Responsibilities of the employer to provide collective and individual protective equipment to employees
In accordance with Art.
221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide workers of his organization with special clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE) if they have to work in difficult or health-threatening conditions. Allowing employees to enter the workplace without the necessary protection or with faulty PPE is strictly prohibited. Let's look at how legislation regulates the provision of workers with protective equipment. In Art. 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides an interpretation of the concept of “personal protective equipment”. These are special clothing and equipment used to protect against pollution, as well as to prevent or reduce the impact of harmful and dangerous production factors on the worker’s body. Such means include special clothing, safety shoes, etc., as well as flushing and neutralizing agents. The employer is obliged to ensure that employees are informed about the protection they are entitled to at the stage of concluding an employment contract. At the same time, the employee becomes familiar with the rules for the provision and use of PPE, as well as with the standard standards for issuing them corresponding to his profession and position.
Responsibility for providing personal protective equipment at the enterprise lies entirely with the employer. When purchasing workwear, the employer must check the availability of certificates and declarations of conformity confirming its safety. The issuance and use of funds that do not have the appropriate documents is not permitted. In addition to the above, the employer is responsible for the care and timely repair of personal protective equipment. These procedures include:
- cleaning;
- degassing;
- deactivation;
- disinfection;
- dust removal;
- neutralization;
- repair.
The employer does not have to provide the care themselves. He has the right to enter into an agreement for the provision of such services with a specialized organization. The employer is also responsible for the quality storage of unused work clothing and equipment; a separate room is allocated for this purpose at the enterprise.
The employer may, taking into account the opinion of the trade union, replace the personal protective equipment specified in state regulations with similar ones that provide equivalent protection from undesirable production factors. Depending on the financial and economic situation and the recommendations of the trade union, our own standard for providing personal protective equipment for workers may be established, improved in comparison with standard protection standards. Or softer standards may be introduced regulating the provision of personal protective equipment; the established procedure according to GOST standards for workwear cannot be reduced, nor can the conditions for their use be tightened.
Management must monitor the provision of personal protective equipment to employees at each workplace, as well as analyze their effectiveness (control in this case is carried out by comparing the actual items issued with the norms for issuance), check compliance with the rules for providing personal protective equipment (the presence of a personal accounting card filled out in the prescribed manner). The assessment of the provision of workers with personal protective equipment is documented using a separate protocol.
Responsibility and control of compliance with the rules for providing workers with PPE
Responsibility and implementation of control measures for compliance with the requirements of local regulations at the enterprise is carried out by a specialized labor protection service or a specialist in this field of activity. Such employees must have a full range of knowledge in the field of safe activities, as well as issue orders for the implementation of protective measures, establish a special list of means, depending on the specifics of the work. In addition, such employees at the local level establish the manner of supplying personnel with work clothes, safety footwear and other PPE, as a rule, by issuing relevant local acts.
Conditions for providing personal protective equipment to employees
The need to issue PPE arises in the following cases:
- if the enterprise has harmful and/or dangerous factors that adversely affect the health of employees;
- if employees perform their work duties in special temperature conditions or in a polluted environment.
Each employee is provided with personal protective equipment at the expense of the employing company. The directorate may not purchase new personal protective equipment, but take it for temporary use under a lease agreement. In any case, the employer does not have the right to take a penny from employees for issuing protection (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Workwear and footwear are allocated in accordance with the gender, size and nature of the employees’ work. At the end of the period of use, as well as in case of damage, the employer must issue the employee a new protective kit. Otherwise, the employee has the right to refuse to perform work duties, and the employer, without the right to demand their fulfillment, will be obliged to pay for the downtime that arises for this reason.
Workers who combine professions or jobs must additionally receive PPE depending on the work performed in each specific case, as provided for by the relevant standard standards. Workers temporarily transferred to another job or undergoing vocational training (retraining), as well as students of educational institutions while undergoing practical training (on-the-job training), are issued protective clothing in accordance with standard norms and rules for the period of acquiring working skills (undergoing vocational training, retraining, industrial practice, industrial training).
Providing PPE as an employer's responsibility
The framework of labor legislation establishes (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) that the employer must, at his own expense, ensure the timely issuance of special clothing, shoes and other equipment intended for personal protection to his employees.
In addition, the responsibilities of the immediate manager or person responsible at the enterprise include storing products, drying them, washing them, carrying out repairs, and replacing them.
Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Providing workers with personal protective equipment”
The procedure for providing workers with personal protective equipment
The employer guarantees that employees must use PPE in accordance with the Regulations on the Occupational Safety and Health System (OSS). Employees are not allowed to perform work without PPE issued to them in the prescribed manner, or if it is faulty, not repaired and/or dirty.
The issued workwear must be specially registered and controlled by the employer. For this purpose, a personal card is created for each employee in the form specified in the Appendix to Order 290n. Such an account card can be developed by the organization independently. It should contain the following information:
- date of issue;
- return date;
- wear percentage;
- signatures of the employee and the person responsible for accepting PPE from the employee.
In some cases, the type of PPE may not be specified in the relevant standard standards (we are talking, for example, about signal vests, balaclavas, mittens, etc.). In such cases, they are issued to employees with a service life “until wear out” or as duty workers based on the results of certification of workplaces for working conditions, as well as taking into account the conditions and characteristics of the work performed. Duty PPE for general use is issued to employees only for the duration of the work for which they are intended. Such PPE, taking into account the requirements of personal hygiene and the characteristics of workers, is assigned to certain workplaces and transferred from one shift to another. They are issued under the responsibility of the heads of structural units authorized by the employer to carry out such work.
Workwear intended for use in special temperature conditions caused by periodic seasonal temperature changes is issued to employees once a year, with the onset of the corresponding period, and at its end they are handed over to the employer for organized storage until the next season. The service life includes the time of their organized storage.
Workwear returned by employees after the wear period has expired and is suitable for further use is used for its intended purpose after taking measures to care for it. The suitability of the specified PPE for further use, the need for and the composition of measures to care for them, as well as the percentage of wear are established by an official authorized by the employer or the labor protection commission of the organization (if any) and are recorded in the personal record card for issue.
When issuing special protection, the use of which requires practical skills from workers (respirators, gas masks, self-rescuers, safety belts, mosquito nets, helmets, etc.), the employer must provide instructions on the rules of its use, the simplest ways to check functionality and serviceability, and also organize training by application.
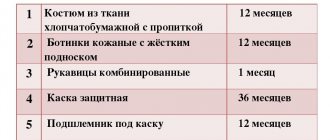
How PPE tests are carried out
Enterprises periodically conduct tests of PPE
Tests are also carried out with PPE:
- Products such as glasses, protective screens, headphones and earplugs are tested at the manufacturer and are written off as needed and after the wear period has expired, that is, after a year.
- Construction helmets are also tested immediately after manufacture and only after that they can be used. However, at the enterprises where they are used, they also need to be tested once every six months. It is worth noting that the lifespan of a helmet is no more than two years.
- Tests of mounting belts are carried out after manufacture, and in organizations that use such tests, they are carried out once every six months. There are special guidelines for this.
- Dermatological products are tested during production using the testing method.
- Gas masks are checked directly at the manufacturer, and then at production once every six months.
The test stand can be organized directly at the enterprise itself, and it is necessary to ensure verification of this technical device. It is not forbidden to enter into agreements with organizations that have the right to engage in this type of activity.
To learn about testing dielectric gloves, watch this video:
What documents regulate the standards for issuing PPE to employees?
The rules for providing workers with personal protective equipment were approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated 06/01/2009 No. 290n (as amended on 01/12/2015) on the introduction of “Intersectoral rules for providing workers with special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment and in order to improve the procedure for providing workers with special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment.” This order contains instructions:
- on the procedure for issuing PPE;
- rules for their use.
Requirements for their storage and care are also listed.
The Appendix to the Order contains a personal record card for the issuance of PPE. If necessary, in addition to unified primary accounting documents, an organization can use independently developed forms of primary documents, but the employer must necessarily consolidate them in the accounting policy.
Compliance with the requirements of Order No. 290n is mandatory for the employer. Based on it, the organization can develop its own regulations on providing workers with personal protective equipment. In such a document, the employer should describe in detail the procedure for providing personal protective equipment to employees of the enterprise. Standard standards for issuing PPE by profession are contained in Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 9, 2014 No. 997n, Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated October 3, 2008 No. 543n and in other similar industry and intersectoral regulatory legislative frameworks. For example, standards for the issuance of PPE in construction are contained in Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 20, 2006 No. 297. Standards for the provision of signal protective clothing are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 20, 2006 No. 297, and insulated workwear - in Decree of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 1997 No. 70.
If an employer introduces independent standards, a separate order is issued regarding the provision of workers with personal protective equipment, which is based on the results of certification of workplaces for working conditions, taking into account the opinion of the trade union organization. Additional security standards can be included in the employment contract indicating standard standards, in comparison with which the provision of workers with protective equipment is improved.
Workwear is written off from the register only when it is actually disposed of (wear and tear or shortage). At the same time, workwear can be completely worn out morally or physically even before the end of its standard service life. The condition of PPE and its suitability for use is assessed by the inventory commission (in accordance with the Guidelines for accounting of special tools, special devices, special equipment and special clothing, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 26, 2002 No. 135n). The write-off of workwear that is unsuitable for use should be documented in a separate act.
The procedure for issuing and recording PPE by the employer
The procedure for issuing and accounting for such items is determined based on industry legislation and the presence of hazardous production factors by the enterprise itself, by issuing its own internal documents. Responsibility in this area is carried out by a specialist in the field of labor protection, who reports directly to the head of the organization.
Legal requirements for the use of protective segments by personnel of enterprises
Employer's responsibility for supplying PPE
All employees are provided with personal protective equipment if production involves difficult or hazardous conditions. Russia assigns control over compliance by employers (legal entities and individuals) with these Rules in accordance with Articles 353 and 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments, as well as trade unions, their associations and they are under the supervision of technical labor inspectors and authorized persons for labor protection. Failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment can result in big troubles and penalties for the head of the company from regulatory authorities. The amount of the fine in case of failure to provide an employee with PPE will be:
| Primary disorders | Repeated violations | ||||
| For officials | For individual entrepreneurs | For legal entities | For officials | For individual entrepreneurs | For legal entities |
| From 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. | From 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. | From 130,000 to 150,000 rubles. (Part 4 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) | From 30,000 to 40,000 rubles. or disqualification from 1 to 3 years | From 30,000 to 40,000 rubles. or suspension of activities for up to 90 days | From 100,000 to 200,000 rubles. or suspension of activities for up to 90 days |
Results
Russian employers whose production infrastructure is characterized by harmful and dangerous working conditions are required to equip their employees with personal protective equipment. The main legal regulations, the provisions of which the company must follow when providing PPE to employees, are the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n.
You can get acquainted with other aspects of ensuring labor safety at an enterprise in the articles:
- “Dangerous and harmful production factors (list).”
- “What are the responsibilities of a labor protection employee (list)?”
- “What are the responsibilities of an employer in the field of labor protection?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is it possible to take into account the costs of personal protective equipment when calculating taxes?
Changes in calculating employer income tax, in accordance with Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 16, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/244, depend on the period of use and the cost of protection:
- if the useful life of workwear exceeds 12 months and the initial cost is more than 40,000 rubles, then the workwear is included in depreciable fixed assets, and its cost is written off during the standard wear period (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the useful life is less than 12 months or the cost is no more than 40,000 rubles, then the cost of the purchased workwear is included in material expenses at a time at the time of transfer to the employee (subclause 3, clause 1, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The accounting option is chosen by the employer independently and is fixed in the accounting policy. If the requirements for PPE at an enterprise are increased compared to the standards, when calculating taxes, you can use the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, which allow, when calculating the tax base for the company’s profits, to take into account the costs of issuing protective clothing in accordance with independently approved standards (unless, of course, organizations are required by law provide employees with personal protective equipment) (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 23, 2007 No. 03-04-06-01/128, dated November 14, 2007 No. 03-03-05/254).
Since workwear is not transferred to the ownership of employees, operations for its issuance are not subject to VAT. Accruals will need to be made if, upon dismissal or transfer to a position that does not provide for the issuance of protective equipment, the employee either buys out special clothing or receives it free of charge (subclause 1, clause 1, article 39, subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code RF).
Since PPE is the property of the organization and is issued to employees temporarily on a refundable basis, there is no need to withhold personal income tax from the cost of the workwear. If, upon dismissal (transfer to a position that does not require the provision of protective equipment), the employee does not return PPE and the employer decides not to recover its cost (i.e., transfers it to the employee free of charge), personal income tax will have to be withheld, since in this situation the cost of unreturned protective clothing will be income in kind employee. Moreover, the tax will need to be calculated from the market value of the workwear, taking into account its depreciation. If the employer decides not to collect the cost of clothing or withhold personal income tax, you can write off such workwear as worn out.
Organization of PPE care at the enterprise
According to the requirements of regulatory documentation, in any organizational structure it is necessary to ensure the care of PPE, that is:
- organize washing stations (staff involved in washing these products or an agreement with laundries): at least once a week, workwear must be washed and ironed;
- it is necessary to organize repair points for personal protective equipment and workwear;
- establish control over the implementation of the above measures. It is recommended to assign responsibility to one of the employees by administrative document.
Only with proper organization can results be achieved in accordance with the requirements of occupational safety standards and regulations.