Regulatory framework of the issue
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges all employers to provide safe working conditions for their employees (Articles 22 and 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Specific definitions of the workplace and safe working conditions are given in Article 209 of the same document:
- A workplace is a designated area where an employee works, which is in one way or another under the control of the employer,
- Working conditions are criteria that affect the efficiency of performing work duties and the health of the personnel themselves.
- A permanent workplace is understood as a territory where an employee is permanently located for more than half of his working time.
- A remote workplace is an area for work that differs from the location of the organization itself. This may be the territory of another company, or work from home.
All employer organizations are required to comply with established labor standards, which include:
- Providing all necessary conditions for employees to work,
- Organization of favorable working conditions,
- Conducting periodic assessments of working conditions at production sites.
In addition, the employer is required to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards and requirements regarding the workplace. For example, the presence of a rest room and meals, a first aid kit, and so on.
The standards and requirements for the microclimate in an organization are established by SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96, which also includes standards for establishing temperature conditions, ventilation, noise levels and illumination.
UT in the employment contract: regulatory framework
Russian legislation quite strictly considers the concept of UT and provides additional features of the legal regulation of this issue. Therefore, it will be useful for both workers and employers to know exactly how this aspect of labor relations is regulated from a legal point of view. To do this, you need to study the provisions of the following provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Article 1 regulates that ensuring favorable labor conditions in the Russian Federation is one of the basic tasks of labor legislation in general.
- Article 2 assumes, as one of the basic principles of labor legislation, the implementation of the right of workers to carry out work activities in fair workplaces that meet safety or hygiene requirements, as well as to compensation in case of violation of these requirements.
- Article 6 places issues related to the regulation of industrial safety at enterprises under the responsibility of the executive branch of the Russian Federation.
- Article 21 regulates the rights and obligations of workers, in particular the right to familiarize themselves with information about labor standards.
- Article 22 is devoted to the responsibilities and rights of the employer, and these include the obligation to ensure compliance of the employer with legal standards.
- Article 41 provides legal regulation of the collective agreement, which may provide for special principles of interaction between employees and employers in the field of determining labor standards and their improvement.
- Article 45 provides for the possibility of legal regulation of certain aspects of labor protection within the framework of tripartite territorial, sectoral and intersectoral agreements.
- Article 57 obliges to indicate information about working conditions in employment contracts with employees.
- Article 74 regulates the obligation to notify employees in advance of changes in the labor regulations, as well as the possibility of their dismissal subsequently if they do not agree with such changes.
- Article 94 regulates the duration of the work shift and assumes the possibility of changing it depending on the work schedule.
- Article 116 prescribes the mandatory provision of additional leave to workers employed in certain types of hazardous work.
- Article 147 presupposes a mandatory increase in wages for hazardous work.
- Article 209 ensures the fixation of a specific definition of the concept of UT and other terms important in the context of the issue under consideration.
- Article 212 fixes the obligations of employers to ensure labor protection.
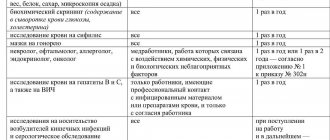
- Article 213 regulates the conduct of medical examinations of employees, including in the context of their work activities in hazardous workplaces.
- Article 216 is devoted to the responsibilities, rights and actions of the state within the scope of labor protection.
- Article 216.1 provides regulations for conducting SOUT.
Separately, it should be noted Federal Law No. 426 dated December 28, 2013, which regulates the environmental safety standards in general and other aspects related to industrial safety at the enterprise.
This list of information about labor regulations contains only basic regulations that are relevant at the federal level for absolutely all workers and employers. Many individual areas of activity have much more regulations governing the principles of establishing UT.
Classification of working conditions
Optimal
These are safe for humans,
Acceptable
Having harmful effects on the human body, but within acceptable limits,
Harmful
The level of harmfulness of the identified unfavorable factors is quite high, so this type is also divided into subclasses :
- – 1st degree employees do not have the opportunity to recover before the next working day,
- – 2nd degree when working in similar conditions for more than 15 years, occupational diseases of mild severity manifest themselves,
- – 3rd degree leads to mild or moderate severity of occupational disease and disability,
- – 4th degree – characterized by the development of serious forms of occupational diseases.
Dangerous
These are the ones that pose a real threat to the lives of employees.
What is indicated in the order of conditions of employment: nature of the work
- passport or other document capable of confirming identity;
- for persons under fourteen years of age, a birth certificate must be presented;
- for those Russian citizens who live abroad, it is necessary to present a foreign passport;
- if you have a work book, upon entering your main job;
- if there is no work book, the employer is obliged to issue a new one upon the written application of the employee;
- state insurance certificate of pension insurance;
- for men - this means having a military ID, and for guys of military age - a certificate confirming his future conscription for military service;
- a document indicating the existence of education or special knowledge required by his future work.
We recommend reading: Tax When Selling An Apartment Less Than 3 Years Owned What Is The Tax
To draw up an order, a special unified form T-1 is used. If you need to hire several employees at once, then it is best to resort to the T-1a form, which is called a payroll. After the order is issued, an entry is made in the work book, and then the procedure for issuing a personal card in the T-2 form takes place.
Types of working conditions
- Physical (vibration, temperature, humidity, etc.),
- Chemical (the presence of substances in the air that can adversely affect the health of employees),
- Biological (presence of inertia in the work, pathogenic microorganisms, etc.).
To create a favorable working environment, special standards for regulating working conditions are developed and established, which must not be exceeded.
In general, the performance of employees depends, first of all, on meteorological working conditions, ergonomic equipment of the workplace and, naturally, on the personal characteristics and motivation of each employee.
The technological features of work processes have the greatest impact on the efficiency of employees. It is most difficult to work in the so-called “hot shops”, and the procedure for optimizing working conditions in this case will not be simple.
In addition, productivity will be affected not only by physical working conditions, but also by violation of established work rules or sanitary standards.
A separate branch of science, the scientific organization of labor, studies and improves working conditions. Based on the results of research and observations, standards for working conditions are created and established for individual workplaces, which must be strictly adhered to.
Employee compensation
As benefits or precautions, employees may be offered:
- shortened work week;
- additional leave issued once a year;
- additional wages;
- issuing special food products that can neutralize the effects of harmful factors;
- passing medical examinations;
- insurance;
- early retirement;
- prohibition on combining other work under the same harmful conditions.
Important! To reveal all the features of each workplace and ensure the most convenient work process is the owner’s task.
Physical working conditions. Details
As noted above, these include the level of humidity, temperature, degree of dust and noise in the work area, vibration, lighting and other factors.
Temperature has a special impact on performance. Heat sources at work can be special equipment, machines, work machines, as well as the person himself. In the course of life, a person also generates heat as a result of metabolism.
Science identifies several types of severity of energy consumption by a person during work:
- Light type of work – consumption of kilocalories per day is 2200-2600,
- Moderate - heavy - 2880-3400 kilocalories per day,
- Heavy – 3600-4000 kilocalories per day,
- Very heavy – 4200 – 6000 kilocalories per day.
The established standards allow consumption of no more than 4800 kcal per day over a relatively short period of time. Constantly exceeding established standards leads to serious occupational diseases among workers.
Temperature standards are also established regarding the types of energy consumption by humans, so the optimal temperature is:
- For light work – 22-24 degrees Celsius,
- For moderate-heavy – 17-21 degrees Celsius,
- For heavy - 16-18 degrees Celsius.
IMPORTANT temperature and sanitary standards are not constant, they fluctuate depending on seasonal changes, the presence of radiant heat, convection and/or the degree of training of the place of work.
To create optimal temperature conditions, air conditioners, air showers or ventilation units can be used. The level of humidity in the room also affects heat exchange. For optimal functioning of the body, it is enough to maintain air humidity at 30-60%.
Air pollution also has a negative impact on human health. Pollution has a particularly negative impact on the human respiratory system, vision and skin.
Pollution can be caused by the presence in the air of aerosol particles, dust of various kinds (organic (plant or animal origin), inorganic (particles of mineral or chemical substances), radiation or mixed).
The most harmful dust is of chemical origin. It is possible to reduce air pollution through the use of technological cleaning equipment, individual or collective protective equipment, as well as through periodic monitoring of the state of the environment and the elimination of negative factors.
Labor productivity is negatively affected by the presence of noise and vibration, from the strong and constant impact of which a person gets tired quickly enough, which affects his performance, while the speed of his thought processes may decrease, as well as a sense of danger.
Long-term noise exposure leads to diseases of the hearing system and disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular system. Noise level is measured in decibels, and its frequency is measured in hertz. The noise can be divided according to the degree of intensity and volume into normal, increased, high and very high, maximum.
By frequency, low-frequency noise, medium- and high-frequency noise can be distinguished. The duration of the noise can be permanent or temporary, as well as impulsive. Vibration refers to mechanical vibrations or vibrations of solid bodies; they can also have a negative impact on the health of workers.
Strong vibration, first of all, affects the human nervous system, which leads to a decrease in performance and increased fatigue. High-frequency vibration leads to increased blood pressure, decreased muscle endurance and motor functions in general.
To reduce the negative effects of vibration on the human body, it is necessary to constantly monitor its level and ensure that it remains within normal limits.
Mandatory terms of an employment contract - what are they?
Social insurance covers two types of expenses: payment of sick leave or maternity leave and compensation for damage to employees from accidents or illnesses arising from their professional activities. When an employer writes down the clauses of an employment contract, he may not list all existing types of insurance. It is enough just to provide a link to this article of the Labor Code.
Based on what position is indicated in the employment agreement, an entry is made in the work book. In the future, these records will be used to determine the employee’s benefits and retirement date. All currently existing professions are listed in the Unified Tariff and Qualification Edition.
Illumination
Another important factor that directly affects employee performance. Lack of light in the workplace leads to fatigue, drowsiness, and decreased performance.
Lighting standards for the workplace include:
- The average illumination of the work place, that is, the ratio of luminous flux to the area of the working surface, is measured in lux,
- Illumination pulsation coefficient is a criterion for assessing the depth of illumination fluctuations due to changes in light flux over time,
- Discomfort index (URG) is an assessment of discomfort that causes unpleasant sensations due to the uneven distribution of brightness elements in the field of view,
- Daylight Efficiency (KEO) is the ratio of the level of natural skylight indoors to the outdoor horizontal illuminance from the fully open sky, expressed as a percentage.
The lighting of the workplace should be uniform and rich.
IMPORTANT: rooms in which employees spend more than 50% of their working time must have natural light. Work without natural light is permitted only if the following conditions are met:
- When lighting the room, local and general lighting devices with a temperature of 2400-6500 K are used,
- The normalized illumination is increased if necessary to perform a number of tasks that require visual strain.
If there is a lack of natural light, the workplace should be equipped with additional sources of artificial lighting. Equally important is the direction of light. The shadow should not fall on the work surfaces, and the light should not hit the eyes. When performing certain types of work, the spectral composition of light is also important.
The efficiency of the work process is also influenced by the color in which the workroom itself is painted. The influence of color on performance has long been established; some colors increase it, while others cause depression of the nervous system or aggression:
- Red color in the interior increases immunity and blood pressure, but can also cause neurosis. Orange color has a beneficial effect on the respiratory system,
- Yellow color helps improve the functioning of the digestive and nervous systems,
- Green – promotes wound healing,
- Blue – has a beneficial effect on the restoration of the nervous system.
Description of the workplace
All working conditions must be specified in the employment contract without fail. The job description will largely depend on the employee’s field of activity.
So a job description for an office employee might look like this:
- The workplace is equipped with an ergonomic desk for the direct performance of job duties. In addition to the computer desktop, there should be a designated place for storing papers and office supplies (if they are necessary for work).
- The workplace should be equipped with an ergonomic chair that promotes free blood circulation in the body.
- Workplace equipment includes a computer or laptop, a set of office supplies, and a trash bin.
Indoors or outdoors
Now consider the example of a real estate agency employee. Unlike, for example, a teacher or a bank employee, this specialist often moves from one area of the city to another.
Occasionally appears in the office. Accordingly, the working conditions of a teacher and a bank employee are calmer - in any weather they are warm and under a roof. A realtor, on the contrary, must visit one or another property in any weather.
Results
In recent years, the degree of control over compliance with sanitary and hygienic working conditions in the workplace has significantly decreased in Russia, which has a negative impact on the health of a fairly large part of the country’s adult population.
First of all, this applies to workers in the production sector - metallurgical, fuel and energy and engineering enterprises, textile industry, transport and construction enterprises. In private enterprises, the situation is even less encouraging - in 80% of cases, employees work in unfavorable conditions.
Work and rest schedule
When applying for an official job, a person must undergo an interview and become familiar with his future place of activity. But first, let's look at the working conditions associated with the regime. Let's say the shift starts at 8:00 and ends at 17:00. Lunch break - from 12.00 to 13.00.
This is one of the working conditions. Now imagine that an employee in the same position works on a different schedule due to a complex technical process. His shift starts at 13:00 and ends at 22:00.