Contents of the employment contract
The most important document in the relationship between employer and employee is the employment contract . Properly drawn up, it is able to protect the rights of both the employee and the employer. The structure of Section III “Employment Contract” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is presented in Fig. 2.4.
Rice.
2.4. Structure of Section III of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The content of an employment contract refers to the rights and obligations of the parties. Its contents consist of information and conditions. According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employment contract specifies:
- – last name, first name, patronymic of the employee and name of the employer (last name, first name, patronymic of the employer - an individual) who entered into an employment contract;
- – information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
- – taxpayer identification number (for employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs);
- – information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract, and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers;
- – place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
The following conditions are mandatory for inclusion in an employment contract:
- – place of work, and in the case where an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of an organization located in another area – place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location;
- – labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee). If, in accordance with federal laws, the performance of work in certain positions, professions, specialties is associated with the provision of compensation and benefits or the presence of restrictions, then the names of these positions, professions or specialties and the qualification requirements for them must correspond to the names and requirements specified in the qualification reference books approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- – the date of commencement of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also the duration of its validity and the obligations (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law;
- – terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments);
- – working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
- – compensation for hard work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired in appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions in the workplace;
- – conditions that determine, in necessary cases, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of the work);
- – a condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- – other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
This is important to know: Fixed-term employment contract with a foreign citizen temporarily residing in the Russian Federation (under a patent)
If, when concluding an employment contract, it did not include any information and (or) conditions from those provided for in Parts 1 and 2 of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this is not a basis for recognizing the employment contract as not concluded or for its termination. The employment contract must be supplemented with missing information and (or) conditions. In this case, the missing information is entered directly into the text of the employment contract, and the missing conditions are determined by an annex to the employment contract or a separate agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, which are an integral part of the employment contract.
The employment contract may provide for additional conditions that do not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with established labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements, local regulations, in particular:
- – on clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit and its location) and (or) the workplace;
- – about the test;
- – on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
- – on the employee’s obligations to work after training for no less than the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
- – on the types and conditions of additional employee insurance;
- – on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
- – on clarifying, in relation to the working conditions of a given employee, the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
By agreement of the parties, the employment contract may also include the rights and obligations of the employee and employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, as well as the rights and obligations of the employee and employer arising from the terms of the collective agreement and agreements . Failure to include any of the specified rights and (or) obligations of the employee and employer in the employment contract cannot be considered as a refusal to exercise these rights or fulfill these obligations.
Employment contracts, depending on their duration, can be concluded for an indefinite or definite period.
When concluding an employment contract for an unlimited period, the parties do not stipulate its duration at all. The agreement determines the date of its entry into force.
When concluding an employment contract for a specific period (fixed-term employment contract), the parties must provide for a specific period of its validity: one, four years, etc. As a rule, a fixed-term employment contract is concluded for a period not exceeding 5 years.
It is prohibited to conclude fixed-term employment contracts in order to evade the provision of rights and guarantees provided for employees with whom an employment contract is concluded for an indefinite period.
The written form of the employment contract is mandatory (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The agreement is drawn up in two copies, each of which is certified by the signature of the employee and the representative of the employer or the employer - an individual. One copy of the employment contract is given to the employee, the other is kept by the employer.
When concluding an employment contract, by agreement of the parties, it may provide for a condition on testing the employee in order to verify his compliance with the assigned work (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The probationary agreement must be specified in the employment contract. The employer may recognize the test results as unsatisfactory and terminate the employment contract with the employee. With an employee who fails the test, the employment contract is terminated on the basis of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation without taking into account the opinion of the relevant trade union body and without paying severance pay.
The grounds for termination of an employment contract are (Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- – agreement of the parties;
- – expiration of the employment contract, except for cases where the employment relationship actually continues and neither party has demanded its termination;
- – termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employee;
- – termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer;
- – transfer of an employee, at his request or with his consent, to work for another employer or transfer to an elective job (position);
- – the employee’s refusal to continue working in connection with a change in the owner of the organization’s property, a change in the jurisdiction (subordination) of the organization or its reorganization;
- – the employee’s refusal to continue work due to a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties;
- – the employee’s refusal to transfer to another job, required for him in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, or the employer’s lack of relevant work;
- – the employee’s refusal to be transferred to work in another location together with the employer;
- – circumstances beyond the control of the parties;
- – violation of the rules for concluding an employment contract established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law, if this violation excludes the possibility of continuing work.
An employment contract may also be terminated on other grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
Labor function of an employee - what is it according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The concept of an employee’s labor function, like most other aspects of the legal regulation of relations between employees and employers, is considered, first of all, in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a labor function is a range of tasks that an employee must perform as part of his work activity, and which are documented in the local regulations of the organization.
The following articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation consider the question of what the labor function of an employee is:
- Art.15. This article examines labor relations in principle, and the very definition of this type of relationship presupposes the performance of a labor function for remuneration.
- Art.57. It is in this article of the Code of the Russian Federation that the labor function of an employee is defined and the mandatory legislative requirement for its mention in the text of the concluded employment contract is indicated.
- Article 72.1. The provisions of this article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulate the procedure for transferring workers to another job or moving them within the same enterprise - the key aspect in this issue is precisely the change or maintenance of the employee’s labor function.
- Art.74. This article discusses the procedure for changing certain terms of the contract in the event of a change in working conditions due to a change in organizational or technical conditions. In particular, it is assumed that it is impossible for the employer to carry out such actions unilaterally if their result is a change in the employee’s labor function.
Labor function is the basis of the employment contract
The most important component of an employment contract is the labor function (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Labor function
– any work for a specific position in accordance with the staffing schedule, profession, specialty, indicating qualifications, as well as the specific type of work assigned. The specific type of work entrusted to an employee may constitute the content of the labor function both in itself and along with work in a particular position, profession, or specialty.
Job title
- this is an established set of responsibilities and the corresponding morals that determine the place and role of the employee in the organization. The name of the position is indicated in the employment contract in accordance with the organization’s staffing table.
This is important to know: Order to extend the term of an employment contract (sample)
Under profession
refers to the type of labor activity, occupation of a person who possesses a complex of special knowledge, skills, and abilities acquired through education.
Speciality -
This is a type of professional activity improved through special training (HR manager, surgeon), a certain area of work, knowledge.
Qualification
– level of preparedness, skill, degree of suitability for performing work in a certain specialty or position, determined by rank, class, rank and other qualification categories. The indicator that determines the level of qualification of an employee is the qualification category. The qualification category is established taking into account the complexity, responsibility and working conditions on the basis of the tariff and qualification reference book.
The performance of a labor function must be subject to the internal labor regulations of the organization. The employer's response to the performance of a labor function by an employee is the payment of remuneration in the form of wages.
Before signing the contract
Drawing up an employment contract is usually the responsibility of the personnel department .
An applicant for a vacant position meets with a manager or other official who is responsible for concluding employment contracts with employees. During the conversation, the parties come to a verbal agreement on all issues of further cooperation, and the HR manager draws up a draft employment contract. The applicant is introduced to all labor regulations of the organization, insofar as it relates to his work activity, and the collective agreement, if any. The procedure for drawing up an employment contract may be different, but it is important to familiarize the applicant for a vacancy with the regulatory documents of the organization before a written agreement is reached.
Judicial practice shows that the court can side with the employee in controversial situations if he was not familiar with the VTR Rules or other regulations before the contract was signed . The responsibility for timely familiarization rests with the employer.
Employment contract with the employee
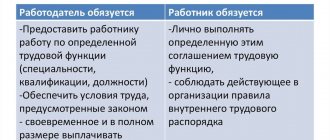
An employment contract with an employee is an agreement between the employer and the employee, according to which the employer undertakes to provide the employee with work for a specified labor function, to provide working conditions provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations acts and this agreement, pay the employee wages in a timely manner and in full, and the employee undertakes to personally perform the labor function determined by this agreement in the interests, under the management and control of the employer, to comply with the internal labor regulations in force for this employer.
The employment contract specifies:
- surname, name, patronymic of the employee and the name of the employer (surname, name, patronymic of the employer - an individual) who entered into an employment contract;
- information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual;
- taxpayer identification number (for employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs);
- information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers; place and date of conclusion of the employment contract.
The parties to the employment contract are the employer and the employee.
The following conditions are mandatory for inclusion in an employment contract:
- place of work, and in the case when an employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another area - place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location;
- labor function (work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work assigned to the employee). If, in accordance with this Code and other federal laws, the performance of work in certain positions, professions, specialties is associated with the provision of compensation and benefits or the presence of restrictions, then the names of these positions, professions or specialties and the qualification requirements for them must correspond to the names and requirements specified in qualification reference books approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, or the relevant provisions of professional standards;
- the date of commencement of work, and in the case where a fixed-term employment contract is concluded, also the period of its validity and the circumstances (reasons) that served as the basis for concluding a fixed-term employment contract in accordance with this Code or other federal law;
- terms of remuneration (including the size of the tariff rate or salary (official salary) of the employee, additional payments, allowances and incentive payments);
- working hours and rest hours (if for a given employee it differs from the general rules in force for a given employer);
- guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired under appropriate conditions, indicating the characteristics of working conditions at the workplace;
- conditions that determine, in necessary cases, the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, other nature of work);
- working conditions in the workplace;
- a condition on compulsory social insurance of the employee in accordance with this Code and other federal laws;
- other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
In this case, the missing information is entered directly into the text of the employment contract, and the missing conditions are determined by an annex to the employment contract or a separate agreement of the parties, concluded in writing, which are an integral part of the employment contract with the employee.
The employment contract with the employee may provide for additional conditions:
- on clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit and its location) and (or) the workplace;
- about the test;
- on non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other);
- on the employee’s obligation to work after training for no less than the period established by the contract, if the training was carried out at the expense of the employer;
- on the types and conditions of additional employee insurance;
- on improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members;
- on clarification, in relation to the working conditions of a given employee, of the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
- on additional non-state pension provision for employees.
Sample employment contract with an employee
Drawing up a contract with piecework payment
It is permissible not to indicate a specific salary figure in the employment contract in the only case - if the employee has a piece-rate wage system. This method is used in organizations where the use of labor standards is realistic, mainly in manufacturing enterprises. This system is designed to stimulate an increase in the volume of manufactured products. For the production of a unit of product, the performance of a certain amount of work, a piece rate is established. Based on it, the amount of the employee’s salary is calculated.
Changing an employee’s job function – how and when it is permissible
The employer, as mentioned earlier, cannot independently change the employee’s labor function as a whole. However, there are some nuances and features of regulating changes in the terms of an employment contract that both employees and employers should know:
Changing the terms of the employment contract, including the employee’s labor function, is permitted by agreement of the parties. If the employer and the worker voluntarily wish to change the latter’s labor function, there is no need to enter into a new contract - it will be sufficient to use an additional agreement.