Repeated training on labor protection: frequency
This article contains information about repeated briefings on labor protection: frequency, volume and timing of their implementation, who should and should not undergo them, answers to frequently asked questions about this type of briefing.
Instructions on occupational safety in organizations are carried out to ensure that workers promptly:
— became familiar with the inherent dangers and hazards of specific production processes and workplaces; — have mastered or refreshed their memory of safe work practices and safety requirements; — demonstrated sufficient knowledge of regulatory, operational, technical documentation, quality skills and safe work skills for safe work.
Therefore, re-instruction is an integral part of any production process. Its main goal is to maintain workers’ occupational safety knowledge, skills and safe work habits at a level sufficient to maintain health and performance. The main difference between this type of instruction is the absence of other reasons for conducting it, other than the onset of the deadline established by regulatory documentation.
″ Repeated instructions are carried out at least once every 6 months. This frequency of repeated training on labor protection does not mean that it cannot be carried out more often than once every six months.
At the employer's discretion, repeated instructions for certain categories of workers can be organized, for example, quarterly.
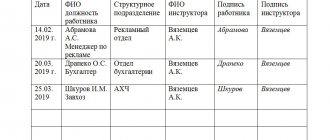
Registration log - sample filling, storage period
Each company manager is required to draw up a report on the training of his employees. For this purpose, a special journal is created in which all data on the training of each employee is entered.
How to fill out the introductory briefing logbook
The logbook is filled out as follows:
- The title page should contain basic information about the company. In the lower right corner is written the start date of the journal, as well as the end date of entering data into it.
- The following pages are filled out in the form of a table. Each table consists of seven columns:
1. Date—the date the employee completed the training is indicated here. 2. Full name of the employee who completed the training. 3. Year of birth. 4. The position of the person undergoing training. 5. Full name of the person responsible for conducting the induction training. 6. Signature of the employee who conducted the training course. 7. Signature of the employee who completed the training course.
A completed log of induction training for employees of an organization must be kept for ten years. After which a new log is filled out.
The introductory briefing registration form can be downloaded here.
For whom should repeated occupational safety training be organized?
Repeated instruction is organized for workers who have undergone initial instruction. Workers who did not undergo it (were exempted from it in accordance with the established procedure) also do not undergo repeated instruction. If working conditions change for a certain category of persons who have not previously received instruction, they must first undergo initial instruction, and after a specified period - again.
All workers must undergo repeated instruction, regardless of their length of service. It can be organized individually or collectively. Collective retraining is possible for workers of the same specialty who perform the same (same type) work.
How does induction training differ from other types?
- Induction briefing, unlike other types of briefings, is carried out by a responsible person appointed by the head of the enterprise.
- All newly hired employees are required to undergo this training, regardless of what knowledge they have.
- All data on the completion of the introductory briefing is recorded in a special logbook.
- Induction training is carried out after the employee is hired for the position.
- During the induction training process, the employee receives the general rules of the work process at the enterprise.
Watch also the video on types of briefings:
Receive the best articles by email every week
Repeated training on labor protection: frequency and content
Repeated instruction is carried out at least once every 6 months. This frequency of repeated training on labor protection does not mean that it cannot be carried out more often than once every six months. At the employer's discretion, repeated instructions for certain categories of workers can be organized, for example, quarterly. Such a decision should be agreed upon with the trade union committee. In this case, the rule “the more the better” does not work. By setting too short a time interval between briefings, the employer risks receiving a formal repeated briefing on labor protection.
If the operating conditions of the organization are such that there is no point in conducting repeated instructions every six months, then, in agreement with the state supervision authorities, the “inter-instruction” period can be increased. In this case, the period for undergoing repeated instruction should not exceed 12 months. This can be done for seasonal work that workers perform in addition to their main duties. For example, if a seller of a small store must clear the porch of snow and ice, repeated instructions on this type of activity can be carried out once a year - at the beginning of winter.
Repeated instruction at the workplace is carried out according to the same program as the initial one. This means that during the repeated briefing on labor protection the following issues should be covered:
— safe working methods; - operations that the worker must perform before starting and finishing work; — features of the design and operation of equipment, instruments, characteristics of materials that are used in the performance of production tasks; — causes of accidents, accidents, accidents that have occurred or may occur in this department, in similar production facilities in other organizations; — working documentation, its requirements, completeness, where you can familiarize yourself with it if necessary; — PPE, other means of protection, fire extinguishing, methods of their use; — safety equipment for devices, machines, mechanisms, tools; — movement patterns around the unit, workplaces, evacuation patterns; — requirements for the maintenance of the workplace: its preparation for the start and completion of work, who and on what grounds can be within its boundaries; - characteristics, features, production factors inherent in specific technological processes, workplaces in which workers will work; — what to do in dangerous situations.
The main tasks that are solved during repeated instruction:
— refresh your knowledge of occupational safety, develop safe work skills, and pay attention to important nuances that may be forgotten; — check the quality of knowledge, skills and abilities, their sufficiency for the safe performance of work; — make notes in the documentation (briefing logs).
Who is exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace?
- familiarization with protective equipment, as well as the procedure and standards for their issuance;
- description of possible accidents and injuries with recommendations on how to avoid them, taking into account the application of the Work Safety Instructions;
- rules of conduct in emergency situations, in particular fires, as well as fire prevention rules;
- training program for providing first aid in the event of an injury to an employee.
Sample program: Induction program Who conducts it and when? In accordance with Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, at every enterprise or institution with a staff of more than 50 people, an occupational safety and health service must be created or a specialist position with similar functions must be introduced.
Who organizes and conducts repeated instruction?
The immediate supervisor prepares and conducts repeated instructions. Before the briefing:
1. An order/instruction is issued, which stipulates the fact of its implementation, appoints responsible persons, and provides a list of professions, positions, and persons who need to be instructed.
2. The instruction program is reviewed, if necessary, the old one is adjusted or a new one is developed.
3. Instruction is carried out: workers are invited, material is read, safe work techniques are demonstrated, knowledge is tested, and entries are made in the journal.
4. If necessary, repeated instructions are provided for workers who did not pass the knowledge test the first time.
5. Instructed workers are sent to carry out their production tasks.
The re-instruction program must correspond to the initial instruction program. Therefore, both of these programs should be adjusted. Changes must be coordinated with the OT service. The re-instruction program is approved by the head of the department or the organization as a whole. At the time of the instruction, the person conducting it must have completed full OT training on all issues covered by the program.
Who can be exempted from instruction?
According to the Labor Code and the Procedure established by Resolution 1/29, employees whose activities are not related to the operation and repair of equipment may be exempt from instruction. In addition, persons employed on the basis of a civil contract are exempt from participating in the event (Article 11 of the Labor Code). However, release is not automatic. An appropriate order must be issued for him.
Before issuing an order, the employer must weigh the pros and cons of this decision. It must be taken into account that it is the company that will be responsible for the risks that arise when an employee operates the equipment. The presence of widespread training will reduce the employer's liability in case of accidents.
Timing and duration of instructing new employees
The employer is required to conduct induction training for a new employee on the day of his actual hiring. This follows from the explanations given by the Ministry of Labor in letter dated 05.05.2017 N 15-2/OOG-1277. At the same time, the candidate for the vacant position is not an employee, so there is no need to instruct him on occupational safety. Employers should also remember that in addition to induction, there is also initial training at the workplace. It must be carried out directly at the employee’s workplace after introductory instructions, but before admission to independent work.
The duration of the event must correspond to the Program approved by the organization, which is developed on the basis of legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, taking into account the specifics of the activity. Typically, the time it takes is from 4 hours to two working days (depending on production volumes).
Appointment of a person responsible for instruction
The law does not specify who should provide training to employees when hiring for a new position. But often such a person is selected from the following areas:
- Civil defense specialist.
- Workplace safety specialist
In any case, a person appointed to such a responsible position is required to understand the following topics: occupational safety, civil defense and first aid. To do this, such a person must undergo training. In addition, the law obliges this specialist to undergo regular checks, such as passing an exam in a special course.
Inspections must be carried out once every five years.
As soon as the head of the organization appoints a responsible person responsible for conducting training for new employees, he will be sent to undergo training at the local emergency department. During the training, the employee will receive a special document giving him the right to conduct induction training at his workplace.
If a person is appointed to such a position for the first time, then during the first year he is required to take advanced training courses.