Home / Labor Law / Occupational Safety and Health
Back
Published: 08/24/2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
5869
One of the elements of labor protection at an enterprise is the provision of personal protective equipment (PPE) to employees. At the legislative level, the state obliged the employer to provide free and periodically special clothing, shoes, protective equipment (respirators, masks, earplugs), cleaning agents and disinfectants for the personal use of employees.
Questions arise:
- what regulations should be followed;
- what characteristics should PPE have;
- who is provided with PPE, whether every employee is entitled to it;
- how often should the enterprise replace PPE with new ones;
- what is the procedure for accounting and taxation of personal protective equipment.
- Legislation
- Issuance procedure
- Accounting and tax accounting
How does an occupational safety specialist issue PPE?
PPE: the procedure for issuing by a specialist has a clear sequence. To organize the issuance of personal protective equipment, a labor protection specialist:
- determines the list of professions in the organization that require the issuance of PPE;
- clarifies working conditions at the workplace for these professions;
- based on the profession, selects standard standards for issuing PPE for an employee, and based on the working conditions at his workplace (point 2), if necessary, provides him with additional PPE;
- creates an internal order to familiarize employees with the PPE they are entitled to and takes measures aimed at getting it signed by employees upon employment;
- organizes the purchase and storage of necessary personal protective equipment. Moreover, storage is both warehouse and individual (availability of places for changing clothes and storing PPE after the end of the shift);
- builds the process of actually providing employees with PPE in such a way that it is possible to directly control the issuing process itself, as well as recording the issuance with the personal signature of the employee;
- monitors the timing of issuance and condition of used PPE, and, if necessary, replaces them.
Responsibility for violating the rules for issuing workwear
The employer must follow the procedure for issuing personal protective equipment to employees. Failure to comply will result in a fine for the administration of the organization and for the legal entity. When calculating the fine, the number of employees not provided with protective equipment is taken into account. For repeated violations, fines are increased or activities are suspended for up to 3 months.
In addition, if an employee is not provided with proper protective equipment, then he has the right not to start work while maintaining his salary.
Attention! If an employee refuses to use PPE, disciplinary action may be taken against him.
What PPE must be issued to an employee?
The list of what needs to be given to an employee is regulated primarily by standard standards for issuing personal protective equipment. Large industrial sectors of the economy have their own lists. If your organization can be classified as such, then you need to start by searching for a regulatory document for your industry. If not, then use the Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation No. 997n “On approval of the Standard Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers of cross-cutting professions and positions of all types of economic activities engaged in work with hazardous and (or ) hazardous working conditions, as well as work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution.”
In addition, it is necessary to use the results of a special assessment of working conditions (SOUT). Based on its results, harmful production factors affecting the employee during work are identified. Accordingly, the SOUT card indicates recommendations for the selection of PPE for a given workplace.
Please note that you can provide workers with PPE in excess of the standard standards and recommendations specified in the SOUT card. Very often this is even necessary, because now labor protection is on the way to transitioning to a risk-oriented approach. Thus, the selection of PPE is made in accordance with the identified risks that are present in the employee’s workplace. It is in your best interests to keep your employees as safe as possible.
Personal protective equipment - we provide workers
“Human Resources Department of a Commercial Organization”, 2012, N 4
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT - WE PROVIDE WORKERS
Due to unfavorable environmental factors and not always perfect labor processes, issues of labor protection and safety are one of the main directions of state policy. Particular attention is paid to the procedure for providing workers with personal and collective protective equipment. According to statistics, a large number of accidents at work (as well as an increase in occupational diseases) occurs due to the failure of workers to use personal protective equipment (hereinafter referred to as PPE). In this article, we will tell you what guides an employer when it comes to providing employees with PPE, what responsibilities are established for him by legislation in this area, and what liability may follow in the event of a violation of the procedure for issuing PPE.
So, according to Art. Art. 212 and 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, work performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution, the employer is obliged to ensure that employees use personal protective equipment that has undergone mandatory certification or declaration of conformity in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on technical regulation. and collective defence.
The legislation has approved both general rules that apply to all employers - legal entities and individuals, regardless of the organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership of organizations, and special ones that apply in certain industries.
One of the main regulatory documents establishing state requirements for providing employees of all legal entities and individuals with PPE are the Intersectoral Rules for Providing Workers with Special Clothing, Special Footwear and Other Personal Protective Equipment, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 1, 2009 N 290n (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) .
In addition, there are general standards and procedures for issuing PPE, which are applied in all sectors of the economy with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions:
— Standard standards for the free issuance of certified special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers in cross-cutting professions and positions in all sectors of the economy, engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, as well as in work performed in special temperature conditions or related with pollution, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated October 1, 2008 N 541n;
— Norms for the free issuance of warm special clothing and warm special footwear to workers in climatic zones that are common to all sectors of the economy (except for climatic regions specifically provided for in the Standard Industry Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to maritime transport workers; civil servants aviation, workers carrying out observations and work on the hydrometeorological regime of the environment; permanent and variable composition of educational and sports organizations of the Russian Defense Sports and Technical Organization (ROSTO)), approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 1997 N 70;
— Standard standards for the free issuance of certified special high-visibility signal clothing to workers in all sectors of the economy, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 20, 2006 N 297;
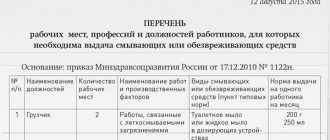
— Standard standards for the free distribution of flushing and (or) neutralizing agents to employees, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 17, 2010 N 1122n (hereinafter referred to as Order N 1122n).
Note! Despite the fact that the issuance standards are established by regulatory legal acts, by virtue of Part 2 of Art. 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization or other representative body of workers, has the right to independently establish standards for the free issuance of personal protective equipment to employees, which, compared to standard standards, improves protection from harmful and (or) dangerous factors existing in the workplace, and special temperature conditions or pollution.
For certain categories of workers, you need to consider:
— Standard standards for the free issuance of certified special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment to workers engaged in construction, construction and repair work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, as well as those performed in special temperature conditions or associated with pollution, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated July 16, 2007 N 477 (hereinafter referred to as Order N 477);
— Standard industry standards for the free distribution of special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment for medical workers to employees, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 29, 1997 N 68; etc.
Requirements for PPE
According to Art. 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, PPE includes special clothing, shoes, flushing and neutralizing and other means. The classification, requirements and list of basic personal protective equipment are established by GOST 12.4.011-89 (ST SEV 1086-88) “System of occupational safety standards. Protective equipment for workers. General requirements and classification”, put into effect by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated October 27, 1989 N 3222.
For your information. GOST 12.4.011-89 also establishes a list of collective protective equipment and requirements for them. Such means include means of normalizing the air environment, lighting, protection from increased levels of ionizing and other radiation, vibration, etc.
Protective equipment is purchased at the expense of the employer. However, they must meet certain requirements:
1. PPE (including foreign production) must be certified or have a declaration of conformity (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 5, 8 of the Rules). Certification is carried out in the manner established by the Rules for Certification of Personal Protective Equipment, approved by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated June 19, 2000 N 34. And the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2009 N 982 approved the Unified List of Products Subject to Mandatory Certification and the Unified List of Products, Confirmation of Conformity which is carried out in the form of accepting a declaration of conformity.
As for the declaration of conformity, it is carried out according to the rules established by the Technical Regulations “On the safety of personal protective equipment”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2009 N 1213 (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations), which comes into force on July 1, 2012. At the same time, PPE issued before the date of entry into force of the Regulations is subject to mandatory safety requirements that are in force until the day of its entry into force. Certificates of conformity issued before that date are valid until the end of the period specified therein. PPE imported before the entry into force of the Regulations is allowed for sale within one year from the date of its entry into force.
Note! The Regulations do not apply to specially designed PPE for military purposes, for fire protection, for use in aviation, space technology and underwater work, for use for medical purposes and in microbiology, the safety requirements for which are established by the relevant legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation and technical regulations.
2. PPE issued to employees must correspond to their gender, height, size, as well as the nature and conditions of the work they perform (clause 12 of the Rules).
3. According to GOST 12.4.011-89, PPE must:
— ensure the prevention or reduction of hazardous and harmful production factors;
— meet the requirements of technical aesthetics and ergonomics;
— be assessed based on protective, physiological, hygienic and operational indicators;
— comply with GOST 12.4.115-82 <1> and labeling standards for specific types of personal protective equipment;
- have instructions indicating the purpose and service life of the product, rules for its operation and storage.
———————————
<1> “System of occupational safety standards. Personal protective equipment for workers. General requirements for labeling”, approved. Decree of the State Standard of the USSR dated June 28, 1982 N 2559.
PPE should not:
— be a source of dangerous and harmful production factors;
- change their properties during washing, dry cleaning and disinfection.
4. The Regulations establish the necessary requirements that ensure mechanical, thermal, biological, chemical, electrical and radiation safety when handling PPE and depend on their class. In this case, security means:
— absence of unacceptable effects on humans caused by the use of personal protective equipment, including exposure to the materials from which they are made;
— ensuring human safety when exposed to harmful (dangerous) factors during the operation of personal protective equipment;
— absence of unacceptable impact on the environment.
Clause 8 of the Regulations establishes both general requirements for personal protective equipment and special requirements for each type of personal protective equipment. The general requirements are, in particular, the following:
— components (materials) of personal protective equipment in contact with the user’s body should not have protrusions that could cause skin irritation or injury;
— personal protective equipment should not release substances in quantities harmful to human health;
— personal protective equipment and their components, components (materials) must comply with sanitary-chemical, organoleptic and toxicological-hygienic indicators.
Washing and neutralizing agents
Order N 1122n, in addition to the Standard Standards for the issuance, use and organization of storage of flushing and (or) neutralizing agents, approved the Occupational Safety Standard “Providing workers with flushing and (or) neutralizing agents” (hereinafter referred to as the Standard), which also applies to employers - legal entities and individuals regardless of their organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership.
The purchase of flushing and (or) neutralizing agents (hereinafter referred to as flushing agents), like all other PPE, is carried out at the expense of the employer. These funds are divided into:
- protective;
- cleansing;
- restorative, regenerating effect.
Rinsing agents must also comply with state regulatory requirements and be confirmed by a declaration of conformity and (or) a certificate of conformity, issued in the Procedure established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 07.07.1999 N 766 <2>.
———————————
<2> “On approval of the List of products subject to declaration of conformity, the Procedure for accepting a declaration of conformity and its registration.”
The Standard names flushing agents dispensed when performing certain types of work. For example:
— persons engaged in outdoor and other work associated with exposure to ultraviolet radiation in ranges A, B, C, high and low temperatures, wind, etc., should be provided with means to protect the skin from the negative influence of the environment (creams, gels, emulsions, etc.) etc.);
— persons employed in industries with increased requirements for the sterility of workers’ hands, when working with bacterially hazardous environments, as well as when the workplace is located remote from stationary sanitary facilities, should be provided with means to protect against bacteriological harmful factors that have an antibacterial effect, etc. d.
Note. The purchase of flushing and (or) neutralizing agents that do not have a declaration of conformity and (or) a certificate of conformity or that have a declaration of conformity and (or) a certificate of conformity that has expired is not permitted.
The procedure for issuing and using PPE
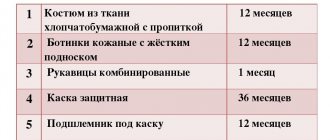
First of all, let’s clarify which categories of workers should be issued PPE. First of all, these are employees of those professions and positions that are listed in the standard issuance standards. In addition to the names of professions and positions, the issuance standards indicate the number of PPE issued and the period of their use. For example, according to the Standard Standards approved by Order No. 477, a worker in the bricklayer profession is required to be issued for a year 1 signal suit, 1 pair of leather boots, 1 pair of leather boots, 1 pair of rubber boots, 12 pairs of mittens, 12 pairs of gloves and goggles.
Note! The names of professions and positions in the Model Standards are indicated in accordance with the unified qualification directories of professions and positions, therefore the names of professions and positions in the organization's staffing table must correspond to the names given in the directories.
In addition, according to clause 5 of the Rules, PPE is issued to employees whose jobs have been certified for working conditions in the Order established by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 26, 2011 N 342n <3> (hereinafter referred to as the Certification Procedure). During the certification process, the provision of workers with personal protective equipment is assessed by checking:
— compliance of the protective equipment actually issued to the organization’s employees with the standard standards for free issuance;
— availability of certificates (declarations) of compliance with personal protective equipment;
— the procedure established by the Rules for providing workers with PPE.
———————————
<3> “On approval of the Procedure for certification of workplaces based on working conditions.”
If all the specified requirements are met, the workplace is considered to comply with the requirements for providing workers with PPE. If at least one is violated, it does not comply with such requirements. If necessary, the certification commission prepares proposals to make changes and (or) additions to the employment contract regarding the employer’s obligations to provide the employee with PPE (clause 12 of the Certification Procedure).
It may happen that the position title of a person employed in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, according to the staffing table, does not coincide with the position title according to standard standards. In this case, the employer needs to either bring the name of the position (profession) in accordance with the standard standards (by making changes to the staffing table and the employment contract), or apply the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and clause 6 of the Rules and, taking into account the opinion of the trade union, independently establish standards for the free issuance of PPE to workers in hazardous and (or) harmful working conditions. But even in this case, the working conditions of these workers must be recognized as dangerous, harmful and (or) associated with pollution as a result of certification.
Note! Based on the certification results, independently established standards for the free issuance of PPE are approved by the employer’s local regulations, and can also be included in a collective and (or) employment agreement (clause 6 of the Rules).
But even if the employer does not independently establish issuance standards, but is guided by standard standards, we still recommend approving a local regulatory act on the issuance and use of PPE by employees and reflect in it the categories of employees who are entitled to protective equipment, frequency (once a year, a month, etc.) ...) and the procedure for their issuance, storage, responsibility of employees for damage and loss, etc.
Clause 9 of the Rules establishes the employer’s obligation to inform the employee about the funds due to him and, against signature, familiarize him with the Rules, as well as standard standards for issuing PPE corresponding to his profession and position. If the organization has approved a local regulatory act, the employee should be familiarized with it when concluding an employment contract or when transferring to another position, if the previous position did not provide for the issuance of PPE.
The rules also require instructing workers on the rules for using PPE, the simplest ways to check their functionality and serviceability, as well as training on their use. As a rule, such briefings are carried out during initial and repeated briefings on labor protection. When instructing on the rules for using PPE, the instructions for use provided by the manufacturer are used.
According to the Rules, the employer is obliged to organize proper accounting and control of the issuance of PPE to employees within the established time frame. Issuance is carried out, as a rule, by a financially responsible employee: supply manager, storekeeper, occupational safety engineer, etc. Receipt of PPE by an employee is confirmed by his signature on a personal record card for their issuance, the form of which is given in the Appendix to the Rules.
If the employer does not have protective equipment suitable for the employee, the Rules provide for the opportunity to replace the type of PPE provided for by the standard standards with a similar one. Replacement is carried out taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization or another representative body authorized by the employees.
Note! According to the Standard, the replacement of certain flushing agents is not allowed. Thus, it is impossible to replace soap or liquid detergents with agents aggressive to the skin (solvents, abrasive substances), and in work involving stubborn stains, it is not allowed to replace cleansing agents (creams, gels and pastes) issued in addition to solid detergents. or liquid washing soap (items 20, 21).
As already mentioned, PPE is purchased at the expense of the employer, but the Rules provide for the possibility of renting PPE. In this case, the employee is assigned an individual kit, on which the appropriate marking is applied.
Accounting for protective equipment is carried out using software (information and analytical databases). In this case, the electronic form of the registration card must correspond to the established form of the personal registration card for the issuance of PPE. In the electronic form, instead of the employee’s personal signature, the number and date of the accounting document on the receipt of PPE, which bears the employee’s personal signature, is indicated.
For your information. To perform certain work, under the responsibility of heads of structural units, employees may be issued with general use PPE on duty, which is assigned to certain workplaces and transferred from one shift to another (clause 20 of the Rules). Also, protective equipment is issued for the duration of vocational training, retraining, industrial practice, industrial training or implementation of control (supervision) measures (clause 18 of the Rules).
The period for using PPE, if it is not determined by the Rules or standard standards, is established by an official authorized by the employer or the labor protection commission of the organization. These deadlines are recorded in personal cards for recording the issuance of PPE. Thus, clause 21 of the Rules establishes that products intended for use in special temperature conditions caused by annual seasonal temperature changes are issued to employees at the beginning of the corresponding period of the year, and at its end are handed over to the employer for organized storage until the next season. In this case, the time for using the specified PPE is set by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization or other representative body of workers and taking into account local climatic conditions.
Note. The period of use of flushing and (or) neutralizing agents should not exceed the expiration dates specified by the manufacturer. Moreover, if the product remains unused after the expiration of the reporting period (one month) before the expiration date, it can be used in the next month (clause 6 of the Standard).
The period for using PPE is calculated from the date of actual issue to employees.
The employer ensures the mandatory use of PPE by employees and must not allow them to perform work without duly issued PPE or with faulty, unrepaired or contaminated ones.
Upon expiration of the wearing period or dismissal of the employee, personal protective equipment is handed over to the employer, which is also recorded in the personal record card. Returned, but suitable for further use, PPE is used for its intended purpose after carrying out certain measures: washing, cleaning, disinfection, degassing, decontamination, dust removal, decontamination and repair. The suitability of the specified PPE for further use, the need for and the composition of measures to care for them, as well as the percentage of wear are established by an official authorized by the employer or the labor protection commission of the organization. When re-issuing PPE, a note “used” is made on the personal accounting card and the percentage of wear is entered.
If PPE is lost or damaged in the designated storage areas for reasons beyond the control of employees, the employer must provide them with other serviceable PPE. In addition, he is obliged to replace or repair PPE that has become unusable before the end of the wearing period for reasons beyond the employee’s control.
If the PPE was lost in violation of clause 27 of the Rules, that is, taken outside the territory, material damage can be recovered from the employee. In this case, the employer is obliged to conduct an inspection to establish the amount of damage caused and the reasons for its occurrence, and also request a written explanation from the employee. If the employee refuses to give an explanation or evades it, a corresponding act is drawn up (Article 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Storage and care
The rules provide for the employer’s obligation to organize measures for the storage and care of PPE. In this regard, he must:
— provide specially equipped premises in accordance with the requirements of building codes and regulations for storing PPE issued to employees;
- promptly, at the expense of the institution, carry out dry cleaning, washing, degassing, decontamination, disinfection, neutralization, dust removal, drying of personal protective equipment, as well as their repair and replacement. In this case, the employer has the right to issue employees with two sets of appropriate PPE with double the wearing period.
If the employer does not have the technical capabilities to provide care for PPE, then this work is performed by a third-party organization under a civil contract.
The organization (in workshops, on sites) should install dryers for special clothing and special footwear, chambers for dust removal of special clothing and installations for degassing, decontamination and neutralization of personal protective equipment, when required by production conditions.
The employer ensures, in accordance with the time frames established in national standards, testing and checking the serviceability of PPE, as well as timely replacement of parts of PPE with reduced protective properties. After checking the serviceability of the PPE, a mark (stamp, stamp) is placed on the timing of the next test.
In conclusion, we note that the employer is responsible for the timely and full issuance of PPE that has been duly certified or declared conformity to standard standards to employees, for organizing control over the correct use of it by employees, as well as for the storage and care of PPE.
If violations are detected by regulatory authorities (GIT), the employer may be held administratively liable under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, according to which violation of labor and labor protection legislation entails the imposition of an administrative fine on:
- officials - in the amount of 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 1000 to 5000 rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
— legal entities — from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
An official who has previously been subjected to administrative punishment for a similar administrative offense may be disqualified for a period of one to three years.
And for violation of labor safety rules, as a result of which harm was caused to the life and health of an employee, criminal liability is provided for under Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation - punishment from a fine of up to 200,000 rubles. to imprisonment for a term of up to one year.
In addition, in case of failure to provide a person engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, with special temperature conditions or associated with pollution, PPE in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the employee has the right to refuse to perform labor duties, and the employer does not have the right to demand their execution and is obliged to pay for downtime arising for this reason (clause 11 of the Rules).
L. V. Kurevina
Journal expert
"Human Resources Department
commercial organization"
Signed for seal
29.03.2012
How to purchase PPE?
The question seems to be quite simple, but it is not so. Unfortunately, most often, the employer adheres to the principles of “as cheap as possible” and “as long as it’s there, in case of an audit.” This approach is extremely undesirable, because it will result in a fine. Accordingly, you will have to pay twice. The first time was for incorrectly selected PPE that did not meet all the necessary requirements, and the second time the costs were directly related to penalties. To avoid this, you must adhere to the following rules:
Rule 1. PPE must protect against precisely those harmful and dangerous factors that affect employees.
If the standard regulations specify a respirator, you do not need to buy the cheapest or the most expensive. First of all, it is necessary to identify the harmful factor. In the event that an employee is exposed to dust, a dust respirator must be worn. It, in turn, also varies and the filter element must protect against exactly the type of dust that affects the employee. The same applies to respiratory protection against various fumes.
Rule 2. PPE must correspond to the level of exposure to harmful and dangerous factors
All standard standards specify the required protection class. Accordingly, PPE issued to employees should in no case be lower than that prescribed. Issuance is permitted only in accordance with the law or higher. However, issuing PPE of a higher protection class is not always justified from the point of view of feasibility and economics. Thus, the correct selection will not only avoid a fine, but also save money with the correct selection. Most often, the employer purchases the cheapest item, not realizing that it does not meet the requirements for the degree of protection.
Rule 3. All personal protective equipment must be certified and have supporting documents.
According to the law, all personal protective equipment, before going on sale, must undergo a series of technological tests confirming their protective properties. Based on the results of their implementation, a certificate of conformity is issued, and the information is entered into the appropriate register, where all information is publicly available. Accordingly, before purchasing the necessary PPE, you must request a certificate of conformity from the supplier, which he is obliged to provide. You need to make sure that it has not expired and that the information in the registry matches what the supplier gave you.
The legislative framework
The law provides for differences in special protective equipment for workers in different professions. In addition to the Model Rules that are common to all, work with protective equipment is regulated by other documents. Thus, the provision of warm overalls and footwear to personnel in climatic regions not specified in the TN is provided for by Decree of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 70, and special signal clothing - by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 297.
The legislative framework
Additionally, there are more than 70 acts on industry standards, adapted to the specifics of specific areas of activity and approved by the relevant ministries and departments. As an example, we can consider TN for oil industry workers. Specific PPE is allocated to them in accordance with orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 970n, Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 1110n. For employees of OJSC Gazprom, Order No. 43n of the Ministry of Labor applies.
The availability, issuance of PPE and accounting for PPE do not relate to the purposes for which the enterprise was created. But this process, properly organized, allows employees to effectively perform their job duties and is an important part of protecting their health and life.
In what quantity should I purchase PPE?
The standard standards indicate the number of PPE issued per year per employee. However, it should be understood that these figures are very approximate. It is necessary to start first of all from real indicators.
The degree of wear and loss of protective properties is influenced by a huge number of factors, ranging from the quality of the PPE itself to weather conditions, which can significantly shorten its service life. Therefore, the best option would be to first purchase a small amount of PPE from different manufacturers, or different models of the same item. Next, monitor the degree of wear and tear in specific working conditions, and based on this, choose the best option for yourself.
For example, loaders use cotton gloves with dotted PVC coating in their work. This option is very cheap, but not very durable. If you use latex-coated gloves, which are more expensive, the service life of the gloves will be longer, since the wear resistance of such gloves is much higher. However, you can understand which option is more profitable only in practice, in real “field conditions”.
Please also note that there is PPE on duty. They are issued to employees only for the duration of the work for which they are intended. For example, raincoats that are not used constantly, or insulating gloves and a mat that are worn while electrical repairs are being carried out. Such PPE is used by different employees and is assigned to jobs, not to specific people. They are used “until wear” - that is, the actual loss of protective properties.
In addition, some PPE has an expiration date. Often, to reduce purchase costs, employers practice wholesale purchasing and store them in warehouses, forgetting about this factor. As a result, issuing PPE with an expired expiration date leads to the imposition of penalties.
Employer's responsibility for supplying PPE
All employees are provided with personal protective equipment if production involves difficult or hazardous conditions. Russia assigns control over compliance by employers (legal entities and individuals) with these Rules in accordance with Articles 353 and 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments, as well as trade unions, their associations and they are under the supervision of technical labor inspectors and authorized persons for labor protection. Failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment can result in big troubles and penalties for the head of the company from regulatory authorities. The amount of the fine in case of failure to provide an employee with PPE will be:
| Primary disorders | Repeated violations | ||||
| For officials | For individual entrepreneurs | For legal entities | For officials | For individual entrepreneurs | For legal entities |
| From 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. | From 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. | From 130,000 to 150,000 rubles. (Part 4 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) | From 30,000 to 40,000 rubles. or disqualification from 1 to 3 years | From 30,000 to 40,000 rubles. or suspension of activities for up to 90 days | From 100,000 to 200,000 rubles. or suspension of activities for up to 90 days |
How and where to store PPE?
Before purchasing PPE, you must take care of the premises for their placement. It must meet the storage requirements recommended by the manufacturer (humidity, air temperature, etc.).
After all, if for such types of PPE, such as, for example, a helmet, which is practically not exposed to external factors, this point does not play a big role, then with mounting belts the situation is completely different. Their fabric base, if storage conditions are violated, can reduce or completely lose its protective properties, which in turn can lead to disastrous consequences.
In this case, you will be the culprit, since you did not ensure proper storage of PPE.
On the procedure for providing PPE
How is special clothing, safety footwear, PPE and RPE properly provided at enterprises? The support strategy is developed in a regulatory act, and the requirements of the Labor Safety Rules must be taken into account.
Recommended provisioning algorithm:
- A standard is being developed to describe the sequence of receipt and issuance of PPE. This document must be familiarized with farm managers, storekeepers, occupational safety specialists, as well as economists in supply departments. This document must set out a clear sequence of providing workers with special clothing and other protective equipment.
- It is necessary to fill out an application for the purchase of PPE and workwear for a year. Applications are collected from all departments of the enterprise, and then summarized into a document, on the basis of which the required amount of funds for the purchase is calculated. This will make financial planning easier.
- Next comes the purchase of special clothing and PPE directly for workers. When purchasing, you should take into account that all purchased products must comply with government requirements and standards.
- After purchase, it is necessary that the purchased product undergoes incoming inspection so that it truly meets quality requirements. Plus, a representative of the supply department must request a certificate for workwear, which must indicate GOST in accordance with the SOUT map.
- Direct issuance of workwear and PPE is carried out in the departments where employees work. In this case, the issuance is carried out against a signature on the personal clothing issuance card.
What should employees know?
Before issuing, you must familiarize employees with the list of PPE they are required to wear and familiarize them with the rules for their use. Including, bring to their attention that the use of PPE is mandatory. This employee obligation is enshrined in Article No. 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Please note that providing for employees is the responsibility of the employer. You are not entitled to make any deductions for PPE issued to employees.
Thus, you need to create an internal order that will specify the standards for issuing PPE for each profession in your organization. Next, prepare a statement of familiarization with this order. In it, the employee, after you provide instructions on the rules for using the specified PPE, the simplest ways to check their functionality and serviceability, and also familiarize yourself with the standards for issuing, puts his signature and writes “I am familiar with the standards for issuing PPE and the rules for their use.”
The order and the statement of familiarization with it are made in free form. The main requirement is to communicate the norms, requirements and rules to the employee, followed by recording this event through his personal signature.
Responsibilities of the employer to provide collective and individual protective equipment to employees
In accordance with Art.
221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide workers of his organization with special clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE) if they have to work in difficult or health-threatening conditions. Allowing employees to enter the workplace without the necessary protection or with faulty PPE is strictly prohibited. Let's look at how legislation regulates the provision of workers with protective equipment. In Art. 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides an interpretation of the concept of “personal protective equipment”. These are special clothing and equipment used to protect against pollution, as well as to prevent or reduce the impact of harmful and dangerous production factors on the worker’s body. Such means include special clothing, safety shoes, etc., as well as flushing and neutralizing agents. The employer is obliged to ensure that employees are informed about the protection they are entitled to at the stage of concluding an employment contract. At the same time, the employee becomes familiar with the rules for the provision and use of PPE, as well as with the standard standards for issuing them corresponding to his profession and position.
Responsibility for providing personal protective equipment at the enterprise lies entirely with the employer. When purchasing workwear, the employer must check the availability of certificates and declarations of conformity confirming its safety. The issuance and use of funds that do not have the appropriate documents is not permitted. In addition to the above, the employer is responsible for the care and timely repair of personal protective equipment. These procedures include:
- cleaning;
- degassing;
- deactivation;
- disinfection;
- dust removal;
- neutralization;
- repair.
The employer does not have to provide the care themselves. He has the right to enter into an agreement for the provision of such services with a specialized organization. The employer is also responsible for the quality storage of unused work clothing and equipment; a separate room is allocated for this purpose at the enterprise.
The employer may, taking into account the opinion of the trade union, replace the personal protective equipment specified in state regulations with similar ones that provide equivalent protection from undesirable production factors. Depending on the financial and economic situation and the recommendations of the trade union, our own standard for providing personal protective equipment for workers may be established, improved in comparison with standard protection standards. Or softer standards may be introduced regulating the provision of personal protective equipment; the established procedure according to GOST standards for workwear cannot be reduced, nor can the conditions for their use be tightened.
Management must monitor the provision of personal protective equipment to employees at each workplace, as well as analyze their effectiveness (control in this case is carried out by comparing the actual items issued with the norms for issuance), check compliance with the rules for providing personal protective equipment (the presence of a personal accounting card filled out in the prescribed manner). The assessment of the provision of workers with personal protective equipment is documented using a separate protocol.
Issuance and accounting of personal protective equipment
PPE: the procedure for issuing and accounting is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia N 290n “On approval of Intersectoral Rules for Providing Workers with Special Clothing, Special Footwear and Other Personal Protective Equipment.”
The main document confirming the issue is a personal card for recording the issuance of PPE. It can be filled out both in paper and electronic form.
A journal is also maintained for the issuance of personal protective equipment, which contains lists of workers who have received personal protective equipment.
Issuance procedure
Based on the SOUT protocol and standards, the enterprise determines its own
list of special clothing needs.
A personal card is created for each employee included in such a list. PPE is issued taking into account the gender, height, and size of the employee. They provide protective items, clothing and shoes against signature. At the end of the period of use, a write-off note is made. If the card is maintained electronically, then it must still contain a link to the register or document in which the employee personally signed for the workwear received.
One of the latest additions to the rules for the provision of PPE allows for their issuance through vending equipment, automatically.
If the wear period has not expired and the employee quits, it is possible to return it to the warehouse or reimburse the employee for the residual value determined by the wear period of the item. The period of use is calculated from the date of transfer to the employee.
The enterprise, at its own expense, is obliged to take care of personal protective equipment (washing, cleaning, drying, repairs, degassing, disinfection). This norm is contained in Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
To ensure timely care of PPE, it is permissible to issue two sets, increasing their service life to the total.
When hired, an employee must be familiar with the composition and timing of replacement of personal protective equipment for his profession and work schedule.
According to the Rules set out in Order No. 290n dated 06/01/2009, PPE that has passed the mandatory certification procedure is used. If an enterprise expects to receive reimbursement from the Social Insurance Fund for expenses on workwear (Order No. 580n dated December 10, 2012 “On financial support”), the product must be manufactured in Russia and from Russian materials.
For persons visiting areas with harmful (dangerous) working conditions, the employer provides on-duty PPE (for example, when delegations or management visit production shops, “on-duty” gowns and helmets are issued). For workers performing work in related professions on a part-time basis, PPE is issued for each of the professions (for example, a mechanic working part-time as a welder will receive two sets of PPE).
How to use and achieve compensation for employees during the liquidation of an organization is described in detail in our article. What are incentive payments and who is entitled to them? Read more about this in our article. Are you preparing for retirement? Then this material will be useful to you.
Operation of PPE
Some PPE during operation requires periodic testing to ensure that its protective properties are maintained. This primarily includes mounting belts and some modifications of respiratory protection equipment. Such PPE has a technical passport, which contains notes on the results of such checks and the possibility of their further use.
You must monitor this and, in case of wear, carry out the necessary repairs or completely replace the PPE that has become unusable. Failure to comply with these operating requirements can lead to dire consequences.
In addition, PPE may require constant maintenance, depending on the specifics of the work performed (washing, cleaning, disinfection, degassing, decontamination, dust removal, neutralization and repair). All necessary requirements can be found in legislative acts related to the area of activity of your organization.
Basic requirements for the issuance of workwear
Requirements for providing workers with PPE
An employee engaged in labor activity must be provided with all necessary means to protect himself from dangerous and harmful factors. First, you need to understand what factors of the labor process we are talking about:
- harmful factors are factors, when exposed to substances harmful to health (industrial dust, excess gas content in the air and the presence of hazardous substances that a person inhales, electromagnetic radiation, physical overload, etc.);
- dangerous factors are factors in the presence of which a worker may be injured (open moving parts of machine equipment that cannot be protected with a casing due to the conditions of the technical process).
If an employer has any doubts about what kind of workwear and PPE to issue to an employee, then you can always refer to the certification card; this document contains all the details, so that errors are excluded.
But in addition to SOUT, there are requirements at the legislative level:
- The labor legislation states that the employer is obliged to provide the employee with special PPE and RPE clothing in accordance with the standards.
- The standards establish what special clothing is required for a certain category of workers and types of production.
- The requirements of documents developed at the state level can be recorded in local regulations for the enterprise and organization.
Under any circumstances, the requirements of regulations adopted at the legislative level must not be violated.