13.06.2019
0
88
6 min.
An employment agreement is a written document. It establishes the settlement of the main points between the employer and the work unit in the creation of labor products. The list of issues for discussion is diverse and requires detailed study. There are different types of contracts, the features of the main ones will be discussed below.
Contract for seasonal work
Please note that this type of contract is concluded for seasonal work, but is terminated not upon completion, but at the end of the season .
does not determine the start and end dates of climatic or other seasons . Therefore, a fixed-term contract should indicate the calendar date of termination of the employment relationship.
If it is not specified, can be used.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
In this case, the basis for dismissal is the legal fact of the onset of the calendar date, which is indicated in the act of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation as the end of a specific climate season for the current year.
Employer as a subject of labor law
See also paragraph 2 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2018 No. 15 “On the application by courts of legislation regulating the labor of workers working for employers - individuals and for employers - small businesses that are classified as micro-enterprises”
Employer is an individual or legal entity that has entered into an employment relationship with an employee. In some cases established by law, another entity with the right to enter into employment contracts may act as an employer.
In order to act as a party in labor relations, the employer must have labor legal personality, but first of all, employer legal capacity - the ability to hire citizens and enter into employment contracts with them. Thus, an employer can be an individual citizen who hires a nanny, a housekeeper, a personal driver, etc., or a private entrepreneur, both a Russian and a foreigner, or a public organization that hires employees for its staff, or a religious organization. etc.
But in most cases, as a rule, in labor relations, the role of employer is a legal entity - an enterprise, organization, institution.
In labor law, the term “employer” refers to an organization that acts in the labor market as an entity that offers work and organizes the work of workers. As a subject of labor law, an employer is, as a rule, a legal entity that has entered into an employment contract with an employee.
A legal entity is an organization in which citizens work under the terms of an employment contract. In accordance with Art.
50 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, commercial and non-profit organizations can be legal entities. The former pursue profit as their main goal, the latter pursue other goals.
Current legislation links the formation of an employing organization as a subject of labor law with the procedure for its official establishment. Such an institution is possible:
- by decision of the owner of the property or the body authorized by him;
- by decision of the labor collective of a state or municipal enterprise;
- on the basis of separating one or more structural divisions (units) from the existing organization, with these structural divisions (units) retaining the rights of a legal entity;
- as a result of forced separation in accordance with the antimonopoly legislation of the Russian Federation.
From the date of state registration with the justice authorities, the organization is considered established and acquires the rights of a legal entity, i.e. and labor legal personality as an employer.
Labor legal personality is determined by two criteria:
The operational criterion characterizes the features of the content of the organization’s activities as a subject of labor law. It comes down to recognizing its ability to select and place personnel, organize the work of workers, and create for them the necessary conditions for high-quality and highly productive work.
The property criterion characterizes the organization’s ability to pay employees for the results of their labor. In other words, in order to carry out production and economic activities, an organization must have a certain property potential (fixed and working capital).
The activities of an organization (employer) as a subject of labor law may be terminated due to its liquidation:
- by decision of the owner of the organization or the body authorized to create such an organization;
- By the tribunal's decision.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
Employees dismissed due to the liquidation of the organization are guaranteed compliance with their rights and interests provided for by labor legislation.
Types of work contracts are fixed-term and concluded for an indefinite period: as defined by the Labor Code. These are basic concepts, then employment contracts are detailed depending on the specifics of the parties and additional conditions.
Special cases of working relationships: with an individual, a foreigner - are also described in labor legislation. Contracts with municipal and government employees and civil transactions are considered separately. They do not relate to labor agreements and are regulated by other rules.
Next, we will consider what types of employment contracts exist, based on their specifics.
Classification criteria
What kind of employment contracts there are with employees is a question that deserves attention. There are several agreements, each is drawn up under certain conditions and has its own nuances. Therefore, it is quite understandable that people want to know more about the types of employment contracts and their features.
Working conditions
The main condition in the application of labor legislation is the creation of a favorable and safe environment for employees to carry out labor activities. The responsibility to fulfill these conditions in full rests with the employer; the main provisions must be specified in the contract.
Advice! Compliance with work and rest schedules, lighting parameters, temperature and ventilation, and hygiene standards in the workplace allows you to achieve the best results in the production cycle.
Validity
The term of a labor agreement may be a limited period of time or may not be specified at all. An open-ended contract is a separate type of employment contract. It is more advisable to enter into a forward transaction to complete a task within a period of time.
The legislator limits the prerequisites for drawing up labor agreements limited in time. The Labor Law establishes the conditions under which this transaction is considered valid:
- When filling the position of another person.
- When carrying out activities for no more than sixty days.
- When working during the season due to climatic conditions.
- A new employee posted to a foreign subsidiary and his or her employment will be treated as a fixed-term relationship.
- To carry out work that is not inherent to the employer.
- The short-term period of economic activity laid down when creating the organization will be the basis, and the conclusion of a transaction with a limited period of work will not cause any complaints.
- The effect of time-limited labor transactions is acceptable for citizens when working under conditions known in advance.
- The concept of “internship” creates the prerequisites for the execution of labor transactions with a time limit.
A special case when the conclusion is made by agreement. This is imperatively enshrined in the norm in question. This type of transaction is executed in the following situations:
- With persons who get a job with an employer from the small business category with a small staff.
- The presence of medical contraindications and retirement age will be the reason for signing an agreement with a temporary nature of work.
- When moving with employees of enterprises located in the Far North and equal (in terms of working conditions) territories.
- When participating in emergency response.
- With theater artists, media workers, workers of concert and film groups.
- Compliance with the position held in the “managers” category will be the basis for concluding a temporary agreement.
- Full-time study will also have an impact on the signing of a fixed-term agreement.
- The legislator considers the performance of labor duties by those hired on sailing vessels through the prism of fixed-term agreements.
Specifics of labor relations
The main employment is understood as the employee’s carrying out labor activities for the employer, on his premises and under a standard workload. Most mercenaries perform their labor functions in this way.
Part-time work is the right to draw up labor agreements on work in personal time, without prejudice to the main activity. Its variety lies in the possibility of applying labor in different places: both with the “native” employer (internal part-time work) and with a new one (external part-time work).
Labor legislation allows for the possibility of working from home. Homeworkers are citizens who have entered into a labor agreement on professional activities at home. This feature is a characteristic difference in such work.
Employer
The types of employment contracts and their conditions differ between individual entrepreneurs and legal entities. There are no significant differences for a private owner and an organization acting as a hirer. The difference is that taxation, payment of contributions and payments, registration of pension certificates - all this in everyday operating activities falls on the fragile shoulders of individual entrepreneurs. Additionally, the employer - an individual - has the obligation to register a labor agreement with the employee with a local authority by notification.
It is important to know! A private employer is not given the authority to draw up and make changes to work books. He will have a hard-working agreement concluded in writing as proof of the work being completed.
Urgent
Depending on the nature, type, conditions of the work or by agreement of the parties, an urgent TD is concluded. When applying for a job, these types of contracts imply the end of the activity for various reasons. This:
- seasonality;
- practice, internships;
- performing alternative service;
- participation in elected bodies or provision of this activity;
- other.
Second part of Art. 59 of the Labor Code determines cases of concluding an urgent TD by agreement of the parties:
- with pensioners;
- with creative workers and managers;
- full-time and part-time students;
- sailors:
- other.
Fixed-term types of contracts with employees are concluded:
- in organizations located in the Far North;
- when eliminating the consequences of disasters;
- if the number of employees of the enterprise does not exceed 35.
The maximum period for which a fixed-term TD is concluded is 5 years.
Form and sample employment contract
For external part-time
| Type of agreement | Form |
| Indefinite | |
| Urgent | |
| Seasonal | |
| With an internal part-time worker | |
| With IP | |
| With a government employee | |
| With the executive director | |
| With a disabled person | |
| With a minor | |
| To work in hazardous conditions | |
| To work in the Far North |
Effective contract
The classification of employment contracts set out in the Labor Code does not take into account such a form as an effective contract. This is not a separate type of TD, but a link between labor results and incentive payments.
The document must clearly indicate performance criteria, conditions and amounts of incentive payments. This concept was introduced by the government of the Russian Federation and enshrined in its resolution No. 2190-r dated November 26, 2012.
The mechanism for introducing an effective contract is determined by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated April 26, 2013 No. 167n and applies to employees of state and municipal institutions.
With a foreign citizen
Labor legislation applies to all working people in the Russian Federation, including foreigners and stateless persons. Therefore, the often asked question about what types of employment contracts exist when hiring a foreign citizen is not entirely correct.
However, an agreement with a foreigner has a number of features. In addition to standard provisions, it contains information:
- about a document permitting residence on the territory of the Russian Federation - temporary residence permit or residence permit;
- about a patent or other permission to work in the Russian Federation;
- on the basis of which medical care is provided to a foreigner - insurance policy number.
Requirements for the content of an employment contract
The employment contract is the main institution of labor law. It can be considered in several aspects:
- as an employment agreement, which is concluded between the employer and employee in writing;
- as an institution of labor law, whose rules regulate the nature of hiring, transfer to another job, as well as dismissal, which is expressed in the conclusion, amendment and termination of an employment contract;
- legal fact of initiation, change and termination of labor relations and their derivatives.
The parties and content of the employment contract form its basis. The content of the employment contract is determined by the mutual consent of the parties. In essence, it constitutes a set of conditions that determine the range of rights and obligations of both the worker and the employer.
Requirements for the content of an employment contract require information about information and conditions. Information represents those facts that are characterized by significant legal significance. Their provision is characterized by a fixed form. There can be quite a lot of contract terms, some of them are mandatory, and some are additional. Each of these groups of conditions has its own characteristics.
Differences in the nature of work
The types of employment contracts concluded with employees differ according to the nature of the work:
- for registration at the main place of work,
- to regulate part-time work,
- for seasonal work,
- for employment by an employer - an individual,
- for home work,
- for registration in the civil service.
Important elements of an employment contract include the types of conditions for future activities. Samples of different types of employment contracts include mandatory terms on remuneration, work and rest hours, and compensation for special working conditions.
The type of work is specified in the employment contract. In addition to the main aspects of work, the contract includes optional clauses on continuous improvement of skills, rental housing for the employee, and payment for mobile communications.
Employment contracts by volume of work performed
Russian labor legislation defines the classification of contracts concluded depending on the volume of work performed:
- main job agreement,
- part-time work agreement.
In turn, the agreement on the performance of the main work presupposes that the employee carries out work in full and in accordance with the internal regulations established at the enterprise. Working at the main place also requires a place to store the work book. An employment contract concluded for the performance of combined work (Chapter 44 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) provides for the employee to perform other functions with regular payment, in his free time from his main job. The duration of part-time working hours should not exceed 4 hours a day, that is, 1/2 of the total working time for the corresponding accounting period. A part-time employment contract can be internal (with the employer at the main place of work) and external (with the employer of a third-party organization). The conclusion of a part-time employment contract can be concluded with an unlimited number of employers, unless prohibited by law. For example, professional coaches and athletes have the right to enter into a contract for part-time work only on the basis of permission from the employer of the main job. Employment contracts concluded for part-time work should be distinguished from:
- combining positions - when an employee is offered to perform another job for additional pay during the same working hours, which are provided for in the main contract;
- expanding service areas and increasing the volume of work - when an employee performs his job functions with greater intensity.
Concluding an employment contract for part-time work is not permitted with persons under 18 years of age, as well as with persons working in hazardous/harmful working conditions, if the proposed combined work has similar characteristics.
Differences in terms and legal status
The types of employment contracts concluded by the parties differ in terms:
- standard conditions,
- work in special climatic conditions,
- night work
- hard work in dangerous conditions.
Certain types of TD differ according to the legal status of the employee:
- employees under 18 years of age,
- persons performing family duties,
- foreign citizens, stateless persons.
It should be noted that drawing up an employment contract with a foreign citizen who has a residence permit in the Russian Federation is no different from employing an employee with Russian citizenship.
Alteration
The conclusion of an employment contract does not depend on its type. In particular, in the Russian Federation, all types of employment contracts must be drawn up in two copies and signed by the parties. After concluding an employment contract, the following types of changes can be made to it:
- employee transfer,
- changing the terms of the contract,
- change of owner of the organization,
- removal of an employee from performing duties;
The need for changes caused by a change in working conditions, as a result of which the employee will work at night, in shift mode, in another city, can be included in the contract at the initiative of the employer after prior notification of this to the employee two months before the proposed changes. The employee has the right to refuse to change working conditions.
In this case, the employer offers all available vacancies to the employee to choose from. If a compromise is not found, the contract is terminated.
A change of owner allows the new owner to terminate employment relations with the management team of the organization within 3 months after the transfer of ownership. This fact cannot be considered as a basis for the dismissal of other full-time employees.
The introduction of a condition related to the need to remove an employee from work is associated with his appearance in a state of intoxication at the workplace, failure to undergo a medical examination or a TB knowledge test, and other circumstances described in the legislation. During the period of suspension from work, payment of wages is not provided.
What does an employment contract with an employee look like?
Follow simple rules when concluding an employment contract with an employee: print out the sample in two copies, certify each of them with the signatures of both parties, and in the “header” indicate the place of preparation and the current date. For convenience, divide the document into thematic sections: general provisions, social insurance, operating hours, etc. This is what an employment contract (sample) looks like, filled out in accordance with the requirements of GOST R 7.0.97-2016.
When hiring a temporary or seasonal worker, be sure to include a urgency clause in the contract. If this is not done, the employee is automatically considered hired for an unlimited period. This is an example of an employment contract with a limited duration:
Have the employee sign for their copy in the log book or on the contract retained by the HR department. And don’t forget: an employment contract is not an empty formality, but an important document that protects the interests of the employer and clearly regulates relations with the employee.
Source
KA "Personnel Method" is a recruitment agency in Moscow for fast and effective search and selection of personnel in Moscow and Russia. Our recruitment agency will provide recruiting services for the personnel you need. We are looking for and selecting top personnel (top managers, directors, senior managers), middle management personnel, IT specialists, sales managers, line personnel, accountants, doctors, stylists, ... We offer for Moscow and the Moscow region - mass recruitment of personnel - the cost is discussed separately . We provide guarantees for the personnel selected by our agency. Information for employers on personnel search and selection services can be found on this page . On the “Promotions” page you can find out about our latest promotions and special offers on personnel recruitment for Customers (employers). On the job description catalog page, read what the job description should be and download the basic versions of the job description. We will search for employees and search for workers for you in a short time. For your convenience, we have created a section “Recruitment by profession” in which we have posted detailed information on the main positions of popular applications from Search and Selection Customers, but linked to a specific job title, for example, secretary, sales manager, merchandise manager, remote sales manager sales, purchasing manager, top personnel, managers, etc., as well as the section “Search and selection (recruiting) of personnel by specialization.” We also have a personnel selection service at a fixed cost!
Termination procedure
Termination of an employment contract depends on its type. With a fixed-term type of employment contract, the legal relationship ends within the time period specified in the contract. The employer warns the employee in writing about the upcoming dismissal 3 days before the date specified as termination of the contract.
To terminate a permanent contract, the employer must present compelling circumstances. Dismissal at the initiative of an employee requires only written notification to the employer a few days before the expected date of dismissal.
In addition to individual contracts of various types, it is possible to conclude a collective agreement to regulate social and labor relations. The main points included in the collective agreement relate to the mutual obligations of the parties and are listed in Article 13 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Collective Agreements”.
The stage of discussing the draft agreement with employee representatives is an integral part of the development of a collective agreement.
Clearly defined functions of the employer and the contractor
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
According to the articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employment contract between an employer and an employee is a written agreement. Requirement of Art. 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates in detail the relationship between employee and employer.
The concluded contract must indicate the duration of its validity and stipulate the responsibilities of the employer:
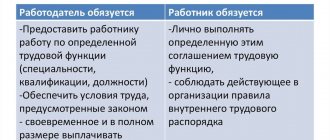
- The employer requires the individual to complete tasks, providing the necessary mechanisms, protective equipment, and decent wages to perform the assigned functions.
- Obliges to pay the employee wages in full on a specific day of the month.
- The contractor is obliged to ensure that the contractor does not delegate the work to third parties.
For his part, the contractor must come to work on time, perform functional duties, avoid violating safety rules, and so on.
I. Concept and distinctive features of an employment contract
Any relationship between employer and employee must be regulated by relevant documents. An employment contract concluded between two parties is the root cause of the emergence of labor relations.
An employment contract, according to Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is “an agreement between an employer and an employee, according to which the employer undertakes to provide the employee with work for a specified labor function, to provide working conditions provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, laws and other regulatory legal acts, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations acts containing labor law norms, pay the employee wages in a timely manner and in full, and the employee undertakes to perform the labor function determined by this agreement and to comply with the internal labor regulations in force in the organization.”
Thus, in its definition, an employment contract is clearly distinguished from other civil law agreements concluded to perform certain work (for example, a contract, an assignment), which is very important for the correct application of the law.
The difference between employment and civil law contracts is as follows:
- according to the employment agreement, the employee works in a specific position in accordance with his qualifications, and under civil contracts related to labor, the worker (contractor or performer, but not the employee) performs a certain task with an end result (for example, repairs or writing a book);
- under an employment contract, the work is performed personally by the employee, since only he controls his ability to work;
- In the course of his activities, the employee is obliged to obey the internal rules established by the employer, and their violation entails disciplinary sanctions or even dismissal. While failure to fulfill a contract related to work, but not being an employment contract, leads to civil liability;
- the conditions for performing the work are provided by the employer (and not the performer), and he is also responsible for the loss of the fruits of labor;
- the employer does not pay remuneration under the contract, but wages in the amount established by the employment contract.
Indefinite
An open-ended contract is signed with an employee on a voluntary basis when he is hired for permanent work without indicating its end.
In case of an open-ended contract, a trial period is concluded, the duration of which is no more than 3 months. This is indicated in the text of the document.
It also defines the position for which the employee is hired, the mode and conditions of work, salary and bonuses, rights and responsibilities.
When drawing up an open-ended contract, the text does not indicate the reason for its conclusion . This clause is required for a fixed-term agreement.
If changes are required to the terms of an open-ended contract, an additional agreement to it must be drawn up. This may be necessary when moving to another position, changing salary, regime or working conditions.
This type of contract is considered more reliable for the employee.
VI. An example of an employment contract and its main points
Let's look at an example of a real employment contract with an explanation of the main points.
A cap
The header indicates the place and date of conclusion of the agreement, the full name of the parties, as well as on the basis of which documents they act.
Clause 1. Subject of the Employment Agreement
This paragraph indicates where and for what position the employee is being accepted, the place of work, the type of contract according to the nature of the employment relationship, the start date of work and the presence and duration of a probationary period.
Clause 2. Rights and obligations of the Employee
The subsection “Rights” must specify the basic rights of the Employee, including the right to rest; wages; for compensation for harm received in the performance of work duties; for social insurance; to additional rights provided for by internal regulations and the Labor Code.
The subsection “Responsibilities” indicates the main responsibilities of the Employee, including the performance of job duties; compliance with discipline, internal regulations and labor protection requirements; information about the relationship to the Employer’s property; non-disclosure of information; other duties specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and regulatory documents of the company.
Clause 3. Rights and obligations of the Employer
The “Rights” subsection states the Employer’s right to incentives; to requirements to perform job duties; the right to hold the Employee accountable in accordance with the law; other rights that do not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The “Responsibilities” subsection specifies the Employer’s responsibilities to comply with Labor legislation, internal company regulations and agreements; on providing the Employee with work and ensuring his safety; obligation to pay wages; To provide information; carry out social insurance; compensate for possible harm caused to the Employee and other obligations.
Clause 4. Working hours and rest time
This section specifies the weekly number of working days and weekly working hours; the number of vacation days and the procedure for providing it.
Clause 5. Remuneration
The official salary and types of compensation payments are indicated here.
Clause 6. Amendment and termination of the Employment contract, dispute resolution
This section specifies the procedure in which labor disputes will be resolved and changes will be made to the employment contract, as well as the date it comes into force.
Collective
A collective agreement is a document fixing social and labor relations between the administration of an enterprise and its employees. The main sections that should be included in the contents of the document are described in Article 41 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It cannot include conditions that would violate the rights of employees guaranteed by the Labor Code. When a collective agreement is adopted, everyone has the right to participate in its creation.
The parties to the collective agreement are all employees of the enterprise and the administration. His conclusion is not necessary. The contract is drawn up for 3 years. Before the end of the term, it can neither be canceled nor terminated. Upon expiration, if it has not been renewed, it is automatically renewed for the same period.
The agreement is drawn up in 2 copies. One is kept by the manager, the second by the chairman of the trade union.
The content of a collective agreement usually includes the following points:
- remuneration, which indicates the system and types of payment, forms of bonuses, material incentives, cash benefits and compensation.
- Working hours. All work schedules with the necessary rest time are drawn up.
- Working conditions. Measures to protect health and reduce negative impacts on workers during the production process are included.
- Social guarantee. Possibility of providing free health vouchers or partial payment for them for employees and members of their families.
Individual
An individual agreement is drawn up between an individual employee and the administration of the enterprise. It stipulates the individual terms of the employment relationship. The agreement is provided in writing.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Ivan Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
The employee undertakes to perform work in his specialty in accordance with his qualifications. The employer undertakes to provide normal working conditions, as well as pay the employee in accordance with the salary and tariff rate of the enterprise.
The contract includes the following necessary items:
- place of work;
- position or profession;
- salary;
- date of start of work.
The individual agreement also includes additional points: operating mode, test period, preservation of trade secrets.
Contents of the employment contract: additional conditions
Additional or optional conditions cannot affect the very fact of the existence of an employment contract. Additional terms and conditions include:
- establishing a probationary period;
- establishment of part-time work;
- non-disclosure of secrets protected by law;
- the worker's obligation to work a certain amount of time after training on or off the job, paid for by the employer.
Both mandatory and additional conditions are characterized by a certain legal significance, namely:
- obligatory for both parties;
- are able to influence the content of the employment contract and labor relations;
- failure to comply with them entails legal consequences for each of the parties.
Both mandatory and additional conditions are subject to change only by mutual agreement of the parties, recorded in writing. An agreement to change conditions becomes an integral part of the employment contract. The general legislative rule involves a ban on requiring a worker to perform work that is not specified in the employment contract (Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).