Types of penalties
Clarifying comments to Art. 192 and 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on disciplinary sanctions of 2021 most fully interpret both the types of measures of influence on guilty employees and their application. In particular, Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation divides methods of punishment into two types:
- material;
- intangible.
When imposing any punishment on an employee, the manager must take into account the degree of his guilt, as well as the severity of the offense committed. But it should be remembered that the conditions under which the violation occurred can greatly affect the assessment of what happened. Thus, a specialist being intoxicated at work may be caused by a leak of a toxic substance at work. In this case, even though the employee violated labor discipline, it is unlawful to punish him.
Material sanctions
Material measures include penalties, deprivation of bonus payments, as well as material compensation for damage caused by an employee to the organization’s property. It should be noted that these penalties are not always legal.
For example, the imposition of fines on employees is not established by any legal act of Russian legislation, and therefore the employer may incur administrative or criminal liability for such actions. In addition, deprivation of an employee’s bonus is allowed only if this norm is enshrined in a collective or labor agreement.
Dismissal of an employee
The most severe sanction is dismissal. To apply it to an employee, there must be compelling reasons listed in Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- regular absenteeism;
- actions due to which the accident or accident occurred;
- disclosure of secret information;
- being at work in a state of intoxication;
- theft or embezzlement.
This is also important to know:
What is a strike according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Before deciding to terminate an employment relationship due to a disciplinary offense, the employer should take into account the specifics of this type of punishment. Thus, disclosure of secret information can serve as grounds for dismissal only when such a condition is specified in the contract. If the absenteeism was an isolated incident, then according to the law the offense is not considered a sufficiently serious reason for terminating cooperation.
Remark and reprimand
Other non-material penalties include reprimand and reprimand. A reprimand is most often made orally and is a warning to the offending employee. Sometimes, on its basis, a written order is drawn up, which is not entered in the work book. A reprimand is formalized and given for more serious violations. Based on the order, it can be recorded in the work book.
Statute of limitations for violations of labor discipline
- the employee is warned in writing about dismissal, the timing is set by the employer, as it is more convenient for him;
- an order is prepared for the enterprise in the standard T-8 form, to which, if necessary, acts, explanatory notes and similar documents are attached;
- on the last working day, the final payment is made: the employee is given all the necessary documents (employment, income certificate, additional certificates at his written request, if necessary) and money (salary with all bonuses and allowances, if any, as well as compensation for unused days of calendar vacation).
The employer has no right to withhold any funds from an employee, for example, not to provide compensation for vacation. Unless, of course, the employee caused significant material damage to the company and funds are not recovered from him for this.
What are the terms of dismissal for violation of discipline?
Deadlines after which it is too late to impose a penalty According to the set of labor laws, later than six months later, the employer does not have the right to recover from an employee for an offense committed. If during this period there were no repeated violations, you can completely forget about the offense committed.
That is, for example, your employee committed absenteeism on January fifteenth, for which he received a reprimand, then behaved impeccably, and on August tenth he absented himself again. You cannot dismiss an employee for violating labor discipline for systematic absenteeism, since the previous case has expired.
Attention The date – the starting point – will be considered the date of signing the collection order. Time limit for imposing a penalty The law allows a month to punish the offending employee.
Deadline for disciplinary action
Important The employer should consider how this or that type of punishment will affect the production process. There is no need to punish employees for the slightest insignificant offense.
Being a couple of minutes late is a reason to express dissatisfaction, but not so significant as to issue an official reprimand.
As a result, an employer who abuses penalties develops a bad reputation in the labor market, and it becomes increasingly difficult for him to find new employees.
Disciplinary action affects both the employee and the organization. Employees should understand that such measures are often forced and almost always temporary.
Dismissal for violation of labor discipline: judicial practice
They are not included in the monthly period calculated from the date of discovery of the fact of committing a disciplinary offense (Part 3 of Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, subparagraphs “b”, “c”, “d” of paragraph 34 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 No. 2):
- periods of employee incapacity;
- the time of all vacations that the employee may take;
- waiting time for a trade union decision.
There is also a statute of limitations for disciplinary action. In general, it is six months from the date the employee committed the offense. However, there are exceptions to this rule.
If a violation is discovered by an inspector (auditor, auditor), the period for imposing a disciplinary sanction is increased to two years.
It is important to understand that the period of incapacity or vacation of the offending employee is not excluded from this period.
Statute of limitations for violation of labor discipline
That is, if your employee, after ten years of impeccable service, is half an hour late at the start of the working day, and you dismiss him for this for violating labor discipline, no one will understand you, and the judge, if the dismissed person goes to court, will definitely not be on your side. side. In fact, even a serious violation, for example, of labor protection, will not be a sufficient basis for dismissal if the employee can justify his usefulness to the enterprise and prove that he has worked honestly and diligently for many years.
And of course, the most controversial reason for dismissal is improper performance of one’s duties - this is a rather difficult to measure category, especially in terms of, for example, office work.
Calculation On the last day, the employee must be paid the following:
- wages for the period worked;
- bonuses (if the employee is not deprived of these payments due to compensation for damage to the organization);
- compensation for unused vacation.
The listed payments are mandatory and provided for by law, so the employer cannot deprive the employee of the specified funds. An exception is a premium, which can be used to pay off damage caused to the enterprise (again, if this fact is proven).
The employee is not entitled to any additional payments. Recording in the labor record On the last day, in addition to payments, a labor book is also filled out, where the basis is dismissal for violation of labor discipline.
Entry into the labor record must be regulated by Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An example of a recording is shown in the photo below.
Violation of the procedure for bringing an employee to disciplinary liability is recognized by the court as a basis for declaring such an employer’s decision illegal.
In the case considered, the employer ordered an inspection regarding the violation too late, as a result of which disciplinary liability was declared invalid due to the missed period of a month from the day the fact of the violation became known to the employer.
Based on the definition in question, all consequences of illegal disciplinary liability are canceled. For example, in the case under consideration, the employee was paid bonuses, which he was deprived of as a result of being held accountable.
Also in such cases, employees in accordance with Art. 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation can count on compensation for moral damage.
In addition, with regard to the case of a violation of labor protection - in order to fire an employee for this, it is not enough for him to simply, for example, forget to check the voltage; it is necessary that someone suffered from the actions taken or significant damage was caused to the property of the enterprise.
Back to content How is dismissal for non-compliance with labor discipline formalized? It has been mentioned several times above and, in our opinion, needs to be mentioned again: the imposition of a penalty must be commensurate with the misconduct; you must collect a very impressive and thorough evidence base if you still intend to fire someone. What might this include? Acts on absenteeism and violations of labor protection requirements, testimony from colleagues of the offender, official and explanatory notes, and the like - it is better if all your evidence is not in words, but in writing.
It is very important, for example, to comply with the terms of dismissal for violation of discipline. And if you don’t know exactly what labor law says on this topic, you definitely need to read this article. articles
- 1 Labor Code
- 2 Why can you be dismissed due to violation of discipline?
- 3 Labor discipline and dismissal. Deadlines 3.1 Deadlines after which it is too late to impose penalties
- 3.2 Deadline for imposing penalties
- 4.1 What penalties are provided?
Labor Code To begin with, it is worth noting where exactly in the Labor Code you need to look for information on the issue raised above.
If an employee refuses to sign for familiarization with the document, an appropriate act must be drawn up in the presence of witnesses.
- Receiving an explanatory note. An explanation from the offending employee is also an important part of the dismissal process. For example, if delays occur systematically, an explanatory statement regarding this fact must be provided each time. The same applies to other cases when an employee violates the established procedure in the organization. An explanatory note can both help a citizen and establish the fact of a violation. Therefore, the employee must think about what he writes and in what form.
- Order This document has a standard T-8 form.
It should be remembered that any labor function must be specified in the contract. Disciplinary sanctions include a reprimand and a reprimand, and they are applied for the violations already specified. It is not a disciplinary offense and is not subject to penalties:
- refusal of the employee to carry out personal instructions from the employer;
- employee’s disagreement to carry out public work, including absenteeism at clean-up days, demonstrations and rallies;
- refusal of additional work if this obligation is not specified in the contract;
- the employee’s disagreement to perform actions contrary to the law;
- refusal of any work not expressly stated in the employment contract;
- a strike, if it is carried out in accordance with the law.
The procedure for imposing a penalty Punishment of an employee requires compliance with clear rules.
Source: https://pbcns.ru/srok-davnosti-po-narusheniyam-trudovoj-distsipliny/
What can lead to disciplinary action?
Sometimes an employer has to deal with the fact that an employee does not fulfill or improperly performs his direct duties. In this case, the labor legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the right of the employer to take disciplinary action against the offending employee.
A disciplinary sanction is applied to an employee when it is established that he has committed a disciplinary offense. A disciplinary offense may be considered a violation of an employee’s obligations as stated in the employment contract, job description, internal labor regulations and other provisions of the organization. Most often, punishment follows for non-compliance with labor discipline - in the case of:
- systematic tardiness and/or absenteeism;
- premature departures from work;
- failure to comply with management instructions;
- reporting to work under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
The list of disciplinary offenses can be continued depending on the specifics of the organization. As a rule, violations of labor safety rules, disclosure of confidential information, and non-compliance of the work performed with accepted quality criteria are most severely punished.
Sample order for disciplinary action
An order to impose a disciplinary sanction is printed on the organization’s letterhead and registered in a special journal.
ORDER
03/09/2017 Ekaterinburg
In connection with the improper performance by storekeeper Viktor Petrovich Nesterov of the labor duties assigned to him by employment contract No. 5 dated 09/01/2005 and the storekeeper’s job description dated 08/06/2004, which resulted in a lack of control over the preparation of shipped products, which led to a delay in delivery of goods to the customer,
ORDERS:
reprimand storekeeper Viktor Petrovich Nesterov.
Base:
- Memorandum of the Deputy Head for Administrative and Economic Affairs O. V. Skvortsov dated 03/01/2017.
- Act on the employee committing a disciplinary offense No. 45 dated 03/05/2017.
- Explanations of the employee dated 03/02/2017.
Director of LLC "Horns and Hooves" ________________ Strelkov I. P.
Specifics of disciplinary sanctions for certain categories of citizens
Another type of disciplinary sanction is provided for civil servants: a warning about incomplete compliance with official duties.
For military personnel, the list of disciplinary punishments has been significantly expanded:
- severe reprimand;
- deprivation of an award badge;
- warning about incomplete job compliance;
- early dismissal. The reason in this case is failure to comply with the terms of the contract;
- demotion;
- demotion in rank;
- deduction from fees;
- expulsion from an educational institution;
- disciplinary arrest.
These types of punishments are enshrined in special legislative acts on public and military service.
Statute of limitations for misconduct for disciplinary action
Appealing a disciplinary sanction by staff An employee has every right to appeal the disciplinary action. To do this, he should contact the district commission for resolving labor disputes. Further consideration of the case may be referred to the prosecutor's office or court.
If the employer made gross errors in the preparation of documents, or overlooked any stage, then the court decision will be on the employee’s side. If the foreclosure is declared invalid, all documents about it are subject to destruction. If an employee is fired, he is reinstated in his previous position.
At the same time, he is paid compensation for all days missed at work in the amount of average earnings. Dismissal is an extreme disciplinary measure. Of the three types of disciplinary penalties, dismissal is permanent and often irreversible. For example, by order of the Ministry of Justice of Russia, instructions were approved on the procedure for applying the regulation “On service in the bodies of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation...” dated 06.06.2005 No. 76 (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions), containing penalties not provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Dismissal as a form of punishment is allowed only on the grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or a regulatory act. The exception is special categories of workers, for example, those working remotely (Part 1 of Article 312.5 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or managing an organization (Clause 2 of Part 2 of Article 278 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For these categories, additional grounds for dismissal can be agreed upon in the employment contract. IMPORTANT! Bringing employees to types of disciplinary liability that are not enshrined in legislative and by-laws is not allowed (Part 4 of Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The employer should assume how this or that type of punishment will affect the production process. There is no need to punish employees for the slightest insignificant offense. Being a couple of minutes late is a reason to express dissatisfaction, but not so significant as to issue an official reprimand.
As a result, an employer who abuses penalties develops a bad reputation in the labor market, and it becomes increasingly difficult for him to find new employees. Disciplinary action affects both the employee and the organization. Employees should understand that such measures are often forced and almost always temporary. Date of publication: November 26, 2015 Complain and discuss on the website Distribute the information on social networks, maybe it will help someone: Similar articles
- The employer does not pay wages, what should I do?
- Who pays for sick leave and according to what documents?
- Amount of maternity benefit and processing sequence
- Forced to resign - what to do in this situation?
Authorized persons
The head of the enterprise has the right to decide on the application of penalties for violation of discipline. But an organization may have a practice of redistributing powers among officials at different levels. It is fixed by local regulations, such as:
- manager's order;
- job description;
- internal labor regulations.
Thus, the head of a department may have the authority to issue comments and reprimands to employees of his department. In this case, the director of the representative office, who has the appropriate power of attorney, may be vested with full disciplinary powers up to and including termination of the contract with the specialist who committed the offense.
In what cases is it possible
Article 192 of the Labor Code establishes that the employer has the right to punish employees who do not perform or incorrectly perform their job duties. They must be recorded in the internal documents of the organization: job description, employment contract or local regulations of the employer.
The employee is required to familiarize himself with the documents, he puts his signature on each of them. Only if the employee does not perform labor functions that he knows about, the employer will be able to apply a penalty.
For example, for disobedience to the orders of the manager, failure to fulfill duties, tardiness and other violations of labor discipline, etc.
As a general rule, the employer is obliged to take into account the gravity of the offense and the circumstances under which the violation was committed before holding the employee accountable.
If an employer decides to fire an employee, the employment relationship can be terminated in the following cases:
- did not show up for work or was late for 4 or more hours without good reason, regardless of the length of the shift;
- if the employee is outside the workplace without good reason;
- if the employee decides to terminate the employment contract with the employer without following the procedure for terminating the employment relationship. First you need to warn the employer, then work for 2 weeks, and then quit;
- the employee left the workplace without a good reason and without notifying the boss, employer or other employees;
- when an employee goes on vacation without permission or uses time off without the consent of the employer.
Application procedure
Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation clearly establishes the procedure for applying disciplinary sanctions. Thus, it is prohibited to punish an employee for one offense with several penalties at once. The manager should choose a certain preventive measure and issue an order based on it. Sometimes, before making a decision on the guilt of an employee, it is necessary to conduct a commission investigation, but usually written evidence in the form of memos and witness statements is sufficient.
This is also important to know:
How to file a claim for recovery of wages
At the same time, it is necessary to bring the guilty person to financial or civil liability if the violation he committed resulted in damage to the property of the organization, colleagues or third parties. In this case, it is important to comply with all rules and deadlines established by law.
In addition, the employer can apply material penalties to the employee along with non-material penalties. For example, an employee can be reprimanded and deprived of bonuses for the period during which he committed a violation of discipline.
Timing of imposition
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
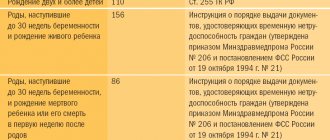
The deadlines for imposing penalties are also specified in Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Disciplinary punishment may be imposed no later than one month from the moment the offense was discovered. But you need to take into account that the following are excluded from this period:
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
- employee days of incapacity;
- annual leave;
- time spent on the procedure for agreeing on a penalty measure with the trade union;
- period of criminal proceedings.
It should be remembered that there are deadlines after which the issuance of a penalty is considered illegal. So, you cannot punish an employee if:
- 6 months have passed since the date of the disciplinary violation;
- More than 2 years have passed since the misconduct revealed as a result of an inspection or audit.
Compliance with deadlines in the matter of sentencing is very important. Any deviation from the norms established by law is grounds for challenging the penalty.
Explanation of the guilty employee
To find out the essence of an employee’s misconduct, the manager needs to take a written explanation from him. In the document, the specialist must describe the reasons for his behavior and the circumstances under which the offense was committed.
If the guilty person refuses to provide an explanatory statement, this should not be regarded as a new violation of discipline. The employee’s refusal to write a document within two working days must be reflected in a special act. When drawing up the act, you must indicate the date, place and reason for its preparation. In addition, you should list the witnesses who were present when the specialist was asked to write an explanation, but he refused. The act must be signed by the witnesses indicated in it and a person authorized by the employer.
An employee’s refusal to provide an explanation is not an obstacle to prosecution. Any evidence that the offense was committed by this particular person, as well as an act of refusal to explain, are considered sufficient grounds for imposing a penalty.
Order of punishment
There is no established sample order for disciplinary punishment in the legislation. However, there is a list of information that must be included in this document:
- name of the enterprise;
- number, date and title of the document;
- reason for compilation;
- description of the violation;
- article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in accordance with which the employee was punished;
- surname, name, patronymic of the person responsible for execution;
- director's signature;
- signature of the offending employee;
- Stamp of the company.
This is also important to know:
How is the average salary collected during forced absence?
The rules for drawing up a document on disciplinary responsibility must be followed exactly, especially if the dismissal of an employee is chosen as a sanction. In the comments to Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation of 2021 contains information that the employee must be familiar with the order within three days from the date of publication of the document. In this case, the employee must confirm his/her familiarity with the order by signing it. If the specialist refuses to sign, then an act should be drawn up, which in form and content is similar to the document refusing to give an explanation.
Sample order for disciplinary action
How to cancel a foreclosure early voluntarily
Current legislation leaves the employing company the right to remove punishment from an employee ahead of schedule, i.e. before the expiration of 12 months from the date of its establishment. After this procedure, the citizen is considered to have committed no offenses. Its initiator is:
- specialist guidance;
- punished employee;
- trade union structure operating in the company.
There are the following reasons for reducing the validity period of a reprimand or reprimand:
- no violations on the part of the offending specialist;
- high results of his work, which caused an increase in the performance of the department or the company as a whole;
- personal beliefs of management regarding a particular employee;
- doubts about the legality of imposing a penalty (for example, its inconsistency with the severity of the offense).
To remove punishment from a citizen ahead of schedule, a written document from the initiator of the procedure is required:
- memo from the specialist’s immediate superior;
- a written request from the employee himself;
- union petition.
If management is ready to lift the penalties, the document is transferred to the personnel department, and an order is issued on its basis. It is prepared in free form; the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a unified form. The following information is indicated:
- number and date of the order according to the numbering system adopted by the company;
- place of its publication;
- name of the hiring company;
- Full name and position of the employee;
- number and date of the order that previously imposed the penalty;
- reasons for punishing the employee;
- reasons for early removal of foreclosure;
- link to the supporting document (for example, a memo from the employee’s immediate supervisor).
The completed order is certified by a handwritten visa from the head of the organization. The document is given to the employee for review, who confirms reading with a signature.
Information that the period for imposing a disciplinary sanction was reduced by a decision of management must be entered into the organization’s internal database, maintained by representatives of the HR department. It is issued in paper or electronic form.
Systematic violation of labor discipline is recognized as grounds for dismissal of a citizen at the initiative of the employer. If an employee from whom the penalty was lifted early commits a violation again in the near future, it will be considered the first, i.e. management will not be able to terminate the contract on the basis of systematic non-compliance with internal regulations until another, second case is recorded.
What period is established for bringing an employee to justice under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
Disciplinary liability has a statute of limitations. Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation explains in great detail the actions of the employee and the employer regarding this difficult issue.
From the date of discovery of an illegal or violating labor discipline action, the statute of limitations of no more than a month must pass before the application of a disciplinary sanction. Otherwise, the employer will remain “out of business” and will not be able to punish the culprit.
There is also such a concept in the law as “the day the offense was committed.”
A disciplinary sanction can be applied no later than six months after the day the offense was committed, otherwise it cannot be imposed on the employee.
Thus, disciplinary liability is applied no later than 1 month from the date of discovery of the disciplinary offense and no later than 6 months from the date of its commission.
At the same time, if a person is “caught red-handed” during an inspection or audit, the employer has the right to apply punishment within a period of no later than two years after the commission of the offense.
If the employee worked conscientiously throughout the year after the penalty was imposed and did not make previous mistakes, the penalty will be lifted automatically.
When a person steps on the same “rake” again, the disciplinary process begins again against him, and the period for “automatic withdrawal” opens again - from the date of the new order for collection.
You can reduce the statute of limitations for disciplinary liability by making a request to your employer.
Sometimes the manager himself goes to meet the guilty employee halfway, relieving him of the burden of responsibility.
Important
If an employee has committed one offense, then the employer has the right to impose only one penalty on him for it.
When the time of application of punishment for a misdemeanor changes
The statute of limitations for disciplinary action is extended if the person is on sick leave or on vacation.
The concept of “vacation” in this case should be understood as all leaves regulated by law: annual, for study, without pay.
This is also important to know:
What compensation is paid for delayed vacation pay?
The fact is that there is a certain algorithm for bringing an employee to disciplinary liability and imposing penalties on him, according to which a corresponding order is issued: the offending employee must familiarize himself with this document personally.
A similar scheme also applies in cases where time is needed to take into account the opinions of the representative body of workers in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 82 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
According to Part 6 of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is given a period of three days to familiarize himself with the boss’s order to impose a penalty, and the document must be signed.
This possibility is excluded if the person is on vacation or has issued a certificate of incapacity for work. In this case, he can familiarize himself with the order on the first day of going to work.
The employee may refuse to sign the document. Then, in the presence of witnesses, a corresponding act of refusal is drawn up.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
The act must indicate the date, place, reason for drawing up, and list the witnesses who were present during the conversation about the proposal to indicate the reasons for this decision.
Controversial situations
The most difficult thing to apply a disciplinary sanction is absenteeism.
A person may be absent from work for several days, but he does not answer calls or report his whereabouts.
Naturally, the organization suffers large losses, and the employer cannot solve the problem because it does not know what the reasons for the employee’s absence are.
In this case, it is necessary to send a notification letter to the address where the employee lives, which clearly states that without explanation and in case of failure to appear before a certain time, sanctions will be applied to the culprit, including termination of the employment contract.
A new disciplinary sanction can be applied in the case of a continuing misconduct, when the employee continues to commit not similar, but identical violations. If a person makes the same mistake over and over again, the employer has the right to subject him to a new penalty.
Documenting
Taking into account the above procedure, when bringing an employee to disciplinary liability, the employer must prepare and store the following documents:
- Resolution or act of the commission to investigate the circumstances of the incident (if one operated at the enterprise).
- Requirement to provide written explanations from the employee.
- Written explanatory note or act of refusal to give explanations.
- Order to impose a disciplinary sanction.
- Certificate of refusal to familiarize yourself with the order (if applicable).
Proper documentation of the committed offense and the imposition of penalties makes it possible to record the legality of the application of punishment.
It is worth noting that the employee is a full-fledged subject of this procedure and has the right to familiarize himself with all documents that are drawn up during disciplinary proceedings. Failure by the employer to provide information on the case is a violation of labor legislation. In complex cases, the employee has the right to demand an audit or an independent audit, based on the results of which it can be concluded that he is at fault.
An employee can also involve external specialists or a representative of a trade union organization for consultation.
No later than what period applies
Disciplinary action is applied no later than the employee’s illness on sick leave, and the days it takes for the union to check the situation. The employer does not have the right to apply disciplinary sanctions later than 6 months from the date of the violation.
If the commission finds violations after an audit, revision or verification of the financial activities of employees, the punishment is allowed to be imposed within 2 years from the date of its commission. This time does not include the days required to conduct a criminal case (in extreme cases).
From the date of the offense
The day the act was committed, from which the calculation of 30 days begins, is considered the date on which the employee committed the unlawful act.
The violation may not be recorded on the same day if the employee was not noticed by other employees. However, if the violation is discovered later, the severity of the punishment will be higher.
From the date of discovery
The day of discovery is the date on which it became known that the offense had been committed. It does not matter whether the discoverer has the right to impose disciplinary sanctions.
This is also important to know:
How is downtime due to the employer’s fault paid?
Most often, such an employee is the immediate superior of the offender. For an employee to be punished, it is enough to write a statement to the manager about checking the misconduct.
Another comment on Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. To understand the essence of the employee’s misconduct, the employer must obtain an explanation from him in writing. In the explanation, the employee must indicate the reasons for the offense and the circumstances under which it was committed. The employee may refuse to explain, which should not be considered an independent disciplinary offense, but may nevertheless affect the employer’s assessment of the employee’s personality. If the employee refuses to give an explanation, the employer must draw up a statement of refusal after two working days. This act must indicate the calendar date, place and reason for its preparation, as well as indicate the witnesses present when the employee was asked to provide an explanation and his refusal to do so. The act must be signed by an official of the employer and the witnesses present.
An employee’s refusal to give an explanation cannot be an obstacle to bringing him to disciplinary liability if there is other evidence of an offense (for example, memos from his immediate supervisor) and an act of refusal to give an explanation. They may provide documentary grounds for the application of disciplinary measures.
2. The educational value of a disciplinary sanction is preserved if it is applied directly after the commission of an offense. Therefore, the rule has been established that the penalty must be applied no later than one month from the date of discovery of the offense. The day of detection must be considered the day when the immediate supervisor of the violating employee became aware of it. In cases where there is a question of dismissal of an employee for committing theft (including minor) of someone else’s property at the place of work, embezzlement, intentional destruction or damage, the month period will be calculated from the date the court verdict or the act of the body authorized to do so enters into legal force. application of administrative penalties (for example, resolutions of an official of an internal affairs agency). The monthly period can be increased by:
- he is on vacation;
— necessary to take into account the motivated opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
The time of illness of an employee is understood as a period of temporary incapacity for work. The time spent on vacation should be understood as the periods of all vacations provided by the employer to the employee (including educational, in connection with pregnancy and childbirth, as well as those provided without pay). In accordance with the provisions of Art. 373 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (see commentary to it), upon dismissal for repeated failure by an employee who is a member of a trade union without good reason to fulfill labor duties, if he has a disciplinary sanction (see paragraph 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and commentary to it), the employer is obliged notify the elected body of the primary trade union organization so that the latter can assess the legality and justification of the upcoming dismissal. The elected trade union body, no later than seven working days from the date of receipt of the documents, reviews the submitted documents and communicates in writing to the employer its reasoned opinion on this issue (including the illegality or inappropriateness of dismissal). If you disagree with this opinion of the trade union committee, the employer has the right to terminate the employment contract with the employee no later than one month from the date of receipt of the reasoned opinion of the elected trade union body. This period can no longer be extended while the employee is ill or on vacation.
This tough position of the legislator and the judiciary is due to the need to protect the interests of the parties to the employment contract. Firstly, the effectiveness of any punishment depends on its efficiency and inevitability. Secondly, the employee should not be under the threat of disciplinary sanctions being applied to him for a long time.
This is interesting: Organizational property tax 2021 - how to calculate, declaration, Tax Code of the Russian Federation, calculation, benefits, terms, object of taxation, who is the payer, rate
In any case, disciplinary sanction must be applied no later than six months from the date of the offense, and based on the results of an audit, inspection of financial and economic activities or an audit - no later than two years. These deadlines can be extended only for the duration of the criminal case by the bodies of inquiry and investigation.
3. As a general rule, for each disciplinary offense, the employer can apply only one disciplinary sanction provided for by the Labor Code or the charters and regulations on discipline. Along with this, it is possible and necessary to simultaneously bring the employee to property (material - according to labor law) or civil liability in the event that his misconduct resulted in property damage. In this case, the rules and deadlines provided for by labor and civil legislation must be observed. In addition, along with disciplinary measures, disciplinary measures may be applied to the employee at the same time. For example, an employee may be reprimanded and deprived of a bonus for the period when labor discipline was violated.
4. As a general rule, the head of the organization exercises the full authority to apply disciplinary measures. At the same time, local regulations (orders of the manager, job descriptions or internal labor regulations) can redistribute the competence to bring employees to disciplinary liability between officials of the employer organization at various levels. Thus, the head of a workshop may be authorized to issue comments and reprimands to the workers of the workshop, and the head of a branch or representative office, on the basis of a power of attorney, may have full disciplinary powers, including dismissal of employees for violations of labor discipline. In some cases, the distribution of competence to apply disciplinary measures is carried out centrally. For example, the Charter on the discipline of crews of support vessels of the Navy provides that the commander of the ship (captain) can issue a reprimand, reprimand, severe reprimand and warn about incomplete performance, and an official who has the right to hire can exercise full disciplinary powers , - commander of a formation of ships or a military unit (clauses 15 and 16 of the Charter).
5. The order (instruction) on punishment is announced to the employee no later than three days from the date of publication against signature. This is necessary to confirm that the employee is familiar with the penalty applied to him. To optimize and record this procedure, it is advisable to include a note on the order (instruction) form itself indicating that the employee has familiarized himself with it. If the employee refuses to sign the acknowledgment, then an act is drawn up, similar in form and content to the act of refusal to give an explanation for the commission of a disciplinary offense (see paragraph 1 of the commentary to this article).
6. An employee may not agree with his being brought to disciplinary liability or with the type of penalty applied. In this case, he can appeal the employer’s actions to the state labor inspection authorities or labor dispute resolution authorities.
In accordance with the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 357 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (see commentary to it) in the event of an appeal by a trade union body, an employee or another person to the state labor inspectorate on an issue that is being considered by the relevant body for consideration of an individual or collective labor dispute (with the exception of claims accepted for consideration by the court, or issues on which there is a court decision), the state labor inspector, upon identifying an obvious violation of labor legislation or other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, has the right to issue an order to the employer that is subject to mandatory execution. This order may be appealed in court within ten days from the date of its receipt by the employer or his representative. Moreover, in accordance with the provisions of Art. 23.12 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses The Federal Labor Inspectorate and state labor inspectorates subordinate to it are vested with the right to consider cases of violations of labor legislation and bring guilty employer officials to administrative responsibility.
Courts of general jurisdiction consider labor disputes related to bringing workers to disciplinary liability, both at first instance and by appealing decisions of the labor dispute commission and magistrates. In cases involving applications for reinstatement of an employee at work, courts of general jurisdiction are necessarily the first instance. Based on the results of the consideration of the case, the court makes a decision or issues a court order. In accordance with the provisions of Art. 211 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, a court decision or court order is subject to immediate execution if it is made on an application for payment of wages to an employee for three months and reinstatement at work.
Methods of challenging
When an employer has violated the procedure or deadlines for bringing to responsibility, the employee can appeal the imposed punishment. It should be borne in mind that the manager does not have the right to impose a penalty without requiring an explanatory note from the employee. It is also impossible to apply disciplinary measures if an employee was absent from work due to illness, as evidenced by a certificate of incapacity for work. It is not allowed to impose several punishments for one offense. In addition, the specialist may not agree with the fact of being held liable or with the type of penalty.
The employee is given three months from the date of the sanctions to appeal the employer’s actions, but if the person was fired, then the period is one month. To challenge a punishment order, you can file a complaint with the state labor inspectorate, a labor dispute commission, or file a claim with the judicial authorities.
If an employee goes to court, a judicial investigation will be conducted, following which the government agency will make a decision in favor of the plaintiff or his employer. If the court takes the employee’s side, the employer will be obliged to compensate the employee for all expenses, cancel the punishment, and in case of dismissal, reinstate the plaintiff in his position.
Order to impose disciplinary liability
An order to impose a disciplinary sanction can be issued only in cases where the employee’s guilt is fully proven.
If a disciplinary sanction in the form of a reprimand or reprimand, then the order for disciplinary action is drawn up in any form.
After issuing an order to impose a disciplinary sanction, the employee must be familiarized with it within 3 days. If he refuses to familiarize himself, then a corresponding act must be drawn up about this. Disciplinary action will be imposed in any case. This period of time does not include the period when the employee was absent from service.
If the employer does not comply with this deadline, the employee has the right to appeal the imposition of a disciplinary sanction .
Recording a violation of labor discipline by an employee in the form of a punishment order is necessary for the employer. After all, if there are several outstanding disciplinary penalties, the employee may be dismissed under clause 5, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (an employee repeatedly fails to perform job duties without serious reasons, subject to disciplinary action ).
Removal of responsibility
Disciplinary liability, in addition to dismissal, has a certain duration, which should not go beyond the boundaries of the labor relationship. The law establishes that if an employee has not violated labor discipline within one year from the date of receiving the punishment, then he is considered exempt from punishment.
In addition, the Labor Code provides for the removal of disciplinary liability ahead of schedule under the following circumstances:
- desire of the leader;
- employee statement;
- boss's request;
- request of the representative body.
If the employee has managed to restore his reputation, then release from punishment is quite possible. It is issued by a special order.
Disciplinary sanctions are a way of influencing employees who violate labor regulations and are regulated by Art. 193 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Comments to it with changes for 2021 allow both heads of organizations and employees of personnel services to hold guilty employees accountable in strict accordance with the law.
What is a disciplinary offense by an employee?
This is a violation of labor procedures, rules and norms of behavior in the workplace, and not only in the performance of official duties, which entailed damage and loss for the enterprise. Characteristic of labor misconduct are cause-and-effect relationships. The employee must have explanatory conversations about the essence of his offense and the consequences for the company.
Actions that violate labor rules include:
- Systematic disregard of the work schedule: unauthorized absence (absenteeism) and absence from the workplace, tardiness, frequent breaks for personal needs;
- Refusal to perform work;
- Refusal to undergo a medical examination and training program when this is a condition for admission to work;
- Providing false information and documents during employment;
- Being drunk at work;
- Amoral behavior;
- Disclosure of official or commercial secrets.
What disciplinary sanctions can be applied to an employee for a disciplinary offense?
If detected, what disciplinary sanctions does the employer have the right to apply to the offender for a disciplinary offense?
The company may apply the following measures to an employee who has committed a crime:
- Comment;
- Rebuke;
- Dismissal under an article with a corresponding entry in the work book;
- Fine – if the employee is financially responsible or if the employment contract specifies penalties;
- Administrative or criminal liability is possible based on a court decision.
This is interesting: How to register an easement for access to a site in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation?
Before deciding on punishment, the company is obliged to request a written explanation from the culprit. The request is made through an act. The employee must sign for its receipt and provide explanations within the specified time frame. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, two days are provided for this. Refusal to accept the act and provide explanations is also considered a violation of labor standards and evasion of responsibility.
Based on such employee behavior, the company can significantly increase the severity of the punishment. The absence of explanations from the perpetrator, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is not a reason for canceling the punishment.
Within what period from the date of discovery of the misconduct can a disciplinary sanction be applied?
The period for applying the penalty is 30 calendar days, excluding the time the culprit is absent from the workplace and the time it takes to make a decision. After audit, financial and other verification - no later than 2 days.
Punishment cannot be applied after six months from the date of its commission. The decision on the penalty is issued to the employee no later than three days from the date of its issuance in writing and signed. His refusal to accept the notification is documented in an act.
Explanation from the employee who committed the disciplinary offense
The offender must provide an explanation of the illegal labor action committed in writing within two days.
Requesting an explanation from the worker is preceded by two reports:
- The leader of the offender;
- Head of HR.
Next, an act of requesting an explanation is drawn up, the receipt of which must be signed by the culprit.
Time limits for imposing a disciplinary sanction under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and validity period
The internal rules of the organization and the implementation of planned indicators are the main responsibilities of the employee. Obviously, if the norms established by the employer are violated, management has the right to impose a disciplinary sanction against the culprit (in this case, you must follow the procedure specified in Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: more details on this issue in the article at the link).
This is important to know: Sample application to bailiffs for collection of arrears of alimony
Such measures are aimed at punishing the employee and can lead to his dismissal. At the same time, one of the conditions for imposing a disciplinary sanction is compliance with the time limit (this is relevant for all types of disciplinary sanctions).