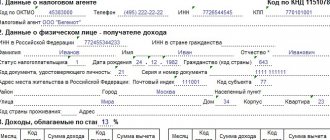
Tax rates payable upon dismissal by agreement
From the salary accrued to the employee, the employer, as a tax agent, is obliged to pay personal income tax and insurance contributions to funds. They are charged in the following amounts (Articles 224, 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Personal income tax – 13%;
- pension contributions (PPS) - 22% of income within the annually established limit and 10% of the amount exceeding it;
- contributions for compulsory health insurance (CHI) – 5.1%;
- contributions in case of disability and in connection with maternity (VNiM) - 2.9% of the amount of income within the maximum allowable tax base.
Companies also pay contributions for injuries in the amount of 0.2% to 8.5%, depending on the class of production risk determined by the Social Insurance Fund for each employer.
For organizations that have workplaces with harmful and dangerous working conditions, there may be an obligation to pay additional contributions to the Pension Fund of up to 9% (Article 428 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax payment certificate (form 2-NDFL)
In 2021, an employee who decides to resign must obtain a certificate of the specified form, since it confirms that the person was actually employed in a particular company, and during his employment, taxes and insurance fees were paid to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. The employer must pay taxes. The certificate can be issued at any time, but it must be issued within three days from the date of dismissal.
According to the Labor Code, you can contact your employer for a certificate either orally or in writing, but mainly in writing. In any case, the manager does not have the right to refuse to issue you such a document.
Object of taxation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties
All of the above taxes are paid from the total amount of accruals to the employee upon dismissal. However, some types of payments are classified as preferential. And they are not charged contributions to the budget and funds (Article 217, Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, it must be taken into account that the total volume of the tax base is reduced by the amount of standard, social, property deductions for personal income tax to which the employee has the right.
Important
Severance pay within the limits of 3 average monthly earnings, provided for by agreement, employment or collective agreement, is a non-taxable payment upon dismissal by agreement of the parties. There is no taxation of such amounts as personal income tax or contributions (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 23, 2019 No. 03-04-05/29191).
The general procedure for determining the size of the taxable base is as follows:
- Distinguishing payments accrued to an employee into taxable and non-taxable.
- Summation of accruals from which taxes and contributions are collected.
- Application of deductions to the total total of taxable charges.
The amounts payable to the budget are calculated using the formula:
(Taxable settlement amounts upon dismissal - Deductions) × Tax rate (contribution) |
Severance benefits
Typically, upon termination of an employment contract, financial compensation (benefits) is paid. Without payment of benefits, there is very little chance that the employment relationship can be terminated on the basis of an employment contract, since the employee is interested in receiving compensation. Accordingly, the employee will not agree to dismissal without financial assistance. At the same time, it is worth noting that benefits cannot be paid in two situations:
- if the need to pay compensation was not specified in the terminated employment contract;
- if the manager does not want to pay by agreement of the parties (personal income tax is included) voluntarily.
Deadlines for paying taxes upon dismissal by agreement
For dismissal by agreement of the parties, the standard deadlines for paying taxes on wages are applied:
- for personal income tax - no later than the day following the date of payment of income (clause 6 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for insurance premiums - no later than the 15th day of the month following the month of payment of income (clause 1 and clause 3 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 9 of Article 22.1 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
If this day is a holiday or a day off, the deadline moves to the next working day.
Income tax for the employer
It is important for an organization to know whether deductions made to an employee when he leaves the organization by agreement of the parties are included in labor costs. The employer's interest is to reduce income taxes.
This issue is clearly regulated by Article 225 of the Tax Code, which states that all deductions stipulated in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, labor and collective agreements and in the agreement on termination of the contract will be labor costs.
The legislator clearly states that the entire amount paid upon dismissal is labor costs.
Important
From all of the above, it follows that all monetary expenses incurred by the employer when dismissing an employee, regardless of the amount, are deductions for wages and are not subject to income tax.
Problems with exemption from taxes and compensation contributions by agreement of the parties
Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases, employers manage to defend their right to be exempt from personal income tax and payments under the agreement within 3 average earnings, there are exception situations.
In judicial practice, there are cases where local tax authorities demanded taxes and contributions for the entire amount of compensation upon dismissal based on a termination agreement. At the same time, courts of several instances supported the Federal Tax Service .
Example
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North-Western District dated October 27, 2016 No. F07-8057/16 in case No. A42-7562/2015.
In this case, the employer settled the employees by agreement of the parties to terminate the collective labor agreement. According to the agreement, each person leaving was provided with severance pay.
Federal Tax Service inspectors decided that the company in this case did not have legally established obligation to pay these employees a one-time monetary compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties. Therefore, the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not applicable to them .
The court of first instance also considered that the disputed payments are not severance pay in the sense given to them by labor legislation. Therefore, they must be subject to personal income tax.
The appeal decided otherwise. The arbitrators pointed out that labor legislation does not contain a prohibition on establishing in an employment contract the amount and conditions for the payment of severance pay, therefore there is no need to establish such conditions in local regulations. Exemption from personal income tax applies to payments related to the dismissal of employees. And the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are applied regardless of the grounds for dismissal and the position held by the employee.
The case went to cassation, which unexpectedly upheld the decision of the court of first instance. According to the conclusion of the cassation judges, paragraph 3 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of exemption from taxation of all types of compensation payments established by current legislation, without mentioning payments provided for by collective labor agreements.
For the peace of mind of employers, we note that there are very few such solutions, but they do exist . Therefore, taking into account the above, in case of problems with exemption from personal income tax and payments under agreements of the parties, we still recommend going to court . The chances of winning are much greater.
Read also
23.01.2021
What is included in severance pay?
According to Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, depending on the reasons for dismissal, the amount paid at the time of dismissal may vary. The employee will receive a monthly average income as severance pay if the employment contract was terminated for the following reasons:
Liquidation of the organization.- Reduction of staff.
- Violation through no fault of the employee of the rules established by law for concluding an employment contract, if this excludes the possibility of him continuing to work and there is no possibility of transferring him to another job.
Also, the payment amount will be two weeks’ average income for the following reasons for termination of the employment contract:
- refusal to transfer to another position for medical reasons;
- conscription for military service;
- reinstatement at work by decision of the court or labor inspectorate of an employee who previously held this position;
- refusal to transfer to another location together with the employer;
- the employee is unable to perform his or her job duties due to health conditions;
- changes to the employment contract associated with changes in technological or organizational working conditions, entailing the impossibility of subsequent performance of job duties.
Two weeks' average earnings as compensation for dismissal are always paid by a seasonal employee.
The amount of severance pay always includes compensation for unused vacations, if any.
For the period of employment after dismissal, the employee continues to receive a salary, but no more than for two months from the date of dismissal. In some cases, payments may last 3 months. The entire amount paid as a result is the amount of severance pay.
The amount of compensation for employees hired for a period of no more than two months must be specified in a local regulation, or a collective or labor agreement. If this point is not regulated in any way, then the payment of severance pay will not be made.
Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties retains the employee’s all rights to compensation payments and severance pay. Also, in this case, the employee can apply to retain his average earnings for the next two months after dismissal (and in some cases for 3 months) or until employment.
Taxation – are they subject to income tax?
All funds that the company's management transfers to the employee's account are subject to taxation. Ultimately, the employee receives money, of which 13% is withheld and transferred to the Tax Authority.
The employer's company acts as a tax agent.
This is important to know: dismissal of pensioners due to staff reduction, compensation 2021
Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that severance pay, which, if necessary, is paid to an employee upon dismissal, is not subject to income tax. It is important to take into account several nuances.
The above standard is valid only if the compensation that the employee receives does not exceed 3 times his salary.
The amount he receives above these funds is subject to taxation.
It does not matter what position the specialist held - ordinary or managerial.
In the situation with workers living in the Far North, everything is a little different.
In this case, the severance pay limit is 6 times the salary.
That is, if the amount of compensation exceeds 6 salaries, personal income tax is imposed on the amount paid in addition to the allowable amount.
In the case of salaries and vacation pay, everything is standard. These payments are subject to taxation according to the general rules.
Are insurance premiums charged?
In addition to personal income tax, an amount intended for payment of insurance premiums is withheld from workers' income. Upon dismissal by agreement of the parties, the issue of their retention is resolved in the same way as with personal income tax.
Wages and vacation payments are subject to insurance contributions on a general basis. Severance pay - no.
The following situations are exceptions:
- compensation amount is more than 3 salaries;
- the amount of compensation is more than 6 salaries (relevant for residents of regions belonging to the Far North region).
If the amount of severance pay exceeds the specified limits, insurance premiums are assessed on funds paid in excess of the limit.
In other cases, contributions are not deducted.
GPC agreements: taxes and insurance premiums in 2021
When the customer withholds and transfers insurance premiums, the main base for accrual can be reduced by subtracting additional expenses of the contractor. This is possible when formalizing relations under contracts involving the payment of royalties or the transfer of intellectual property rights. All expenses incurred must have official confirmation. If not, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes a percentage within which unconfirmed additional expenses can be written off:
Any fees are paid only if the agreement between the contractor and the customer involves the provision of copyright services or the performance of contract work. When drawing up agreements regarding a lease or a cash loan, social payments are not transferred to the local education budget.
How to calculate compensation?
First you need to establish the employee's average daily income. To do this, you will need to summarize all the data on his income for the previous 12 months before the day of his dismissal. The calculation base includes all remunerations issued to a person for the period of time worked. Amounts of payments for days of absence from work, including those not related to the fulfillment of labor obligations, are not paid:
- Vacation pay for regular, additional or educational vacations;
- Compensation for certificates of incapacity for work;
- Travel allowances;
- Material aid.
Thus, only remunerations received while at work are included in the average daily earnings.
Payment of compensation upon termination of employment relations: legislative basis
Compensation upon dismissal by agreement is an independent type of compensation for a dismissed employee under labor law.
Legislative regulation of this payment is extremely scarce.
The Labor Code generally contains only one article on dismissal by agreement.
More detailed regulation can be outlined in a collective agreement, if one is concluded between the company and the team.
It is possible to consolidate the rules for the provision of severance pay in other local documents of the company, for example, in the regulations on compensation.
Finally, when drawing up an employment contract personally with each employee, a clause regarding compensation can be entered upon its termination by agreement.
Typically, such provisions fall into the contract with an executive or other employee in a high position, who could easily lose his job if the ownership of the corporation changes.
The composition and amount of payments are not specified in the law . These payments should not be confused with other funds that the dismissed person receives upon final payment, namely:
- with salary for the past period;
- with vacation pay for the days of vacation that he did not have time to take off.
The employee receives both of these amounts by virtue of the law, and the payment we are considering is due to the dismissed person only on the basis of a contract.
Maximum and minimum size in 2021
Let us remind you that the amount of such benefits for ordinary workers is not limited. There is no minimum or maximum amount. Payment is made in the amount agreed upon by the parties. To formalize the payment, there is no need to indicate the amount in the dismissal order, but the amount of payment must be indicated either in the local act, or in the employment contract, or in the termination agreement.
In 2021, compensation can be paid:
- in a fixed amount,
- depending on salary,
- depending on the employee's average earnings.
What is paid to the employee - list of payments
In a situation where termination of an employment agreement is a mutual decision of both parties, the working citizen must necessarily receive the following types of payments:
- compensation for all remaining days of annual paid leave;
- salary for time worked but not yet paid.
Severance pay , which is also often paid in such cases, belongs to the category of additional payments (according to Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In other words, the law does not oblige the employer to provide this type of financial assistance to the employee.
Indemnities are only due on the condition that the technology and rules for their payment are reflected in the collective agreement or other internal documentation.
Normative base
To find out in detail whether taxation occurs, you must refer to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely Article No. 217. According to the provisions of this article, there is no need for taxation of compensation for unused vacation or severance pay, however, at the same time, there are exceptions, which will be discussed in more detail below in this material.
On the salary due to the employee for the last month worked by agreement of the parties, taxes are paid as usual.
Payment of insurance premiums
If the policies of different authorities regarding the payment of personal income tax differ, then they adhere to the same position regarding the payment of insurance. Starting this year, this type of payment began to be regulated exclusively by the Tax Code.
All cases where there is no need to pay an insurance premium are provided for in Article No. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This list also includes compensation, but its amount should not exceed three average salaries of an employee (for those who live on the Extreme Server, the maximum amount of severance pay does not exceed six salaries).
What it is?
Severance pay is a material payment, which includes funds paid to the employee if desired by the head of the company.
In this case, these cannot be included:
- salary;
- payment of unused vacation days;
- other payments due to the employee according to the information reflected in the collective agreement.
The listed remunerations are paid without fail, regardless of the reason for which the employment relationship is terminated.
If the employer wishes, the benefit may include a specified amount of money.
This accrual is usually called compensation. In most cases, they involve the payment of several salaries.