2. Special clothing and other personal protective equipment with a cost of over 40,000 rubles* and a service life of more than a year are taken into account as part of fixed assets in the manner established by PBU 6/01. Special clothing and other personal protective equipment that do not meet the specified criteria are taken into account as part of the MPZ.
* The organization has the right to establish another cost criterion for classifying inventories as fixed assets, but not more than 40,000 rubles. (paragraph 4, clause 5 of PBU 6/01)
Since the second option for accounting for personal protective equipment corresponds to the reflection of personal protective equipment in tax accounting, it is advisable to choose and register it in the accounting policy: this will bring tax and accounting accounting as close as possible.
The procedure for writing off the cost of purchased personal protective equipment as expenses depends on the option of their accounting.
- If personal protective equipment is accepted for accounting as part of the inventory, then its cost, in accordance with the Methodological Instructions, should be written off as expenses linearly throughout the entire period of use (clause 26 of the Methodological Instructions).
! Please note: The cost of personal protective equipment, the service life of which does not exceed 12 months, can be written off as expenses at a time at the time of transfer to the employee (clause 21 of the Methodological Instructions). However, this accounting option needs to be fixed in the accounting policy for accounting purposes, and it is better if it coincides with the option chosen for tax accounting purposes.
- If personal protective equipment is taken into account as fixed assets (that is, it meets the criteria for recognizing assets as fixed assets), then their cost is written off as expenses by calculating depreciation.
Accounting for special clothing and other personal protective equipment
| Account debit | Account credit | Contents of operation |
| Accounting for personal protective equipment as a fixed asset | ||
| 08 “Investments in non-current assets” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | PPE purchased |
| 01 "Fixed assets" | 08 “Investments in non-current assets” | PPE is accepted for accounting as fixed assets |
| 01 “Fixed Assets” / Responsibility Center (MOL) | 01 "Fixed assets" | PPE was given to the employee for use |
| 20 “Main production” (26, 44) | 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” | Monthly during the period of use of PPE: Depreciation is calculated on the cost of PPE |
| Accounting for personal protective equipment as part of the inventory (use period more than 12 months) | ||
| 10-10 “Special equipment and special clothing in the warehouse” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | PPE purchased |
| 10-11 “Special equipment and special clothing in operation” | 10-10 “Special equipment and special clothing in the warehouse” | PPE was given to the employee for use |
| 20 “Main production” (26, 44) | 10-11 “Special equipment and special clothing in operation” | Monthly during the period of use of PPE: the cost of PPE is partially written off as expenses |
| Accounting for personal protective equipment as part of the inventory (use period no more than 12 months) | ||
| 10-10 “Special equipment and special clothing in the warehouse” | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | PPE purchased |
| 20 “Main production” (26, 44) | 10-10 “Special equipment and special clothing in the warehouse” | The cost of personal protective equipment is written off as an expense upon transfer to the employee |
| Off-balance sheet account “Special equipment and special clothing in use” | The cost of personal protective equipment transferred to employees for use is reflected off the balance sheet (if, by decision of the organization, off-balance sheet accounting is maintained) | |
If you find the article useful and interesting, share it with your colleagues on social networks!
If you have any questions, ask them in the comments to the article!
Normative base
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund”
- Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ “On compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases”
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n “On approval of intersectoral rules for providing workers with special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment”
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated October 1, 2008 No. 541n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of certified special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers of cross-cutting professions and positions in all sectors of the economy engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, and also for work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution"
- Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 09, 2014 No. 997n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers in cross-cutting professions and positions of all types of economic activities engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, and also for work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution"
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 20, 2006 No. 297 “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of certified special high-visibility signal clothing to workers in all sectors of the economy”
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 1997 No. 70 “On approval of the Standards for the free issuance of warm special clothing and warm special footwear to workers in climatic zones that are common to all sectors of the economy (except for climatic regions specifically provided for in the Standard Industry Norms for the free issuance of special clothing and special footwear and other personal protective equipment for maritime transport workers; civil aviation workers; workers carrying out observations and work on the hydrometeorological regime of the environment; permanent and variable composition of educational and sports organizations of the Russian Defense Sports and Technical Organization (ROSTO))"
Find out how to read the official texts of these documents in the Useful sites section
How to account for workwear costs
Workwear owned by the organization is accounted for in the accounts/sub-accounts for materials accounting before being put into operation. Like other materials, it is taken into account at the cost of actual acquisition costs. The procedure for accounting for workwear is fixed as an element of the company’s accounting policy. The purchased workwear arrives at the warehouse on the basis of a receipt order.
There is another way. As can be seen from paragraph 9 of the Guidelines, an organization can keep records of special tools, fixtures, and equipment in the manner prescribed for accounting for fixed assets. This method has a number of disadvantages. Firstly, the cost of workwear will have to be subject to property tax. Secondly, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the workwear so that it can be written off on time.
Establishment of the period: “until wear”
As already mentioned, some personal protective equipment is issued to the employee “until worn out.” This list includes a signal vest, the service life of which is unlimited, safety glasses, noise-cancelling headphones, knee and elbow pads, some types of support belts, etc. The issuance of new PPE is provided only in the event of loss, theft, breakage, obsolescence and beyond the operational time frame , installed by the manufacturer.
Sample order for standards for issuing workwear
Thus, for example, if for supporting belts GOST provides for maximum use for a period of up to 25 years, then if during this time it has not become unusable, it is in any case subject to write-off.
In addition, the employer must conduct regular inspections of personal protective equipment. The enterprise must have a log in which each inspection will be recorded.
Additional Information! Typically, for long-life PPE, inspections are carried out every six months or a year.
How to determine for accounting purposes the wear period of workwear if the issuance rate is set “until worn out”
Any wear time can be set for items of equipment, the main thing is that it does not exceed the standards for maximum use of the product by GOST or the manufacturer of the product.
For example, the useful service life of safety glasses can range from a couple of months to 20 years. Therefore, for accounting purposes, it is possible to establish a systematic write-off every year, referring to the conditions of the work performed.
Issuance of protective clothing to employees
When transferring workwear from a warehouse to other divisions of the company, it is necessary to draw up a primary document on the basis of which the workwear is kept accountable. Such paper will be enough to write off the cost of workwear as an expense both in accounting and tax accounting.
If you choose a unified primary, you can use one of these forms:
- demand-invoice;
- invoice for materials release.
If you decide to develop your own form, then you can take the invoice for the release of materials as a basis, removing unnecessary things from it.
The employee responsible for receiving workwear issues it to employees. His actions also need to be recorded somewhere. It is advisable to create a special statement for each person in all departments for a year or month, so as not to fill it out every time you issue special clothing.
Records can also be kept on a special card, which is filled out for each employee of the organization who has received special clothing.
Example
Let's add the conditions of the previous example. Safety precautions at the enterprise include the use of vests by transport service employees. The storekeeper of the conditional LLC issued these IBPs on March 17. The movement of workwear between departments is formalized by an invoice requirement. The issuance of vests to drivers is recorded in the statement. Based on these primary documents, the accountant makes entries in the balance sheet:
DT10 subaccount “Working clothes in operation” KT10 subaccount “Working clothes in warehouse” - 1080 rubles - moving the IBP to the department.
Documents from accountable persons reached the accounting department at the end of the month. The accounting policy stipulates that small business enterprises with a useful life of up to 12 months are written off at a time. The following records are made in the BU:
DT20 KT10 — 1080 rub. — write-off of workwear as expenses of the enterprise.
DT012 “Workwear in use” - 1080 rubles. — issuance of IBP to employees.
How to retain the cost of workwear from a resigning employee?
When you issue workwear to an employee, you must conclude an agreement with him on the transfer of soft equipment for use or a one-time document on acceptance and transfer.
The employee’s obligation to compensate for direct actual damage caused to the employer is provided for in Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, therefore termination of the employment contract does not entail the release of the employee from financial liability for non-return of workwear.
Thus, in the case of correct registration of the issue of special clothing if it is not returned by an employee leaving the organization, the employer has the right to demand reimbursement of the cost of the special clothing (the useful life of which has not expired) taking into account the degree of wear and tear (Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The programs “Kontur-Accounting Asset” and “Kontur-Accounting Budget” allow you to avoid errors when keeping records of workwear or uniforms.
Yulia Volkhina , project manager
When does the period of use of the issued workwear begin?
The shelf life of workwear according to the law depends on the specifics of the activity, climate and work performed. The standards for the terms of use of workwear for 2021 are prescribed in the corresponding order of the Ministry of Finance No. 997n. It also indicates how and from what point the service life of CO begins to be calculated, when it needs to be changed, what rules apply to different enterprises, how to determine the wear and tear of clothing and the service life of PPE (personal protective equipment).
So, according to the order of the Ministry of Finance, the time of use of the “special clothing” begins to be recorded from the moment the worker signs in the journal about receiving the CO. This rule applies to the standard form. The accounting for the winter kit, which is often used for 4-5 months a year, depending on the region, includes the time that the CO remains in the warehouse.
Documents establishing the framework for the operation of overalls