Three-stage control over labor protection is a form of control voluntarily chosen by the employer over the state of conditions and labor protection in the organization, a kind of internal audit. Although the form is voluntary, control is mandatory, for example, within the framework of the occupational safety and health management system.
After all, as practice shows, many violations, even minor ones, that can lead to injury, can be avoided by regular checks. Therefore, if your manager has determined that the organization will carry out three-stage control to check compliance with labor protection requirements, then I recommend reading an article in which we will analyze in detail what tasks it pursues and how three-stage control is organized. I will provide samples of documents required when maintaining control, both for large organizations and for public sector employees, for greater understanding by various categories of readers.
At the end of the note, as always, I will share useful material, this time these are checklists for conducting your own internal audit for different types of work and for different areas and types of organizations.
I prepared this note at the request of an occupational safety specialist with whom I have known for a long time, almost personally, so if you have any difficulties, I can sort out the material of interest in the next article . And if you want to share your experience in conducting inspections, or you still have questions, write in comments.
. And if you want to share your experience in conducting inspections, or you still have questions, write in comments.
Is the employer obligated to introduce graded control?
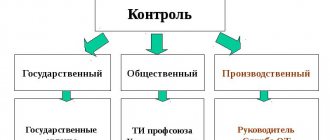
Staged control over labor protection is a check of compliance with safety requirements in the workplace by representatives of different levels of management of the organization.
Whether every employer is obliged to introduce graded control is a controversial issue. On the one hand, at the moment there is a direct requirement only in construction (clause 19 of the Rules on labor protection in construction, approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 06/01/2015 No. 336n). On the other hand, any employer is obliged to create and ensure the functioning of a labor safety management system (hereinafter referred to as the OSHMS; Article 212 of the Labor Code).
In turn, OHSMS implies monitoring compliance with labor protection requirements at several levels of management. Moreover, the Standard Regulations on OSMS, which was approved by the Ministry of Justice, presupposes step-by-step control (clause 55 of the Standard Regulations on OSMS, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated August 19, 2016 No. 438n, hereinafter referred to as the Regulations on OSMS). Therefore, there is no direct requirement to introduce graded control for all employers, but there are indirect instructions.
Step control can become a reliable system for preventing industrial injuries. It will allow:
- promptly identify and eliminate violations of labor protection requirements;
- apply measures that will prevent repeated violations;
- effectively distribute responsibilities for labor protection control;
- involve all employees in monitoring.
How many control stages to choose
To determine how many levels of control are needed for a particular enterprise, you need to analyze the characteristics of production: type of activity, number of employees, enterprise structure, location of structural units, current working conditions.
Two-stage control. Suitable for small organizations or companies where most of the staff are office workers.
Three-stage control. It will be optimal for enterprises that consist of several production workshops located in one place.
Four-stage control. Suitable for large organizations with a large number of personnel and an extensive organizational structure, where there are remote divisions and branches in the regions.
The four stages are also used in enterprises with a large number of workplaces with harmful and dangerous working conditions. In this case, stage IV is strategic control, which is carried out by a labor protection commission consisting of department heads.
The most common version of step control is three-stage. It is universal and is used both in small companies and large enterprises. Therefore, using his example, we will show what documents need to be prepared and who should be appointed responsible in order to introduce multi-level control of compliance with labor protection requirements in the organization.
How to organize stepwise control in different organizations
| stage | Who conducts | When is it carried out? | |
| Two-stage control for an enterprise with 35 employees | |||
| I | Work manager, qualified personnel | Before the start of the work shift and continuously during the work shift | |
| II | Labor Safety Commission: - General Director; — occupational safety specialist; - Director of Sales Department | 1 time per month | |
| Three-stage control for the mechanical workshop of an industrial enterprise | |||
| I | Site foreman and authorized representative of the trade union | Before the start of the work shift and continuously during the work shift | |
| II | Workshop manager, authorized trade union representative, occupational safety specialist, equipment specialist | 2 times a month | |
| III | Labor Safety Commission: - General Director; — occupational safety specialist; - Production Director; - chairman of the trade union committee | 1 time per quarter | |
| Four-stage control | |||
| I | Site foreman and authorized representative of the trade union | Before the start of the work shift and continuously during the work shift | |
| II | Deputy shop manager, authorized trade union representative, occupational safety specialist, equipment specialist | 1 time per week | |
| III | Occupational Safety and Health Commission: - shop manager; — chief technologist; - Chief Power Engineer; — head of the labor protection service; - Deputy Chairman of the Trade Union Committee | 1 time per month | |
| IV | Labor Safety Commission: - General Director; - Chief Engineer; - Production Director; — HR director; - Director of Development; - chairman of the trade union committee | 1 time per quarter | |
Goals and objectives
The use of three-stage control allows you to achieve the following goals and objectives:
- proper compliance with the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation on labor protection;
- ensuring the safety of using production facilities, equipment, technological processes, means of production, etc.;
- maintaining production and work areas in appropriate condition;
- increasing the labor literacy of enterprise employees;
- ensuring proper sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- implementation of medical and preventive services for employees.
What documents should be developed for three-stage control?
In order to introduce three-stage control at an enterprise, they are developing (clause 4, Regulations on OHSMS):
- order to introduce control,
- regulations on the procedure for conducting three-stage control,
- log form and inspection report.
Order on the introduction of three-stage control and the creation of a commission on labor protection. It is published by the head of the organization. The order states:
- those responsible for conducting inspections at each stage;
- an employee authorized to manage and coordinate actions;
- composition of the labor protection commission;
- frequency of control;
- a list of local acts that need to be developed.
As the basis for the order, indicate Article 212 of the Labor Code and the Regulations on OSH. Employees are introduced to the order and signed.
Regulations on the procedure for carrying out three-stage control. It is designed to establish structure, duties and responsibilities at each level of control. The regulations define the main activities, specific control parameters, for example, the serviceability of the working tool, the level of illumination in work areas, etc.
In practice, most often the regulations are developed by the labor protection service, involving specialists who are well aware of the specifics of the work in their area. The provision must be agreed upon with the trade union or other body that represents the interests of workers, if there is one.
To introduce three-stage control over compliance with labor protection requirements in an organization, it is not necessary to develop a separate provision. The control procedure can be made an integral part of the OSMS.
Journal of three-stage monitoring of compliance with labor protection requirements. The log records violations that were detected during inspection at each control level. It indicates the person responsible for eliminating the identified violations, the necessary measures and the deadlines for their implementation. Using the information in the log, you can view the dynamics of labor protection violations and monitor how the responsible persons carried out the established measures.
There is no mandatory journal format, but there are recommended samples. The employer determines the number of magazines at his own discretion, depending on the structure of the organization. A convenient solution is to create a separate journal for each department. In this case, it will be available for carrying out shift checks at the first stage of control. The head of the department is appointed responsible for maintaining and storing the three-stage control log. When carrying out the following stages of control, the log is requested from the person in charge.
The law does not require the three-stage control journal to be numbered, laced and sealed; each organization decides this for itself. This design of the logs raises fewer questions for inspectors during inspections, as it eliminates the possibility of data falsification. The form of the journal can be approved by the provision on three-stage control.
Act of carrying out the third stage of control over the state of labor protection. The employer develops the form of the act independently.
The document is drawn up by the commission after the third stage of control. It records identified violations, determines the necessary measures to eliminate them, assigns responsibilities and deadlines for implementation.
Occupational safety inspection log, what can be written there
Free legal advice: All Russia > Occupational safety > Control > Standard form of a logbook for monitoring the state of labor protection and fire safety - sample + rules for filling out a logbook for monitoring the state of labor protection and fire safety helps to identify and take into account violations that exist at the enterprise and are associated with safety and fire safety regulations. Such a document is assigned so that the manager can always know exactly why violations occur and punish those responsible for this.
Dear readers! The article describes typical situations, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, use the online consultant form in the lower right corner of the site or call direct numbers: +7 (499) 653-60-72 ext.445 – Moscow – CALL+7 ext.394 – St. Petersburg – CALL here – if you live in another region. It’s fast and free!
The main purpose of the journal for labor protection control is three-stage control over safety during the operation of the enterprise.
It must be carried out by the shift supervisor, and this document is kept by him. In addition, filling out the log can be carried out by special employees who are responsible for labor protection and fire safety in a particular organization.
In accordance with the law and document flow rules, the journal is filled out in tabular form. The table consists of the following columns:
- Marking of completed work.
- Stage number.
- Violations that were discovered.
- Signature of the responsible person.
- This specifies the deadline by which problems must be resolved.
- Actions to be taken to correct the violation.
- Appoint a responsible person who will follow all instructions in column 4.
- Date when control was carried out.
We recommend reading: Documents confirming having many children
As for the title page, it must indicate the name of the organization and its structural unit, as well as the start date of the journal and the end date.
Who should be appointed responsible for three-stage control?
If the selection of those responsible is approached formally, then monitoring of compliance with labor protection requirements will be carried out poorly. Thus, violations will not be identified and eliminated in a timely manner, which can cause accidents or accidents at the enterprise.
Mistakes that employers most often make when assigning responsibility:
- involve in control employees who do not have sufficient production experience or knowledge in the field of labor protection to promptly identify violations;
- they appoint an insufficient number of responsible persons to fully monitor all structural divisions of the organization;
- do not create a system of interest and motivation for those responsible in conducting quality control.
Assign responsible employees who:
- competent as specialists;
- have extensive work experience;
- completed occupational safety training according to the program for managers and specialists.
For employees who will be appointed responsible, conduct a lesson in which you talk about the basic principles of the procedure and the procedure. Additional responsibilities related to control are listed in job descriptions. Set bonuses for those responsible for additional work.
How each stage of control is completed
At stage I, employees verbally report to their immediate supervisor about all violations. The person responsible for monitoring ensures that any violations identified are corrected immediately. If it is impossible to do this with the help of the department, then the violations are reported to the head of the workshop.
The person responsible makes an entry about each violation in the three-stage control log. The representative of the trade union also signs the entry if he took part in the inspections.
At stage II, the person in charge records violations in the three-stage control log, and a group of inspectors ensures that they are immediately eliminated.
After the third stage is completed, the commission draws up a report. All detected violations are also recorded in the three-stage control log of the unit in which it was carried out. The commission jointly develops measures to eliminate violations, appoints performers and deadlines for implementation.
In order for the three-stage control system to work more efficiently, the manager can bring disciplinary action against employees who have committed labor safety violations. And vice versa, encourage those who have achieved positive results in their work on labor protection, for example, by issuing a bonus.
Composition of control measures
The specific composition of activities is determined by the specifics of the type of activity. For clarity, let us consider three-stage control in the printing industry.
1st. A master with a safety representative controls:
- workplaces and approaches to them;
- ventilation, lighting;
- equipment, tools, devices, their condition;
- alarms, blockers, braking devices;
- electrical safety;
- availability of special clothing, safety shoes, and protective equipment for each employee;
- check the entries in the equipment technical control log, compare them with the actual condition, record the inspection and its results in the 3-stage control log;
- eliminate deficiencies if they are found.
2nd. The shop manager and the safety representative check:
- premises, workplaces therein and working conditions;
- how the deficiencies discovered at the first stage of the audit were eliminated;
- similar: lighting, room ventilation, equipment, protective equipment;
- selectively: employee knowledge of occupational safety standards and rules;
- make an entry in the 3-stage control log;
- develop ways to eliminate shortcomings if they are identified.
3rd. The chief engineer and the safety commission headed by him monitor:
- condition of premises and workplaces;
- condition of equipment involved in production;
- operation and condition of protective equipment, safety equipment, including individual ones;
- the process and result of eliminating deficiencies identified at previous stages of control;
- implementation of decisions, orders of management and the trade union committee on occupational safety.
The results of the commission’s work are entered into the 3-stage control log and discussed at a meeting of its members. Ways to improve safety in the field of occupational safety are outlined. The commission draws up and signs a corresponding document, which reflects all the work it has done.
Members of the commission, in addition to the chief engineer himself, may be other chief specialists: a power engineer, a technologist, a mechanic, a representative of the trade union committee who heads its commission on occupational safety; OT engineer. The commission also includes representatives of the fire and medical services of the enterprise (according to the text of Order No. 237).
According to a similar principle, taking into account the type of activity, control is carried out in other production areas.