The Labor Inspectorate ensures that the workplace is safe, that the law is observed, and that workers' rights are not violated. It is the labor inspectorate that is called upon to protect our interests as workers.
The control agency can visit the inspection object of any organizational and legal form at any time of the day. Can request any documentation of the enterprise, explanations from employees and management, and collect information of any kind from the enterprise. The functions of the labor inspectorate are reduced to training enterprise employees in safe methods of performing work: they give lectures, conduct instructions, and maintain reports on the enterprise. If an emergency occurs, representatives of the labor inspectorate must come to the enterprise and find out the reasons for the incident: order an examination, and possibly more than one, interview employees and administration, and establish the damage.
The labor inspectorate is also called upon to prevent dangerous situations: carry out scheduled inspections, assess the safety of workplaces, issue orders in cases of violations, monitor the elimination of problems, remove from work those who do not know the safety rules and do not comply with established standards. Our lawyer, within the framework of protecting the employer from the employee, stands up to protect the business, but at the same time, if the employee asks for help, he protects the rights of workers. We can say that we participate in the dispute from both sides, and see all the flaws and nuances thanks to our diverse experience.
Who is checking
The state monitors compliance by firms and enterprises with laws related to work activities with the help of the Federal Labor Inspectorate and divisions of this organization (GIT).
The state inspector has the right to enter the territory belonging to any organization in order to carry out his duties.
To do this, he needs to provide:
- documents confirming his authority;
- order ordering an inspection.
What should a business manager do?
The manager undertakes to provide employees at the enterprise with working conditions that do not pose danger or harm, a rational regime for changing work activity to rest, and adequate provision of medical services.
In addition, his responsibilities include:
- careful adherence to labor safety standards, which vary depending on the activity being conducted;
- monitoring employee compliance with safety regulations;
- formation of regulations and instructions for maintaining safety in the organization;
- ensuring that everyone in production adheres to sanitary and hygienic standards.
Any organization engaged in any production that employs more than fifty people is required to have a special position of occupational safety specialist or a separate unit performing similar duties. In another situation, these responsibilities fall on the employer himself, a special responsible employee or an invited specialist.
All employees of the enterprise undergo regular specialized training, and in the case of their initial occupation or change from one position to another, they are trained in safety rules. Mandatory assessment of working conditions in production is a whole set of measures that helps to identify potentially harmful or dangerous factors of work activity in a given production.
Documents for labor safety inspection
The labor inspectorate can study and inspect any company or individual entrepreneur.
In this case, first of all, special attention is paid to those legal entities that infringe on the rights of employees, violate legal requirements, and have working conditions that are dangerous to life and health.
Sources of information about the presence of any violations in a company may be employees, the prosecutor's office, other inspection agencies, the police, funds, tax authorities, and printed publications.
However, information received from newspapers cannot be the basis for an unscheduled visit to the company. Such data may serve to include the company in a scheduled audit.
When carrying out inspection activities, inspectors examine the quality of the company's compliance with labor legislation. For any violations of laws, fines may be imposed on officials of the company under study or the entrepreneur.
During the study, the following documents are examined:
- charter and certificate of registration;
- employment contracts (including fixed-term ones) and additions to them (their presence or absence, design features and content);
- collective agreement (its features and correctness of execution);
- work books and their log books, personal cards of employees (availability, correct filling);
- internal labor regulations (the presence in it of a description of the procedure for hiring and dismissing employees, working hours, deadlines for issuing wages, responsibilities of the parties, bonuses, and so on).
These are the main documents that are checked during the enterprise research. In addition to documentation, inspectors examine the correctness of transferring workers from one position to another, the legality of dismissals, wage reductions, vacations, etc.
What does the inspection pay attention to?
There is no specific closed list of documents that the State Tax Inspectorate pays attention to. Specific documentation is determined by the type of activity of the enterprise and the reasons for the inspection.
The inspector may be interested in documents such as:
- documentation relating to the establishment of the organization;
- personnel documentation (inspectors are interested in the correctness of employee registration);
- accounting documentation;
- local legal acts relating to the organization (internal regulations of the enterprise, schedule for recording the time of the work process, and so on);
- documentation directly related to labor protection, etc.
Companies classified as micro-enterprises, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, have the right not to formulate local legal acts. Organizations of this kind enter into an employment contract with the employee, which is developed in accordance with the established documentary form and contains a special section on labor protection.
Types of checks
There are two main types of inspections - scheduled and unscheduled. Planned ones differ in that they are carried out at certain time intervals. For each calendar year, a schedule is generated with a list of organizations to be inspected and the timing of inspection visits. This plan is published on the official page of the State Labor Inspectorate (GIT), and is also re-published on the official page of the Prosecutor General's Office of the Russian Federation.
The company is additionally warned about the scheduled inspection three days before it begins. The notification can be sent in various ways - by mail, fax, e-mail, courier delivery, etc.
During a routine inspection, the inspector is given the right to check a list of special control issues. They may relate to various types of regulations related to labor protection. This is determined by the goals and objectives of a particular inspection and is recorded in the order for its implementation.
From the beginning of spring 2021, the time intervals between scheduled inspections of an organization will depend on the risk category of its activities. For example, organizations whose activities are assigned a high risk group are subject to inspection once every two years, a significant risk group - once every three years, etc. If the risk level is low, scheduled inspections are not carried out at all.
Unscheduled inspections are carried out in situations where:
- there is an order issued by the head of the inspection, which is based on instructions from federal authorities or the request of the prosecutor's office.
- The time has expired to correct violations identified during the previous inspection.
- There is information that the requirements of labor legislation are being neglected in production (workers are not given wages, there is a risk of harm to the health of workers in production, etc.).
- the employee filed a complaint about neglect of his labor rights.
- a request was received from an employee to check the workplace.
Please note that the organization is notified of an unscheduled inspection one day before it begins. In a situation where an inspection of this kind is carried out due to the reasons specified in paragraphs. 3-4 lists, the inspector has the right not to notify the production manager about this. The time intervals between unscheduled inspections are not determined by law.
According to the law, anonymous applications are not considered, and the verification that began on such a request is terminated. Information about existing violations can be received by the inspectorate not only from employees, but also from the media, from other inspection bodies, trade unions, etc.
Training of organization employees
If a company hires a new employee or transfers an employee to another position, then the employer’s responsibility is to organize labor safety training within up to one month. If the employee's break in work lasts more than a year, instruction should also be provided, and the period for training is also one month.
The organization of training is divided into two types: (click to expand)
- next;
- extraordinary.
The next one is held once every three years or more often if this is provided for in the organization. The need for extraordinary training arises when new requirements arise or any changes or additions are made to legislative acts, when purchasing new equipment, mastering new technologies and production processes, etc. Before the training itself, an instruction program is developed, adapted for each profession separately.
What forms of inspections exist?
Both types of checks can be carried out in two forms:
- documentary;
- away
Documentary verification is carried out by the auditor at his workplace. He requests a package of documentation from the company in accordance with the purposes of the audit. The company has 10 days to fulfill this request. All necessary documentation is issued to the inspector in the form of copies certified by the signature of the responsible person and seal, or in electronic form with a certified electronic signature. Please note that the inspector does not have the right to request originals or notarized copies.
If during the inspection process inaccuracies or inconsistencies are identified in the information provided, the inspector has the right to request additional explanations in writing from the enterprise. As in the previous case, the organization has 10 days to fulfill the request.
An on-site inspection is carried out directly where the company, production or office is located in the case when:
- the inspector needs to make sure that the information provided is true;
- it is necessary to assess whether the company's activities meet legal requirements.
Training in safe methods and techniques for performing work
It is determined that the training is carried out under the guidance of an industrial training instructor who has undergone appropriate training in occupational safety as an occupational safety instructor and has extensive practical experience.
For your information
If the training organizer does not have the necessary training and material base, it is allowed to conduct training at existing workplaces.
For blue-collar workers and junior service personnel, if there is insufficient training in the form of instructions for the safe performance of the work assigned to them, training is provided in safe methods and techniques for performing work.
Implementation deadlines
According to the law, a standard inspection cannot last more than 20 days. But for some enterprises, the maximum time frame for conducting on-site inspections has been reduced. These include:
- small businesses - the inspection cannot exceed 50 hours per year;
- microenterprises – 15 hours per year.
In emergency situations (for example, if additional investigation is necessary), these deadlines may be doubled. The period of operation of the organization for which the documentation is checked is no more than three years.
How does the check end?
The information obtained as a result of the inspection is recorded in a special act, which must be signed in two copies: for the inspection and for the head of the enterprise that passed the inspection.
If violations were revealed during the inspection, the inspection has the right to:
- file an appeal to the judicial authorities to liquidate an enterprise where labor laws are violated;
- remove from work specific insufficiently competent employees.
Violation of laws regulating work activities entails administrative liability in accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In a situation where the company's management does not want to agree with the decision made based on the results of the inspection, it can appeal it to a superior manager or in court. The results of an inspection carried out with violations are subject to cancellation.
Testing knowledge on OT
The main and main criterion for the mastery of labor protection requirements by those who have undergone instruction is the successful testing of their knowledge of labor protection requirements. Each briefing is considered successfully completed if the employee has proven that he has mastered the information received. Usually this is done through an oral examination. Only after this the employee can begin to perform work duties.
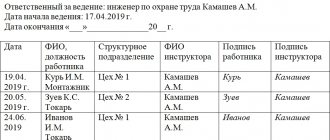
The fact of carrying out occupational safety training is recorded in a special journal indicating the date. The instructor and employee must sign.
All data related to the briefings and testing of occupational safety knowledge must be taken into account during the external audit of occupational safety and health.
If, when checking the State Labor Inspectorate, it is discovered that there are no documents confirming that briefings and inspections were actually carried out, the employer, on the basis of Art. 5.27.1. The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation faces a fine of 15 to 130 thousand rubles.