Subtleties of labor relations with the head of the company
Legal entities (organizations), essentially, without people, are just an entry in the register. It is no coincidence that the legislator in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) established that legal entities acquire civil rights and assume civil responsibilities through their bodies acting in accordance with the law, other legal acts and the constituent document (clause 1 of article 53 Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Such bodies include collective and individual management structures that make decisions on the fate of the organization. These may be boards of directors, supervisory boards, boards, general meetings of participants (shareholders), etc. It is through them that the legal entity operates.
One of the key bodies is the head of the organization - the sole executive body
(see, for example, paragraph 3 of Article 65.3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). As a rule, it is he who is entrusted with the functions of interaction between the organization and the outside world. Sole executive body:
- carries out current management of the organization’s activities, incl. in the field of personnel management, in labor and related legal relations;
- makes personnel decisions on behalf of the employer in relation to the organization's employees.
At the same time, from the point of view of labor legislation, a manager is just one of the employees, albeit with a special status (Chapter 43 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). A manager is an individual who manages an organization, including performing the functions of its sole executive body (Part 1 of Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employment contract is concluded with him, like with any other employee.
(Articles 274, 275 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) 1.
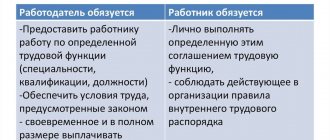
An employment contract, let us recall, is an agreement between an employer and an employee about the latter performing a certain labor function for a fee in the interests, under the management and control of the employer (Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The manager is paid a salary (Articles 15, 56, 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), granted leave (Chapter 19 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), different working hours can be established, he has the right to work part-time (Article 276 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), etc.
So, within the meaning of the above norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the manager enters into labor relations with the organization, like any other citizen-employee, and agrees to personally perform for a fee the labor function of managing the organization (Article 15, 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The only difference, as mentioned above, is its special status, the nuances of which are enshrined in a separate chapter of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, labor legislation also recognizes other workers with a special status, for example part-time workers (Chapter 44) or teaching staff (Chapter 52).
It turns out that an organization as a legal entity and a manager as a sole executive body are not the same thing. They do not coincide in one person, just as a legal entity and its founders (participants) do not coincide. Even if the manager is the only participant in the LLC, the statuses of the manager, founder (participant) and the organization itself will not be identical.
Yes, the director in such a situation will make decisions regarding himself and others on behalf of the LLC, but from the point of view of the law, he seems to be bifurcated, acting separately: both as a founder and as a director.
The employer in relation to the manager is the organization (legal entity). This approach is also reflected in judicial practice: the head of an organization is vested with the rights and responsibilities of an employer only in relations with other employees of the organization and himself acts as an employee in relations with the employing organization 2.
Features of an agreement with a director in a state organization
When applying for a job as a director of a government institution, he, like any employee, must
- obtain a passport, work book and tax identification number. In addition, he must submit: a certificate of his own income and property;
- a similar certificate regarding the income and property of the spouse and minor children.
Certificates are submitted at the time of hiring and are updated annually.
You should know that a contract with the head of a state organization must be concluded according to the standard form from Government Decree No. 329 of April 12, 2013. But an employment agreement with the director of a commercial company can be developed independently - there is no standard form provided.
Commentary to Art. 275 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. Depending on the type of organization, the specifics of the procedure and conditions of the employment contract concluded with the manager can be established centrally (see, for example, Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated March 2, 2005 N 49 “On approval of a model employment contract with the head of a federal state unitary enterprise” / / BNA RF. 2005. N 23) or in accordance with the constituent documents of the organization or agreement of the parties.
2. The conclusion of an employment contract with the head of an organization may be preceded by a competition (see commentary to Article 18 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), election (see commentary to Article 17 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or appointment to a position (see commentary to Article 19 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ) and etc.
Features of the employment contract concluded with the head of the organization
FEATURES OF AN EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT CONCLUDED WITH THE HEAD OF THE ORGANIZATION
E. Dolgova
The legal regulation of relations regarding the labor of executive employees is a certain complexity, mainly due to the fact that such employees simultaneously perform the functions of a representative of the employer in relation to other workers who are in labor relations with the organization. The specifics of regulating the work of the head of an organization, as well as members of the collegial executive body of organizations, are reflected in Chapter 43 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and a number of articles placed in other chapters. Thus, the legislator emphasizes that the head of the organization is an employee with a special status.
The head of an organization is an individual who, in accordance with the law, the constituent documents of a legal entity (organization) and local regulatory legal acts, manages this organization, including performing the functions of its sole executive body (Part 1 of Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Due to the dual legal status of the head of the organization, the employment contract concluded with him is unique and has a number of distinctive qualities.
1. CONCLUSION OF AN EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT The procedure for concluding an employment contract with the head of an organization is regulated in relatively detail and depends on the specific organizational and legal form of the legal entity.
Labor legislation and other regulations containing labor law norms, or the constituent documents of an organization, may establish procedures prior to concluding an employment contract with the head of the organization (holding a competition, election or appointment to a position, etc.).
Thus, the formation of the executive bodies of a joint-stock company is carried out by decision of the general meeting of shareholders, if the company’s charter does not include the resolution of this issue within the competence of the board of directors (supervisory board) of the company.
The director of a limited liability company is elected by the general meeting of participants for a period determined by the company's charter. In this case, the leader may not be elected from among its participants. The company's charter may provide that the formation of executive bodies falls within the competence of the board of directors (supervisory board) of the company.
The above provisions on the procedure for concluding an employment contract with the head of a limited liability company are applicable to the situation of concluding an employment contract with the head of a company with additional liability. The heads of state and municipal unitary enterprises are appointed by the owner of the property of the unitary enterprise. At the same time, on behalf of the Russian Federation or a subject of the Russian Federation, the rights of the owner of the property of a unitary enterprise are exercised by state authorities of the Russian Federation (subject of the Russian Federation), and on behalf of the municipality - by local government bodies. The appointment of heads of unitary enterprises is carried out on a competitive basis. This procedure is two-stage.
The first stage is carried out in the form of tests (written). At the second stage, proposals for the enterprise’s activity program are considered. Relatively recently, a rule has appeared that when hiring the head of an organization, it is mandatory to obtain information about him from a special register - this is due to the fundamental innovation of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (CAO RF) , which introduced a new type of punishment - disqualification.
Particular attention should be paid to Article 14.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which provides for liability in the form of an administrative fine for the implementation by a disqualified person of activities related to the management of a legal entity, for concluding an agreement with a disqualified person for the management of a legal entity (50 minimum wages), as well as the non-application of the consequences of termination of his actions (up to 1 thousand minimum wage).
When concluding an agreement to carry out activities to manage a legal entity, the person authorized to enter into the agreement is obliged to request information about the presence of disqualification of an individual from the body maintaining the register of disqualified persons. The deadline for providing information contained in the register is 5 days from the date the authorized federal body receives the relevant request. Only after receiving this information is it possible to conclude an employment contract.
The specificity of the norms of the institution of employment contracts regulating the work of the organization's managers can be traced in the specifics of the representative office on behalf of the employer. The employment contract with the manager on behalf of the joint-stock company is signed by the chairman of the board of directors (supervisory board) or his authorized person. On behalf of the limited liability company, the agreement is signed by the person who chaired the general meeting of participants at which the director was elected, or by the person authorized by the decision of the general meeting of participants of the company, or in certain cases by the chairman of the board of directors (supervisory board). When concluding an employment contract with the head of a unitary enterprise, the employer acts as the head of the relevant executive body under whose jurisdiction the unitary enterprise is located.
2. CONTENT OF AN EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT Traditionally, the content of an employment contract refers to all its terms that define the rights, duties and responsibilities of its parties. Both the general norms of the Labor Code contained in Section III and the special norms of Chapter 43 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply to the content of an employment contract with the head of an organization.
All terms of an employment contract are usually divided into mandatory and additional.
2.1. MANDATORY CONDITIONS OF AN EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT From the point of view of the general norms of the institution of an employment contract, an employment contract with the head of the organization must contain: Full name of the employee and the name of the employer who entered into the contract;
- information about the employee’s identity documents;
- information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers;
- information about the place and date of conclusion of this agreement, as well as all mandatory conditions of any employment contract (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Listing these conditions might be redundant if not for certain features of their content regarding the agreement concluded with the head of the organization. Like any employment contract, the contract with the manager must contain a condition regarding the place of work. In accordance with the latest edition of the Labor Code, specifying the place of work (indicating the structural unit) is an additional condition of the contract, but given that we are talking about the head of the organization, there is no need to indicate the structural unit, since the manager heads the entire organization as a whole.
When specifying the job function and job title, it is necessary to take into account the requirements of the law and constituent documents. For example, in accordance with Article 40 of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies,” the sole executive and administrative body may be called the general director or president. An inaccurate or arbitrary name for the position of the head of an organization may subsequently create difficulties in determining his status and powers, including in relations with government authorities or other business entities.
The condition on the start date of work is mandatory to the same extent as for any other employee, however, it should be borne in mind that when determining the start date of work, it is necessary to take into account the term or expiration date of the previous manager. Naturally, this is necessary to avoid dual power, as well as to prevent misunderstandings related to the exercise of administrative powers, especially in the financial and economic sphere. In addition, an employment contract with a manager can be concluded for a period established by the constituent documents of the organization or by agreement of the parties (Part 2 of Article 59 and 275 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, the contract contains a condition on the period of its validity, indicating the basis for concluding it on an urgent basis.
The conditions for remuneration of the manager are also distinguished by the originality of their establishment in the employment contract. As a rule, the manager is set an official salary and all kinds of additional payments and allowances, including those of an incentive nature, like all other employees. However, the employment contract may contain conditions for additional material incentives for the head of the organization. For example, an agreement may contain a condition on the participation of the manager in the distribution of part of the profit, establishing remuneration based on the results of the organization’s work for the year as a percentage of net profit. If high economic indicators are achieved, the contract may provide for the manager's right to receive part of the company's shares, etc. Currently, more and more attention is being paid to these issues in employment contracts with managers. In this way, the tasks of both increasing motivation for the most efficient management of property and increasing labor productivity through increasing the level of organization of labor and production are solved.
Remuneration for the work of heads of organizations financed from the federal budget must be made in the manner and amount that must be determined by the Government of the Russian Federation, in organizations financed from the budget of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation - by the state authorities of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, and in organizations financed from the local budget, — local government bodies (Part 1 of Article 145 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The working hours and rest hours of the head of the organization are also determined by the terms of his employment contract. The law prohibits contractually worsening the position of an employee in comparison with current legislation. This prohibition fully applies when determining the relevant section of the employment contract with the head of the organization, however, a number of comments can be made here. Since the manager’s functions include organizing the work of other workers, this requires additional time, including time that goes beyond the normal working hours established by law. In addition, the manager’s working time is difficult (if at all) to be strictly accounted for and regulated. Therefore, the manager’s employment contract, as a rule, provides for the establishment of irregular working hours. It would seem that everything is clear, but Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines an irregular working day as a special regime, according to which an employee, by order of the employer, if necessary, occasionally performs his labor functions outside the established working hours. Naturally, in relation to the work of a manager, there is no need to talk about any order of the employer and illusory episodicity: the manager not only organizes the work of others, but also organizes his own work, independently and in accordance with the goals and objectives set for him, related to the most efficient work of the entire organization .
Taking into account that the employment contract determines the specifics of the manager’s working hours, it must undoubtedly contain special conditions regarding rest time, namely vacation. The manager's leave consists, as usual, of primary and additional leave. The main annual paid leave can be established by contract for a duration exceeding the usual 28 calendar days (extended main leave). The employer, taking into account its production and financial capabilities, can establish additional annual paid leave for the head of the organization.
In addition, additional leave may be provided for irregular working hours and other special working conditions.
Also, these contracts often contain conditions on the amount of financial assistance allocated to the manager for the main paid leave for rest and treatment (including sanatorium-resort).
Characteristics of working conditions and the nature of work, as a rule, are omitted in the content of the employment contract with the head of the organization, in contrast to employment contracts with other employees. This, of course, is due to the absence of unfavorable production factors directly at the workplace for the manager. As for the costs of psychological and mental stress, they are traditionally compensated by the presence in such an agreement of additional conditions of a material and everyday nature.
The provision of compulsory social insurance is also a mandatory condition of any employment contract.
2.2. ADDITIONAL CONDITIONS OF THE EMPLOYMENT CONTRACT
Additional terms of an employment contract with a manager can be either quite traditional, for example a probationary period, or special, specific only to this type of employment contract.
An employment contract with a manager, like with any other employee, may contain a probationary period clause. However, probation for heads of organizations may be provided for a period of up to six months (Part 5 of Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, a test when hiring cannot be established for persons elected to an elective position for paid work, and for persons applying for work through a competition, therefore it seems that the rules regarding a six-month probationary period for managers of an organization will not find practical application.
The employment contract with the manager includes a condition on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, commercial and official). This condition seems quite justified, since it is the manager, by the nature of his activity, who has unlimited access to any confidential information, the disclosure of which could lead to serious property damage.
An employment contract with the head of an organization must provide for his obligations to ensure the protection of the confidentiality of information owned by the organization and its counterparties, and responsibility for ensuring the protection of its confidentiality (Part 6 of Article 11 of the Federal Law “On Trade Secrets”). The manager's responsibility for disclosing trade secrets is stricter than that of other employees: the manager compensates for losses caused to the organization. In this case, losses are determined in accordance with civil law (Part 7 of Article 11 of the Federal Law “On Trade Secrets”). However, it should be noted that this provision loses force on January 1, 2008 (Article 34 of the Federal Law of December 18, 2006 No. 231-FZ).
In addition to the types of compulsory social insurance common to all employees (pension, medical, etc.), more and more often in the contract with the head of the organization one can also find conditions for additional (optional) insurance, for example, life and health insurance, accident insurance, etc. At the same time An employment contract may provide for insurance not only of the employee himself, but also of his immediate family members.
Formalize labor relations for the founding general director
The norms of Chapter 43 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on the peculiarities of the work of managers do not apply to the head of an LLC, who is its sole founder. Including from the point of view of drawing up a written employment contract. In this situation, according to the Ministry of Finance, it is not needed. Labor relations are formalized by a written order of the founder to assume the labor function of a manager.
Labor function of a manager
The head of the organization is an employee of the organization who, in accordance with the employment contract concluded with him, performs a special labor function (part 1 of article 15, part 2 of article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This labor function consists of exercising management of the organization, including performing the function of its sole executive body (Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) to carry out actions on behalf of the organization to implement its rights and obligations arising from civil, labor, tax and other legal relations. That is, to act without a power of attorney:
- in the scope of the owner’s powers to own, use and dispose of the company’s property;
- in the field of rights of the copyright holder of exclusive rights to the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization equivalent to them;
- in the area of the rights and obligations of the employer in labor relations with other employees of the organization, etc.
Appointment of a manager
The manager is appointed to the position (as well as dismissed), as a rule, by the general meeting of participants (shareholders). In a number of cases, if the issue of appointment or dismissal of a manager (sole executive body) is within the competence of the board of directors, the board of directors.
The founders can appoint a person from among themselves or from outside to fill this position of CEO. The employer in relation to the employee - general director is the organization represented by one of its participants (founders).
First, the corresponding decision (minutes) of the general meeting of participants or the board of directors is drawn up. Then an employment contract, usually a fixed-term one, is signed with the manager.
It includes all the mandatory and additional conditions provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation when drawing up an employment contract - taking into account the peculiarities of the work of managers provided for by Chapter 43 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In an LLC, an employment contract with the manager can be signed by:
- the person presiding over the general meeting of the company's participants at which the manager was elected;
- a member of the company authorized by the decision of such a meeting;
- Chairman of the Board of Directors (Supervisory Board);
- a person authorized by a decision of the board of directors (supervisory board) of the company (Clause 1, Article 40 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ dated 02/08/1998, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 14-FZ).
On behalf of the JSC, the employment contract is signed by the chairman of the board of directors (supervisory board) or a person authorized by this board (clause 3 of article 69 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ).
The validity period of the employment contract with the manager is determined by the constituent documents of the organization or by agreement of the parties (Part 1 of Article 275 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on the decision of the authorized body and the employment contract, the head (or other authorized person from among the participants, board of directors) issues an order to take office.
An entry about the appointment is made in the manager’s work book. Column 4 makes reference to the decision of the general meeting or to the order to take office (letter of Rostrud dated September 22, 2010 No. 2894-6-1). They even issue a personal card for the elected manager, just like for other employees of the company.
If in an LLC the director is the only founder
One person has the right to establish a limited liability company (Article 11 of Law No. 14-FZ). Therefore, he has the right to unilaterally decide who will manage the company. The law does not prohibit him from assigning these responsibilities to himself.
But the norms of Chapter 43 of the Labor Code do not apply to the head of an organization (LLC), who is its sole founder (Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The main feature of this situation is that if the sole owner and manager are the same person, a paper employment contract is not drawn up, since there cannot be the same signature on both sides of the contract. It turns out to be a situation of an agreement “with oneself”. But there are no other owners who could sign it for the employer.
Therefore, in this case we are talking about the assignment of responsibilities, when the only participant in the company, by his own decision, assumes the functions of the sole executive body. This could be a director, general director, president, etc. - as you like.
The absence of a “paper” employment contract does not mean the absence of an employment relationship.
Labor relations take place both on the basis of an employment contract concluded in the prescribed manner, and on the basis of the actual admission of the employee to work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer. This is stated in Article 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Even if there is no employment contract in writing, it is considered concluded from the moment the employee begins to perform his job duties (Part 3 of Article 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The situation with the combination of the sole founder and director of the company in one person was considered by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation. The Determination of 06/05/2009 No. 6362/09 (hereinafter referred to as the Determination) sets out the position according to which labor relations with a person performing the functions of the sole executive body of the company as a general director, as with an employee, are formalized not by an employment contract, but by the decision of a single participant.
This position is confirmed by the courts, which expressed themselves even more bluntly. The labor relations that arise as a result of the appointment of a director to this position are characterized precisely as labor relations on the basis of an employment contract (see the resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated June 10, 2010 in case No. A21-8374/2009, the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated 06.08.2008 No. F04-4841/2008(9485-A45-41), etc.).
Payments to the manager who is the sole founder
Note that the existence of an employment relationship obliges the employer to pay wages to the employee (Article 21, 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The condition of remuneration is a mandatory condition of the employment contract (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
As stated in the commentary letter, the absence of a concluded employment contract with the head of the organization does not mean the absence of an employment relationship. Confirmation of this statement is also contained in the Definition. Payments in favor of the head of the organization, including the sole founder (participant) of the organization, are considered as payments made within the framework of labor relations.
At the same time, it is necessary to pay wages for the work of the founding director. The fact is that the founder of a company has the right to dividends regardless of whether he manages the company or not (clause 1 of article 8, clause 2 of article 28 of Law No. 14-FZ). This means that dividends cannot be a substitute for wages. In addition, dividends can be paid once a quarter and only if there is net profit.
Of course, the director, who is the sole founder, can receive both wages and dividends.
The amount of wages, especially in the absence of an employment contract, should be established in the staffing table.
In conclusion, we would like to remind you that the salary of the director, the sole founder, is generally subject to insurance contributions. Therefore, he has the right to all types of social insurance benefits - temporary disability, maternity and child benefits - on an equal basis with all other employees (Clause 5, Article 2 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006).