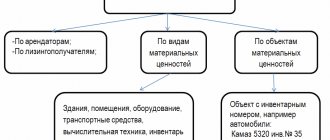
What is account 08 used for in accounting?
08 accounting account is an account designed to accumulate costs for the acquisition or construction of a non-current asset in order to form its initial cost.
At the same time, non-current assets include fixed assets, intangible assets, profitable investments in non-current assets, land plots, and other environmental management facilities.
This account reflects information on the costs of capital new construction, reconstruction, modernization of re-equipment of existing facilities, the cost of acquiring movable and immovable property, land plots, purchasing intangible assets, productive and working livestock included in the main herd, costs of creating perennial plantings.
Reflection of this data on account 08 allows you to generate in a timely manner complete information on all costs incurred, monitor all stages of commissioning of objects, and also establish the initial cost of a non-current asset in accordance with current rules.
On the account, the initial cost of each object is formed on the basis of actual expenses incurred by the company.
Attention! It is important to understand that once an object is put into operation, its value can no longer continue to be taken into account on account 08. For this, the corresponding accounting accounts must be used - 01, 03, 04.
Young animals
Its assessment is carried out at actual cost. Young animals of any type of working and productive livestock that are transferred to the main herd are written off throughout the year from the account. 11 in db sch. 08. In this case, the cost is indicated, which is listed at the beginning of the period, including the planned cost of growth or weight gain from the beginning of the year until the day of transfer. The following is recorded in the records:
Db 01 Kd 08.
At the end of the year, after the reporting calculation is generated, the amount of the difference between the present value of the transferred young animals during the period and the actual cost is additionally written off or reversed from the account. 11 to 08 accounting account. In this case, postings are made with simultaneous clarification of the livestock valuation according to the account. 01.
Account characteristics
The question of which account 08 is active or passive is answered by the Chart of Accounts, which establishes that it is active and is reflected in the balance sheet as part of non-current assets in the first section.
The initial balance in the debit of account 08 shows the cost of expenses incurred for the acquisition and construction of non-current assets that have not yet been put into operation. The debit of the account reflects the costs incurred for the creation or purchase of long-term objects, and the credit must reflect the cost of the property transferred for operation.
The balance at the end of the period shows the amount of costs incurred by the entity for the creation or acquisition of non-current assets that have not yet gone through the commissioning process. It is calculated as the sum of the balance on account 08 at the beginning of the period plus the turnover in the debit of the account and subtracting the credit turnover.
Typical transactions for account 08
Let us indicate the main transactions for account 08:
- Purchasing an OS
| Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| 08 | 60 | OS received (price excluding VAT), expenses for transportation, materials, setup, storage are taken into account |
| 19 | 60 | VAT allocated |
| 68 | 19 | VAT refund claimed |
- Creation of an asset in an economic way
| 08 | 23 | Expenses of auxiliary workshops |
| 08 | 10, 70, 69 | Costs of materials, wages of workers involved in the creation of the asset, and insurance premiums from it |
- Free admission
| 08 | 76 | Free transfer of an OS object |
| 08 | 98-2 | Accepted for accounting as a result of the inventory |
- Contribution as a contribution to the management company
| 08 | 75 | Accepted asset - the founder’s contribution to |
- Equipment to be installed
| 08 | 07 | The equipment is ready for installation |
- Transfer of animals to the main herd
| 08-6 | 11 | Accounting for the cost of grown animals throughout the year |
| 07 | 08-6 | Registration of grown young animals in the main herd |
- Putting the property into operation
| 01, 03, 04 | 08 | Accepted for accounting of fixed assets (income investment, intangible assets) |
What subaccounts are used?
Analytical accounting of unfinished non-current assets is carried out by groups of this property.
The following subaccounts can be opened for account 08:
- “Purchase of land” – to reflect the costs of purchasing land.
- “Purchase of environmental management facilities” – to account for the amount of expenses for the purchase of environmental management facilities.
- “Construction of fixed assets” – to account for the costs of construction of fixed assets. This takes into account the cost of purchased equipment requiring installation, and the costs of this process themselves. Inside the subaccount, analytics can be maintained by cost components (materials, wages, deductions, etc.)
- “Purchase of fixed assets” – to account for the cost of purchasing fixed assets. If the OS does not require installation, then it is taken into account in this subaccount.
- “Purchase of intangible assets” – to account for the costs of purchasing intangible assets.
- “Transfer of young livestock to the main herd” – in livestock farming, when livestock is raised independently by an economic entity.
- “Purchase of adult livestock” - in livestock farming when purchasing adult livestock.
- “Planting and growing perennial plants” - in crop production to account for the costs of growing trees.
- "Purchase of operating systems on lease."
- "Other unfinished investments"
You might be interested in:
Account 71 in accounting: what is it used for, correspondence, subaccounts, main entries
Practical examples of entries for account 08
Using one of the practical examples of this kind of business transactions, we will clearly consider how the 08th position of the balance sheet works.
Let's assume that an agreement was concluded between a certain enterprise and a subcontractor for the construction of a new premises intended for a warehouse. The subcontractor estimated the cost of construction work at RUB 3,250,000. At the same time, the amount of VAT amounted to 125,000 rubles.
According to the terms of the agreement, the company is obliged to make an advance payment of 100%. This condition was met by the customer. After the construction work was completed, the corresponding act was signed. At the same time, the customer’s accounting service made the following accounts:
- Dt 60 – Kt 51 – prepayment in the amount of RUB 3,250,000;
- Dt 08 - Kt 60 - costs for the construction of a warehouse in the amount of 3,125,000 rubles;
- Dt 19 - Kt 60 - accounting for the amount of tax;
- Dt 60 - Kt 60 - offset of the prepayment made in the amount of 3,250,000 rubles;
- Dt 68 - Kt 19 - the amount of tax to be deducted.
Which accounts does it correspond with?
Account 08 can correspond with the following accounts.
From the debit of account 08 to the credit of accounts:
- Account 02 - when calculating depreciation of fixed assets that are used for modernization or creation of other operating systems;
- Account 05 - when calculating depreciation of intangible assets that were used to create other fixed assets or intangible assets;
- Account 07 - regarding the cost of equipment that was transferred for installation at the site;
- Account 10 - regarding the cost of materials that were used for the construction or modernization of the OS facility;
- Count 11 - when transferring young animals to the main herd;
- Account 16 - regarding the deviation in the price of inventories that were used in the creation of the fixed asset;
- Account 19 - when writing off VAT tax, which is not subject to reimbursement from the budget;
- Account 23 - when writing off the costs of auxiliary production to increase the cost of the capital investment object;
- Account 26 - when writing off general business expenses to increase the value of the capital investment object;
- Account 60 - when reflecting non-current assets received from suppliers, reflecting construction costs;
- Account 66 - when calculating interest on short-term loans and credits with the help of which the capital investment object was acquired (until it was accepted for operation);
- Account 67 - when calculating interest on long-term loans and credits with the help of which the capital investment object was acquired (until it was accepted for operation);
- Account 68 - when writing off amounts of non-refundable taxes on a capital investment object;
- Account 69 - when reflecting the accrual of social contributions on the salaries of workers who were involved in work with the object of capital investment;
- Account 70 - when calculating wages to employees who were involved in work with the investment object;
- Account 71 - when writing off expenses for accountable persons for a capital investment object;
- Account 75 - when one of the founders of the capital investment object makes a contribution to the authorized capital;
- Account 76 - when reflecting other services related to the commissioning of a capital investment facility;
- Account 79 - upon receipt or transfer of capital investment objects to the parent organization or branch;
- Account 80 - when transferring a capital investment object as a contribution under a joint activity agreement;
- Account 86 - upon receipt of a capital investment object in the form of investments or financing;
- Account 91 - when capitalizing MTs that were identified as a result of inventory and are intended for use when working with a capital investment object;
- Account 94 - the amounts of previously identified shortages and losses are written off to the capital investment object;
- Account 96 - when creating reserves at the expense of the investment object;
- Account 97 - deferred expenses are written off to the cost of the capital investment object;
- Account 98 - capital investment items received for free are taken into account.
You might be interested in:
Order of payment in a payment order: what to put in field 21 in 2021
According to the credit of the account, it corresponds with the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 01 - when commissioning a capital investment as an OS object;
- Account 03 – when commissioning a capital investment that is supposed to be rented out;
- Account 04 – when commissioning a capital investment as an intangible asset;
- Account 76 - when writing off part of the cost of capital investment as insurance compensation, when making claims to contractors, etc.
- Account 79 – upon receipt or transfer of capital investment objects to the parent organization or branch;
- Account 80 - upon return of the investment object upon termination of the joint activity agreement;
- Account 91 - when writing off losses, selling part of the capital investment, disposal, etc.
- Account 94 - identified shortfalls or losses in investments in assets are written off;
- Account 99 - writing off part of the cost of the investment object as a loss (as a result of an emergency, natural disaster, etc.)
Features of record generation
When purchasing an OS, logically, the following wiring is assumed:
Db 01 (03, 04) Kd 60 (76, etc.)
However, the funds spent on the purchase must be transferred in transit through the 08 accounting account. In this case, it will have no balance, and it will become a screen article. The specificity of the account is also due to the fact that capital investments extend over time. In particular, this occurs during the construction process. In this case, accounting account 08 becomes material. In this case, unfinished construction can either be sold or given away free of charge. The new Plan has significantly expanded the functions of this article. Currently, it is used not only to summarize information about the company's actual investments, but also to reflect the amount of property received as an investment in capital and free of charge.
Postings in accounting
Let's look at typical accounting entries that use account 08.
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| Acquisition of fixed assets | ||
| 08/4 | 60 | OS object purchased |
| 19 | 60 | The VAT tax on the asset is reflected |
| 68 | 19 | VAT tax credited |
| 08/4 | 76 | Commissioning work completed |
| 01 | 08/4 | The OS object is put into operation |
| Creating an OS in-house | ||
| 10 | 60 | Materials for creating an OS have been purchased |
| 19 | 60 | VAT reflected on the material |
| 68 | 19 | VAT tax credited |
| 08/3 | 10 | Materials written off for the creation of the OS |
| 08/3 | 70 | The salaries of employees involved in the creation of the operating system have been calculated |
| 08/3 | 69 | Salary contributions have been calculated |
| 08/3 | 23, 26 | The costs of auxiliary and other types of production were written off |
| 01 | 08/3 | The created OS was put into operation |
| Creation of OS by contract method | ||
| 08/3 | 60, 76 | The services of a contractor for the construction of an environmental facility are reflected |
| 19 | 60, 76 | VAT on the contractor's work is reflected |
| 08/3 | 07 | The cost of equipment given to the contractor for installation is reflected |
| 08/3 | 70 | The salaries of the workers who brought the facility to a condition suitable for use are reflected. |
| 08/3 | 69 | Social contributions on salaries have been calculated |
| 08/3 | 23, 26 | Other production costs reflected |
| 01 | 08/3 | The completed OS object has been accepted for operation |
| 68 | 19 | VAT tax credited |
How to work with account 08 chart of accounts
Accounting Account 08 is a synthetic account that is needed to reflect information on the formation of the initial value of non-current assets.
Legislators allow the initial cost of property to include not only the cost of its acquisition, but also some additional expenses that are associated with the acquisition of this property. Let's figure out how the initial cost of an asset is formed.
April 1, 2021 Evdokimova Natalya
According to Order No. 94n, to form the initial cost of a non-current asset, it is necessary to use accounting account 08. This account allows you to accumulate all the costs that were associated with the creation, acquisition and development of new property of the institution.
Costs can be grouped into five main sections:
- Fixed assets of the organization. Such objects include not only fixed assets on which depreciation is charged (buildings, transport, equipment), but also non-depreciable assets. Which? For example, land plots, subsoil.
- Intangible assets of an enterprise (patents, rights, intellectual property, all types of assets that do not have a physical shell, but generate profit and are used in business for more than 12 months).
- R&D results (relevant for research activities).
- Increasing the number of livestock (for agricultural enterprises).
- Development of natural resources. For example, which ones? Non-current exploration assets, exploration and exploration activities of the mining industry).
The first two groups are used almost everywhere, since fixed assets and intangible property are objects without which an economic entity will not be able to conduct its activities or it will be significantly difficult. The other three groups are less common. They are relevant for narrow specializations and types of economic activity.
Subaccounts 08 accounts
The current accounting regulations provide for the opening of additional sub-accounts, which will allow for more detailed systematization and structuring of information on investments in non-current assets of the enterprise.
You can open separate sub-accounts for account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”.
Number and name of the subaccount to account 08What we include in the calculation
| 08-01 “Purchase of land” | We reflect the costs of the enterprise associated with the acquisition of land plots. |
| 08-02 “Purchase of natural resources” | We generate information on the acquisition of environmental management facilities, with the exception of land plots. |
| 08-03 “Construction of fixed assets” | On account 08-03 we accumulate information about the costs of an economic entity for the construction of fixed assets. |
| 08-04 “Acquisition of fixed assets” | We summarize the costs and expenses of the enterprise aimed at purchasing buildings, structures, equipment, transport and other fixed assets. |
| 08-05 “Acquisition of intangible assets” | We record information about the company’s expenses on the purchase of intangible property. |
| 08-06 “Transfer of young animals to the main herd” | Declaration of costs for raising young productive and working livestock in the organization, transferred to the main herd. |
| 08-07 “Acquisition of adult animals” | We reflect the cost of adult and working livestock purchased for the main herd. We also include expenses for shipping animals. |
| 08-08 “Performing research, development and technological work”, etc. | We reflect information on the expenses of an economic entity for conducting R&D activities and other types of technological research, research and development. |
The organization independently decides whether to open additional subaccounts or not. This decision must be justified in accounting policies. But maintaining separate analytics in the context of fixed assets and intangible property is mandatory.
Methods of receiving property
The volume of non-current assets of an enterprise is characterized not only by the property status of the economic entity, but is also used to analyze production capacity, profitability and financial stability in general. Consequently, the organization is directly interested in strengthening and expanding its property base. Moreover, acquiring property yourself is not the only way to strengthen logistics.
The following methods of receiving property are distinguished:
- purchase or acquisition;
- free admission;
- creation in-house;
- creation by third parties;
- mixed method.
Depending on the method of receipt of the asset, the composition of costs included in the initial cost of the property is determined.
Formation of initial cost
The procedure for forming the initial cost of an asset is a list of costs, which is reflected in account 08 in accounting. The current PBU standards determine a specific list of institution costs that can be included in the initial cost of an asset. That is, they are reflected on account 08. The composition of such costs depends on the method of receipt of the asset into the ownership of the organization.
Here is a general list of the enterprise’s expenses for the receipt of property, which is taken into account in account 08 in accounting:
- The accounting value of an asset (property, fixed assets, intangible assets, R&D objects), that is, the price that was directly transferred to the seller. Including customs duties, commission fees, taxes owed and extra charges included in the price and paid to the seller. VAT and other non-refundable taxes are also included. The amounts of refundable deductions, tax bonuses and benefits should be deducted from the price when determining the initial cost.
- The fair value of the asset as of the date of its receipt in the event of a gratuitous transfer of property into the ownership of an economic entity. For example, receipt of fixed assets from the founder or investor.
- Other expenses associated with the acquisition, creation, development of a new facility (transportation, installation, consultations, etc.).
Including:
- expenses for remuneration of personnel involved in the creation of property;
- insurance premiums accrued for wages;
- the cost of work to create assets, paid under contracts to third-party organizations, individual entrepreneurs and individuals (for example, remuneration under a construction contract);
- state duties and other payments to the budget related to the creation, acquisition or production of a non-current asset (SAI);
- payment of intermediary services paid to third parties;
- costs of shipment, transportation, delivery, assembly, preparation, installation and other actions to bring the SAI into a condition suitable for operation;
- expenses for carrying out control activities to verify the readiness and proper functioning of the SAI;
- payment for materials, components and raw materials used to create or manufacture the VOA;
- payment of interest on installment payments to pay the cost of the asset;
- information, consulting and other support services;
- other types of services related to the creation or acquisition of objects, for example, payment for state construction supervision.
These costs of the enterprise, and along with them the accounting value, are reflected in the debit of the account. That is, debit turnover forms the initial cost.
Credit turnover is formed immediately at the time the asset is accepted for accounting or at the time it is sold by a third-party company. In other words, the initial cost of the property is written off to a corresponding accounting account.
For example, on the account. 01 “Fixed assets” when accepting fixed assets for accounting.
Interaction with other accounting accounts
Account 08 is often used in the preparation of correspondence with separate accounting accounts. Let's consider controversial situations.
Corresponding account Essence of the transaction
| Account 07 “Equipment for installation” | Account 07 reflects information about the cost of equipment that cannot be operated without special installation or assembly work. To recognize such expenses as part of the initial cost of property, documentation is required. Form OS-15 or another format approved by the organization is used. Posting:
|
| Account 20 "Main production" | Account 20 is used in correspondence with account 08 if the organization decided to use part of its independently produced products in its activities. Then the finished product at its actual cost is credited to account 08, from which the object will be put into operation as an SAI produced on its own. Unfinished SAI objects for your own needs can be written off by reverse posting:
|
| Account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” | Used to reflect various types of costs that should be hidden in the original cost of the property. For example, make a wiring:
|
| Account 79 “Intra-economic settlements” | Use account. 79 to reflect calculations within the organization. For example, between structural divisions allocated to a separate independent balance sheet. Posting: Or:
|
| Account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” | On the account 94 includes losses and shortages in relation to property, regardless of the perpetrators. Postings are made in the following order:
|
Depreciation of investments in SAI
The question of whether depreciation is calculated from the 08th account remains relevant to this day. Until the object is accepted for accounting, depreciation is not accrued.
Why? In accordance with Instruction No. 94n, depreciation on fixed assets and intangible assets is accrued only from the month following the month in which the organization accepted the property for accounting.
Consequently, depreciation cannot be charged on objects that are at the stage of investment in SAI.
After accepting the property for accounting, depreciation should be calculated using the method that was enshrined in the accounting policy of the institution.
Accounting entries for account 08
OperationDebitCredit
| Write-off of material costs for construction or development of an object | 08 | 10 |
| Reflects the cost of a property or intangible asset paid to the seller (price) | 60 | |
| Wages and insurance premiums were calculated for the main specialists involved in the creation of non-current assets | 7069 | |
| The OS object was received free of charge from a third party | 98 | |
| Intangible assets received from a superior founder as a contribution to the authorized capital of a non-profit organization | 75 | |
| Depreciation on fixed assets of workshops and production facilities used in the creation of property is reflected | 02 | |
| OS accepted for accounting | 01 | 08 |
| The intangible asset is accepted for accounting | 04 | |
| Property not accepted for accounting was sold externally | 91 | |
| The shortage of investments in non-current assets identified during an inventory audit is reflected | 94 |
The article was prepared using materials from ConsultantPlus. Get access
Source: https://gosuchetnik.ru/bukhgalteriya/kak-rabotat-so-schetom-08-plana-schetov