Current labor legislation defines working time as part of the calendar time spent by employees performing their direct duties. These responsibilities may consist, for example, of performing certain work, producing goods or providing services to citizens. In order to use working time as efficiently as possible, every employer needs to know about such a concept as working time balance.
Working time balance is a whole set of specific indicators that characterize the efficiency of employees’ use of the work process. In fact, a working time balance can be described as a special document that includes all the important information regarding the hourly costs regularly incurred by employees.
The above document can be drawn up by absolutely any employer who wishes to receive the most detailed information regarding the competent use of the working time provided to them by its employees. The formation of a balance can be carried out both in relation to the entire organization and in relation to individual structural divisions. The latter option usually helps to achieve more accurate results.
The main purpose of a work time balance is usually to establish the average number of hours that an employee must work during a certain plan period. When drawing up a balance sheet, the responsible person must take into account the following key indicators:
- Average number of employee attendance days. In this case, the number of days in which the employee was at his workplace and fulfilled his obligations should be taken into account.
- Average duration of one working day for an employee. As is known, employees perform their professional duties during their working hours. However, as practice shows, most functions are performed by employees at a specific time. This is usually followed by a decline in work.
- Duration of the planning period. It represents a certain time period for which the responsible person collects all the necessary indicators.
Working time balance in 2021
Working time balance can be called a special and very effective tool that should be used by every employer without fail. As a rule, responsibilities for working with this document are assigned to employees of the accounting department or personnel department.
The working time balance, as a legal document, has a number of distinctive properties and features. In particular, the approval of this document in our country is carried out officially. For this purpose, the corresponding resolution is issued by the Government of the Russian Federation. It is on this basis that employers can plan their professional activities for the next year. The balance sheet itself is an official summary, which includes the following key indicators:
- The total number of calendar days for each month.
- The total number of working days in each month. To do this, from the first value it is necessary to subtract the number of official days off, as well as public holidays.
- Breakdown of all working days by working hours. At the same time, the Government of the Russian Federation takes into account various work schemes and schedules. For example, 40-hour, 36-hour work week, etc.
After the Government of the Russian Federation issues an official resolution, each employer must take care of approving the working time balance in their organization for 2021. To do this, the authorized person must create the appropriate local acts and other necessary documents. In this case, the director of the enterprise must be guided exclusively by the provisions of Russian legislation, which regulate the establishment of weekends or holidays in the country. The main provisions include the following:
- Art. 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - contains information about official public holidays, which are recognized as days off in our country;
- Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - includes information regarding the procedure for transferring weekends, as well as some other important features on this issue;
- Russian Government Decree No. 1163 sets specific dates for postponing weekends and holidays in 2021.
It should be noted that in a particular organization, the balance of working time should always be formed on an individual basis. The fact is that the content of this document will largely depend on the work schedule at the enterprise, as well as on other important features.
Personnel economics
Working time management
Russian labor legislation on working time
Working time refers to the period during which an employee, in accordance with the law, internal regulations of the organization and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties.
This period is measured by the length of the working day, working week, working month, working year and is usually regulated by national legislation, which determines its limit for a calendar period, which is most often a week.
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week. It is reduced for certain categories of personnel (minors, disabled people, as well as persons employed in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, teaching, medical and some other categories of workers).
By agreement between the employee and the employer, a part-time or part-time work week may be established with payment in proportion to the time worked or depending on the amount of work performed (with reduced working hours, wages are paid in full).
The time from 22:00 to 6:00 is considered night time, which implies a reduction in the duration of work (shift) by one hour (except for persons who have a reduced working time, as well as for workers hired specifically to work at night, unless otherwise provided by the collective agreement).
Pregnant women and minors are not allowed to work at night, with the exception of persons involved in the creation and (or) performance of artistic works.
Employment outside the normal working hours (but not more than 16 hours per week) can be at the initiative of both the employee (part-time work) and the employer (overtime).
The working time regime should provide for the length of the working week (five-day with two days off, six-day with one day off, work week with days off on a sliding schedule), work with irregular working hours for certain categories of workers, duration of daily work (shift), time the beginning and end of work, the time of breaks in work, the number of shifts per day, the alternation of working and non-working days.
Irregular working hours are a special work regime, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the normal working hours.
The flexible working time regime means that the beginning, end or total duration of the working day, the place and time of work is determined by agreement of the parties within the framework of the total number of working hours provided for by law for the relevant period.
This mode allows employees to use:
- sliding schedule (it is allowed to change the start and end times of work, but work for 8 hours);
- flexible schedule (work is structured around certain (office) hours in the middle of the day and within the limits established by the manager; employees themselves determine the start and end dates of work in accordance with the operating conditions of transport, child care facilities, etc.); when the employee also determines the period of work in such a mode, we are talking about a flexible cycle;
- very flexible schedule (attendance at specified times is required);
- division of responsibilities of one staff unit between two performers;
- working at non-standard hours (before and after working hours);
- variable working day (it is allowed to change the length of the working day by day of the week within the monthly or weekly norm);
- flexible placement (carrying out duties at home, in the library, etc.).
This mode of work is appropriate for people with mental work, in cases where it is necessary to rationally use limited resources, for example, a computer. But it cannot be used where there is interdependence between large groups of workers, i.e. where control is required.
A flexible schedule reduces turnover and the severity of the transport problem, improves the moral and psychological climate, creates convenience for workers, and simplifies the organization of leisure time.
All this ensures the maximum combination of the interests of workers and production: human biological rhythms are taken into account, time loss due to delays and fatigue is reduced, time use is improved, resulting in an increase in labor productivity of 3-12%.
True, at the same time, the work of managers becomes more complicated, and management costs increase.
Currently, a compressed work week, involving 3 days off, is being increasingly introduced abroad, but it causes increased fatigue among workers.
Flexible working hours also include on-call, rotational and seasonal work.
In those jobs where this is necessary due to the special nature of the work, the legislation allows for a fragmented working day (with one large or several small breaks) so that the total working time does not exceed the established duration of daily work. It is usually used in situations where there are several “peak” periods of intensive work, for example, in passenger transport enterprises or in livestock farming.
Shift work - work in two, three or four shifts (in accordance with a special schedule) - is introduced in cases where the duration of the production process exceeds the permissible duration of daily work, as well as in order to more efficiently use equipment, increase the volume of products or services provided . But working two shifts in a row is prohibited.
Workers alternate shifts evenly in accordance with a schedule approved by the administration, taking into account the specifics of the work and the opinion of the team.
There are different options for such alternation, but from a physiological point of view, direct is considered the most acceptable, i.e. when the first shift is followed by the second, and then the third. At the same time, the minimum duration of daily rest between shifts must be no less than double the duration of the shift preceding the rest, and if this is not possible, it must be compensated by other methods provided for by law.
A number of categories of workers, including pregnant women, mothers with children under three years of age, persons under 18 years of age, should not be involved in night shift work, even in cases where the specified hours account for only part of it.
Currently, a modular system for organizing flexible shift work is being used in foreign companies. All working time is divided into modules with different “prices” in order to eliminate the physical and social inconveniences of working in shift mode. For example, an hour of work during the worst period of the night shift is equivalent to several hours in the morning. Over a certain period, workers must accumulate the required number of conditional working hours, which will be less than the number of astronomical ones. Thus, monetary compensation is replaced by a proportional reduction in working hours.
The work of performers must be organized so that every week or on average for the period provided for in the schedule, the legally established duration of the working week and the annual balance of working time, calculated according to the six-day working week calendar, are observed.
In continuously operating organizations, divisions and in certain types of work, where the duration of working time established for a given category of employees cannot be observed, its summarized recording is allowed so that the duration of working time for the corresponding period does not exceed the norm established by law.
Most often, summarized accounting is established at the request of employees interested in reducing the number of trips to work.
The daily or weekly duration of the working day may deviate from the norm within certain limits, and underwork and overtime are balanced, but the maximum duration of work shifts is still limited to 10 or 12 hours. Overtime in excess of the established shift duration cannot be compensated by reducing another and is considered overtime work.
During the working day (shift), the employee must be given a break for rest and food lasting no more than 2 hours and no less than 30 minutes, which is not included in working hours. For certain types of work, provision is made for special breaks determined by the technology and organization of production and labor.
The start and end times of daily work are provided for by internal regulations and shift schedules in accordance with the law and taking into account such circumstances as the schedule of urban and suburban transport, children's and cultural institutions serving this organization.
Working on weekends and non-working holidays is generally prohibited. Exceptions with the written consent of employees are allowed in the same cases as overtime work.
Working time balance in the Russian Federation
The working time balance is a fairly popular document in Russia, which helps to form a correct idea regarding the use of working time by employees, as well as ways to help optimize it as much as possible.
In accordance with established rules, the balance of working time should consist of several basic elements, these are:
- Calendar balance. Its determination occurs in accordance with a certain duration of the calendar period, taking into account the working and non-working time of employees.
- Nominal balance. It represents the actual amount of working time spent by employees to fulfill their obligations. In addition, this time period should also include moments when employees are absent from their workplaces, for example, due to them being on regular leave or being on sick leave.
- Effective balance. It contains information regarding working hours, taking into account all non-working days.
- A useful balance. This indicator is determined by establishing the average productivity of a working day and then multiplying it by the exact number of working days. The final stage is the deduction from the results obtained of certain days in which employees were on vacation or sick leave.
If we talk about the exact units in which the balance can be expressed, this includes man-days, as well as man-hours. The latter indicator can certainly be called more accurate. That is why it is most often used by modern employers.
Annual working time balance
The annual working time balance is a special document, which is compiled once a year for the next annual period. In this case, the authorized person during the formation of this document must take into account all important factors, for example: the operating mode that was established at a particular enterprise, the length of the working week in hours, etc.
When preparing the annual balance sheet, special attention should be paid to the following important factors:
- In most cases, the preparation of an annual balance sheet is carried out only in relation to working persons.
- The estimated nominal fund can be calculated as follows: weekends and holidays must be subtracted from the total amount of time worked. This is done on the basis of existing legislative provisions, namely Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- In addition, it is necessary to remember some important features of calculating working time directly related to weekends or holidays. In particular, the duration of a regular working day, before a weekend or holiday, should be reduced by exactly one hour. This aspect will also have a certain impact on the procedure for generating the annual balance sheet.
- Separately, you should keep in mind certain types of work activities that require continuous work. For example, this operating principle is often used in various manufacturing enterprises. If there is overtime, the employer will be obliged to provide his subordinate with the required monetary compensation. This act must also be taken into account when drawing up the annual balance sheet.
Time balance of one average worker
Balance sheets are drawn up per person, usually at industrial enterprises.
Stages of compilation:
- Determination of the number of working days. Holidays and weekends, absences from work for valid reasons, and downtime (if they took the whole day) are subtracted from the number of calendar days.
- Calculation of the duration of the working day. Temporary losses established by law (for nursing mothers, for those working in difficult conditions, etc.) are subtracted from the nominal duration.
- Calculation of the effective time fund of one average worker.
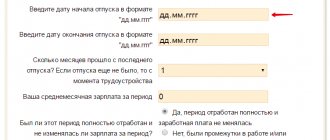
Let's enter the indicators and known values into the Excel table:
We will find all other numerical values for the indicators using the formulas:
Let's divide by “mathematical” actions:
- First, let's find the working time budget: shift duration * available days.
- With a five-day work week, the numerator is: established shift duration * worker budget. hour + 5 * temporary losses.
- The denominator is the sum of the budget and losses.
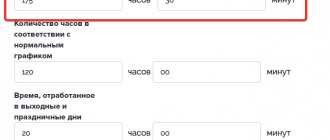
Calculation result:
Actual and standard working time balances
We expand the table with the standard balance - add a column with actually used working time for the period and with deviations.
We enter the actual values. We find deviations using formulas. The analysis is ready.
Actual working time balance
To record working time as accurately as possible, the responsible person must draw up an actual balance sheet. This procedure is characterized by the presence of some features:
- During the formation of the actual balance, all direct losses of working time that occurred during a certain period must be excluded from the calculations.
- Due to the above operations, the operational work time of employees increases. It represents a certain period during which employees were fully engaged in the performance of their professional functions, with maximum efficiency.
- The time spent by employees on rest, as well as other periods during which they are not engaged in actual professional activities, must be established as a certain percentage of operational time.
- Next, by comparing operational and actual time, the authorized person draws appropriate conclusions about the activities of employees.
How to properly balance working hours
When drawing up a working time balance, several specific indicators will be most important:
Depending on the employer’s goals, as well as the characteristics of a particular situation, the working time balance can be formed in days or hours. The main stage of the balance sheet formation procedure will, of course, be the calculation of the nominal and effective working time fund.
The nominal fund is determined by subtracting weekends, as well as official public holidays, from the entire calendar time of the year. However, this rule, in most cases, can only be applied to organizations that operate on a regular, standard schedule. As a rule, it is a 5-day work week, 8 working hours each day.
If we talk about various industries, it can be noted that they most often have completely different work schedules, including shift modes for employees to fulfill their professional obligations. In this case, only standard days off, which were established by the employer at a particular enterprise, in accordance with the shift schedule, should be excluded from the total calendar time.
In addition, to ensure the most accurate calculations possible, all internal temporary losses must be properly excluded from the nominal fund. The main ones include the following: breaks from work to eat, providing breaks for nursing mothers, etc.
How to calculate working time costs
When studying the cost of working time during a work shift, a photograph of working time (FW) is used. It is carried out:
— to identify shortcomings in the organization of labor and production that lead to direct losses and waste of working time;
— establishing service standards and standards for the number of employees;
— identifying the reasons for non-fulfillment or significant over-fulfillment of production standards by individual employees.
Regardless of the type of PRV, its implementation includes several stages:
1) preparation for observation;
2) observation;
3) processing of observation results;
4) analysis of the results and preparation of measures to improve the organization of work or establish norms and standards.
In preparation for observation, the technological process, labor organization at the workplace(s), maintenance procedures, technical characteristics, operating modes and condition of the equipment are studied. Before starting the observation, general information regarding the equipment and workers being inspected is entered into the observation card.
The observation process and processing of its results depend on the type of PDF.
Individual photo
When conducting individual photography, the object of study is an employee at a specific workplace. In some cases, this place can be mobile (a repair worker servicing equipment in a workshop). Such a photograph is the simplest and most effective examination method.
Observation and measurement are carried out according to the current time. The observation sheet indicates all the performer’s actions and work breaks in the order in which they actually occur, while simultaneously recording the current end time of each type of cost or loss. This time, in turn, is considered the beginning of the next type of cost. Let's give an example of filling out an observation sheet for the cost of a machine operator's working time (Table 1).
To analyze the obtained PDF, the actual and standard balance of working time is compiled (Table 2). When compiling it, all direct losses of working time and irrational costs are eliminated, thereby increasing operational time.
Preparatory and final time, time for organizational and technical maintenance, time for rest and personal needs are calculated as a percentage of the received operational time according to the relevant standards.
The standard preparatory and final time is given for a batch of parts.
Processing of a batch of parts may not coincide with the time of the work shift. Therefore, the preparatory and final time for a shift must be recalculated using the formula:
Tpz. cm = Tcm x Npar : Tpar = Tcm xTpz : (Tpz + Npair x Tpz),
where Tpz. cm - preparatory and final time per shift;
Tcm—work shift time;
Npar — batch size of parts;
Tpar is the processing time of a batch of parts;
Тпз — preparatory and final time for a batch of parts;
Tsht - piece time per part.
For example, if Npar - 30 pieces, Tpz - 50 min, Tpz - 25 min, then Tpz. cm - 30 min [480 x 50: (50 + 30 x 25)].
To calculate the standard time for servicing a workplace and time for rest and personal needs, you need to know the amount of operational time in the standard balance. It is calculated using the following formula:
Top. n = (Tcm – Tpz cm): (1 + Kob + Boiler).
So, if according to the standards Cob is 0.04 (4%), Boiler is 0.05 (5%), then Top. n - 413 min [(480 – 30) : (1 + 0.04 + 0.05)].
Next Tob - 17 minutes (413 x 0.04), Totl - 21 minutes (413 x 0.05).
The calculation data is entered into the table. 2.
When comparing actual time expenditures with standard ones, unnecessary costs of preparatory and final time, organizational and maintenance time, time for rest and personal needs are identified that need to be reduced. The reasons that caused irrational and unnecessary costs and losses of working time are studied, and the necessary costs of working time are established.
At the end of the calculations, a possible increase in labor productivity is determined:
PT = (Top. n – Top. f) : Top. f x 100%,
where is Top. n, Top. f — accordingly, operational time according to the actual and operational balance.
In our example, PT is 51.8% [(413 – 272) : 272 x 100%].
The downside of an individual PDF is its high labor intensity - 8 working hours for a standardization specialist to obtain one PDF. To combat this shortcoming, group DFWs were developed, in which a rater monitors several workers simultaneously.
Group PDFs
The main types of group FRFs are simple group, brigade, interval, route. Depending on production conditions, they may overlap. Let us sort these types of PDFs depending on the number of observed workers and production conditions.
A simple group PDF is used to monitor several workers (from two to five) who are not connected to each other by a single labor process. These can be machine workers, operator workers, repair and transport workers. Observations are carried out in the same way as with individual photography, but only indices of types of working time costs are recorded (Table 3).
Depending on the purpose of observation, the PDF can be processed individually (as four individual PDFs) or collectively (all the time added up by type and then divided into four parts). In the second case, an averaged PDF is obtained by type of cost and loss of working time.
The observer will not cover more than 4 or 5 workers with this method: he will not have time to track their labor process. In this case, an interval PDF is used, which is most often a route one. Observations are carried out at a certain time interval, which depends on the number of workers observed: up to 10 people - 2-3 minutes, up to 20 people - 4-5 minutes.
The number and composition of workers, the route of movement are selected in advance, trial FRFs are carried out, and observation forms are prepared. They are the same as for group FRF. Only in the column “Current time” time intervals are entered in advance, and in the column “Working order number” the required number of columns is entered.
During the observation process, the standardizer walks around workplaces along the chosen route and enters working time cost indices into the observation sheet. During processing, the observation time is summed up and an averaged PDF is obtained by type of cost and loss of working time.
The method is less accurate than individual PDF, since it is conventionally assumed that the entire time interval the employee was engaged in the same work as at the time of observation. However, it provides a large amount of material at once.
Another option for group FW is team photography. It is used when workers are directly involved in a single labor process, usually in assembly processes (assemblers), when servicing technological installations (operators), and repair work (repairmen). In this case, it makes no sense to carry out individual PDFs, since workers often collectively perform one operation. Then the method of direct time measurements or the method of momentary observations is used. The first of them is used to examine a team (link) of 2-3 people who are in the field of view of the observer. The order of observations is the same as for a simple group PDF. Working time balances are compiled for each worker, but in a general FW card. The method of momentary observations is used if there are 5-10 people in the team. Another area of application is to study the time expenditure of large numbers of individual workers. The method is complex and accessible only to specialists.
Self-photography and photo-timing
Self-photography refers to individual PRVs and, as the name suggests, is carried out by the employee himself. It is usually used to study the working time costs of specialists and employees. The form and the observation itself are not fundamentally different from the standard PDF. This requires more thorough training and instruction of the employee. Processing of FRF is also more complex.
And the last, widely used method is phototiming. Its essence is simple. In serial and large-scale production, as well as in continuous processes, operational work takes up a significant amount of time. In many cases, it is possible to combine PDF and timing. The observer conducts an individual PDF, and during operational work - timing. When processing phototiming, calculations are carried out separately for PDF and timing. The method allows you to use observation working time more productively.
Table 1
Observation sheet of individual FRF
| No. | Types of time spent | Current time | Duration | Index |
| 1 | Beginning of work | 8.00 | ||
| 2 | Receiving a task | 8.04 | 4 | PZ |
| 3 | Unfolding the tool | 8.09 | 5 | PZ |
| 4 | Setting up the machine | 8.23 | 14 | PZ |
| 5 | Parts processing | 9.28 | 61 | OP |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| Total | 480 |
table 2
Balance of working time costs
| Index | Categories of time spent | Actual working time balance | Standard working time balance | ||
| min | % | min | % | ||
| PZ | Preparatory and final time | 62 | 12,9 | 30 | 6,3 |
| OP | Operating time | 272 | 56,7 | 413 | 86,0 |
| ABOUT | Workplace service time | 61 | 12,7 | 17 | 3,5 |
| OTL | Time for rest and personal needs | 29 | 6,0 | 20 | 4,2 |
| PNT | Time of interruptions caused by disruption of the normal course of the production process | 24 | 5,0 | — | — |
| HDPE | Time of breaks in work caused by violations of labor discipline | 32 | 6,7 | — | — |
| Total | 480 | 100,0 | 480 | 100,0 | |
Table 3
Observation sheet of group FRF
| Current time | No. worker (machine) | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 8.00 | — | — | — | |
| 8.05 | PZ | PZ | PZ | PZ |
| 8.07 | PZ | OP | OP | PZ |
| 8.10 | PZ | OP | OP | PZ |
| 8.14 | OP | OP | OP | PZ |
| 8.35 | OP | OP | OP | OP |
Source: Economics and Life
Yuri Ivanov, head. Department of Economics and Management of the University "Dubna", Associate Professor, Doctor of Economics.
Results
Thus, the working time balance is a truly important document that can provide the employer with the most accurate information regarding the effective distribution of working time in a particular organization. This document must be compiled as follows:
- First, the specialist must summarize all working hours for a certain time period, for example, one year.
- Next, it is necessary to subtract temporary losses from the obtained value. They represent certain periods of time during which employees are not engaged in fulfilling their professional obligations. This may include absences from work due to illness, previously issued days of administrative leave and other time periods.
- The employer has the right to slightly adjust the resulting values in accordance with the procedure and characteristics of the activities of a particular enterprise.