Legal regulation
This issue is regulated by Art. 78 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, this norm is quite laconic. All that it regulates is the possibility of terminating labor relations by mutual consent of the parties. From this we can conclude that issues relating to payments and compensation are regulated in a general manner.
The amount of compensation payments for certain categories of citizens is limited by Article 349.3 of the Labor Code.
The lower limit of compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties with payment of compensation in 2021 is established by Part 1 of Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states that a citizen must receive additional payment for unused periods of vacation provided annually, according to the number of days. The company is obliged to issue settlement documents to the dismissed person out of turn, on the day when the citizen receives the documents. This procedure is provided for in Articles 84 Part 1 and 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Advantages
When signing an agreement to terminate an employment contract, an employee has some advantages than with a regular dismissal.
- There is no mandatory work for 14 calendar days, that is, you can quit either on one day or for a longer period, for example, only after a few months. During this time, it is possible to find a new job.
- Upon dismissal by mutual agreement of the parties, the employee has the right to register with the labor exchange on the 1st day after dismissal. He may also qualify for unemployment benefits.
Advantages of dismissal by agreement of the parties
Reasons for dismissal by agreement of the parties
What prompts the “owner” to conclude an agreement with the worker?
- The desire to get rid of an “inconvenient” employee who cannot be fired under the article, since he is always pedantic and sober, efficient and professional and is not going to write on his own, despite persuasion.
- The second case when it comes to dismissal by agreement is the upcoming reduction in personnel. Formalizing a reduction is much more difficult and costly than offering to part ways on mutually beneficial terms.
- And thirdly, when, although this violates labor laws, it is necessary to get rid of an employee who has benefits and is not subject to dismissal for any other reason. There is a certain amount of risk for the manager here. If the dismissed person agrees and then writes a statement to the judge or the prosecutor, a bad story may turn out with the reinstatement of the dismissed person at work, payment to him for forced absences and a fine for illegal dismissal to the local budget.
What motivates an employee to resign by agreement of the parties with payment of compensation?
- Interest here can only be material. When the employment contract stipulates severance pay, some additional monetary “goodies” that are due upon dismissal, and the format of the agreement, in addition to them, allows you to talk the employer out of a certain amount on top. It is clear that bargaining will only work if the owner strongly desires to part with the employee.
- Quite often, dismissal by agreement becomes a lifesaver for someone who is threatened with being thrown out into the street “under an article”: for drunkenness, theft, or other gross violations of labor order. There is no point in bargaining here, since dismissal by agreement in itself saves the future career of the person being fired and is a big favor on the part of the “boss”.
- Psychological pressure from superiors, pressure to leave of one’s own free will. The benefit is obvious: on your own, only debts for salary and vacation will be returned, but by agreement you can agree on some additional compensation.
Usually it is the employer who first proposes this method of dismissal. But the law does not prohibit it if the worker himself, after weighing all the pros and cons, offers the owner “mutually beneficial” to fire him.
Is it possible to ask for 4, 5 or 6, what quantity can you get?
Since the legislator does not determine the amount of compensation paid to an employee in the event of termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties, the employer and employee have the right to independently determine its amount. Local acts may indicate how much is allocated for payment of compensation:
- in the amount of several salaries of the resigning employee (two, three, etc.);
- in a fixed amount of money.
In practice, most often the amount of compensation is equal to the amount of three average salaries of the person whose employment contract is terminated by agreement of the parties.
An employee has the right to demand that the employer pay four, five or six salaries, however, if such an amount of compensation is not specified in the collective agreement or other documents of the enterprise, the employer may refuse to assign the requested compensation, paying, for example, 2 salaries or not paying anything. In this case, the refusal of compensation payments will be lawful.
The parties to an employment contract may decide on the need to conclude a dismissal agreement in accordance with Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for various reasons. Most often, such a decision is beneficial for both the employee and the employer.
For example, an employer needs to get rid of an unwanted employee. In order to minimize losses to the company’s reputation in this case, the parties should come to an agreement to pay a certain amount of compensation.
In some cases, the employer dismisses employees by agreement of the parties , although in fact there is a reduction in the number or staff of the company. To prevent dismissed persons from contacting the relevant authorities, the head of the enterprise may also offer them compensation in a certain amount.
Often the increased amount of compensation is caused by the reluctance of the parties to labor relations to make public any nuances related to work or directly to the dismissal of a person. This only applies to situations where the amount of compensation payments is not specified in the employer’s local regulations.
When to use
The agreement cannot be considered a civil contract, since its conclusion is made within the framework of labor relations. The employer may send a written proposal to the employee regarding possible dismissal if the latter is on sick leave or on a planned vacation.
This option is proposed in the case when the enterprise has financial difficulties and its reorganization or liquidation is expected. For an employee, it is, of course, preferable to wait for liquidation, since financial benefits are paid upon redundancy. But the negotiated departure entails a benefit for the employee who faces dismissal for inconsistency, absenteeism, and drunkenness.
The scheme is often used in situations where, due to family circumstances or health conditions, a person needs to leave without two weeks of work. In this case, the employee asks, and the manager releases him within the agreed period. There are other cases in which the agreement justifies itself.
The difference between a mutual decision and an initiative on the part of the employee to resign is the ability to change the date of departure and provide for other circumstances. For example, an employer can assign a financial additional payment, and an employee can leave without working.
Rules for drawing up an agreement
Legislators have not developed a standard, generally applicable sample agreement, so enterprises and organizations can create a document form at their own discretion and based on their own needs. True, at the same time, some rules must still be observed, in particular, the document must indicate the full name of the employer, position, surname, first name, patronymic of the employee, record the fact of the agreement reached and specify its terms in detail. The latter must fit within the framework of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Usually the agreement is drawn up at least a few days before the dismissal, but some companies act differently. The employer does not draw up the document, but instead writes a corresponding resolution with the future date of termination of the employment contract on the employee’s statement of desire to resign by agreement of the parties.
The agreement has two equal copies, one of which remains with the employer, and the second is given to the dismissed employee. Each copy must be signed by both parties.
Necessary conditions for dismissal by agreement of the parties
In Article 77 of the Russian Labor Bible, dismissal by agreement of the parties is given as the first general basis for dismissal. Despite the silence of the legislation regarding the procedure itself for this specific method of dismissal, it is clearly subject to the general requirements for the termination of any employment contracts. It is impossible to put pressure on an “inconvenient” worker or employee using administrative resources or force him to resign.
The Code and the Constitution declare the priority of freedom of labor, and this principle should be followed when offering dismissal of mutual good will.
Voluntariness is the main imperative characterizing the dismissal transaction between the manager and the employee. The parties themselves agree on the remaining conditions by drawing up an agreement in writing.
Stages of the procedure
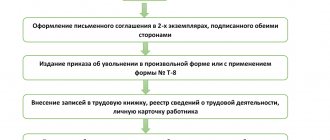
The process of dismissal by agreement can be started by both the employee and his employer. The first thing to do is to send the other party a written proposal to terminate the employment relationship. This can also be done orally, but in this case there will be no evidence on hand that such a proposal took place. If everything goes well and the employer or employee agrees with the initiative expressed by the opponent, it is time to proceed directly to the agreement, which must be formalized in writing.
Documenting
The form of the agreement to terminate an employment contract is not defined by law. As a general rule, it is accepted that it is drawn up in the form of a separate document, and is drawn up in two copies having equal legal force. Each copy is signed by the parties, then one document is given to the employee, and the other remains with the employer. In addition, there must be a letter of resignation from the employee and an order from the management of the organization.
If all these documents are drawn up and there are no contradictions in them, termination of the contract under clause 1, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation will be legal. From the point of view of registration and timing, the dismissal procedure by agreement of the parties is the simplest and fastest way to part with an employee. Indeed, in this case, the legislation does not require notification of dismissal in advance, offering another job, or exercising the preferential right to remain at work. It is not prohibited to terminate employment relations under Part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with those categories of citizens whose dismissal usually causes certain difficulties:
- pregnant women;
- minors;
- employees who are on vacation or sick leave.
This state of affairs often makes it possible to “mask” other reasons for termination of a contract under the agreement of the parties. As the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation noted in paragraph 20 of the already mentioned resolution of the Plenum dated March 17, 2004 No. 2, cancellation of the agreement regarding the period and grounds for termination of the employment contract under paragraph 1 of part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is possible only with the mutual consent of the parties.
Registration procedure
Termination of an employment agreement consists of several important stages, each of which has its own characteristics.
Termination of the employment agreement
Stage 1. An expression of the desire of one of the parties, either the employer or the employee, to terminate a previously signed employment contract. It must be in strictly written form, in which, upon consent, a mark to this effect must be made.
If the initiative belongs to the employee, he must submit an application to the personnel department indicating the reason for dismissal. The text must specify the article under which the employment relationship is terminated: “in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.” The employee must also include the desired date of dismissal in the application. It is not associated with any deadlines and is indicated only depending on the wishes of a particular employee.
When the initiative comes from the employer, he must send notice directly to the person with whom it is planned to terminate the employment contract. There are also no clearly established forms of this document. It is important that the idea of the proposal to terminate the contract is presented in a sufficiently clear and unambiguous manner.
An employment contract can be terminated at any time by agreement of the parties to the employment contract
Stage 2. After obtaining consent from both parties, it is mandatory to draw up a document on termination of the employment relationship, which also does not have an approved form. It should definitely include the following points:
- the document must have the title “Agreement on Termination of Contract”;
- the participants in this operation are entered into it: the name of the enterprise, the full name and position of the employee, as well as the name of the department where he is registered;
- the form should include the number and date of the employment contract that is being terminated;
- the conditions under which the relationship will be terminated are specified. It is in the text that compensation should be specified. It is indicated either in a fixed amount or with an indication of the multiple of the salary received;
- the date from which the employment relationship will be terminated must be recorded;
- The place of its conclusion and date are entered into the agreement. Without these details, the document may be considered invalid;
- the agreement must contain signatures and their transcripts, as well as a phrase stating that the parties have no claims against each other.
Termination Agreement
The document is drawn up in 2 copies, one of which is stored in the archives of the enterprise, and the other is given to the dismissed employee.
When an agreement is concluded, an employee can resign only on the day specified in the document. Any change must be additionally agreed upon by the parties to this transaction.
Stage 3. When the day comes, which is considered the last in the labor relationship between the employee and the employer, an order is issued for the enterprise. It has a unified form, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 1 of 01/05/2004. An order issued for one employee is filled out on form T-8. When signing an order for several employees at once, the T-8a form is used. Both contain the following mandatory points:
- Full name of the person being dismissed;
- the name of the unit where he was registered;
- title of the position held;
- the basis that served as the termination of the employment relationship. This paragraph contains either a statement from the employee or a notification coming from the employer;
- date of dismissal;
- Full name of the head of the enterprise, his signature;
- signature of the dismissed employee.
Order to terminate the employment contract, form No. T-8
| Document type | Form | Sample |
| Order (instruction) on termination (termination) of an employment contract with an employee (dismissal) N T-8 | ||
| Unified form N T-8a |
Stage 4. After signing the order for the enterprise, a record of dismissal is made in the work book and it is handed over to the citizen. He is also provided with all monetary payments specified in the agreement on the day of dismissal.
The table shows the main aspects of concluding a dismissal agreement:
| Aspects | Peculiarities |
| Initiator | Any party to the labor relationship, both represented by the employer and the employee |
| Notice period | Not legally established. Discussed between the parties and written down in the document |
| Cause | Document signed by two parties |
| Payments | The employee receives all the money due upon dismissal. Compensation is negotiated additionally |
| Cancellation | Review only by mutual consent |
What documents are required?
The dismissal procedure is preceded by the submission of an initiating document. Application example:
- the upper right corner of the document includes the name of the enterprise, the full name of the director and the compiler;
- below in the middle part of the form the heading “Application” is written;
- its text, where the reason for dismissal is stated in clause 1 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- signature and date.
Also, the procedure for dismissing an employee within the framework of a mutual agreement includes the following points:
- execution of the contract in 2 copies, if a particular enterprise does not provide for more copies;
- registration of the agreement in the accompanying book;
- delivery of one copy to the employee, confirmed by a signature on the company document;
- an order to terminate the employment relationship between the company and the employee;
- registration of the order to terminate the employment relationship between the company and the employee in the accompanying book;
- familiarization of the employee with the order to terminate the employment relationship, his signature on the document.
The absence of an employee or his refusal to sign a document is recorded accordingly.
- preparation of settlement documentation;
- payment to the employee of all due funds, including compensation and severance pay.
Settlement actions are performed on the day of dismissal. If the employee is absent from the workplace, he may demand payment on another day. From this moment on, the company is obliged to pay him within 24 hours.
- an entry is made in the work book and a stamp is placed;
- making a copy of it for the company’s archives;
- the employee is issued a work book.
If he is absent or refuses to receive it, the company is obliged to notify him of the need to pick it up in person or agree to send it by mail. Subsequently, the document is issued no later than 3 working days from the date of the employee’s application. Having received the document, the employee confirms the action with a signature.
According to Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the agreement is drawn up only in writing.
The finished document must contain the following information:
- consent of the parties to the agreement;
- details of the employment agreement that cancels the document;
- end date of the employment relationship;
- amount of compensation, terms of payment, if provided for in the agreement;
- time and place of conclusion of the contract;
- Full name of the employee, position, passport details;
- official name of the employer's company, its legal form, TIN;
- Full name and position of the authorized representative of the company;
- signatures of participants and their transcript.
Two salaries for lack of notice
We look at the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 180 “Guarantees and compensation to employees upon liquidation of an organization, reduction in the number or staff of an organization’s employees”:
Employees are notified by the employer personally and against signature of the upcoming dismissal in connection with the liquidation of the organization, reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees at least two months before the dismissal
. The employer, with the written consent of the employee, has the right to terminate the employment contract with him before the expiration of the period specified in part second of this article,
paying him additional compensation in the amount of
the employee’s average earnings, calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the notice of dismissal.
What payments are due?
On the day of dismissal, the employer must pay the employee and pay him all due funds for the period of work. Mandatory payments upon dismissal by agreement of the parties include:
- salary for hours worked (including bonuses and bonuses provided for in the company’s remuneration system);
- compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal in accordance with Art. 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (paid for the current year and previous periods if the employee was not on vacation).
But usually, upon voluntary dismissal, the question of additional compensation and payments in favor of the employee arises.
As for severance pay, its payment upon termination of an employment contract by agreement between the parties is not mandatory. The law does not provide for such compensation. But the condition for payment of compensation may be contained in an employment or collective agreement (this rule is contained in Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If these documents do not contain any mention of the employer’s obligation to compensate the employee for dismissal, then the employment contract is terminated without additional benefits. The employee is entitled only to legally guaranteed payments in the form of wages and compensation for unused vacation. This option is possible when termination of an employment contract by agreement occurs in the interests of the employee. For example, if he was threatened with dismissal under an article for violating labor discipline, but the employer met halfway.
The employee and the employer can agree on the payment of severance pay and stipulate it in the agreement that they sign upon termination of the employment contract. If a clause on the need to pay severance pay in a certain amount is specified in the agreement, then the employer cannot unilaterally refuse to fulfill its obligations (even though there is no such provision in the Labor Code).
If the employer refuses to pay severance pay, the employee has the right to claim it in court. In this case, he will be able to receive not only the compensation itself, but also a penalty for each day of delay.
Often, employees refuse to be fired as part of an agreement if this does not promise them certain material benefits and the contract does not stipulate additional compensation.
What to pay attention to when calculating the amount of debt for vacation
Many employers try to save money when dismissing employees, even by agreement of the parties on the payment of this compensation. This is illegal and accounting departments must take into account the following points when making final payments to a colleague:
- Compensation for dismissal for any reason is paid for the entire period during which the employee, having worked, did not rest. If he worked without a break for 4 years, then on the day of dismissal the company compensates him for vacation pay for this entire period of time.
- If an employee, after starting work, managed to work for a full 11 months before his dismissal, then vacation compensation on the day of dismissal is due in full for the entire year.
- The procedure for calculating the average daily wage is similar to the principle for calculating it for annual paid leave.
Cash compensation upon dismissal by agreement
Article 140 of the Labor Code obliges the management of companies and government organizations to pay employees in full directly on the day of dismissal. Issued for calculation:
- everything that the dismissed person has earned but has not yet received;
- vacation pay for unused days of legal rest;
- compensation for dismissal, according to the amount specified in the agreement.
For the most part, compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties is a disguised form of so-called “compensation”. We are talking about an amount established as a result of “bargaining” between the employer and the employee, which is paid as a guarantee of the waiver of any claims by the former employee against the company after his dismissal.
What is the amount of payment upon dismissal by agreement of the parties on the basis of paragraph one of article seventy-seven? It is not described in the novelties of the law. However, in practice, they pay amounts no less than in case of staff reduction, and no more than three employee salaries (six for residents of the northern regions of the country). In any case, this amount must be clearly indicated in the text of the agreement. Since if the employer refuses to pay it, thanks to this record it is possible to restore justice in court.
Is severance pay mandatory upon dismissal by agreement?
Compensation for dismissal under paragraph one of article seventy-seven does not apply to mandatory payments. The manager is not obliged to pay, but that is the purpose of the agreement, to persuade him to do so.
Article 178 of the Labor Code obliges companies to compensate for the dismissal of employees with severance pay only in the following cases:
- the worker went to repay his filial debt to the Motherland;
- the organization has lost its significance and will soon be liquidated;
- staffing is being reduced due to optimization of production processes;
- a specialist has to vacate a position due to the reinstatement of an unfairly dismissed employee;
- an employee quits because working conditions have changed;
- the employee is unable to work due to illness or injury;
- they wanted to transfer the employee to a branch office of the company in another region, but he refused.
But the size of the “farewell” benefit depends on the reason for dismissal. If we are talking about staff reduction or liquidation of the company, then the average monthly salary is paid, plus a salary while looking for a new job. No job found within the second month? Another salary is paid, if, of course, the dismissed person managed to join the labor exchange within two weeks after the dismissal. In rare cases, at the request of the employment center, the company pays for the third month of job search.
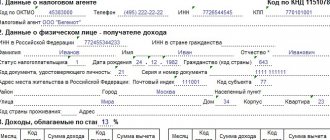
Personal income tax on payment to an employee upon dismissal by agreement of the parties
According to Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payments for compensation of unused vacation are not taxed, as well as the amount of severance pay that is equal to or does not exceed three times the average income or six times (in relation to employees of the Far North).
When the amount of the benefit exceeds the salary by 3 times, then taxation occurs in the usual way exclusively on the part that exceeds this amount. At the same time, the worker’s wages paid to him upon leaving the enterprise are subject to duties as usual.
Regarding payments to the Social Insurance Fund: insurance contributions are not deducted from payments to the employee due to dismissal from office. The only exception is reimbursement of unused vacation. Insurance premiums are deducted from the employee's remaining salary as usual.
How to determine the amount of compensation
Payments upon dismissal by agreement of the parties are specified in the agreement. They are rarely a fixed amount and are determined by the employer on an individual basis. The calculation of a specific amount is done by the accounting department in the following ways: based on average monthly earnings; in the amount of salary; in the form of a fixed amount.
Fixed amount
Compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties is mainly prescribed in the contract or collective agreement. Often such a payment is equal to the tariff rate, however, another figure may be determined. In the amount of official salary Monetary compensation upon dismissal by agreement of the parties in most cases is paid in the amount of salary. If a worker is transferred from one position to another, then the salary at the last place of work is taken into account. It is important to take into account that directors, as well as some other management specialists, are entitled to 6 salaries.
Based on average earnings for a certain time
When a dismissal occurs, accounting sometimes determines the amount of payments based on average monthly earnings. To do this, you need to know the salary, as well as the number of days worked this month.
How to correctly calculate this value
The calculation rules are determined by the standards. For them, payments are tied to the last 12 months of a person’s work. It is noted that the employer has the right to establish his own calculation rules, the main thing is that they are more profitable for workers compared to the standard ones.
So, average monthly cash earnings are calculated using the following formula:
SZ = SZD (average earnings per day) x D (number of working days) For someone who has worked for less than a year. If the employee’s side has worked for less than a year, you will have to use a different formula: SZ = SZD x Salary (full amount of payment) x M (fully worked months) x NM (months not fully worked)
What to do if they refuse to pay money?
If the employer has not fixed the amount of severance pay either in the local regulations of the organization or in the employment contract, then the employee does not have the right to request it upon dismissal. Then he can only count on mandatory payments.
However, if the employer refuses to pay the required amounts (compensation for unused vacation or wages for days worked), this is regarded as a violation of labor legislation.
An employee can restore his rights by contacting:
- to the trade union;
- to the state labor inspectorate;
- to the prosecutor's office;
- or in court.
This possibility is enshrined in Art. 382 TK.
As evidence of violated rights, all documents confirming the employment and dismissal of the employee, as well as a bank statement on the movement of funds on the card to which payments were received from the employer, are attached.
conclusions
Dismissal by agreement of the parties is quite common, as it has a large number of advantages for both the employer and the employee.
The employer does not have to report to trade union organizations, and the employee does not have to work for two weeks.
But you must resign on this basis according to the rules. First of all, a direct agreement between the employee and the employer is necessary.
After this, an agreement is concluded. And on the basis of this document, the employee writes a statement, and the employer writes an order to terminate the employment relationship.
Penalties for late payments
On October 3, 2021, amendments to Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, which tighten liability for late payment of wages, vacation pay and other amounts due to the employee. Therefore, if within a year from the date of the violation the company is visited by the State Tax Inspectorate, it may be brought to administrative liability (Article 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses establishes the statute of limitations for violations).
Delays in the payment of wages, compensation for unused vacation, and bonuses upon dismissal entail financial liability for employers under Art. 236 TK. From October 3, 2021, this amount of compensation is one hundred and fiftieth of the current refinancing rate for each day of delay in amounts not paid on time. Moreover, the employer’s liability for delays in amounts due to the employee occurs automatically.
Moreover, if the employer still does not pay the money, then during the inspection it will be revealed that he has a continuing offense, for which the State Tax Inspectorate has the right to bring administrative liability within a year from the date of discovery of this violation.
Calculation of compensation for unused vacation
The accounting department of an enterprise calculates the amount of compensation in a similar way to calculating the amount of vacation payments. First, the employee’s average daily earnings are determined. It is calculated for the last twelve calendar months for the period actually worked by the employee and the actual salary accrued to him. Let's consider the formula for calculating this indicator:
SDZ = accrued salary / (RegFullMon * 29.3 + RecIncompleteMon *29.3 / CalendarDay),
where SDZ is the employee’s average daily earnings; OtrFullMons - number of full months worked; OtrIncompleteMes - the number of days worked for an incomplete month; CalendDn - the number of calendar days in an incomplete month; 29.3 – average number of calendar days per month;
Next, compensation for missed vacation must be calculated, which is calculated by multiplying the number of days worked for an incomplete month by the average daily earnings.
Features of dismissal by agreement of the parties
Maternity maids
For women on maternity or child care leave, there are a number of benefits. In particular, they cannot be fired due to staff reduction; if a fixed-term employment contract expires, they have the right to demand its extension, etc.
That is why, in order to get rid of such employees, employers often dismiss them by agreement of the parties. If such an agreement is concluded, no benefits apply, and the maternity leave may be dismissed.
However, we repeat once again: such dismissal is permissible only if the woman agrees to this option. If the employer exerts pressure, it will be absolutely illegal, and then the labor inspectorate, the prosecutor’s office and the court will side with the employee.
However, it should be remembered: if a woman nevertheless agreed to such a dismissal, then she will not receive any benefits or other payments unless their payment is directly indicated in the agreement. That is why, in practice, cases of dismissal by agreement of the parties to this category of workers are very rare.
When staffing is reduced
Employees subject to staff reduction are entitled to severance pay not lower than the average monthly salary, payment for unused vacation and salary at the time of dismissal. If in the next two months he was unable to get a job and turned to the employment service, the employer pays compensation for this period.
An employee is given 2 months notice of dismissal. He must sign, confirming familiarity with the document, and at the same time, the company must notify the trade union and employment services.
Naturally, this procedure makes dismissal by mutual consent the preferred procedure only for the employer. The employee’s only motive is decent compensation, covering the amounts due to him by law.
Pensioner
Working pensioners enjoy all the rights provided for other categories of workers. Moreover, Art. 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly prohibits restrictions on labor rights and freedoms based on age.
That is why the same rules apply to them when dismissing them by agreement of the parties as when dismissing any other employees on this basis.
Part-timer
The only difference in such dismissal for a part-time worker will be only a slightly different wording of the entry in the work book.
If the job from which he quit was not the main one, then in the work book, where, at the employee’s request, entries about part-time work can be made, it will be written: “Dismissed from part-time work...”.
The rest of the entry (including references to clause 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) will be absolutely the same as for other employees.
During the period of sick leave
Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation denies the employer the right to dismiss a sick employee on his own initiative.
However, its effect does not apply to the mutual consent of the parties. As a result, the employee’s incapacity to work is not grounds for termination of the dismissal agreement. It is carried out exactly within the specified period and cannot be challenged by certificates and sick leave certificates.
In the absence of a sick employee, a corresponding entry is made in the dismissal order, and a notification is sent to him with a request to appear for a work book or to express consent to receive it by mail.
If the disability occurred during the validity of the employment contract, benefits are also paid for the period following the dismissal, namely 30 days from the moment the employee is familiar with the dismissal order. When sick leave is received by an enterprise, it is paid on the next day of payment of wages. Payments are made on a general basis, even if there is an agreement of mutual consent to dismissal.
A similar principle applies to injuries or illnesses that occur within 30 days after dismissal, if the employee did not manage to get a job elsewhere. Only illnesses resulting from a proven suicide attempt, deliberate self-harm, or commission of a crime are not covered.
Large family and single mother
Since dismissal by agreement of the parties is completely attributed to the will of the parties by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when dismissing a mother with many children and a single mother who has agreed to terminate the employment contract, the general rules will apply.
They will not have any additional benefits not specified in the agreement. The only thing you should pay attention to is that consent to dismissal must be absolutely voluntary.
During pregnancy
According to the law, an employer cannot fire a pregnant woman, except in cases of liquidation of the enterprise or termination of the individual entrepreneur’s activities.
Dismissal by agreement of the parties is carried out on a general basis; the employee does not receive any benefits. She can only count on the amount specified in the contract. Payment of maternity benefits required by law is not made.
Judicial practice shows the possibility of challenging a contract. To do this, the woman must prove that she did not know about the pregnancy at the time of signing it. Consequently, she did not calculate the consequences of voluntarily refusing to work.
The protection of motherhood and childhood is the prerogative of the state, prescribed in Article 38 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation; as a result, the court often sides with the mother, annulling the agreement.
To avoid such situations, the employer is recommended to reach an agreement with the employee out of court by paying compensation. In turn, she acts at her own risk and if the outcome is unfavorable, she pays legal costs.
Dismissal without work
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not know what a fourteen-day work period is. This is a figment of the imagination of employers. Another thing is that you need to submit a resignation letter just two weeks before the date of dismissal. Clause 1 of Article 77 of the TCRF allows, by agreement, to terminate the employment relationship at any time. It is illegal to demand mythical work.
From a legal point of view
The legislation of the Russian Federation is laconic in this case. It only states that the employment contract can be terminated by mutual agreement at any time. This means that such dismissal is possible both during part-time work, while on vacation, during a probationary period, etc., i.e. even in cases where the dismissal of an employee by the employer is prohibited in the usual manner.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES