Assigning additional responsibilities to employees
Additional responsibilities: how to assign an employee
Here it is worth referring to Article 60 of the Labor Code. According to this rule, employees cannot be required to fulfill obligations that are not contained in the original agreement between them and their employers.
Each enterprise draws up special job descriptions that describe in detail the range of responsibilities. Often it is wide enough without additional loads.
The employee must familiarize himself with this document, as well as with his responsibilities, on the day he signs the agreement with the other party.
The following options are available if additional work is required:
- Standard registration of combined positions. In this case, it is recommended to rely on the provisions of Article 60.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This means that an additional agreement is signed to the current contract.
- The employee is hired as an internal part-time worker for another position. Here the main support is Article 60.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Then another Labor Agreement is drawn up.
In any case, it is impossible to do without paying the employee additional remuneration.
The Labor Code does not regulate the issue of payment in any way. That’s why the manager himself and his subordinates do this. It is important to come to a compromise that suits everyone.
For what period can they be forced to perform duties without consent?
site visitor in your case, when urgent work is required on which the normal operation of the enterprise depends, the involvement of employees is possible only with their written consent. At the same time, it is impossible to involve disabled people and women who have young children under 3 years of age in performing these works. Therefore, if you do not agree to work, you are not obliged to work, if your rights are violated, contact the labor inspectorate
“Labor Code of the Russian Federation” dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (as amended on February 5, 2018)
Article 99. Overtime work
Overtime work is work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period.
An employer's involvement of an employee in overtime work is permitted with his written consent in the following cases:
1) if necessary, perform (finish) work that has begun, which, due to an unforeseen delay due to technical production conditions, could not be performed (finished) within the working hours established for the employee, if failure to complete (unfinished) this work may result in damage or destruction of property the employer (including the property of third parties located at the employer, if the employer is responsible for the safety of this property), state or municipal property, or create a threat to the life and health of people;
2) when carrying out temporary work on the repair and restoration of mechanisms or structures in cases where their malfunction may cause the cessation of work for a significant number of workers;
3) to continue work if the replacement employee fails to appear, if the work does not allow a break. In these cases, the employer is obliged to immediately take measures to replace the shift worker with another employee.
An employer’s involvement of an employee in overtime work without his consent is permitted in the following cases:
1) when carrying out work necessary to prevent a catastrophe, industrial accident or eliminate the consequences of a catastrophe, industrial accident or natural disaster;
2) when carrying out socially necessary work to eliminate unforeseen circumstances that disrupt the normal functioning of centralized hot water supply, cold water supply and (or) sewerage systems, gas supply systems, heat supply, lighting, transport, communications;
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 7, 2011 N 417-FZ)
(see text in the previous edition)
3) when performing work the need for which is due to the introduction of a state of emergency or martial law, as well as urgent work in emergency circumstances, that is, in the event of a disaster or threat of disaster (fires, floods, famine, earthquakes, epidemics or epizootics) and in other cases, threatening the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it.
In other cases, involvement in overtime work is permitted with the written consent of the employee and taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
Pregnant women, workers under the age of eighteen, and other categories of workers are not allowed to work overtime in accordance with this Code and other federal laws. Involvement of disabled people and women with children under three years of age in overtime work is allowed only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited for them due to health reasons in accordance with a medical report issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulations legal acts of the Russian Federation. At the same time, disabled people and women with children under three years of age must be informed of their right to refuse overtime work upon signature.
The duration of overtime work should not exceed 4 hours for each employee for two consecutive days and 120 hours per year.
The employer is required to ensure that each employee's overtime hours are accurately recorded.
New responsibilities without extra pay: is it possible?
Is it possible to assign duties without additional payment?
And here you can find a solution, but it is permissible to use only two methods.
Indication of relevant information in the employment contract. It should be written that during the absence of an employee with similar functions, his work can be performed by other team members. It is separately reported that there is no additional charge for such situations.
But this method is relevant only in the temporary absence of an employee. And in the case when the functions are really similar. This option cannot be used if the relevant information is initially missing from the Employment Contract.
It's better to see once
It is well known that it is better to see once than to hear a hundred times. We bring to the attention of readers an order to perform duties without additional payment. A free completed example of an order can be found on our website.
Please note that an order to temporarily replace an absent employee should be issued in each case of replacement. There is no single unified form for this document established by current legislation, therefore the order can be drawn up in any form. The main thing is to indicate all the necessary details.
It is important to understand that the basis for issuing an order to temporarily perform duties without additional payment is an employment contract with a replacement employee.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Temporary transfer and combination: features
This translation is one of the most convenient design options in such situations. The timing of temporary transfers usually depends on the reason.
For example, you can establish that the performance of new duties ends when the main employee returns from vacation. In some cases, this does not even require consent from the employee. For example, when there is a general production need.
Combinations are usually formalized if key employees go on maternity leave or long vacations. This is where Article 60.2 of the Labor Code comes to the rescue.
It is assumed that the part-time worker performs both his main job and additional work. This period is usually also associated with the following concepts and phenomena:
- Recalculation of wages, upward.
- Significant expansion of the service area.
- Increasing the direct volume of work.
General provisions
Responsibilities (additional) include several modes:
- combination (regarding professions and positions held in the company);
- increasing the volume and areas of work;
- fulfilling the duties of their work, as well as those who are temporarily absent from the workplace.
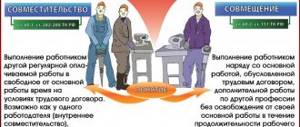
All three modes can exist within the same enterprise: the duration of the working day is established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employer, when determining the combination of positions, analyzes how feasible such a situation is from an economic point of view. Combination of professions (positions) is a term that refers to the performance by an employee of his main work under an employment contract, additionally for another position. This happens without releasing a person from his main activity in one organization, within the framework of the labor process.
Combination and part-time work are two different modes: they need to be distinguished. When working part-time, a person signs an employment contract with the company. The powers specified therein are exercised outside of the work shift or day.
The combination occurs in order to expand the activities of the enterprise, company, as well as increase the volume of work. Expansion of service areas is the performance, together with the main one, of additional work in a similar profession or position.
A person who is temporarily absent and another employee takes over his duties retains his position and workplace.
The employer, if he sees a production need for this, according to Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can transfer an employee to the post of an absent colleague for a period of up to one month. It is logical that the work is not specified in the employment contract. At the same time, the employer pays for the combination at a rate not lower than the average earnings for the main job. But the duration of such a transfer does not exceed one month!!!! Thus, based on the essence of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of an employee to work instead of a temporarily absent person entails release from basic functions.
In case of oral agreements
Verbal agreement to assign responsibilities to an employee
An oral agreement allows you to avoid many formalities. The manager will not have to spend a lot of time on documentation.
But such agreements protect the employee least of all from a legal point of view. After all, the job description is not adjusted, and the salary is not recalculated.
That is, an employee has two staff units at once. And he has no additional remuneration.
An employee has every right to refuse to take over the duties of someone who is currently on leave. But it often happens that after a refusal, the employer threatens to fire you.
But in such a situation, the law is on the side of the subordinates. If dismissal does occur, then you have every right to go to court in order to protect your rights. If the outcome of the case is positive, the citizen is reinstated to his position without any problems.
Formulas used
With a part-time work plan
You should be aware that any combination involves reduced working hours. In this case, the calculation will be carried out in accordance with the actual time worked.
For example, if the established additional payment is a percentage of the total salary, in the amount of 10%, the calculation will be based on the following:
- the total salary must be multiplied by the number of actual hours worked by the employee. Then the resulting value should be divided by 160 - the average number of hours per month, subject to standard employment;
- then the result should be multiplied by the interest rate - 10%, then divided by 100;
- The final stage will be adding the resulting amount with the amount of the established salary.
If an employee worked an additional 90 hours per month, and his salary is 30,000 rubles, the calculations should look like this:
- 30,000 x 90: 160 = 16875 (salary amount for an employee working part-time)
- 16875 x 10: 100 = 1687 (amount of additional payment for combined work)
- 16875 + 1687 = 18,562 (exact salary, including additional allowance for combinations).
Full-time work
The payment scheme for full-time work will look almost the same.
For example:
The accountant additionally performed the duties of a cashier for some time. The basic salary was 20,000 rubles. For the combination, he was given a bonus in the form of a percentage - 20%.
The combination lasted exactly half a month - 12 days.
Calculation of the full amount of earnings will involve the following steps:
- 20,000 x 20: 100 = 4,000 rubles (monthly additional fee for combination)
- 4000 : 2 = 2000 rubles (additional fee for half a month)
- 20,000 + 2000 = 22,000 rubles (full monthly earnings).
Payment based on the actual quantity of items produced or goods manufactured
Some employers adhere to a scheme in which wages are paid based on the actual quantity of products produced. In fact, this form of payment can be called “piecework”.
Let's look at a corresponding example:
An additional payment of 30 rubles was established for the employee for each unit of product produced. While doing combined work, the employee was able to produce 45 products. To determine the final amount of the required additional payment, it is necessary to multiply the price for one unit of goods by its actual quantity produced: 30 x 45 = 1350 rubles - this is exactly the additional payment that the employer must make, adding it to the basic monthly salary.
In case of incomplete work of days per month
In the event that an employee did not work all days in a month, payment should also be calculated in accordance with the actual time of work.
Let's look at a corresponding example:
The total number of employee working hours was 125 per month. The rest of the time he was on leave without pay. During the working period, he also took on the responsibilities of a temporarily absent colleague, for which he was given a bonus of 50% of the total salary. The cost of an hour of work at the main location is 200 rubles, while at the additional location it is 250 rubles.
In this case, the calculation made will consist of the following actions:
- The exact salary for the main job is calculated - 125 x 200 = 25,000 rubles.
- The amount of additional payment for combining is calculated - 125 x 250: 2 = 15625.
- The amount of the total amount that the employee must receive is established - 25,000 + 15,625 = 40,625 rubles.
Replacement of managers: some features
Any manager is the most important person on whom the further successful activities of the enterprise depend. Therefore, the replacement procedure requires a responsible approach.
An experienced director always agrees in advance with who will replace him. For this purpose, all documents are drawn up and specifics are specified.
The main feature is the need to issue a so-called power of attorney to replace and perform duties. It should be separately said that the deputy has the right to sign documents, use company stamps and seals if necessary.
Correct drafting of an order
Order on assignment of duties
Proper documentation will allow all participants in the process to be confident that their rights are protected. In addition, it guarantees safety when it comes to government inspections.
The first stage is to obtain consent from the employee in writing. For example, you can make an offer to combine positions.
At the second stage, they begin to draw up the order itself. Here they write about the validity period of the document, describe the responsibilities themselves that you will have to face. It is impossible to do without determining the amount of remuneration.
The order is registered using a special journal, where the document is assigned a separate number. The employee must be familiarized with the document against personal signature.
Algorithm for drawing up a document
At the top of the paper there is a header in which the name of the document and the date of its preparation are written. Then, after the title, the reasons for the absence of the employee as such are indicated. These reasons may be:
- dismissal of a previous employee;
- going on leave (to care for a child, etc.);
- business trip of the main employee;
- the enterprise is small, and the position itself is not provided, and other reasons.
This is what it should look like:
After the introductory part, the wording (as in any other order) “I order” is required, followed by a colon. Then comes a list of what needs to be done: authorize an employee (with full indication of full name and position) to perform work with one of the types of cash registers.
In this case, the model of the cash register must be clearly stated. It could be:
- AMC 100K – if the organization sells food products;
- autonomous cash registers with ECLZ and fiscal memory type ORION-100K or MERCURY-180K;
- mobile payment terminals with a modem and battery type YARUS C2100;
- printers that do not work without a computer or terminal (they are called fiscal registrars) like FPrint -5200PTK and the like;
- receipt printers (they do not have built-in memory, which means they do not need to be registered with the tax office) of the types Shtrikh 600, MPRINT R58 USB, etc.
In short, regardless of the model, the cash register must be registered.
In addition to appointments, the order prescribes the employee’s authority to keep a journal, draw up the necessary reports, and sign cash documents from the official “cashier” or “administrator.”
The text should also contain information about the employee’s familiarization with such a document as the Procedure for Conducting Cash Transactions. This review will require an additional signature of the employee who assumes the rights and responsibilities of the cashier.
Footnote to the agreement on mat. responsibility will also be useful. Without it, the order will also be valid, but it will need to be supplemented with an annex in the form of this agreement.
At the end of the text of the document there must be at least two signatures: the accountant-cashier and his manager. The date is already at the beginning.
Additional responsibilities within one position
The regulatory documents do not contain clear recommendations for drawing up job descriptions. There are only special recommendations from Rostrud.
Therefore, paperwork remains an entirely voluntary matter for employers. The form of such documentation remains arbitrary. Managers prefer to draw up instructions because they perform several functions at once:
- drafting specifically for each employee depending on the situation;
- eliminating duplication of similar work tasks;
- division of responsibility;
- resolving possible disagreements;
- significant simplification of work organization.
You can take the Unified Tariff and Qualification Handbook for Works and Responsibilities as a basis. But many of its provisions are considered outdated and do not reflect the current needs of managers. Local authorities have the right to make their own amendments to this provision.
The content of the job description is determined directly by the manager. Additional responsibilities are included if they meet the specified conditions:
- Associated with current changes in working conditions.
- Their reason was the technical reorganization of the enterprise.
- It is mandatory to include them in the qualification characteristics.
In other situations, an additional agreement must be drawn up.
How to document an employee’s combination of professions (positions)?
Personnel officer. Personnel records management, 2008, N 4
Question: How to document an employee’s combination of professions (positions)?
V. Nikolaeva, HR specialist
Answer: Firstly, the name of the position for which the issue of combination is being discussed must be reflected in the organization’s staffing table. Secondly, it is necessary to make changes to the employer’s employment contract with this employee.
However, in practice they often resort to drawing up an additional agreement to the employment contract.
Then an order (instruction) is issued on the employee combining professions (positions). There is no unified form for this kind of order. The form can be arbitrary. But the order must certainly reflect the following: the combined (vacant) position, the amount of additional payment, the term of the combination. A sample order is shown in Fig. 1.
Sample order to establish combination of positions
—————————————————————————¬ ¦ Closed Joint Stock Company Neptune ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ Order ¦ ¦ ¦ 12/18/2006 N 57¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ Moscow ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ On the establishment of Sidorova I.P. ¦ ¦ combination of positions ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ In connection with the presence of a vacant position of a personnel inspector and the need to carry out work on the preparation of personnel documentation ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ I order: ¦ ¦ 1. To establish for Irina Petrovna Sidorova a combination of the positions of secretary¦ ¦ and personnel inspector from January 1, 2008 to July 1, 2008 ¦ ¦ 2. Determine I.P. Sidorova. list of responsibilities for the combined positions of secretary and HR inspector in the job description of HR inspector. ¦ ¦ 3. Establish Sidorova I.P. additional payment for combining positions in the amount of RUB 3,000. monthly. ¦ ¦ 4. Bring this order to the attention of all employees of the organization. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ General Director B.F. Anokhin ¦ L——————————————————————————
A similar order is issued when the volume of work performed by an employee increases, but with indispensable reservations: supplement the employee’s job description with new responsibilities and increase the official salary.
A. Demushkin Head of Department of Preschool Educational Institution VNIIDAD
Signed for publication on March 25, 2008
ATTENTION! Messages on the site are not pre-moderated. If you are the author of any material, write to [email protected] to restore legality!