- Article 72. Changes in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties
- Article 72.1. Transfer to another job. Moving
- Article 72.2. Temporary transfer to another job
- Article 73. Transfer of an employee to another job in accordance with a medical report
- Article 74. Changes in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties for reasons related to changes in organizational or technological working conditions
- Article 75. Labor relations when changing the owner of the organization’s property, changing the jurisdiction of the organization, its reorganization, changing the type of state or municipal institution
- Article 76. Suspension from work
back to contents
Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments 2019
Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments for 2021 contains mandatory conditions for changing an employment contract with an employee.
The contract can be adjusted in 2 main situations:
- when transferring an employee to another job;
- in the event of a change in the essential terms of the contract (in this case, the employee remains in the same position with the same job functions).
If a change in 1 condition (for example, the territorial location of the place of work) led to other changes (for example, the assignment to an employee of a monthly compensation for travel to a new place of work), then these consequences can not be taken into account when registering the main innovation. To approve them, a separate internal regulatory legal act (for example, an order for payment of compensation) is sufficient.
Commentary to Art. 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Comments on articles of the Labor Code will help you understand the nuances of labor law.
§ 1. Freedom and voluntariness of will when concluding an employment contract and various legal guarantees when hiring, transferring and dismissing an employee contribute to the stability of employment contracts.
A change in the employment contract entails a change in the employment relationship. And this, in turn, affects the stability of labor relations, in which both employees and the employer are interested.
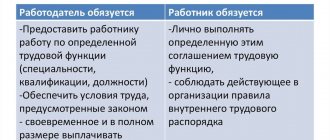
§ 2. The legislator prohibits the employer from requiring the employee to perform work not stipulated by the employment contract, except in cases provided for by the Labor Code and other federal laws (Article 60 of the Labor Code), which enshrines the principle of stability and certainty of the employment contract.
§ 3. A change in an employment contract is a change in its content, i.e. one or more of its conditions.
Changes in the terms of an employment contract determined by the parties themselves can only take place by agreement of the parties to the employment contract, with the exception of cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It should be borne in mind that the agreement to change the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties is concluded in writing. This rule should be strictly followed.
Thus, changing the content of the employment contract is possible in the following forms:
a) transfer to another job (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
b) changing the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
But ch. 12 of the Labor Code, in addition to these two forms of changing the employment contract, contains two articles (Article 75 “Labor relations when changing the owner of the organization’s property, changing its jurisdiction, its reorganization” and Article 76 “Removal from work”), which do not change the essential conditions of the labor contract itself agreement. Therefore, we do not classify them as forms of changing the employment contract. They are only placed by the legislator in Chapter. 12, called “Change of the employment contract”, since they are related to the further validity of the employment contract.
Under what conditions are amendments to an employment contract permitted?
All changes are permitted only by agreement of the parties. That is, the solution should be:
- mutual;
- voluntary.
Situations when the framework of cooperation with an employee needs to be adjusted according to other articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (that is, changes are mandatory) are subject to separate consideration.
To learn about when, if you change the terms of an employment agreement, you will need to issue a notification about this, read the material “Notification of changes to the terms of an employment contract.”
Conditions for changes in the employment contract
Article 72 of the Labor Code provides for the possibility of changing the terms of the contract. This must be done in writing. Typically, adjustments are made to wages, the nature of work or functionality, the length of the working day, the location of the enterprise, and compensation payments related to the use of personal transport.
Changing the information in the contract is also often required by a citizen if he changes his last name, improves his qualifications, or circumstances arise that do not allow him to work under the same conditions. The initiator sends a notification about the need to make changes. If for a legal entity a period of 2 months is determined by law, then for an ordinary citizen it is provided for 14 days, and if the organization is religious, then the period is even shorter and equal to one week.
Options for changes
The article should also be followed when temporarily or permanently transferring a person to another position. In the first case, the period should not exceed 12 months. Most often, this is how people are recruited to replace key employees who go on vacation or sick leave. Making a transfer for no more than a month is permissible without obtaining the consent of the persons in the following situations:
- Prevention of a man-made disaster is required.
- It was necessary to eliminate the consequences of a natural disaster.
- There was a threat to the lives of the population.
- As a result of the circumstances described above, there was downtime at the enterprise.
It is important to know! In other cases, a transfer can be processed only with the written consent of the citizen. He has the right to refuse, for example, if lower qualifications are required to perform the assigned tasks.
Conclusion of an agreement
Changes to the basic terms of the employment contract are carried out only in compliance with the established procedure. Violation of the algorithm calls into question the legitimacy of the employer’s action, so the HR department is obliged to carefully monitor this process. It is divided into several stages:
- If changes occur in the activities of the organization or there is an urgent need to reduce wages, the circle of persons whose interests will be affected by such actions is determined.
- Sending notifications about changes to certain clauses of the employment contract. It should contain detailed explanations of what changes are planned and the reasons that caused them. This is done in writing 2 months in advance, this is the period given for signing the additional agreement.
- If an employee refuses the proposed adjustments, he is transferred to another job or resigns.
- Drawing up an order on changes in working conditions, familiarizing each interested person with signature.
The supplementary agreement to the employment contract must reflect the main changes, and is prepared in two copies for each party. It is signed by the head of the company and the citizen, and one of the options is attached to the contract, without which it is not used. The date and place where the agreement was signed, as well as details of the parties that allow them to be identified, must be indicated.
When is a change to an employment contract necessary under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation identifies groups of cases when the terms of an employment contract should be adjusted:
- Transfer to another job for health reasons in accordance with a medical report. If the employer does not have another job or the employee does not want to work in another position offered to him, the employment contract may be terminated (Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Transfer to another job if the employee does not correspond to the position held (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In a situation where an employee has not passed the certification procedure established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, you should try to transfer him to another, simpler job with a corresponding change in the contract. If the employee refuses, the employment contract can also be terminated.
- The transfer of pregnant workers to another job is negotiated separately in order to reduce the impact of harmful and hazardous production factors on their body. In essence, this is a separate version of translation based on a medical report. The main difference is that the employer does not have the right to fire a pregnant employee and is obliged to find her a job with a workload allowed by doctors.
What are the nuances of transferring to another job under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
The transfer can be temporary or permanent. It is described more fully in Art. 72.1 and 72.2, supplementing and clarifying the basic standards of the original art. 72 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The following should be considered temporary:
- Transfers in connection with the replacement of a temporarily absent employee for up to 1 year. If 1 year has expired, and the employee continues to work in a new place and does not ask to be transferred to the previous one, the transfer begins to be considered permanent.
- Transfers for up to 1 month due to emergency circumstances. Accordingly, it is stipulated that the employee is transferred to perform work to prevent or eliminate the consequences of an emergency (for example, an industrial accident or natural disaster). The peculiarity is that the employee’s consent to such a transfer is not required, except in cases where this work does not correspond to the level of knowledge and skills of the employee.
Permanent transfers include all other types of transfers, including to another location with the organization and to another employer. We should not forget that all of them are possible with the consent of the employee and the employer.
What other changes may be included in contracts?
In addition to translations, it may be necessary to change other significant aspects of the contract. Their range and criteria of significance as such have not been established, however, having studied Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, several key points can be identified that must be reflected in the employment contract. It is logical to assume that their changes should also be formalized in accordance with Art. 72 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
This includes:
- Correction of information about the parties to the contract. The employee can change his full name and organization details (including name).
- Change of location. Current practice allows for quite a few variations. For example:
- moving to another premises where workplaces are located within the same area;
- exit of an employee who worked remotely to the employer’s workplace.
- Changing the term of the contract. For example:
- extension of urgent;
- transfer of urgent to indefinite.
- Supplementation of labor functions. For example, the purpose of alignment.
Read more about combining positions in the article “Order on combining positions - sample for 2019” .
- Changing the size and procedure of salary payment. For example, indexation of rates or the appointment of additional benefits and compensation.
Read about the procedure for salary indexation here.
- Adjustment of work and rest schedules. For example:
- in case of a change in the operating mode of the enterprise itself;
- at the request of an employee due to personal circumstances.
Find out more about such changes in the article “To whom and when is part-time working time established?” .
Changes in the general conditions for performing labor duties. For example, in connection with the use of new technologies or mechanization of production (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this and similar cases, it is permitted to necessarily change contracts with employees in accordance with new circumstances. In this case, a procedure similar to the procedure for transferring employees to another job for reasons beyond their control applies. The employee can either agree or disagree to work under the new conditions. If agreement is not reached, he may be fired.
IMPORTANT! If as a result of the factors specified in Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, layoffs may become widespread or the situation of workers will worsen, the employer should take measures to level out the consequences. Moreover, these measures will have to be agreed upon with the trade union.
How can suspension from work and changes in the contract with the employee be related?
In Art. 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for several options for removal from work:
- for medical reasons;
- due to the employee’s lack of necessary special rights;
- due to lack of necessary knowledge in the field of labor protection and safety.
In most of these situations, the employer is obliged to find another temporary position for the employee so as not to terminate cooperation. Then this is recorded in the same way as a transfer to another job under Art. 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with changes in the terms of the employment contract.
For information on the rules for drawing up an order for transfer to another job, read the material “Order for transfer of an employee to another position - sample.”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Commentary on Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
As a general rule, the terms of an employment contract can be changed only by agreement of the parties and in writing. Accordingly, it is prohibited to require an employee to perform work not stipulated by the employment contract (see Article 60 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto).
A change in the terms of an employment contract determined by the parties is a change in one or more mandatory or additional terms of the employment contract.
Changing the content (conditions) of an employment contract is possible in the following forms:
a) transfer to another job (see Article 72.1 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto);
b) a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties for reasons related to changes in organizational or technological working conditions (see Article 74 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto);
c) change of owner of the organization’s property, its reorganization (see Article 75 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto);
d) transfer of an employee, at his request or with his consent, to work for another employer or transfer to an elective position.
Changing the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties is not allowed unilaterally and can only be by mutual agreement of the parties (except for the cases provided for in Parts 2 and 3 of Article 72.2, Part 2 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code).
An agreement to change the terms of an employment contract determined by the parties is concluded in writing and is an integral part of the employment contract. The written form of the agreement more clearly expresses the will of the employee and eliminates future disagreements regarding the reached agreement to change the employment contract.