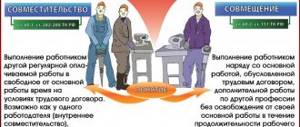
Features of the work of shift workers
A distinctive feature of shift workers is that they perform work outside their place of residence. This form of labor is used if it is impossible to ensure the daily return of workers to their place of residence due to the significant remoteness of the place of work. The employer is obliged to deliver shift workers to their place of work and provide housing.
It is used when it is necessary to reduce the construction or repair time of production facilities or infrastructure in areas that are not provided with the necessary labor resources.
The list of organizations that are allowed to use a rotational work method is given in Decree of the USSR State Committee for Labor dated December 31, 1987 No. 794/33-82. Such enterprises include:
- construction, installation, repair and construction organizations;
- oil and gas industry;
- forest industry organizations;
- railway transport;
- geological exploration.
The place of work of shift workers is the facilities where they actually perform labor duties during the shift. The fact that the work is being performed in this way must be announced to the employee at the stage of concluding an employment contract.
The shift lasts up to one month and is extended to three, but only in exceptional cases (Article 299 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Depending on its duration, methods are distinguished:
- usual: shift period up to 10 days, short distance, administrative and management personnel, as a rule, permanent, located directly on site;
- rotational-expeditionary: the duration of the shift is more than 10 days, considerable remoteness, located in inaccessible areas, administrative personnel also work on a rotational basis.
With this form of labor - a rotational work method - working hours and wages are recorded on a cumulative basis. The accounting period can range from a month to a year. Its duration must be fixed in a local regulatory act (that is, an order or regulation in a specific organization).
Calculation of payments to shift workers
The variety of remuneration schemes for workers on a rotational basis comes down, as a rule, to two options, enshrined in the accounting policies of the organization and its local labor regulations.
Based on salary
To calculate wages, the average hourly rate is first determined based on the standard working hours for the year. The calculation is made at the beginning of a specific period (year), and the indicator is applied until its end. To do this, the employee’s monthly salary or tariff rate is multiplied by 12. The resulting figure is divided by the annual standard of working hours.
You can calculate the average hourly rate for each month separately by dividing the salary or monthly tariff rate by the monthly standard of working hours, in accordance with the production calendar. Then the average hourly rate, calculated in one way or another on the basis of salary, is multiplied by the number of working hours in accordance with the schedule.
Based on hourly (daily) tariff rate
An economically justified estimated tariff rate per day or hour is also often used when calculating wage amounts. If the rate is calculated by the economic service of the organization per hour, then it is multiplied by the number of shift hours of the shift, and then the resulting amount is multiplied by the number of days worked according to the schedule per month.
If the rate is initially calculated per day, then its value is multiplied by the number of days worked according to the schedule per month. In both cases, the result is the amount of wages for the month.
Shift allowance is also calculated in two ways:
- in a fixed amount;
- as a percentage of salary.
In the first case, the number of shift days per month (not excluding weekends and holidays) should be summed up with the employee’s days on the way to work. The resulting amount must be multiplied by the premium rate accepted in the organization.
In the second case, the total number of calendar days of work and travel time of the employee in a specific month is first calculated. Then the average daily indicator is determined by dividing the salary amount by the number of calendar days of this month. The first value is multiplied by the second and then multiplied by the percentage of the salary increase accepted in the organization.
Who should not be hired to work on a rotational basis?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Article 298 establishes restrictions on the involvement of workers on shifts. So, you cannot involve in such work:
- minors;
- pregnant women;
- women with children under three years of age;
- persons for whom this type of work is contraindicated according to a medical opinion.
The conclusion of an employment contract with an employee must be preceded by a mandatory medical examination. Based on its results, a conclusion is issued on the possibility of involving the employee in shift work. The medical examination is carried out in a medical institution with which the employer enters into an agreement. So the question of the possibility of concealing diseases that prevent an employee from working a shift disappears by itself.
Shift work method: salary calculation, examples
When accounting for working hours in total, as a rule, time-based wages are used for rotational work, based on the tariff rate. Although labor legislation does not prohibit calculating wages on a rotational basis based on piece rates. However, in practice this does not happen often.
In the time-based form, payment for the shift method is made as follows:
1. Based on the hourly tariff rate:
2. Based on the daily tariff rate:
3. Based on salary:
In addition to working hours, the daily wage rate for shift workers is paid for:
- every day of inter-shift rest;
- every day the employee is on the way to the place of performance of work duties, for days of delay on the road due to weather conditions or other valid reasons.
In addition, the employer can issue bonuses to rotational employees as incentive payments.
Stages of calculating shift earnings
We can conditionally divide payroll into the following stages:
- calculation of earnings depending on the system used - according to the production rate, tariff, unit of time worked;
- payment for inter-shift rest days for overtime on shift;
- accounting and payment for overtime work;
- accrual of allowances.
Supplements are calculated separately. The following types are provided:
- for the shift method;
- regional coefficients;
- for harmful and/or dangerous working conditions.
Payment of an allowance for shift work, in fact, replaces the payment of daily allowances, which shift workers are not paid.
Examples of salaries for shift work
Using an example, we will consider all the stages of calculating wages for a shift worker working in a construction organization.
Construction Company LLC is building a facility located 1000 km from the company’s location. The accounting period is a quarter. The norm in the 3rd quarter of 2021: working days - 65, working hours - 520.
Foreman of construction and installation works Semenov S.S. in July 2019 the following schedule is set:
- working shifts are set from 2 to 10 and from 20 to 28 July at 11 o'clock. Day off is Sunday. A total of 16 shifts of 11 hours;
- travel days: July 1, 11, 19 and 29 (4 days);
- days of inter-shift rest: from 12 to 18 and from 30 to 31 July (7 working days).
Semenov S.S. The salary is set at 50,000 rubles. per month.
Calculation example in the table:
| Index | Calculation of the rotation method | Result |
| Daily rate | 50 000 × 3 / 65 | 2307,69 |
| Hourly rate | 50 000 × 3 / 520 | 288,46 |
| Payment for time worked | 288.46 × 11 hours × 16 shifts | 50 768,96 |
| Payment between shifts | 2307,69 × 7 | 16 153,83 |
| Additional payment for travel days | 2307,69 × 4 | 9230,76 |
| Payments based on the tariff rate | 2307,69 + 288,46 + 50 768,96 + 16 153,83 + 9230,76 | 78 749,70 |
Shift allowance in 2021
A shift bonus is a payment established to shift workers for the period of duty and for the time spent traveling to the place of work and back to the place of residence. It is paid instead of daily allowance. Commercial companies set the amount of such an allowance independently.
For state-owned enterprises, the amount of allowances is regulated. What legislative document establishes the amount of the shift allowance?
Allowances for employees of government agencies are approved by the government agency at the appropriate level of government. For example, for federal government agencies their size is regulated by the Government of the Russian Federation. Thus, the Resolution of 02/03/2005 established the following allowances from the tariff rate for shift workers:
- 75% - in the Far North;
- 50% - in the regions of Siberia and the Far East;
- 30% - in other areas.
Let's return to our example.
At Construction Company LLC, the collective agreement established a bonus for all shift workers in the amount of 30% of the salary.
| Index | Calculation of allowance | Result |
| Supplement instead of daily allowance (watch time plus travel time) | 50,000 / 31 × (16 days + 4 days) × 30% | 9677,42 |
| Total for accrual to S.S. Semenov for July | 78 749,70 + 9677,42 | 88 427,12 |
Supplement amount
Commercial organizations (not financed from the budget) themselves establish the amount of the bonus in their internal documents: collective agreement, Regulations on remuneration, etc. This is stated in Part 4 of Article 302 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: can the premium for shift work be more than the daily allowance?
Answer: yes, it can.
Restrictions on the amount of the allowance (no more than the amount of daily subsistence allowance for business trips in Russia) are established only for budgetary organizations (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 3, 2005 No. 51). For commercial organizations, as a rule, there are no such restrictions.
Thus, in an employment or collective agreement, an organization can provide for any amount of bonus. For example:
- establish an increase as a percentage of the daily rate (salary), but not more than 100 rubles. per day (as in budgetary organizations);
- establish an increase as a percentage of the daily rate (salary), but not more than the daily allowance provided for in the internal documents of the organization (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- do not set restrictions on the maximum amount of the premium.
Deductions from wages on a rotational basis
From the salary paid to an employee, the employer has the right to make several types of deductions:
- The employer is required, as a tax agent, to withhold personal income tax from payments to employees.
- If the employee receives a writ of execution to withhold alimony or other amounts awarded for collection.
- In addition, the employee is free to express his desire to withhold certain amounts from him: professional contributions, repayment of a loan received from the enterprise, etc.
Withholding personal income tax and calculating alimony during a rotational work schedule have a number of features. Thus, from payments based on salary, established bonuses and other incentive payments, deductions are made entirely in the usual manner.
But income tax and alimony are not withheld from the shift bonus. This is due to the fact that the payment is compensatory.
Let's return to our example.
Semenov S.S. is a resident of Russia, therefore personal income tax is withheld from his income in the amount of 13%. He has a 10-year-old child, for whom he pays child support in the amount of 25% according to the writ of execution. The employee wrote an application for a social deduction for a child in the amount of 1,400 rubles.
| Index | Calculation of allowance | Result |
| Personal income tax | 78 749,70 × 13 % | 10 237,00 |
| Alimony | (78 749,70 — 10 237) × 25 % | 17 128,18 |
| Total payable to Semenov S.S. for July | 88 427,12 — 10 237,00 — 17 128,18 | 61 061,94 |
Payments at the tariff rate and surcharge: taxes
Let's consider the taxation of shift allowance in 2021: the employer pays insurance contributions to the budget from payments to employees working on a rotational basis in accordance with Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- 22% - for pension insurance;
- 5.1% - for health insurance;
- 2.9% - for social insurance.
Shift allowances are not recognized as subject to insurance premiums. Such clarifications are provided by the Ministry of Finance. In its Letter No. 03-04-06/49149 dated July 13, 2018, the regulatory authority concluded that the allowance is a compensation payment and, therefore, not subject to taxation, in accordance with paragraph. 10 pp. 2 p. 1 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
All payments to shift workers under an employment contract are included in the organization’s expenses in full, in accordance with the rules of the applicable taxation system.
Tax and insurance payments
The bonus for shift work is not a salary. The employee receives it even if he does nothing at all (for example, while traveling to the place where the shift will take place). This is a payment for working in extreme conditions. However, it has something in common with wages: it can reduce income taxes. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows this if the collective agreement clearly states that shift payments are among the expenses for remuneration of employees.
Read more: Consultation with a lawyer on labor law in Voronezh
Taxation concerns not only enterprises, but also the people employed in them. So, in particular, personal income tax is withheld from each of them. However, this does not apply to payments to employees working on shifts. This is due to the fact that such payments are considered as compensation, and not as employee income.
The same applies to such things as insurance contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance. Payments to shift workers are not considered as earnings; they only compensate for inconveniences associated with the special nature of the work. Accordingly, insurance premiums are not paid for them.
In passing, we note that insurance premiums are also not paid on daily allowances paid to employees on business trips. The bonus for shift workers is, in fact, the same daily allowance (albeit regulated by other articles of the Labor Code), therefore similar rules apply to them.
What is the difference between a shift and a business trip?
At first glance, it seems that there is a lot in common between the concepts of “shift” and “business trip”. Therefore, unfortunately, situations are not uncommon when unscrupulous employers try to register the work of shift workers as business trips. After all, when traveling on a business trip, you do not need to comply with the legal requirements for the payment of shift bonuses, or apply regional coefficients and allowances that are established when working in the Far North and equivalent areas.
Let's see what the difference is:
- A business trip is a trip by an employee on behalf of the employer to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work (another locality). That is, this is the execution of a one-time order for a limited time.
- A shift is a special method of carrying out the labor process outside the place of permanent residence, when it is not possible to ensure a daily return to the place of residence.
If a company, for example, sends employees in teams to another area to carry out construction work on an infrastructure facility (bridge) regularly for several months, this cannot be documented as business trips. Moreover, such a substitution of concepts is illegal and entails the imposition of administrative fines on the unscrupulous employer. And if your employer commits such a violation, you have the right to challenge his actions in court. After all, such a substitution of concepts is fraught with the loss of a sufficiently large amount of money to employees.
Comparison of payments and bonuses due to rotational workers and seconded employees
| Statutory payments and deductions | Watch | Business trip |
| Salary | Tariff rate. | Average daily earnings. |
| Compensation payments | Shift bonus (usually at least 30% of the tariff rate). Shift allowance is not subject to personal income tax. Regional allowances (from 10% of the tariff rate) plus additional vacation. | Daily allowance (the amount is set at the discretion of the organization, it can be 100 rubles). Daily allowance over 700 rub. are subject to personal income tax. Regional bonuses are not paid. |
| Payment for accommodation | Housing is provided or compensation is paid for its rental. | Living expenses are reimbursed by the employer. |
| Directions | From the collection point to the place of work is organized and paid for by the employer. | Travel expenses incurred will be reimbursed. |
| Nutrition | Organized and paid for by the employer. | Expenses are not reimbursed separately; meals are paid from the daily allowance. |
About the author of the article
Alla Kotova Accountant, chief accountant, tax specialist.
Author of specialized articles in electronic media.