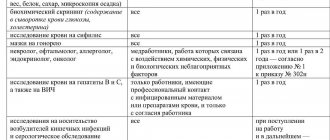
Our specialists participate in webinars on the topic of professional standards, monitor changes in legislation, expert opinions and share the information received with you. When posting articles and reviews, we are guided by trusted sources and, as you can see, we try to cover the topic from different points of view.
On July 20, 2021, we published the article “Professional standard “Occupational Safety and Health Specialist 2017” . Today, the specialist in educational and methodological work of our center is Vlasov V.K. I have prepared for you structured information on this document in diagrams and tables.
Why such attention to this particular professional standard? The qualifications of a labor protection specialist are of great importance, since the organization and effective operation of the labor protection system in the company directly depends on it. And the increasing number of cases of obtaining a certificate in 1 day calls into question not only the professionalism of the specialist, but also creates an immediate threat to the life and health of workers.
Check whether you or your employees meet the qualification requirements specified in the professional standard. If necessary, develop training plans to match employee qualifications.
Please note that even mandatory professional standards are mandatory only in terms of job title and qualification requirements (Article 57, Article 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
With respect to you and your business,
GC ITC PTM
Today, no one doubts the demand for the profession of occupational safety specialist - every enterprise needs such an employee. The state obliges employers to protect the labor of their employees.
Since 2012, in the Russian Federation, along with the ETKS, a new form of determining an employee’s qualifications has been introduced. This is a professional standard.
The professional standard of a specialist in the field of labor protection was approved by order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated August 4, 2014 N 524n.
The main goal of the type of professional activity of an occupational safety specialist is the prevention of industrial accidents and occupational diseases, reducing the level of exposure (elimination of exposure) to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors and levels of occupational risks on workers.
A professional standard is a regulatory legal act that is mandatory and contains state requirements for the profession. In addition, it describes in detail the competencies of a specialist in the field of labor protection.
This material will help you successfully master the profession. For your convenience, we present it in three parts in diagrams and tables. Each part is a generalized work function in graphical form, which will help you streamline and standardize your activities.
Who is a Health and Safety Officer?
This is an employee who monitors compliance with occupational safety and health (OHS) requirements and is responsible for preventing accidents and occupational diseases at the enterprise.
In what case should an organization have such a specialist on its staff? If the number of employees exceeds 50 people (Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Labor dated June 10, 2016 No. 15-2/OOG-2136).
Complete training and receive a certificate of occupational safety specialist Submit an application
With a smaller number of personnel, the director of an organization or individual entrepreneur can take on the functions of a labor protection specialist, entrust them to another employee, or use the services of third-party providers.
Important points
The formation of the OT service occurs after a certain number of employees appears in it. The created department is headed by the chief occupational safety specialist. The number of employees depends on the size of the team. In particular, in enterprises employing 500 people, it is recommended to have at least 6 experts. The director of the enterprise bears direct responsibility for the health and life of employees. It is he who is responsible for checking the quality of performance of functional duties by occupational safety inspectors.
If an emergency occurs at production, a special commission is created, headed by a specialist from the labor protection service. The claims of the injured person regarding compensation for material damage caused to health are satisfied in full if, based on the results of the inspection, the fact of the accident was proven to be the fault of the employer. When selecting OT specialists, the management of large companies primarily pays attention to their education and qualifications. If the candidate does not have them, he will not be able to count on such a vacancy.
What does a labor safety engineer do?
REFERENCE. Today, the term “engineer” is not used for occupational health and safety (OHS) positions. Another name used is “occupational safety specialist.”
Such an employee organizes briefings, monitors conditions in the workplace, investigates work-related injuries, monitors changes in labor legislation, participates in conducting a special assessment of working conditions (see “SOUT (Special Assessment of Working Conditions)”) and much more.
Prepare labor safety documents in a special service Try for free
Features of the organization of the OT management system
It should provide the following points:
- transmit information about labor protection and conditions between different departments;
- facilitate the receipt and documentation of information related to labor protection from external departments and departments;
- transmit information on safety and working conditions for all parties interested in this.
Requirements for a labor protection specialist
A professional standard has been developed for specialists in the field of occupational safety (approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 04.08.14 No. 5245n). It provides for two qualification levels: sixth and seventh (see table).
Table
What are the requirements for occupational safety specialists established by the professional standard?
| Skill level | ||
| 6 | 7 | |
| What positions can you hold? | OT Specialist | Head of OT service or OT specialist |
| Functions | Implement and ensure the functioning of the occupational safety management system and monitor it | Plan, develop and improve the occupational safety management system |
| Education and Training Requirements | Possible options: | |
| — higher education in the field of “Technosphere Safety” or corresponding specialties in ensuring the safety of production activities; — higher education and additional vocational education (vocational retraining) in the field of occupational safety; — secondary vocational and additional vocational education (vocational retraining) in the field of occupational safety | -higher education in the field of “Technosphere Safety” or corresponding specialties in ensuring industrial safety activities; — higher education and additional vocational education (vocational retraining) in the field of occupational safety | |
| Experience Requirements | If you have a higher education, there are no experience requirements; with secondary vocational education, at least 3 years of experience in the field of occupational safety is required | At least 5 years in the field of occupational safety |
| Conditions for permission to work | If there are hazardous production facilities, it is necessary to undergo training and certification in the field of industrial safety | |
Retrain and improve your skills in the field of labor protection
Legal regulation of the issue
Perhaps the only requirements for a labor protection specialist for 2021 are set by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Part 1 of Article 217. According to it, the requirements for the qualifications of a labor protection specialist are limited to what he must have in this area:
- appropriate training;
- or work experience.
This means that the qualification requirements for a labor protection specialist, which are set out in the relevant professional standard, automatically become mandatory. This follows from Part 1 of Article 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The main requirements for a specialist in the labor protection service are given in the order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated August 4, 2014 No. 524n. This regulatory document establishes a professional standard called “Specialist in the field of occupational safety and health” (last edition dated January 28, 2017).
The specified professional standard considers:
- the possibility of hiring a labor protection specialist without experience;
- availability of higher education from a labor protection specialist.
Also see “Content and application of the professional standard of a labor protection specialist.”
It is important that the requirements for the position of “Occupational Safety and Health Specialist” vary depending on what main functions the person will perform. There are only 3 of them:
- Implementation and maintenance of the labor protection management system (OSMS).
- Monitoring the work of the OSMS at the enterprise.
- Planning, development and improvement of OSMS.
Next, we will consider each of these points in relation to what requirements the mentioned professional standard imposes on a labor protection specialist.
Also see “Occupational safety specialist (engineer): functions in the enterprise.”
Who can work as a labor protection specialist?
When hiring a specialist, are employers required to adhere to the qualification requirements set out in the professional standard? Yes, we must. But not always, but only if the same requirements are also established by federal law (Article 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
For the position of “OHS specialist,” the law establishes one requirement: the presence of appropriate training or experience in this field (Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that only a person whose education or experience meets the criteria of the professional standard can apply for the specified vacancy.
IMPORTANT . If a person does not meet the professional standard, but already holds the position of an occupational health or safety specialist, he cannot be fired. You can only reduce the bonus, send them to advanced training courses, etc. But, if this is a candidate for a position, the employer does not have the right to hire him. This conclusion follows from paragraph 6 of the information of the Ministry of Labor dated 04/05/16 (see “Professional standards: when and how employers should apply them”).
Goals and objectives
The company itself can determine what functions the occupational safety department will perform. But it is recommended to use a ready-made list of tasks to formulate goals for labor relations. The main function is clear, but you need to know what it includes to ensure conditions for work.
- Training new specialists in working methods that will minimize harmful effects on health.
- Assistance in selecting candidates for positions that require qualifications in occupational safety issues.
- Checking equipment for serviceability, minimizing the likelihood of a dangerous situation occurring when performing work duties.
- Finding ways to improve working conditions and solve existing problems.
- Ensuring sanitary and hygienic standards that comply with regulatory documents.
- Safety check of buildings owned by the company.
- Providing workers with special suits and other protective equipment necessary to reduce negative impacts.
- Monitoring compliance with the rest regime prescribed to employees.
The person responsible for safety must perform the above tasks. Their list can be much wider, because it is determined by a specific company. If a person does not fully fulfill his duties, then he has the right to fire him. You shouldn’t approach your work tasks irresponsibly, especially since people’s lives depend on it.
Where are health and safety specialists trained?
It is good if a person has graduated from a university in the field of “Technosphere Safety” or relevant specialties in ensuring the safety of production activities. This means that he has received the necessary higher specialized education and can start working.
If he has a higher non-core or secondary vocational education, he will have to undergo additional vocational training in the field of occupational safety. According to clause 2.3.6 of the Occupational Safety and Health Training Procedure (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29), you can improve your qualifications in an educational institution where there are full-time teachers and where occupational safety and health disciplines are taught.
Complete the “Technosphere Safety” course and receive a diploma
How to get occupational safety training
How to undergo professional retraining in labor protection
You need to choose a licensed training center with accreditation from the Ministry of Labor to conduct training for employers and employees on occupational safety issues. Such centers offer retraining programs for both heads of labor protection services and ordinary specialists.
For example, at Kontur.School you can get a diploma in the following areas:
- Technosphere safety for the head of the labor protection service (284 academic hours);
- Occupational Safety and Health. Technosphere safety (256 academic hours).
How to get distance education in occupational safety
Nowadays, distance education has become very popular, and in most cases, the only one available. Therefore, almost every training center has online courses, including OT. Training includes webinars, online tests, feedback from experts, etc. For example, Kontur.School offers various types of training at the School of Occupational Safety and Health. Some webinars can be watched for free.
Prom-Nadzor.ru
On July 1, 2013, changes were made to the qualification directory of positions for managers, specialists and other employees, according to which the positions “Head of the Labor Safety Department” and “Labor Safety Engineer” were excluded from the list (Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated May 15, 2013 No. 205) .
Instead, new positions were introduced - “Head of the Labor Safety Service” and “Labor Safety Specialist” (Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated May 17, 2012 No. 559n).
New qualification characteristics have also been introduced for these specialists.
According to the new requirements, the head of the labor protection service must have higher professional and additional professional education in the field of labor protection and work experience in the field of labor protection of at least five years.
An occupational safety specialist must receive a higher professional education in the field of "Technosphere Safety", or secondary vocational education and additional professional education in the field of occupational safety, and also have at least 3 years of work experience in the field of occupational safety.
Such changes were received ambiguously by both employers and employees of occupational safety and health services.
Let's try to figure out whether the employer is obliged to bring the names of employees' positions in accordance with the new requirements.
The first difficulty an employer faces is finding employees who have received an education in Technosphere Safety. Such specialists are currently in short supply in the labor market. Since the number of universities providing training in a new specialty is very small.
Also, according to Article 143 of the Labor Code of Russia, the qualification directory is considered as a normative document when establishing tariff systems for remuneration, tariffication of work and assignment of tariff categories. However, in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there is no need to include in the employment contract requirements for employees who do not perform work not related to the provision of compensation and benefits.
As practice has shown, more and more often in enterprises and organizations in Russia you can find various modifications of job titles (for example, “labor safety manager”). Which previously did not raise questions among labor inspectors.
Which is quite obvious, since the provision of safe conditions for workers is of paramount importance, and not the title of the positions of occupational safety specialists. Moreover, the job responsibilities of an engineer and a labor protection specialist are almost completely identical.
For these reasons, it is not worth making urgent adjustments to the staffing table at the moment.
A great difficulty is caused by the presence in the qualification characteristics of the requirement to obtain additional education in the field of labor protection.
At the moment, many educational institutions have already begun retraining managers and occupational safety specialists. The duration of the program is approximately 500 hours. Upon completion of training, the student is issued a state-issued diploma with the right to conduct activities in the field of labor protection.
The cost of such training in some regions exceeds 60 thousand rubles. Which is a significant amount for many organizations.
To avoid additional costs, many employers either do not provide training to specialists or try to shift the burden of costs onto the organization's employees.
The main responsibilities of the employer related to training and retraining of personnel are set out in Chapter 31 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In most cases, the employer makes a decision to pay for an employee’s training only on the basis of interest in the services of bona fide specialists. In addition, at the moment there is no alternative in the labor market (i.e. specialists with not only the appropriate education, but also experience).
In most cases, retraining specialists with many years of experience who are well aware of the specifics of the enterprise will be the key to maintaining the labor protection system at the proper level.
Pros and cons of the profession of occupational safety engineer
The advantages include demand due to legal requirements. After all, the head of a company with more than 50 employees, regardless of his desire, is obliged to hire an occupational safety specialist. As a result, well-educated professionals compete for decent pay.
Among the disadvantages is a large amount of paperwork: filling out reports, acts, drawing up instructions, etc. Therefore, before becoming a labor protection specialist, you need to determine how suitable this type of work is to a person’s character.
Attention
If an enterprise hires a person who has neither work experience nor the necessary education, then the person responsible will have to pay a fine. In 2021, the payment is fixed, amounting to 5,000 rubles for an official, 50,000 rubles for a legal entity.
If the requirements for a labor safety specialist are not met again, a fine is again imposed on the enterprise, the amount of which increases for the manager to 20,000 rubles. Also, penalties may include termination of the enterprise’s activities for a period of one to three years.
A legal entity recognized as a persistent violator will have to pay up to 70,000 rubles or cease operations for three years.