Legislative regulation
The main regulatory document regulating the provision of compulsory rest to employees from work is the Labor Code. It sets the minimum duration of rest periods. It is worth noting that vacations can be paid, and without pay.
Additional documents on the basis of which vacations are established are:
- special laws (for example, regulating issues of military service, police, other law enforcement agencies, education);
- government regulations (they mostly apply to civil service employees);
- orders of relevant ministries;
- collective agreements of specific enterprises.
It should be noted that issues of determining the amount of rest for employees should be based on the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and then simply take into account the peculiarities of work in a particular area. In most cases, these regulatory documents increase the number of days of rest or clarify the procedure for providing it.
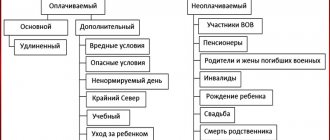
All types of vacations are divided into two main groups:
| View | Description |
| Basic | They are provided to all workers of the enterprise without exception. This is the minimum guarantee that the employer must comply with. |
| Additional | To obtain them, you will need to fulfill certain conditions stipulated by law or local regulations. For example, for working in harmful (dangerous) conditions, for irregular work, in the Far North. Employers are empowered to independently determine additional conditions for their provision (for example, for loyalty to the company). |
| Social | Occurs under certain circumstances and is usually compensated by the government. As an example, maternity leave is due to a young mother after the birth of her baby. This also includes rest intervals of varying lengths for disabled people. |
Remember, all regulatory documents issued on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation can only improve the conditions for granting leave, or specify these issues, taking into account the characteristics of the work activity of a particular category of employees.
Working hours
Today, regulatory documents regulating labor issues separate two concepts, namely working time and working time. It seems to many that these concepts have the same meaning, the words are simply rearranged. In practice this is not the case. And the final decision during the calculation and provision of a specific type of paid time off will depend on the application of each specific term.
Work time . This term includes the time period when the worker directly performed actions useful for the company (for example, worked at a machine, was engaged in intellectual activity).
Working hours . This takes into account the entire time period of the employee’s presence at the workplace, taking into account the preparatory process (preparation of tools, equipment, workplace), technological breaks, waiting for work, as well as direct labor functions.
It is important to note that in the process of calculating the period, determining the main period of legal absence is guided by the total time of work. At the same time, if it is necessary to determine the duration and legality of an employee receiving additional leave for harm, periods of working time are applied.
What is a billing period
Considering that the legislator has obligated companies to annually allocate time intervals for employees to restore their health, their duration will depend on the amount of time worked. Here the billing period will be calculated from the date of employment and should not exceed 12 calendar months. This rule applies regardless of the month in which the citizen began performing labor functions.
The calculation period is necessary to determine the level of average income of the employee with the subsequent payment of vacation pay to him. They are calculated for all calendar days of legal absence from the enterprise. Here you will need to take into account the following basic nuances:
- summarize complete months of work;
- separately count the months where you worked part-time;
- exclude periods of employee illness from the calculation.
When calculating the pay period, you should take into account the time intervals included in the work experience, as well as those that need to be excluded from it.
Included:
- All periods of actual work activity.
- Intervals where the employee legally retained his position (place of work).
- All the time of forced absence.
- If an employee was suspended from work through no fault of his own.
- Free vacations at personal expense (only 14 days per year).
Excluded:
- unreasonable absence, removal due to the fault of the worker;
- intervals of available decrees;
- free holiday exceeding 14 days.
Remember, the billing period is determined for the correct calculation of the amount of average daily income due to a citizen going on vacation. This income is then multiplied by the due days and paid to the worker.
In what cases and when does the right to leave arise?
The same Labor Code of the Russian Federation will help answer this question. If we refer to Art. 122 of the specified legal acts, it states that paid leave must be provided to the employee annually.
However, it should be noted that such a right can arise only if the employee has worked continuously for the employer for 6 months under an employment contract. Moreover, if an employee needs leave before the expiration of such a period, he can submit an application to the employer, who can either give his consent or refuse the employee’s request specified in the application.
After an employee has worked in the organization for 1 year, he can apply for leave at any time, but taking into account the priority schedule provided for by the enterprise. Compliance with this rule is necessary to ensure the stability and continuity of the production process.
It must be remembered that when granting paid leave, the employer takes into account the period not of the calendar year, but of the working year. In other words, 6 months in the first working year must pass from the moment when the employment order was drawn up and signed. This day will be recognized as the beginning of the working year.
Rules for calculating the number of vacation days
Usually the number of days of unused vacation is calculated as of a certain date. As a rule, this is due to the dismissal of an employee and the need to receive compensation for the entire period previously worked.
The general calculation formula consists of the following components:
It is necessary to multiply the number of days due by the number of months worked, and divide the result by 12. This way you will get the duration of legal paid absence from work. But here it is necessary to take into account various nuances, namely the periods that remain and which are excluded from the calculation performed. These intervals are provided for in Part 2 of Art. 121 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
As an example, consider the following case. The employee worked honestly for the company for 10 months; according to the law, he is entitled to a standard absence from work of 28 days.
Minimum duration of annual paid rest: general rules
Many employees want to rest longer at the expense of their employers. But labor legislation clearly regulates how vacation is calculated. According to Part 1 of Art. 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum annual paid vacation is 28 calendar days. The calculation of the number of vacation days does not affect whether the person worked full or part-time, whether the person worked at his main job or part-time, or performed his duties at home or in the office.
The right to release from work duties arises 6 months after the conclusion of the employment agreement, although by agreement of the parties it will be possible to rest earlier. In Art. 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation specifies categories of subordinates who cannot be denied the opportunity not to work until six months have passed. These include pregnant women, minors, employees who have adopted children under 3 months of age. But the rules for calculating vacation do not change in this case.
Typically, vacation days are calculated in proportion to the time worked. Therefore, if, without going on sick leave or absence for unexcused reasons, the period of continuous activity of an employee at the enterprise is six months, he is entitled to at least 14 paid calendar days. You can ask for more, but employers do not always agree to provide breaks from work in advance. In addition, it must be taken into account that in the event of dismissal before the end of a full year of work, part of the money paid will have to be returned.
Remember that official holidays, such as March 8 or May 9, are automatically included in the rest period (extend it). It will also be possible to avoid going to work longer if the employee did not rest, but was on sick leave due to his own illness or injury.
Payments taken into account when calculating
One of the key factors in the process of determining compensation for mandatory rest (both during regular leave and during dismissal) is the employee’s income level. Here it is important to take into account the cash accruals included when determining average earnings.
This includes all monetary remunerations provided for by the company’s employee remuneration system, consisting of:
- Basic salary.
- Bonuses awarded for work.
- All kinds of additional payments, due allowances, constant compensation payments.
- Production one-time remuneration.
- Other payments (for example, for loyalty to the company, for the quarter, for the year), stipulated by the collective agreement.
It should be noted that not all payments provided for by the collective agreement are considered when calculating the average income level. In particular, it is necessary to subtract monetary amounts that fall within the periods that must be excluded from the calculation. This included:
- all accruals that were paid for the periods that were excluded from the calculation. For example, average income during a business trip, various social benefits;
- social assistance from other sources of income, which is not regulated by the salary regulations. Here they will count financial assistance, compensation for housing, gifts, recreation, treatment;
- remunerations and bonuses paid not according to a salary document.
To calculate the average daily income, use the following formula:
You need to divide your earnings for the period (here we take annual income) by 12 months and divide by 29.3 (averaging the number of days). This way you will receive the employee's daily income.
For example, a worker was calculated to have an annual income of 356,000 rubles; he did not go on business trips, did not get sick, did not take free “time off” in excess of the norm, and worked a full year. Has a prescribed relaxation period of 28 days.
His average daily income will be:
Сз = 356,000 / (12 x 29.3) = 1012.51 rubles.
Now, in order to receive compensation (vacation pay), the amount received must be multiplied by the days required by law:
K = 1012.51 x 28 = 28350.28 rubles.
Thus, our virtual employee will have 28 days of rest, for which he will be paid 28,350.28 rubles.
Remember, during the calculation process, accounting will take into account all periods of your work and rest, and the number of individual types of additional leave will be calculated based on the time actually worked.
Step-by-step algorithm for calculating compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal for absenteeism
This section is devoted to a direct answer to the question: upon dismissal for absenteeism, is compensation paid? And what is the procedure for processing these payments? Based on the norms of legislation and the circumstances surrounding the conscientious legal execution of a disciplinary sanction, the days that are included in the designated compensation are determined.
Days are calculated as follows::
- The number of working days that are documented as absenteeism is determined.
- These days are counted from the date of dismissal, changing the period subject to compensation downward.
- From the date obtained as a result of extracting absenteeism, we calculate the number of full months that have passed since the date of return to work from the next leave or from the date of hiring.
- An incomplete month is abbreviated as follows. If less than half a month has been worked, it is not taken into account. If half or more is worked, it is counted as a full calendar month.
- We find out the number of days required for calculation for each month.
- We multiply the resulting number by the sum of the months worked by the absentee. The number of months is determined according to points 1-3.
If reports of absenteeism are not drawn up in accordance with the rules for applying disciplinary sanctions, paragraphs 2 and 3 do not apply.
The formula for calculating the number of days for each month is as follows: KRD (o) = PO: 12 , where:
- KRD (o) – the number of working days due for vacation;
- PO – duration of vacation.
Compensation for dismissal for absenteeism is calculated using the formula: VPO = SDZ x KRD (o) , where:
- VPO - vacation pay for severance pay;
- SDZ – average daily earnings.
The amount received is added to the rest of the accrual, consisting of working days worked and not previously paid.
Accruals for days worked. In addition to vacation pay, earnings for the period worked are calculated. When dismissal for absenteeism, a specific algorithm is also revealed here :
- The number of days worked that were not previously submitted for payment is calculated.
- Days documented in the act as absenteeism are subtracted from them.
- The remaining days are subject to payment based on the average daily earnings.
Upon dismissal for absenteeism, it is possible to cancel the payment of bonuses and other incentive payments, making an accrual from the base salary.
SDZ is found as follows: SDZ = SPZ: CHKD , where:
- SDR – summed wages;
- CHKD – the number of calendar days for the worked period.
That is, the total salary, minus insurance benefits (sick leave, etc.), is divided by the number of days worked.
If reports of absenteeism are drawn up, days of absenteeism will also not be included in the calculations for average daily earnings.
The main calculation period is:
- one calendar year;
- period from the date of hiring, if it is less than a year.
IMPORTANT: If the average daily earnings are less than the minimum wage (minimum wage) provided for by law, it must be increased to the minimum wage.