Who determines the warranty period?
As is clear from paragraph 6 of Article 5 of the current version of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, during the warranty period, a customer who discovers a serious defect in a previously purchased product (for example, spoiling the appearance or affecting the functionality of the device) has the right to demand from the seller (intermediary, manufacturer) ):
- a full refund of the money spent on the product (of course, the product itself must be returned);
- recalculation of the cost of goods taking into account the detected defect and payment of compensation;
- exchange of goods for the same good quality;
- repair of the product at the expense of the seller (manufacturer);
- payment of compensation for repairs already made.
The manufacturer has no right to refuse a buyer who has made such demands during the warranty period; otherwise, the former may go to court.
In general, all products offered on the market can be divided into two large groups:
For goods of the first group, as well as for some products from the second (personal hygiene items, underwear, medicines, dietary supplements, etc.), instead of a warranty period, the manufacturer is obliged to establish an expiration date, after which it becomes unsafe to use the product.
The remaining products from the second group have a warranty period.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Economic Crime Lawyer
- What to do next after you have bought a plot of land?
- Official rating of companies providing bankruptcy support for legal entities
- The bank has demanded full repayment of the loan, what should you do in such a situation?
- ROIS - Customs Register of Intellectual Property Objects
- Electronic trading platforms for bankruptcy
- The theory of consumer behavior suggests that the consumer strives
Guarantee period for roof repairs according to law
Read about the warranty period here.
The length of the warranty period may vary and depends on the nature of the product:
- for motor vehicles the warranty period is from 2 years;
- for household and electrical appliances – from 0.5 years;
- for shoes or clothes – from 1 month;
- for a shared construction project (in accordance with the relevant law) – from 5 years.
In addition, the consumer does not always have the opportunity to exchange/return/repair for free a purchased item with an unexpired shelf life: he will be legally refused if an examination shows that the damage was caused by him or third parties independent of the other party to the transaction.
As follows from the above-mentioned Article 5 of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, the warranty period for any suitable product can be established either by the seller (if the manufacturer has not done so) or by the manufacturer.
The primary right to determine the warranty period remains with the manufacturer; If for some reason you do not use it, the deadline is set by the seller. It is not possible to overlap two warranty periods.
How to extend the service life?
Under different conditions, exactly the same devices can have very different service times. That is, intended use, proper care and timely repairs can significantly increase the actual service life. But with the normative one everything is much more complicated.
Over time, technologies change, new materials and production methods appear. Logic dictates that houses that were built earlier should last less because they used more primitive designs. If this is so, then the standard service life of new buildings should increase over time. In fact, houses built over 100 years ago (such as castles or palaces) still have strong structures. At the same time, modern buildings quickly become unsuitable for use, since builders often skimp on materials, and engineers initially design less durable structures.
From what moment does the period of opportunity to use the product warranty begin to be calculated?
The most important issue regarding the establishment of the warranty period is its duration (duration) and the moment the countdown begins.
The latter varies depending on the coincidence of the following factors:
- In the absence of conditions specifically agreed upon when concluding a purchase and sale transaction - from the moment the item is transferred by the seller to the acquirer;
- If it is impossible to accurately determine the date of purchase, the period is counted from the date of release of the product indicated on the packaging or in the accompanying documentation;
- When purchasing goods through an online store and delivering them by post - from the time the parcel is transferred to the client;
- If the products are delivered and purchased on different days - from the time of delivery;
- If it is impossible to determine the day of delivery, purchase, etc. – from the time of the official conclusion of the purchase and sale agreement;
- If the purchased product will not function without professional assembly or special connection or is known to have a defect that interferes with operation - from the moment the manufacturer (seller) removes these obstacles;
- When purchasing seasonal goods (shoes, clothing, hats) - from the moment of the onset of the corresponding season, officially accepted in a given region of Russia; if the product was purchased during the season for which it is intended - from the moment of purchase (or delivery).
Please note: the above rules also apply to products classified as technically complex and items purchased at sales (despite the seller’s frequent assurances to the contrary).
Particular attention should be paid to the issue of the warranty period for seasonal products. As mentioned above, this period begins to count either from the moment the season formally begins (if you bought the item in advance - for example, winter boots in the summer), or from the moment it is handed over to you (directly from the seller or delivered by post when ordering remotely).
It is impossible to determine exactly what refers to seasonal products, or products for seasonal consumption (Article 19 of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights gives a vague wording: shoes, clothing and “other”).
Therefore, you can draw a conclusion about the seasonal nature of the use of the product based on the instructions attached to it and the general purpose of the product (for example, skis or sleds can most likely be classified as seasonal products). However, it is very likely that you will have to defend the correctness of your conclusions in court.
Since Russia is vast and includes many climatic zones, before purchasing and exchanging goods under warranty, find out exactly when the corresponding season begins in your area. For each region, this point is established by law.
So, for seasonal goods, the warranty period begins:
- from the start of the season - if the item was purchased in advance;
- from the moment the product is transferred to the consumer (from hand to hand, by mail, courier, etc.) - if the product was purchased during the current season.
What is the period of use of the product
According to the Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the service life of a product or the period of use of a product is the time period during which the manufacturer is obliged to:
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
- Provide the consumer with the opportunity to use the object for its intended purpose.
- Bear responsibility for significant defects that arose through his fault.
This is also important to know:
How to get compensation for a flight delay
During this period, the consumer has the right:
- Demand free removal of all defects and maintenance.
- Request compensation for damage if a defect is discovered.
Only the manufacturer can determine the period of use, since it is he who is directly related to the production process.
Units
The manufacturer's liability period is established in units of time and other measurement indicators (kilometers, meters, etc., depending on the purpose).
From what moment can it be calculated
The time period of the manufacturer's obligations is calculated from the date of purchase of the object by the buyer. In cases where the day of purchase cannot be determined, the dates are set from the date of production of the product. The following cases are exceptions:
- The day of purchase does not coincide with the start date of use of the object.
- The time of concluding the contract and the moment of transfer of the goods to the consumer vary. In this case, the time period is calculated from the date of receipt of the product.
- The consumer is not able to use the item for its intended purpose due to the fault of the manufacturer or seller. The liability period is not established until all impeding factors have been eliminated.
- It is not possible to determine the exact date of delivery or installation of the product. In this case, the phase is established from the date of conclusion of the contract between the buyer and seller.
Minimum and maximum
Considering that the law does not define a mandatory warranty period, to resolve controversial issues, the buyer can use a specific GOST for any product or service, indicating the shortest and longest warranty period.
According to the law (Article 19 of the Labor Code) and examples from judicial practice, the consumer has from 14 days to 24 months to make claims regarding the quality of goods or services.
One of the durability indicators is average
Average service life is the mathematical expectation of the service period and one of the indicators of durability.
How is information communicated to the consumer?
Information about the warranty period is indicated in the technical specifications for the products, applied in the form of markings on the packaging and directly on the labels.
If the warranty period is not defined, the consumer has the right to make a claim regarding the quality of the purchased product when deficiencies are discovered within 2 years (clause 1 of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation) from the date of purchase.
Warranty for certain types of goods and services
In construction (in accordance with Articles 724 and 756 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- maximum warranty period – 5 years;
- for an apartment building – 5 years;
- for an individual building – less than 3 years;
- projects – less than 2 years;
- roofing work - from 2 to 10 years.
For a residential building from the developer. According to Federal Law No. 214 of December 30, 2004, the warranty period determined by the developer in an apartment residential building is no more than 5 years from the date of signing the act of transferring the house to another person.
For services. The warranty period is provided for the result of the services, that is, for the material result. There is no guarantee for oral services.
Warranty obligations can be established with the help of the PPA or by agreement of the parties.
By car. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the period for fulfilling warranty obligations is at least 6 months.
Manufacturers determine the warranty period based on service life and mileage (domestic cars - 3 years and 50 thousand, foreign cars - from 2 to 3 years and up to 100 thousand mileage, respectively)
On clothes. Typically, the warranty period for clothing items (dress, blouse, jeans, down jacket) is 30 days from purchase.
Items can actually be exchanged or returned within 15 days, along with the day of purchase.
The warranty period established for workwear is 1 year.
For jewelry. The warranty period is set by the manufacturer, but if the warranty period is less than 2 years, the consumer still has rights in accordance with Art. 18. In addition, there must be a service life of the jewelry, when there is no information on the labels - they mean a period of 10 years.
This is also important to know:
What is the deadline for consideration and response to a claim established by law: refusal to consider a claim, rules for filing a claim
For seasonal goods. The starting point for calculating the warranty time for seasonal products (clothing or footwear, as well as accessories) is considered to be the beginning of the corresponding season, depending on the region of the Russian Federation, taking into account the geographical location and the corresponding climate.
For furniture. The warranty period for furniture is prescribed by the manufacturer in the document for manufactured products.
For wine. Wine belongs to food products; instead of a warranty period, it has an expiration date and a storage period.
What does the warranty end certificate contain?
A document confirming the completion of warranty obligations must contain information about the object or service, the amount of warranty coverage, legal addresses, details and signatures of authorized representatives of the parties.
Products for which no terms are specified in the warranty service agreement
In accordance with the current provisions of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, we can conclude that determining the warranty period is not an obligation, but only the right of the manufacturer (or, if the latter is unwilling, the seller). From this we can conclude that from time to time there is a possibility of purchasing an item for which the warranty period is not established by either one or the other.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
In this case, the period established by the state comes into force - 2 years from the date of manufacture of the goods (in accordance with Article 18 of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights).
Therefore, if you purchase a product without a designated expiration date, do not be upset: you can still exchange it, have it repaired for free, or get your money back before the end of these two years.
You can contact the seller with a written claim even after this period has expired, if you can prove that the defect appeared before the item was completely transferred to you.
Remember: do not delay too much in filing a claim. This will not only save your time (after all, the item cannot be fully used anyway), but will also protect you during the examination (otherwise it may turn out that you yourself were the cause of the final breakdown, and then it will be impossible to get back the money spent).
If the manufacturer flatly refuses to fulfill its obligations, file a claim with the court, which, among other things, will evaluate whether you filed a claim within a reasonable time.
Products (work) may have a service life (or expiration date) and a warranty period. These terms are the terms of responsibility of the seller (manufacturer, performer) to the consumer.
During these periods (and in some cases after all terms have expired), you can make claims to the seller (manufacturer, performer) and demand compensation for losses.
There are lists of goods (works) for which the service life (shelf life) must be established without fail.
If a product (work) does not have a service life (shelf life) or warranty period, then the law stipulates during what period of time you can make claims regarding goods (work) with unspecified periods.
Establishment rules
The responsibility for assigning deadlines for the types described rests with the manufacturer. The following points should be taken into account:
- suitability applies to food products and some other types of products;
- service time is determined for durable goods;
- storage refers to both.
For example, suppliers of sausages and winter shoes must indicate in the technical documentation how long the product will retain its consumer characteristics. But the essence of such work differs. Sausage must be stored under certain conditions: in the refrigerator, with the casing intact. And boots can be stored in a warehouse. But the manufacturer is obliged to use such materials so that the shoes do not become unusable before the date of potential sale.
Suppliers indicate on the packaging container each of the described deadlines, if any are established by law.
Ensuring consumer rights
The legislation allows citizens to make claims for poor-quality goods. It can be addressed:
- manufacturer;
- supplier;
- importer;
- to the implementer.
The legislation provides the following standards for filing a claim:
- during the warranty period;
- before the expiration date indicated on the container;
- within two years from the date of purchase if the warranty is less than this period.
Hint: the countdown starts from the day of purchase. If it is impossible to determine this, then from the date of manufacture.
How to make a claim
A dissatisfied customer can return the product to the store. But this should be done in compliance with all formalities. They are:
- The claim is drawn up in two copies. One is handed over to the seller, on the second the latter puts a mark of acceptance:
- date;
- job title;
- surname and initials;
- signature.
- A purchase receipt is attached to the application. If there is none, then testimony of witnesses is needed.
- Unusable products are returned to the store in the same form in which they were purchased:
- with packaging containers;
- with complete factory seals;
- fully equipped.
- If the seller refuses to accept the application, it can be sent by mail with acknowledgment of receipt.
Obligation of the supplier of unsuitable products:
- carry out quality checks;
- eliminate the defect at your own expense, if possible;
- return funds to the person;
- exchange the product for a new one of appropriate quality;
- compensate for the costs of repairs if they were done by the buyer.
For information: goods that have expired are accepted at retail outlets without problems. Sellers make claims against them to suppliers, and the latter – to manufacturers. Losses are borne only by the manufacturer.
Additional features
The legislator took into account some features of modern trade turnover. They are useful for consumers to know. After all, products are now purchased online. And this leads to a discrepancy between the dates of concluding the purchase and sale agreement and the start of operation of the devices. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 19 of this law, the period is counted in this situation from the moment the citizen receives the product.
This is also important to know:
Resolution No. 55: list of goods that cannot be returned or exchanged when the list is not valid
The same rule applies in the situation of purchasing a product that requires assembly or installation. The guarantee begins from the moment the item is in the person's complete possession. In this case, the latter has the right to make a claim not only to quality, but also to packaging and completeness.
Separately, the legislator indicated the priority of the parties’ agreement. Thus, counterparties can draw up an agreement on calculating the guarantee on their own terms. This must be done in writing in two copies. The parties, subject to their obligations, rely in their relationships on the norms of the contract, not the law.
The expansion of consumer rights is rightly limited by responsibilities. These include collecting evidence of the validity of a claim regarding product quality, if it was received by the manufacturer, two years after the start of use.
Is it necessary to establish a service life?
Establishing the service life of a product (work) is a right, not an obligation, of the manufacturer (performer).
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
Clause 1 of Article 5 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” states: “For a product (work) intended for long-term use, the manufacturer (performer) has the right to set a service life.”
What products must have an expiration date?
The expiration date is established for goods that
- completely consumed when used,
- whose consumer qualities may deteriorate over time,
- may become dangerous over time.
The manufacturer (performer) is obliged to set the expiration date to (clause 4 of article 5 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”):
- Food,
- perfumery and cosmetic products,
- medicines,
- household chemical goods
- and other similar goods (work).
Currently, there is a List of goods that, upon expiration of their shelf life, are considered unsuitable for their intended use, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 16, 1997 N 720.
The sale of goods (performance of work) after the expiration of the established expiration date, as well as goods (performance of work) for which an expiration date should be established, but it is not established, is prohibited (Clause 5 of Article 5 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”) .
Additional questions
Who and on the basis of what laws is responsible for its purpose for durable items and equipment components?
The manufacturer is obliged to establish an acceptable service life for durable goods and components (assemblies, parts, assemblies), which after a certain time become unfit for use for their functional purpose.
The list of this group of products was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 720 of June 16, 1997.
The Contractor has the right to assign service time to durable products (works) that are not included in the list approved by law.
The manufacturer is interested in establishing a liability period for items that are not included in the existing list. Because if the permissible stage of use is not established, then, according to the articles in the law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, the manufacturer is responsible for defects in the objects of sale.
What consumer rights apply if all deadlines have expired?
When the warranty and operational periods expire, the responsibility for the product is removed from the seller and manufacturer. However, if you were harmed as a result of using the product, regardless of whether the deadline has passed or not, this fact is subject to compensation in any case.
So, in accordance with the legislative norms of the Russian Federation, the manufacturer must compensate for damage after the expiration date and period of operation then:
- when the manufacturer should provide a warranty or operational period for a product or service, but it has not been determined;
- when the citizen who made the purchase was not provided with all the information about the operating or warranty period;
- when the citizen who made the purchase of a product or service was not fully aware of the actions that should be taken after the expiration of the operational or warranty period, as well as the possible consequences of failure to take appropriate actions;
- when a product or service, after the expiration of the operational or warranty period, is vitally dangerous to health, or may cause any harm to human health.
For which products is the period of possible use established?
The period of possible use is assigned to durable products. Among them there are 2 main groups:
- Items that become unsuitable for their intended use over time. As a result, such objects become dangerous to the health and life of consumers, and also harm the environment.
- Objects (works) that are not included in the first group.
What to do if the regulatory period has expired
The period during which the building must function is specified during the design. If its service life has expired, it will only be able to perform its original function if it is completely rebuilt.
This is also important to know:
Returning goods of inadequate quality: which goods are considered to be of poor quality, exchange procedure, how to return money
The same approach applies to some other objects. For example, an enterprise has a fleet of specialized cars for transporting various goods. In just 1-2 years, their standard service life will expire, and this is more than 50 thousand units. What can the company do in this case? One option is to write it off. But in this case, you will have to look for a replacement for them, most likely, buy new ones. And this is a huge expense. Perhaps the best option in this case would be to modernize those cars whose service life is coming to an end.
In such cases, you should refer to special technical regulations on the safety of certain objects (railway or road transport, elevators, etc.). It, among other things, lists the conditions under which the service life can be extended. In this case, the regulations say that with the help of modernization, the service life of such cars can be extended by no more than 50% of the original one. A great way to save money, of course, provided that the plant ready to perform such an operation is not very far away.
What can the buyer expect during the expiration date of the product?
The established shelf life for products gives the consumer the opportunity during this period (Clause 1 of Article 18 No. 2300-1):
- If a defect is discovered, contact the seller (manufacturer, importer) and demand that the defect be eliminated;
- receive financial compensation if the consumer independently eliminates the detected defect;
- demand the replacement of a defective product with a similar one of proper quality or a product with distinctive characteristics with recalculation of the cost of the product;
- receive a discount in proportion to the existing defects;
- issue a refund and get back the money spent.
What affects the standard service life of a building?
Of course, how long a particular object should function depends not only on its purpose.
Even at the design stage, many factors are taken into account that will subsequently affect its operational suitability. Simply put, they analyze climatic conditions, terrain features, the possibility of access to structures and elements of engineering systems for their replacement and repair, etc. But whatever the standard established by engineers, the quality of the project largely determines how long the service life will be at the erected building. Errors made during calculations may appear after a few years on an already constructed facility, and then a special operational group will have to correct them with the help of design and construction groups.
The first day from which the life of a building begins to be counted is the date of commissioning, and the last day is the moment it is declared unfit for habitation or work. This could be, for example, a document about the emergency condition of a structure.
If the item requires assembly or special installation
If the consumer is deprived of the opportunity to use the product due to circumstances depending on the seller (in particular, the product requires special installation, connection or assembly, or has defects), the warranty period does not run until the seller eliminates such circumstances.
If the day of delivery, installation (connection) or assembly of the goods cannot be determined, these periods are calculated from the date of conclusion of the purchase and sale agreement (Clause 2 of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”).
When damage is subject to compensation regardless of the time of occurrence
Damage is subject to compensation regardless of the time of occurrence - including after the expiration of the service life (expiration date) - in the following cases (Clause 3 of Article 14 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”):
- if the product (result of work) should have a service life or expiration date established by the manufacturer (performer), but it is not established,
- if the consumer was not provided with complete and reliable information about the service life or expiration date,
- if the consumer to whom the product was sold (work performed) was not informed about the necessary actions upon expiration of the service life or expiration date and the possible consequences of failure to perform these actions,
- if the product (result of work) after its service life or expiration date poses a danger to life and health.
Society for the Protection of Consumer Rights on Social Media:
In the context of legislation on the protection of consumer rights, the term “warranty period” is considered as one of the mechanisms for implementing the seller’s responsibility for the product provided. Moreover, according to the law, establishing a warranty period for a product is a right, and not a direct obligation, of its seller.
Let's look at some of the legal nuances of this concept.
American Eureka
1929, beginning of the Great Depression. The American economy has collapsed, and there is terrible unemployment in the country. People have nothing to buy food with, everything else is an unaffordable luxury. The best economists of that time vied with each other to offer options for overcoming the crisis. In 1932, large real estate dealer Bernard London released a brochure entitled “The End of the Depression through Planned Obsolescence.” The proposal is this: for any product an expiration date is established. Upon completion, it is prohibited to use the item; it must be handed over to a special point and destroyed. In this way, the bourgeoisie was going to kill as many as three birds with one stone: create constant demand for new goods, demand for labor and ensure profit for the capitalists. In his opinion, this was supposed to give impetus to industry, develop the consumer market and provide jobs.
Imperceptibly, technology began to control us, and not we controlled technology
Non-warranty cases under the consumer protection law
- Violation of rules:
- use;
- storage;
- transportation.
- Acts of third parties.
- Force majeure (fire, hurricane, flood).
The legal entity is obliged to prove the presence of these factors after the transfer of the item of sale.
IMPORTANT: the law prohibits conditioning the fulfillment of the buyer’s requirements in a warranty case on conditions that are not related to defects in the product.
Who installs
The PLA establishes that the manufacturer and seller have the right to regulate the warranty period.
IMPORTANT: the manufacturer or representative can enter an additional obligation under which he fulfills the buyer’s requirements even after the warranty expires.
The Civil Code stipulates: if a guarantee is established, then information about the product must contain information about its terms. The law does not specify the minimum duration of this period.
If the seller has set a period of less than 2 years, the buyer can make a claim against him after the warranty expires, but within 2 years. Such an appeal is possible if the buyer proves that the defects arose before the delivery of the item of sale.
Arbitrage practice
After discovering the defect, the buyer filed a claim with the seller to terminate the contract and return the funds. The seller repaired the TV by replacing the component part. But the defect appeared again.
The consumer contacted the organization, which discovered that the speaker's voice coil was defective. At the same time, the examination established that the TV was used correctly, in accordance with the operating rules. After the consumer filed a claim, the court ordered a judicial assessment of the goods, which revealed the same defect.
During the meeting, the defendant (seller) did not present facts to refute the arguments of the plaintiff (consumer). After establishing the circumstances of the case and examining the evidence, the court made a decision to satisfy the plaintiff’s demands:
- Reimburse the cost of insuring the item – 8,000.
- Compensation for moral damage – 3,000.
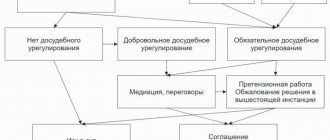
The warranty period is the period during which, if a defect is detected in a product (work), the manufacturer (performer), seller, authorized organization or authorized individual entrepreneur, importer are obliged to satisfy the relevant consumer requirements (Article 5 of the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights).
The establishment of a warranty period plays a special role in the system of means of ensuring the proper quality of goods, works and services.
Legislation
The shelf life of sold items was introduced into the legal field by Federal Law No. 2300-1 of 02/07/1992. Article 19 of the act describes the periods during which the buyer can make claims to the seller of the product. These depend on several factors:
- type of product;
- production difficulties;
- compliance with storage conditions;
- compliance with GOSTs.
Attention: a claim can be addressed to both the manufacturer and the seller of the defective product.
Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992 No. 2300-1 On the protection of consumer rights
Article 19. Time limits for submitting claims by the consumer regarding product defects
Article 16. Requirements for ensuring the quality and safety of new food products, materials and products during their development and launching into production
Storage
The manufacturer is obliged to manufacture the product taking into account the requirements of the law. State standards (GOSTs) are established for each type of product. Compliance with these allows us to guarantee the safe use of the product for a certain period of time. This is recognized as the guaranteed storage period.
However, the item is used by the buyer. That is, the latter has the ability to independently damage the purchased item. The factor is taken into account by law. The warranty does not apply in the following situations:
- violation of storage conditions by a citizen;
- non-compliance with operating rules;
- improper use.
Example. A person purchased butter, for which the supplier guaranteed safe storage for a week. If the buyer left the product next to the heating device for a day, then the claim for spoiled oil will not be accepted. And the decision will be recognized as legal, since the conditions for proper storage of the product were not met.
Fact
Storage refers to the period of compliance of a product with consumer standards, regardless of its intended use.
Suitability
Some types of goods become unusable within a certain period. Suitability is established for these. The specific sales end date is indicated on the packaging. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 16 of Law No. 29-FZ of January 2, 2000, such a mark must be applied to the container:
- food;
- perfumery;
- medicines;
- household chemicals;
- other similar products.
Calculation begins from the moment the product is manufactured. The expiration date indicates that the product can be used for its intended purpose without danger to health or life. After its expiration, sales and use are prohibited.
Important
The law requires manufacturers to inform consumers about the expiration date of the products they sell.
Warranty period
The Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights” requires the manufacturer to take the following measures:
- establishing a specific time for the normal functioning of mechanisms;
- providing the buyer with consistent product quality.
The citizen received the right to demand during the period of the designated guarantee:
- repair of the mechanism by the manufacturer or an authorized enterprise;
- product replacement;
- refund.
The countdown begins from the date of acquisition (conclusion of the purchase and sale agreement). Calculations are made in days, months, years. The period during which quality is guaranteed is indicated in the relevant document (agreement, coupon or other).
The purpose of the guarantee is made with the aim of identifying in the legal field the person responsible for the breakdown.
This is also important to know:
Is it possible to extend the warranty after warranty repairs and how to do this
The law also regulates the time of warranty service. This should be limited to 45 days. However, it is possible to extend the service if it could not be completed within the specified period. But this requires a written agreement between the parties.
Services
Operation of a low-quality product is impossible. However, most of the mechanisms and other products are purchased for long-term use. Therefore, the law imposes an obligation on the manufacturer to ensure that technical parameters are maintained for a certain time. This is called the service period.
The company must do the following:
- produce products of appropriate quality;
- inform the consumer: about the conditions of normal operation;
- about the date after which the product fails or becomes unsafe;
Fact
The manufacturer is responsible for supplying components if the product consists of separate parts. For the latter, periods of normal operation are also established.
Warranty and non-warranty cases
Based on Articles 18 and 29 of the Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights”, the buyer of a product that has been identified as having defects has the right to return the product, exchange for a quality product or refund, or to have a free repair performed. A defect identified during operation of the product can be eliminated under warranty if it was not provided for in the purchase and sale agreement or other conditions.
For example, if a piece of household appliance was purchased with any defect (a scratch on the body or a light bulb that does not light) and the buyer was warned about this and indicated in the accompanying documents, elimination of the defect will no longer be carried out as part of the warranty repair. In turn, non-warranty cases, when the seller does not have the obligation to eliminate defects at his own expense, are considered to be the following cases:
- careless handling (for example, mechanical damage caused by a fall or impact);
- using the product for other purposes than its intended purpose (for example, using household appliances to clean the local area in the country);
- exposure to external factors that are incompatible with the performance of the product in the future (for example, spilling liquid on a laptop or hair dryer);
- improper transportation and storage of goods (for example, transportation of an LCD monitor without fixing and materials that soften impacts on metal parts of the car body).
Turn off and throw away
Manufacturers of household appliances have followed a similar path. It would seem that competition is pushing to make your refrigerator, TV, washing machine, microwave not only the most convenient, but also the longest lasting. Yes, only if the unit will serve for 20 - 40 years, which means that the equipment will be updated once in a generation. Who benefits from this? Only for the consumer. But this is not about him, but about profit. This means we need to make sure that equipment breaks down more often. To do this, it is not necessary to make the entire device of poor quality. All it takes is one part that will quickly fail. Cooling system tubes fly in refrigerators because they are made too thin. Rubber gaskets wear out in washing machines, and plastic drums crack from stress. Heating elements in kettles burn out. The heating temperature regulator in the iron stops working. Microcircuits in TVs fail, which no one will undertake to resolder. Yes, regarding the repair of almost any equipment, the service center will say that it is easier to buy a new one. Because the cost of the work is set so that it is comparable to the purchase price.
“ZiS” became the first Soviet compression-type refrigerator - in them the circulation of the refrigerant occurs forcibly, due to the compressor
Manufacturers always have an excuse: they, they say, reduce the cost of equipment so that it becomes accessible to everyone. The fact that this is not so is clearly seen in the example of washing machines. Just ten years ago they all had a metal drum, and the price depended on the brand and the number of functions. Now all washing machines in the economy segment are equipped with a plastic drum, and it’s not as if they have become much cheaper compared to models from ten years ago. But you have to pay extra for the metal - a car with such a drum doesn’t cost less than 40 thousand.
The first Raketa vacuum cleaner from the Dnepropetrovsk Aggregate Plant was produced in 1956, during the years of space exploration, which is why it received such a name and shape. It roared like a jet engine, but it sucked in any debris. It could be switched to blowing air and used, for example, for whitewashing ceilings