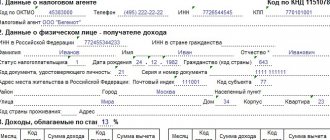
What taxes are imposed on compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal? This question interests not only employers, but also employees. Citizens who officially work at enterprises have the right to go on paid leave every year. Its duration depends on the specialty and type of work.
When an employee is dismissed, the organization’s accounting department is obliged to assign compensation in the form of a sum of money for unused vacation days or send him on vacation with subsequent dismissal, in accordance with Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, having paid all the necessary contributions and taxes.
Basic principles
The duration of leave is determined on the basis of current legislation and the terms of the concluded employment contract. Most often, vacation lasts 28 calendar days. The employer can also provide additional days of rest to an employee working in a certain position, in proportion to the time worked under certain conditions.
The calculation of the compensation amount for vacation not taken is carried out similarly to the calculation of vacation pay. It is based on unused vacation days and the average salary of the resigning employee. Compensation is the income of an individual and is therefore subject to taxes. The transfer of personal income tax to the budget is carried out by the employer.
Insurance premiums
The topic of insurance premiums, which are paid from employees’ salaries, should also be touched upon. When an employer enters into an employment contract with an employee, he must withhold a certain amount from the employee's salary. Such deductions are called insurance premiums. This is made to deposit this amount into funds such as:
- social insurance fund;
- Pension Fund;
- health insurance fund.
From the last salary of the resigning employee, a certain amount is also withheld and sent to these funds in the form of insurance premiums.
As for severance pay, it is not subject to insurance contributions (unless, of course, the established amount is exceeded - 3 months or 6 months (if this is the Far North) salary).
How are compensation payments for unused vacation days documented?
When calculating days to determine the amount of compensation, the accountant must take into account all types of vacations not taken by the employee. As a rule, payment for them is made:
- without an application, special instructions from management, on the basis of an order confirming the fact of dismissal of an employee, and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- when making a payment using form T61. A special form is filled out by personnel officers and accounting department indicating a detailed calculation of the amount to be paid and the accrual of personal income tax;
- minus income taxes withheld from the worker's income.
The final settlement with the employee upon his dismissal is carried out on the last day of work. When calculating accounting, it is necessary to correctly determine the amount of tax and Social Insurance contributions based on the tax base.
Calculation of taxes when issuing compensation payments for vacation upon dismissal
According to Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, all tax fees transferred to the budget must be paid not at the end of the working month, as when calculating salary, but on the day of transfer of compensation for leave upon dismissal. In this case, the date of receipt of the worker’s income will be considered the day:
- transferring funds to the bank to his account;
- payment of income upon dismissal from the employing organization's cash desk;
- receiving money at the cash desk of a banking institution from the employer’s account according to a payment order.
Based on all of the above, the employing organization must pay taxes and contributions on the day the compensation is paid.
When issuing compensation payments to a former employee for a vacation not taken, the employer is required to pay taxes no later than the day following the day of dismissal.
The concept of personal income tax
Personal income tax refers to a type of direct taxes that every person is obliged to transfer to the federal budget from the profit he receives.
This also applies to wages, since they are remuneration for work performed (the profit of an individual).
Mandatory tax payers are all individuals:
- residents of the Russian Federation;
- non-residents - persons who stayed within the territory of the Russian Federation for at least six months (183 days) during the year (Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A person who left the Russian Federation for less than 183 days continues to have resident status.
Residents also include the following categories of individuals, regardless of the time they spent on the territory of the Russian Federation:
- military personnel;
- government service employees;
- employees of self-government bodies in the regions.
Depending on the status of an individual, income received from various sources is taxed.
- For residents of the Russian Federation, personal income tax is calculated on profits received from sources located both within the state and abroad.
- For non-resident persons, tax is levied only on the profit that was received from sources located on the territory of the Russian Federation (according to Articles 208, 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is worth paying attention to the interest rate that is used when calculating income tax:
- residents are required to remit personal income tax in the amount of 13% of the profit received;
- non-residents are taxed at a rate of 30% on profits received as a result of employment.
What taxes are imposed on compensation payments upon dismissal?
In the event that a worker leaves his position this year immediately after vacation, compensation for unused vacation days will not be accrued to him. Accordingly, there is no need to pay taxes. In all other situations, the accounting department calculates not only the main type of paid leave, but also the additional one provided to employees working in certain positions. These include, for example, workers working in hazardous industries. They are entitled to additional days of paid leave. In accordance with this, upon dismissal, compensation is also accrued.
If an employee is transferred to another branch through dismissal, he is also required to receive compensation for vacation pay with the withholding of all necessary taxes and fees.
What you need to know about severance pay?
Severance pay is a type of financial assistance for a dismissed employee until he finds a new job.
Since in this case we mean termination of the employment contract through the fault of the employer (and on the grounds established by Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the company is obliged to pay the employee the amount of compensation.
Upon dismissal by agreement of the parties
The existence of an agreement between the parties indicates that management and the employee agreed on the need to dismiss the latter. In this regard, benefits under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are not paid to the employee. But, as part 4 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states, the employer can include the provision on severance pay in the list of employee rights in other cases, including by agreement of the parties. It is fixed in an employment or collective agreement.
When staffing is reduced
Staff reduction is a reduction in the number of employees in an organization. In this regard, employees dismissed on this basis are entitled to compensation in the form of severance pay.
The payment amount is:
- average monthly earnings;
- the average salary retained by the employee for the period of employment, but not more than 2 months from the date of termination of the employment contract.
The benefit is calculated in accordance with Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the government act. Equal to several average monthly salaries (usually two).
The average salary is calculated based on the amount of money actually accrued to the employee and data on how much time he worked in the twelve previous calendar months (by these we mean the period from the 1st to the 30th/31st inclusive, and in February - to the 28th/29th). All other forms of payments, regardless of their sources, used by a particular employer are also taken into account.
The law lists payments that cannot be used when calculating average earnings. For example, these include bonuses, sick leave, maternity benefits and other paid days away from work.
The average salary of an employee cannot be less than the minimum subsistence level established by law. Also, this amount does not depend on the age, length of service or qualification level of the citizen.
If an employee has worked for an organization for less than 1 year, to calculate the average salary and benefits, the time during which he was officially on the staff is taken into account. In a situation where a citizen worked for less than a month before the reduction of staff, the tariff rate or salary is used for calculation.
Liquidation of the enterprise
Russian legislation understands liquidation as a forced or voluntary, complete cessation of the activities of any organization (manufacturing enterprise or company).
With this form of closure of a legal entity, its rights and obligations are not transferred to another organization, therefore all employees with whom it has an employment contract are subject to dismissal with the payment of appropriate compensation. One of them is also a benefit.
The most important obligation of the employer during liquidation is to promptly notify the employee of dismissal in writing, 2 months before the upcoming termination of activity.
Severance pay during liquidation is calculated in the same way as in the case of staff reduction. Also, the average monthly earnings for 2 months are taken as a basis, which is the total amount of the benefit. It is assumed that during this period the employee will be looking for work.
Funds are disbursed on the day the employment relationship ends, when full payment is ready. Funds to employees are paid from the employer's budget, which includes a certain amount to be spent in the event of liquidation of the company.
Payment of the total amount of severance pay is carried out in the following order:
- benefits on the day of dismissal;
- compensation payment after the expiration of the first month following dismissal;
- refund for the second month, which is final.
However, according to labor legislation, cases arise when an employee can receive payment even after two months have passed from the date of dismissal. If he is registered with the employment center within 2 weeks of losing his job, he can extend the period of detention for another 1 month.
This is possible if no suitable position has been found for the employee within 2 months. Severance pay due to liquidation does not affect the assignment of unemployment benefits.
Sometimes it is possible to reduce the amount of compensation. For example, this applies to those employees who are employed in seasonal jobs. They are given severance pay equal to two weeks' average earnings.
Conscription
If the cancellation of an employee’s employment contract is related to his conscription into military or alternative civilian service, he is entitled to severance pay in the amount of the average salary for 2 weeks. To be eligible for this payment, the conscript must present at his place of work a summons to appear at the military registration and enlistment office to be sent to serve.
Based on this document, an order is issued to terminate the employment contract under clause 1 of part 1 of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. By analogy with the situations described above, the future serviceman receives the severance pay due to him on the day of dismissal.
If he is absent from the workplace at this time, the corresponding amounts must be transferred no later than the next day after the dismissed person submits a request for payment.
To establish the average salary, the amount accrued for a regular working day is used in the following cases:
- vacation pay;
- issuing compensation for vacations that the employee did not take;
- other cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with the exception of the situation when the average earnings are determined in relation to an employee for whom summarized recording of working time has been introduced.
Average earnings are calculated according to the rule: the daily payment that an employee receives under normal conditions is multiplied by the number of days (calendar, working) in the period to be calculated.