Working in production with hazardous working conditions is hazardous to health. That is why compensation methods for employees employed in such organizations were prescribed at the legislative level.
One of the types of compensation for harmful working conditions is established by law for the free provision of milk and milk substitutes. It is dairy products that remove dangerous substances from the body.
By law, milk is understood as any product that complies with the technical regulations for milk and products replacing it.
To whom to issue
Give milk to employees who work in hazardous working conditions, provided that:
- at their workplaces there are harmful production factors provided for in the list of hazardous production factors;
- the level of harmful factors exceeds established standards.
This is indicated in paragraph 2 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
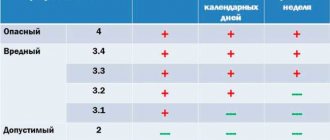
Whether there are harmful factors in the employees’ workplace and whether they exceed the standards is determined based on the results of the special assessment system or production control.
When, where and how much to issue
Provide milk or other equivalent food products to employees on days when they are actually engaged in work with hazardous working conditions. Do not give out milk for past shifts or shifts ahead.
Attention: milk or other equivalent food products are provided to employees at the expense of the employer. You cannot charge workers for milk (Article 222 of the Labor Code).
The norm for free milk distribution is 0.5 liters per shift, regardless of its duration (clause 4 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n). If an employee works in hazardous working conditions for only part of the shift, then he is entitled to milk only if he works in hazardous conditions for at least half of the shift.
Give milk to employees for consumption in buffets, canteens or in premises specially equipped in accordance with sanitary and hygienic requirements.
Question: who should be given fermented milk products instead of milk?
There are two categories of workers who need to be given fermented milk products instead of milk:
- Workers who are constantly in contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals, except for compounds of aluminum, calcium and magnesium. Instead of milk, such workers should be given fermented milk products or products for dietary (therapeutic and preventive) nutrition under hazardous working conditions.
- Workers involved in the production or processing of antibiotics. Instead of fresh milk, they should be given fermented milk products enriched with probiotics (bifidobacteria, lactic acid bacteria), or colibacterin prepared from whole milk.
Such rules are specified in paragraphs 5–6 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Question: who, besides milk, should be given pectin?
For workers who come into contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals, except for compounds of aluminum, calcium and magnesium, in addition to milk, give 2 g of pectin as part of food products:
- drinks;
- jelly;
- jams;
- marmalades;
- juice products from fruits or vegetables;
- canned food
It is necessary to distribute products that are enriched with pectin before starting work.
This is indicated in paragraph 5 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Question: should an employee be given milk and juice if there is lead in the workplace, but its content does not exceed the established standard value?
No, don't give it away. Milk is allowed only for those harmful factors for which harmful working conditions have been established.
Milk should only be dispensed if the following conditions are met:
- the workplace must contain harmful production factors specified in the List of hazardous production factors;
- the level of harmful factors must exceed established standards.
This is indicated in paragraph 2 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Workers who come into contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals (except for compounds of aluminum, calcium and magnesium) are given 2 g of pectin in addition to milk (clause 5 of Appendix 1 to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n).
The words “in addition to milk” mean that the worker who is in contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals already receives milk and is given an additional 2 g of pectin. And he can receive milk only if harmful working conditions are established for this factor.
Question: is it possible to issue milk to employees on a business trip if a special assessment has not been carried out there?
The issue of issuing milk to employees on business trips is not defined in the legislation.
Milk is given to employees on days of actual employment in jobs with hazardous working conditions, caused by the presence of harmful production factors in the workplace, the levels of which exceed established standards (clause 2 of Appendix 1 to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n).
At the same time, the absence of a special assessment of working conditions (during a business trip) is not a basis for depriving workers of the right to receive milk for preventive purposes when performing work with harmful working conditions.
We recommend that local regulations establish the following: if an employee performs work on a business trip that gives him the right to receive milk, he is paid monetary compensation for its purchase.
Question: if an employee works part-time in hazardous working conditions, does he have the right to receive milk?
An employee has the right to receive milk if he is in harmful working conditions for at least half of the work shift (clause 4 of Appendix 1 to the Order).
If the specified employee's working time is at least half of the work shift, then he is entitled to receive milk. If an employee is in hazardous working conditions for less than half of the work shift, then he does not need to be given milk according to established standards.
Question: is it possible to plan the costs of purchasing milk using the cost item “Occupational Safety and Health”?
No, the cost of milk must be included in labor costs. When taxing the profits of organizations, such expenses, in particular, include compensation charges related to work hours or working conditions.
This is stated in Article 255 of the Tax Code.
Thus, labor costs include the cost of milk provided to employees free of charge in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. These expenses cannot be classified as labor protection costs.
Accounting operations for reflecting milk and treatment and prophylactic menu
In accounting, milk and products intended for special meals for employees are included in the 10th account. These goods are classified as inventories. In the accounting data they are reflected at a cost equal to the actual acquisition costs (excluding VAT). The organization of accounting is regulated by the norms of PBU 5/01.
When products are issued to employees, accounting entries are made to increase the expenses of ordinary activities. This group of costs should also include monetary compensation that replaces the issuance of food products. Typical correspondence:
- The company purchased milk to provide it to workers engaged in hazardous production - D10 - K60 .
- VAT included in the price of dairy products is allocated through debiting 19 accounts and crediting 60 .
- When milk has been issued to staff, an entry is made between debit 20 and credit 10 .
- D20 - K73 - compensation paid to employees instead of providing dairy products is included in expenses.
- D73 - K50 or 51 - the employee received compensation for food at the cash register or on a bank card.
When reflecting therapeutic and preventive nutrition, records are made involving 41 accounts. Products are purchased from third-party enterprises and are shown in accounting under debit 41. In correspondence with the commodity account, the credit account goes to account 60. When transferring all purchased ingredients to the canteen for meals for employees, the cost of the products must be written off through debit turnover on account 73 and credit turnover on account 41.
What can be replaced
If it is impossible to provide milk to employees, it can be replaced with equivalent food products, provided that:
- employees agree to a replacement;
- the opinion of the elected trade union or other body authorized by the employees of this organization is taken into account.
Milk is replaced with other products according to the standards that are given in the table in Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Table. Standards for the free issuance of equivalent food products that can be given to employees instead of milk
| No. | Name of food product | Issue rate per shift |
| 1 | Fermented milk liquid products, including fortified ones, with a fat content of up to 3.5% (different types of kefir, yogurt, acidophilus, fermented baked milk), yoghurts with a fat content of up to 2.5% | 500 g |
| 2 | Cottage cheese no more than 9% fat | 100 g |
| 3 | Cheese no more than 24% fat content | 60 g |
| 4 | Products for dietary (therapeutic and preventive) nutrition under hazardous working conditions | Established in a conclusion authorizing their use |
You cannot replace milk with products that are not in the table, for example, sour cream, butter, etc. This is indicated in paragraph 7 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Therapeutic nutrition: principles
When carrying out an important medical prescription - a diet, the doctor takes into account the mechanism of development of the disease, the state of the body, the functioning of metabolic processes, and the individual ability to absorb food. Some foods and dishes are excluded due to poor digestibility, others because of their ability to cause harm, but some foods, on the contrary, are specifically prescribed for their beneficial effects (for example, to remove toxins from the body)
The volume, weight, consistency, temperature of food is determined by a specific diet. The average weight of the daily diet is 3 kg. In therapeutic nutrition, the amount of food can often be increased or decreased due to liquid or plant fiber (non-food carbohydrates).
- The diet should have a targeted effect on metabolic processes, promoting both the treatment of the disease and the prevention of exacerbations of chronic processes.
- Strict adherence to the diet: meals are always taken at the same time, the frequency of meals is determined taking into account the disease and the characteristics of the body.
- The diet should be varied, satisfying the patient’s tastes within the diet. A monotonous diet contributes to a decrease in appetite and a slowdown in digestion, which interferes with treatment.
- The diet is tailored to the individual characteristics of a particular patient, including taking into account concomitant diseases.
- When preparing a diet, the calorie content and chemical composition of foods and dishes are taken into account, taking into account the patient’s energy consumption.
- Application of the most appropriate culinary processing when preparing food. Ready-made dishes should be tasty, and also retain the valuable properties of the products.
- Each meal should end with an optimal filling of the stomach, leaving the patient feeling full without being full.
If necessary, in the process of preparing and serving food, the principles of mechanical, chemical, and thermal sparing are applied. With mechanical sparing, dishes will be liquid, semi-liquid and puree-like. Chemical sparing involves the exclusion of difficult-to-digest and irritating dishes and products.
How to replace it with a compensation payment
At the written request of the employee, instead of milk or other equivalent food products, compensation can be paid to him (clause 10 of the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of February 16, 2009 No. 45n, part 1 of Article 222 of the Labor Code). To do this, issue an order to replace the delivery of milk with monetary compensation.
Pay compensation at least once a month (clause 3 of Appendix 2 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n). The amount of compensation payment is determined by the cost of milk with a fat content of at least 2.5 percent or equivalent food products in retail trade at the employer’s location.
Question: The following is not calculated from the compensation payment:
- insurance contributions to the Pension Fund;
- contributions for compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases;
- taxes on personal income.
Please indicate the specific amount of the compensation payment and the procedure for its indexation (clause 4 of Appendix 2 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n):
- in a collective agreement - if there is a trade union or other representative body of workers;
- an employment contract concluded with an employee - in the absence of these bodies in the organization.
Index compensation payments in proportion to rising prices for milk and other equivalent food products. To do this, every month fill out an order for monetary compensation and its amount, taking into account indexation. For these purposes, you can use official data from the Rosstat website.
Question: what type of waste - food or biological - do expired dairy products belong to?
To food.
The concepts of food and biological waste are given in GOST 30772-2001 “Interstate standard. Resource saving. Waste management. Terms and definitions”, approved by Gosstandart resolution dated December 28, 2001 No. 607-st.
Food waste is food products that have lost, in whole or in part, their original consumer properties during the process of production, processing, consumption or storage.
Biological waste is biological tissues and organs generated as a result of medical and veterinary operational practice, medical and biological experiments, the death of livestock, other animals and poultry, and other waste obtained from the processing of food and non-food raw materials of animal origin, as well as waste from the biotechnological industry .
Information from the site: https://ucstroitel.ru/
Related documents
| Document | Will help you |
| Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n “On approval of the standards and conditions for the free issuance of milk or other equivalent food products to employees engaged in work with hazardous working conditions and the Procedure for making compensation payments in an amount equivalent to the cost of milk or other equivalent food products products, and the List of harmful production factors, under the influence of which, for preventive purposes, it is recommended to consume milk or other equivalent food products" | Determine, based on the results of workplace certification (or preliminary, before certification), which employees are entitled to milk and pectin-containing products, and in what proportions milk should be given to employees who have the right to it. Establish monetary compensation in exchange for milk, determine its size and frequency of payment |
| Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 46n “On approval of the List of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to receive free therapeutic and preventive nutrition in connection with particularly harmful working conditions, rations of therapeutic and preventive nutrition, standards for free distribution vitamin preparations and Rules for the free distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition" | Determine by job title which employees are entitled to therapeutic and preventive nutrition, familiarize themselves with the rules for issuing special food and create a menu based on established rations |
Milk compensation
Milk and dairy products actively remove toxins from the body. In addition, the benefit of dairy products is that it speeds up metabolism and strengthens the immune system. This increases the body's resistance to infections and various diseases.
These beneficial properties of milk became the basis for the adoption of regulations, according to which employees of potentially hazardous industries are entitled to receive milk compensation. This provision is enshrined in Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It specifically stipulates that the administration is obliged to create conditions for the distribution of milk and dairy products to those employees who are forced to work in conditions that deviate from sanitary and hygienic standards.
It is prescribed to organize the distribution of dairy products listed in Government Decree No. 168. At the same time, the staff themselves do not have to pay milk compensation. It is implemented exclusively from employer funds.
How to create a special food menu
The employer can make a decision to provide therapeutic and preventive nutrition to employees regardless of workplace certification, since there is a specific list of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to receive special nutrition (Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 46n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia). But at the same time, the employee’s position indicated in his work book must coincide with the list, and the list is compiled on the basis of the relevant issues of the ETKS.
Next to each position is the ration number according to which the therapeutic and preventive nutrition menu for the employee should be compiled. Rations (their total are given in Appendix No. 2 to Order No. 46n. For example, an electric and gas welder working in a chemical production must receive free special food according to ration No. 2. The rations are made up of ordinary products (meat, fish, bread, vegetables, fruits and etc.), but balanced in calorie content and supplemented with vitamins. The explanations provide recommendations on methods of preparing dishes from these products: they should be boiled, steamed, stewed or baked, without prior frying.
Rations (their total are given in Appendix No. 2 to Order No. 46n. For example, an electric and gas welder working in a chemical production must receive free special food according to ration No. 2. The rations are made up of ordinary products (meat, fish, bread, vegetables, fruits and etc.), but balanced in calorie content and supplemented with vitamins. The explanations provide recommendations on methods of preparing dishes from these products: they should be boiled, steamed, stewed or baked, without prior frying.
Law against practice
On practice
Many organizations with hazardous working conditions provide milk to workers several shifts in advance or over time. This is more convenient than organizing its portion distribution every day
In law
In accordance with Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 45n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, workers must drink milk at work. It cannot be passed off as the future or past tense, or as a house
What happens if…
If milk distribution is not organized properly, there is a risk of liability when inspected by the State Labor Inspectorate. The fine for violations in the field of labor protection is for an official or entrepreneur from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles, and for an organization - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). It is more profitable for an employer to comply with the requirements of regulations (this will not require material investments) than to pay a fine for such violations.
Diet therapy or therapeutic nutrition
Since ancient times, certain foods and specially formulated diets have been used to treat patients. Since the beginning of the 19th century, Russian scientists began to approach nutrition issues from the point of view of the interaction of physiology, hygiene, the chemical composition of food and the technology of its preparation.
Manuil Isaakovich Pevzner, a Russian general practitioner, one of the founders of dietetics and clinical gastroenterology, pointed out in his writings that nutrition for a sick person is the main background against which the doctor can apply other therapeutic effects. Manuil Isaakovich founded a nutrition system of 15 healing tables (diets), which is still used to this day.
To create a therapeutic diet, you need to know the composition of the food needed for the patient, its calorie content, the proportions of the components (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), and the total amount (daily diet). A specialist doctor who develops a diet and prescribes a diet is a nutritionist. A nurse who specializes in patient nutrition is a nutrition nurse (diet nurse).