When is targeted occupational safety training carried out?
In this article we will consider the following questions:
• when it is necessary to conduct targeted training on labor protection; • the procedure for conducting targeted training on labor protection; • how knowledge testing is carried out based on the results of such instruction; • practical issues of organizing targeted briefings on labor protection (sample).
Each of us encountered targeted instruction on labor safety in school or kindergarten. This type of instruction is associated with the characteristics of an activity (not necessarily work), which is not everyday, so its content is always different. Let's figure out when it is held, what its features are and how to organize it correctly.
Where is the mark placed?
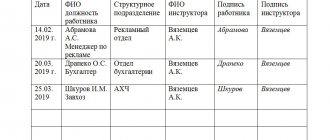
A mark indicating completion of the targeted briefing is placed on the admission order. There is also a briefing log, which states:
- serial number;
- surname and initials of the person being instructed;
- profession or position of the employee;
- the reason for the conduct is indicated;
- in which structural unit it is carried out;
- signatures of the employee and the instructing supervisor.
The briefing log must be registered and recorded in office work.
In what cases is targeted training on labor protection carried out?
Targeted instruction on labor protection is carried out when workers or students have to perform tasks that are not typical for their daily activities. The exception is hazardous types of work that require a permit. They can be carried out regularly. Like other types of instruction, targeted instruction on labor protection is carried out to inform workers about safety rules and teach them to use the acquired safety knowledge in practice.
Cases when targeted training on labor protection is carried out:
— liquidation of consequences of emergency situations: injuries, accidents, disasters, etc.; — public events: excursions, rallies, holidays, competitions; — work for the organization of which work permits, orders, and similar documentation are required; - one-time work: loading and unloading materials or objects, cleaning the area, removing garbage, performing tasks outside the enterprise, other activities that are not performed regularly.
If necessary, even those workers or students who are exempt from regular (initial, repeated) instruction undergo targeted instruction on labor protection. For example, if sales associates of a small store's manufactured goods group are sent to clear ice from the steps with the onset of winter, then targeted instruction will be needed. If this responsibility is assigned to them permanently, instead of targeted instruction, it is necessary to carry out initial and then periodic instruction.
How to apply
Records of employees undergoing training are recorded in the Training Logbook or in a personal card. It is allowed to duplicate information in both documents. The recommended sample form for a personal card and journal is specified in GOST 12.0.004-90 (Appendix 2, 6) . When issuing an admission order, you can put a mark on the form that the admitted persons have completed training.
If necessary,
it is allowed to create a separate journal of targeted briefing. It must contain the following information:
- date of the event;
- information about the employee (full name, year of birth, position);
- type of work;
- information about the person instructing (full name, position);
- signatures of the instructor and the instructee.
The log sheets must be numbered, stitched, and the document must be sealed and signed by the head of the structural unit and the head of the organization. Shelf life – 10 years .
The procedure for conducting targeted training on labor protection
The procedure for conducting targeted instruction on labor protection is prescribed in the “Regulations on occupational safety training” of the institution, company, occupational safety instructions covering this topic, and in other local regulations. They outline the range of professions and positions of workers who must provide targeted instruction. Persons responsible for conducting targeted occupational safety training are appointed by management on a case-by-case basis. If the types of activities that require targeted instruction are known in advance (for example, class teachers will take children on excursions, hikes, to performances), an order to appoint responsible persons can be issued in advance (for example, at the beginning of the school year). At the time of the briefing, each instructor must be trained in the topics he will teach and have a valid certificate.
Targeted instruction programs are developed in advance. These include:
∼ provisions of labor safety instructions; ∼ industrial sanitation requirements, safe performance of various works, equipment maintenance, traffic regulations, etc.
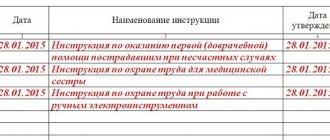
Samples of targeted briefings on labor protection, which are classified as typical for the organization or have already been read, are stored:
∼ in the OT service; ∼ from the persons who will provide instructions.
The procedure for storing samples of targeted instructions on labor protection, issuing them, adding new topics and revising them is determined by the employer.
The procedure for conducting targeted training on labor protection allows documenting its results in two ways:
∼ in the briefing log; ∼ in a document that allows work to begin and be carried out. In this case, there is no need to duplicate the journal entry.
If targeted instruction takes place in an educational institution, you can make entries about it in the classroom/extracurricular work logs. If the company maintains personal occupational safety training cards, the completion of targeted instruction by workers must be registered in them too.
Targeted training program
Since targeted instruction is caused by certain circumstances, its content is determined based on them. As a rule, in any case, employees should be familiarized with safe ways to perform their assigned duties. But what exactly these methods and specific labor functions will be depends on the purpose of the specific instruction. For example, if we are talking about work related to the elimination of post-fire consequences, workers must learn how to deal with fires that have not been completely extinguished, etc. When presenting, you will need specific examples of correct actions.
NOTE! It is advisable to have an internal document at the company, which will highlight the main issues that will certainly be included in the briefing, dedicated to the most common situations that theoretically can occur in this organization. It is better to approve this internal normative act by order of the manager.
The target briefing program is based on:
- labor protection instructions for certain types of work;
- sections of the above instructions related to safety requirements during emergency work;
- instructions on actions that are permissible to perform only with a permit;
- training programs for excursions and other public events.
After informing, the instructor must check the degree of assimilation of the material received by the employees. This is usually done in the form of a survey. The use of technical means is also permitted if time and situation permit. In some cases, practical testing of acquired skills is required.
If it turns out that the information is not sufficiently understood, such an employee does not have the right to start work for which he has unsatisfactorily mastered the instructions (clause 7.8 of GOST 12.0.004-90). Perhaps a repeat course will be needed - but next time.
Testing knowledge based on the results of targeted instruction
After targeted instruction on labor protection, a knowledge test is carried out. The legislation does not provide for a uniform procedure for carrying out this procedure that is acceptable for all categories of workers and students, therefore the instructor should be guided by the requirements of local regulations or organize it at his own discretion. The knowledge test can be carried out in the form of an oral survey, require demonstration of practical skills, or conduct a test.
People who fail the knowledge test must take the instruction again. When targeted training on labor protection is carried out before high-risk work, workers who have demonstrated unsatisfactory knowledge results should not be allowed to perform this work.
Normative base
The procedure for carrying out targeted instruction is regulated by the following legal documents:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29 “On approval of the procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations” (hereinafter referred to as the “Training Procedure”).
- GOST 12.0.004-2015. Interstate standard. System of occupational safety standards. “Organization of occupational safety training. General provisions" (put into effect by Order of Rosstandart dated 06/09/2016 N 600-st)
Sample questions to cover during targeted coaching
When conducting targeted training on labor protection, it is necessary to cover the following points:
— inventory: a list of necessary tools, requirements for them, the procedure for preparing them for work, methods for their safe use, putting them in order after completion of work; — a list of necessary clothing, shoes, PPE; — preparing the workplace for the start of work, its suspension (for lunch, if you need to leave) and completion; — the procedure for performing collective work, the area of responsibility of each group member, a safe sequence of actions; — techniques for performing work safely (procedure for lifting and carrying heavy objects, correct slinging patterns, etc.), handling equipment, materials, inventory; — what to do in emergency situations, how to understand that the situation is abnormal.
The duration of targeted instruction is not regulated.
About the work permit
If an employee needs to be sent to perform hazardous work, then a permit must be filled out. This document is issued once and is closed after the work is completed in full.
The organization must approve a list of works, on the basis of which instructions should be carried out.
The permit specifies:
- Instructions required for carrying out.
- Date and time of start and end of work.
- Safety highlights.
- Surnames of the person being instructed and the person instructing.
The accounting of work orders is carried out at the enterprise by the person responsible for labor protection.
Training course program
The educational material plan is formed by a specialized commission, which approves the final list of disciplines covered:
- Safety requirements for overalls and design features of the equipment used.
- Principles of operation of automatic devices, their dangerous zones.
- Practicing interaction between groups of workers on an individual basis.
- Compliance with precautions when performing assigned tasks, a set of measures in emergency situations.
- Suspension, shutdown, care and cleaning of the workplace, basic provisions on the logistics of the tools used.
It is important to know! The list of disciplines given above varies according to the specification of the production facility. The training program corresponds to the characteristic features of the technological process.
When executed
Targeted communication should be carried out if it is necessary to train or familiarize employees with all types of dangerous and risky cases and situations that may occur while carrying out the assigned task. These tasks are not the primary activity of the represented employees and are not part of their qualifications. The presented type of familiarization and knowledge testing is carried out by the direct superior. It should be performed in the following cases:
- if there is an emergency response or if it is necessary to perform work that requires official registration of a work permit;
- if there is an excursion on the territory of the enterprise;
- when all kinds of public events are organized with the participation of students. This could be sports competitions or hiking;
- if the employee has to perform tasks that are not related to his immediate specialization. For example, cleaning the area, working with cargo.
Unscheduled special assessment of working conditions: in what cases is it carried out?
Completion of targeted instruction is noted in a special document, which indicates permission to perform atypical tasks.
Such familiarization can be carried out with one employee or an entire team. The content and amount of data provided depends on the type of tasks that the staff will have to face. Targeted training is most common in the energy industries.
Note! Training takes place on the job and ends with passing an exam in any form. Those employees who have not passed the exam cannot be allowed to perform practical training or perform assigned tasks. Repeated training is organized for them.
Periodicity
Labor protection establishes that this type of information must be carried out only in cases where unscheduled events, tasks or work are to be carried out. When this is not planned, then targeted instruction is not necessary. It will only be required if the necessary work is repeated.