01.07.2019
0
319
4 min.
Paying taxes is an obligation that applies to every employed member of society. The existing system of collecting fees is a product of gratuitous contributions by individuals and organizations to ensure the functionality of the state, municipalities and the maintenance of disabled categories of citizens. Employees who decide to quit often ask their employer the question: is compensation for vacation subject to an insurance premium or not?
For officially employed people, the employer automatically makes monthly contributions to the inspectorate. Taxable income includes salary, bonuses and vacation payments, work on holidays and overtime, sick leave, compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal.
The procedure for calculating personal income tax on dismissal payments
The amounts that are paid to an employee in the event of dismissal can be divided into taxable and non-taxable with income tax (NDFL).
Taxable include :
- all accruals to the employee for time worked and work performed;
- payment of unused vacation days.
There is no need to charge personal income tax on severance pay within the established limit and some types of compensation payments (Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The process of determining the tax base includes:
- Identification of taxable and non-taxable charges.
- Summation of only taxable accruals.
- Application of deductions to the amount of taxable charges.
The tax is calculated using the formula:
Tax base × 13% (for non-residents 30%) |
Leave compensation upon dismissal and personal income tax
What is the amount (%) of insurance payments? 30% in total is collected from the actual income of an individual, of which:
- pension payments 22%;
- medical penalties 2.9%;
- social payments 5.1%.
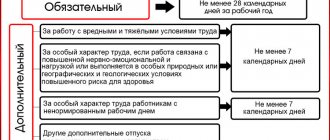
And also the first 3 deductions go to the Federal Tax Service, the last payment goes to the Social Insurance Fund. Taxation of compensation issued to an employee for his unused vacation has its own nuances. To correctly calculate the amount of tax, the accountant needs to know exactly how many days the employee actually worked. If he has been working at the enterprise for 11 months (of the current year), then he is entitled to a full vacation of 28 days.
The accountant looks at how many months the employee who is about to quit has worked. On average, you get 2 vacation days per month.
Deadline for paying personal income tax on salary upon dismissal
All tax accrued on payments upon termination of an employment contract must be paid no later than the day following the date of their actual transfer to the employee (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When the deadline for transferring tax upon dismissal coincides with a day off, settlements with the budget for personal income tax are made on the next working day (Clause 7, Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important
Although now almost all companies pay salaries by bank transfer, and making payments on the day of dismissal is not a problem, there are situations when the date of separation and receipt of money do not coincide. For example, small organizations may issue wages through a cash register, but the employee does not show up to collect the money on the last working day. Then the company is obliged to make payments no later than the next day after the date the dismissed person applied for the debt (Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 1
The company pays employees wages through a cash register. The employee resigns on 08/20/20__. However, he did not show up for the payment and brought a statement demanding its issuance only on 09/02/20__. The company, in compliance with the law, made a full settlement with him on 09/03/20__. When should she remit personal income tax?
Decision: based on the above provisions of paragraph 6 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - no later than 09/04/20__.
Compensation for unused rest days
If the reason for dismissal was not a violation of the employment contract, the employee works for the company for more than 15 calendar days, is hired under a service agreement, then he has the right, upon his application and on the basis of an order from the employer, to claim compensation for unused vacation days (hereinafter referred to as KZNO).
For these purposes, a note is provided to the accounting department of a number of enterprises (directly for accrual purposes) - calculation in form T-61. It is not a mandatory document, but it is quite convenient and can be used as a basis or example for developing an in-house form. This document must indicate the total amount of payments for the calculated period and the number of days.
Payments for completely unused vacation are calculated as follows:
- KZNO = average daily earnings * days;
- Average daily earnings = (salary/12)/29.3.
For the calculation, the employee’s working year is taken, that is, the calculation occurs from the day he joined the company.
To ensure that the employee does not have claims against the organization, it is necessary to understand what taxes are charged on vacation compensation upon dismissal. And most importantly, what taxes were subject to assessment and transfer.
The procedure for calculating insurance premiums upon dismissal
When deciding what taxes to pay when dismissing an employee, you should not forget about insurance premiums, as well as contributions in connection with accidents at work. The composition of payments subject to taxation includes almost all accruals under an employment or civil law contract. The list of non-taxable amounts is clearly stated in Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for determining the taxable base for contributions upon dismissal is as follows:
- Accounting for all amounts due to the employee in connection with termination of cooperation.
- Identification in the list of charges that fall under those given in Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, benefits.
- Deduction from the total amount of accruals of non-taxable amounts - according to Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The calculation of the amount of contributions upon dismissal is carried out according to the formula:
Taxable base × Percentage of contributions to the relevant fund |
Types of insurance premiums
Several insurance premiums have been allocated. Each of them deserves special attention:
- Insurance premiums against accidents and occupational diseases. These deductions are also called “injury” contributions. Transferred by the employer to the Social Insurance Fund (SIF). Their rate is related to the danger of professional activity and can range from 0.2 to 8.5%, depending on which of the 32 risk groups the organization’s activities belong to. Every year, before April 15, organizations submit information to the Social Insurance Fund on approval of the type of economic activity. The FSS confirms with a notification the tariff, according to OKVED, or assigns its own if there is more than one type of activity and the organization did not submit an application on time.
- Pension insurance (contributions from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation). There is a limit on the base for accrual for an employee. It is calculated for each employee separately, from the beginning of the calendar year. Until this limit is reached, a rate of 22% applies. If the employee’s annual income turns out to be higher, then the pension contribution rate above this amount will be 10%.
- Social insurance in case of temporary disability and maternity. It is the system of maternity contributions that allows the employer to subsequently compensate maternity payments to employees from the budget by offsetting the payment of current contributions or reimbursement in monetary terms to the organization’s account.
- Insurance contributions to the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (FFOMS) are stable and amount to 5.1%.
Deadline for transferring contributions from the salary of the dismissed person
All contributions must be transferred no later than the 15th day of the month following the month of payment of income (clause 1 and clause 3 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This rule also applies when dismissing an employee.
However, for the purpose of paying contributions, the date of payment is the day of actual delivery of the amounts to the employee (clause 1 of Article 424 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If this date falls on a weekend, then payments should be made no later than on the next working day.
Example 1
The employee resigned on 9/20/20__. On the same day, full payment was made to him. The due date for payment of contributions is no later than 10/15/20__.
Example 2
The employee quit on 09/20/20__, but did not show up for the payment, and only requested it on 10/01/20__. The accounting department carried out the calculation and payment of the debt on 10/02/20__. The due date for payment of contributions in this case should be 11/15/20__. But this day falls on a weekend, so the deadline is until 11/16/20__.
Read also
23.10.2020
What taxes are the compensation subject to?
- the day of payment of income, by transfer to the bank account of an individual;
- the day of payment of funds to a former employee at the enterprise’s cash desk;
- the day an employee receives a sum of money at the bank’s cash desk, from the company’s current account, according to a payment order.
Based on this, the company transfers taxes on compensation paid on the same day. If the employee receives money in cash, the employer must pay taxes no later than the next day after the day of actual payment.
Compensation for unused vacation by employee
Compensation is a monetary payment that can replace unused vacation time. When an employee worked instead of weekends and vacations. Compensation must be paid upon dismissal or layoff. Moreover, the possibility of receiving payment is not limited by the reason for dismissal. For example, a manager decided to fire a negligent employee who could not cope with his professional responsibilities. They formalize it as dismissal under the article. All the same, the employee has the right to receive a full payment, which is the actual salary plus compensation.
Important: worth remembering. That such payments are subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums. Therefore, the employee receives the remainder of the compensation after deductions.
Severance pay and retained earnings during employment
If the employment contract is terminated due to staff reduction, the employer is obliged to pay him severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). By agreement of the parties, the amount of severance pay can be paid in any amount. In this case, the payment procedure must be specified in the collective or employment agreement, and also specified in the agreement between the employee and the employer.
Also, an employee dismissed due to layoffs retains his average earnings for the duration of his employment, but not more than two months. The calculation of retained income also includes severance pay. In exceptional cases, earnings may be retained for another month if the right to it is confirmed by the employment service.
The calculation of severance pay and retained earnings during layoffs is similar:
The number of working days during the payment period is determined according to the organization’s work schedule. The calculation begins on the working day following the dismissal. For example, if an employee quit on 06/25/18, then severance pay is paid to him for the period from 06/26/18 to 07/25/18. The retained earnings for the second month will be calculated for the period from 07/26/18 to 08/25/18.
The average daily earnings are calculated based on payments for the last 12 months preceding the month of dismissal, in accordance with clause 4 of Resolution No. 922.
Income tax
When calculating income tax, include compensation in current labor costs (clause 8 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This procedure applies regardless of whether the organization creates a reserve in tax accounting for future expenses for vacation pay (annual remuneration for long service and remuneration at the end of the year) or not. The fact is that it is impossible to write off the amount of compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal from this reserve.
Situation: how to take into account compensation for unused vacation provided under a collective agreement (in excess of that established by law) when calculating income tax?
If the internal documents of the organization provide for the provision of additional vacations to employees (in excess of those established by law), do not take into account the monetary compensation paid in return for such vacations when calculating income tax. The fact is that expenses cannot include the costs of paying for vacations provided on the basis of collective agreements (clause 24 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated April 11, 2006 No. F04-4099/2005(21317- A27-29)). This means that compensation for such vacations cannot be taken into account when calculating tax. This position is adhered to by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated October 18, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/284.
Situation: how to reflect when calculating income tax the compensation paid upon dismissal of an employee for vacations not taken by him for two or more years?
Compensation for vacations not taken by an employee for two or more years should be included as expenses when calculating income tax.
This is due to the fact that the organization’s obligation to pay compensation to the resigning employee for all unused vacations is provided for by law (Part 1 of Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that such compensation is included in labor costs (clause 8 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Ministry of Finance of Russia adheres to the same position in letter dated May 20, 2005 No. 03-03-01-02/2/90.
It should be noted that failure to provide an employee with leave for two consecutive years is prohibited (Part 4 of Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). By doing so, the organization will violate labor laws.
The procedure for reflecting compensation in tax accounting depends on the method of accounting for income and expenses that the organization uses.
What taxes are paid on compensation for leave upon dismissal?
Taxes and contributions for compensation upon dismissal, in case of non-use of annual leave, are accrued and paid by organizations and enterprises in favor of an employee who is drawn up in accordance with the law - under an employment contract or a civil one (for the performance of work or the provision of services). Labor legislation establishes the same rights and guarantees for compensation for annual leave in case of dismissal for part-time workers.
Thus, taxes are taken from compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal. Partly due to the fact that compensation is the employee’s income, as well as to make timely and correct payments to the budget. With proper tax planning, an enterprise can optimize these compensation payments, and the taxes and contributions paid on them, to its benefit.