Work book: rules for filling it out
Based on what has been said, it becomes clear the attitude of the labor inspectorate and other authorities supervising personnel records management towards the management and storage of labor records.
The slightest negligence can cause an employee to lose not only a document, but also all the information that was stored in it.
Accordingly, such a situation will become the cornerstone of serious problems not only for him, but also for the person in charge.
Grounds regulating the storage, maintenance and accounting of work books
The central link on which all office work related to the Labor Code is based is the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225. It provided legally established standards that reflect almost all issues that relate to the Rules for maintaining the Labor Code, and also states:
- A new sample Labor Code form and an insert in the work book.
- The validity of the old format TCs, the continuation of their functioning without exchange.
- The need to establish the production of new sample forms for TC and inserts.
- The procedure for providing employers with forms.
- Instructions for maintaining work books and inserts, with the procedure for explaining to employers all the provisions and nuances.
- Rules for maintaining and storing TC. (for example, how to sew an insert into a worksheet)
Rules for maintaining and storing TC are the main, basic provisions of this project . It organically includes all issues that require consideration.
Having the status of a legislative fragment of all regulatory documentation, the provisions of the Rules formulate the requirements of labor inspectors during inspections, as well as any solutions to controversial issues, including those affecting civil claims, and in some cases, criminal cases.
The rules define increased obligations and a high form of responsibility of the employer and authorized person for maintaining the labor code. In accordance with the Rules, labor documents are documents for which an increased form of security must be applied during their storage.
Rules for maintaining and storing work books, Resolution 225.
Further in the article we will look at work books, the procedure for maintaining and storing records.
How to change the last name in the work book?
A change in the surname of the owner of the work book is made by the employer on the basis of an order to change personal information, which, in turn, is prepared after the employee provides relevant relevant documents containing such changes, and in some cases, an application to change the surname. Having received a copy of the internal order, the personnel department corrects the employee’s data in his work book and personal card.
According to the rules for making amendments to the document recording work activity and length of service, the previous name on the first page of the form is carefully crossed out and the new one is entered. An explanation of this change is given on the inside cover with reference to the details of the relevant document.
Maintenance by employer
When hiring an employee, the employer is obliged to make an entry in his book, that is, to enter information that the employee has been hired. This information must be entered no later than 5 days after the date of hire.
This provision is based on clause 3, part 1 of the Rules , which state precisely this period, provided that the work is the main one. Within the same period, a Labor Code must be opened using a blank form from the employer, if the person who got the job has not worked anywhere before.
Information about the employment process is entered based on the Instructions for filling out the Labor Code, which were approved by the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation on October 10, 2003, No. 69.
This document regulating the activities of personnel officers in some cases plays no less significant role than the previously presented Rules. The instructions indicate almost all the details that may play a role when entering data into the TC, taking into account their use in some rather ambiguous situations.
The Rules and Instructions make the employer responsible for the employee’s record book for the entire period of his activity at the enterprise, as well as responsibility for the correct filling out of the record book.
The book is filled out when applying for a job , indicating the name of the organization . This is a mandatory condition prior to entering information. When entering this information, the serial number and date are not entered.
But the number and date must be entered at the time of entering information about employment, where, at the same time, it is necessary to record the position of the employed person and the department to which he is assigned.
It must be borne in mind that when applying for a position, it is unacceptable to put a stamp after the information entered into the Labor Code. The seal must be present on the dismissal record (see here). Each entry made about the movement of an employee:
- reception;
- dismissal;
- promotion or demotion,
must be confirmed by the signature of the person authorized to make entries, indicating his position and surname with initials. Here, in the last column, there must be a link to the order, reflecting the authenticity of the information given in the third column.
All information is entered into the work book carefully , without blots or corrections. If the authorized person makes a blot, mistake or typo when drawing up the Labor Code, it is unacceptable to correct it.
In this case, he is obliged to follow the established standard of the Instructions, which is also reflected in the third part of the Rules and makes it a norm to enter the relevant information that indicates the error of the data entered under the corresponding number. These provisions must be taken into account in order to avoid damage to the labor document.
Upon completion of activities at the enterprise, in accordance with clause 35, part 4 of the Rules, the Labor Code is issued . This paragraph states that it is mandatory to issue a book on the day of dismissal at the request of the owner of the employment record.
That is, by the time of his last day of work, all information about his departure must be entered and certified, the order must be issued and signed. The employer must provide the following information:
- With reference to the relevant article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, indicating the reason for dismissal.
- With the proper serial number.
- Certifying with signature and seal.
All this is brought into line:
- with the date when the dismissed citizen ceased activity;
- with the order:
- date of termination of the contract.
Receipt of a TC by its owner is carried out:
- no later than 3 days;
- for painting;
- with an entry in the card and journal.
If the owner does not pick up his book after dismissal, he must be notified about this, which will completely relieve the employer of responsibility for his document.
Below you can download an order for the appointment of a person responsible: An order for the appointment of a person responsible for maintaining work records - sample.
Will paper work records be abolished in Russia?
In fact, in recent years there has often been speculation that paper work books could be completely abolished in favor of an electronic document. Such a decision has both pros and cons, and is now only being discussed by the public.
One of the provisions of the explanatory note to the draft amendments to the rules for their maintenance may indirectly hint that paper work books will not be withdrawn from circulation. The Ministry of Labor and Social Relations draws attention to the fact that the Ministry of Finance, which is in charge of the procedure for the production of forms for work books, should also introduce amendments to it due to the obsolescence of the existing procedure.
Where are employee work books stored?
The rules establish that throughout the employee’s activities, his book must be kept by the employer, who is responsible for it, and also has the right, at his discretion, to share responsibility with an authorized representative.
In addition, the Rules postulate that the Labor Code is a document that requires an increased degree of protection . Its blank form is a document of strict accountability, which also presupposes special conditions for its storage.
The Rules, Instructions, and other documents do not specifically indicate that books should be stored in any special place. However, every employer understands that in the event of damage or loss of technical equipment, which may occur:
- in case of fire;
- when the premises are flooded;
- in case of theft,
the employer will have to report on the storage of these important documents. Naturally, if the conditions are considered improper or insufficient, liability will be imposed.
Therefore, unspoken rules have developed among employers - to strengthen the storage of technical equipment in every possible way , taking into account at the same time the possibility of non-disclosure of the place of their storage to outsiders.
A safe is a common place for storing technical documents, which determines the conditions for limited access to documents. However, in order to avoid damage to books due to the reasons mentioned earlier, you should have a safe with the maximum degree of protection.
At large enterprises, it is recommended to store technical equipment in especially durable, fireproof safes. Any little detail in case of damage or loss of books can be considered as industrial (official) negligence.
There is a reason for this - after all, the massive loss of this information will result in serious problems for a large team, and he, in turn, will bring a considerable claim to the employer. Find out what to do if your work record is lost in this article.
If the quitter did not pick up his book, and the employer took all measures to return it, it must be transferred for storage. For three years it is stored in the same closet (safe) as the rest of the work documents, in case the owner returns for it.
At the end of this period, it must be transferred to the archives of the organization. The book will be stored in the archive for 75 years, although some experts argue that a sufficient storage period is 50 years.
TC can be written off:
- At the end of the archiving period.
- If the book is damaged and a new one is issued.
- If the form is damaged during the filling process, when an error was made when filling out the title page or the first entry.
During liquidation, an act is drawn up that contains a list of members of the commission appointed responsible for the write-off and a list of workers who are subject to destruction.
The act must contain information:
- the reason for the write-off;
- series and numbers of books;
- owners' surnames.
The act must be approved:
- responsible person;
- employer.
After the write-off procedure, all written-off books must be destroyed, about which a special note must be made in the write-off act, signed by the commission.
The act of writing off work books is a sample. The act of acceptance and transfer of work books is a sample.
Appointment of a responsible person
The person responsible for maintaining work records is appointed by order of the head of the organization. Usually the choice falls on one of the personnel department employees, and if it is absent, this authority is assigned to the secretary, clerk or accounting employee.
The order on work books contains:
- Full name and position of the responsible person;
- an indication of the duties (responsibility) assigned to him;
- number and date of document execution;
- signature of the manager who issued the order.
The order must also bear the signature of the person responsible for maintaining work records. Thus, he confirms his consent to exercise these powers.
Accounting for Labor Code by the employer
The sixth part of the Rules states the procedure for accounting, registration and storage of TC and provides additional references to the legal grounds at the government level that regulate the established procedure:
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 01.03.2008 No. 132.
- Resolution No. 257 dated March 25, 2013.
Registration is carried out under strict accounting and control:
- Valid books in the logbook for recording their movement.
- Forms, as well as forms of inserts in the receipt and expenditure book.
The employee responsible for maintaining the Labor Code (see here) receives the insert forms against receipt, after which the form is written off from the accounting balance. If an error or typo was made when filling out, you must take a new form and fill it out, and write off the old one with the act.
More details on the video:
Storage and accounting rules
All work books received from employees, work books issued by the employer, as well as their blank forms and inserts are subject to strict recording during storage. This is evidenced by section 6 of Rules No. 225.
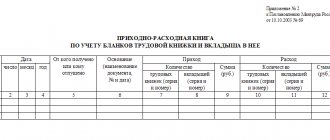
The employer must keep labor record books in the prescribed form. In particular, this is a receipt and expenditure book for recording forms and inserts and a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts.
Both accounting journals must be laced and numbered, and also certified by the manager’s signature and seal. This is stated in paragraph 41 of the Rules.
The receipt and expenditure book for accounting forms is maintained by the accounting department, and it displays a full range of information on the receipt and expenditure of work book forms . When registering a new form, the series and number of the form are entered in the book.
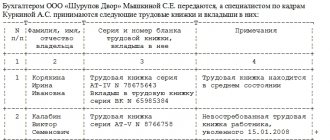
The book for recording the movement of work books records information about the receipt and issuance of all work books of employees and inserts upon dismissal . The accounting book records the series and number of work books issued to employees. Also here is the signature of the employee who received the work book in hand during the dismissal process.
As for the place of storage of work books, neither Rules No. 225 nor Instruction No. 69 contain instructions as to where work books should be stored. But the Regulations on Document Management, approved back in 1983, state that all strict reporting forms must be stored in safes, metal cabinets and special rooms to ensure their safety in accordance with clause 6.2.
The key principle for choosing a place to store work records is to prevent outsiders from free access to them.
Liability for violation of conditions
In order to comply with the conditions that impose increased responsibility on the employer for storing books, raids are carried out by the labor inspectorate authorized to supervise personnel records management. Their inspections are preventive in nature, and each violation is subject to a fine.
After the employer is issued a fine, the amount of which depends on the form of the enterprise and the volume of books stored, as well as on the number of violations committed in relation to their storage, maintenance or completion.
At this level of regulation of the order in personnel documents, responsibility is determined in accordance with Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which announces the principles and rules of the employer’s proper approach to the issue of maintaining and storing labor records.
Art. 353 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation delegates the authority to inspect employers to the labor inspectorate. The gaps in personnel records revealed by her are subject to fines. In accordance with Art. 357 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, inspectors have the right to request for inspection any documentation related to the maintenance and storage of books and inserts.
The audit is carried out according to the main, most significant parameters of personnel activities. For failure to fulfill necessary obligations based on violation of labor legislation, fines are collected in accordance with clause 1, art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which are:
- For officials 1-5 thousand rubles.
- For individual entrepreneurs - in the same amount or as an alternative - suspension of the activities of individual entrepreneurs for up to 90 days.
- For companies with legal status. fines for individuals are much higher: 30-50 thousand rubles or suspension of activities for the same period.
If an official does not correct these shortcomings in his activities, he may be subject to disqualification for a period of one to two years.
Smaller defects that can be found everywhere in the activities of a not entirely accurate personnel officer or individual entrepreneur are punishable by fines from 300 to 500 rubles. And if such comments are found in the activities of a legal entity. persons - fines can be 3-5 thousand rubles.
The employer must keep in mind that the slightest mistake can lead him to criminal liability for negligence or forgery of documents if he corrects the record improperly or purchases an employment form of inadequate quality.
And this responsibility involves large fines and the possibility of more serious punishment . In addition, the employee can recover from the employer for moral damages and hold him accountable by a court decision - to restore the completely lost work experience at the enterprises where he previously worked.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225 “On work books”
In accordance with Article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Russian Federation decides:
1. Approve the attached:
the form of the work book and the form of the insert in the work book;
Rules for maintaining and storing work books, preparing work book forms and providing them to employers.
2. Establish that work books of the new sample will come into effect from January 1, 2004.
Work books of a previously established form that employees have are valid and cannot be exchanged for new ones.
3. To the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation:
a) approve samples of the work book and its insert, as well as the technical requirements for the production of their forms;
b) ensure at subordinate enterprises the production of work book forms and an insert in it according to a single sample;
c) approve the procedure for providing employers with work book forms and an insert in it.
4. To the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation:
a) approve instructions for filling out work books;
b) provide explanations on the application of the Rules approved by this resolution.
5. The executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation must carry out the necessary work to introduce a new sample of work books and inserts into them in organizations located on their territory.
| Chairman of the Government of the Russian Federation | M. Kasyanov |
Moscow
April 16, 2003
N 225
Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 N 225
Work book form
(Cover)
Coat of arms of the Russian Federation
Employment history
(Title page)
Coat of arms of the Russian Federation
Employment history
Surname ________________________________________________________________
Name ____________________________________________________________________
Surname _______________________________________________________________
Date of Birth __________________________________________________________
(day month Year)
Education ____________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Profession,
speciality __________________________________________________________
Date of completion ________________________________________________________
(day month Year)
Signature of the book owner ________________________________________________
M.P. Signature of the person responsible for maintaining
work records
________________________________________
(clear)
Job details
| Series and number* | (10 spreads) |
| N entries | date | Information about hiring, transfer to another permanent job, qualifications, dismissal (indicating reasons and reference to the article, clause of the law) | Name, date and number of the document on the basis of which the entry was made | ||
| number | month | year | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
Information about the award
| Series and number | (10 spreads) |
| N entries | date | Information about awards (promotions) | Name, date and number of the document on the basis of which the entry was made | ||
| number | month | year | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
_____________________________
* The series and number are indicated on one of the four pages of each unfolded sheet of the work book.
Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 N 225
Form of insert in work book
Insert in the work book (without a work book is invalid)
Coat of arms of the Russian Federation
Surname ________________________________________________________________
Name ____________________________________________________________________
Surname _______________________________________________________________
Date of Birth __________________________________________________________
(day month Year)
Education ____________________________________________________________
Profession,
speciality __________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Date of completion ________________________________________________________
(day month Year)
Signature of the book owner ________________________________________________
M.P. Signature of the person responsible for maintaining
work records
________________________________________
(clear)
The insert in the work book is made according to the approved form of the work book. Insert volume: “Information about work” - 9 spreads, “Information about awards” - 8 spreads.
Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing them to employers (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 N 225)
I. General provisions
1. These Rules establish the procedure for maintaining and storing work books, as well as the procedure for producing work book forms and providing employers with them.
2. The work book is the main document about the employee’s work activity and length of service.
3. The employer (with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs) maintains work books for each employee who has worked for him for more than five days, if the work for this employer is the main one for the employee.
An employer - an individual who is an individual entrepreneur - is obliged to keep work books for each employee in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
An employer, an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur, does not have the right to make entries in the work books of employees and draw up work books for employees hired for the first time.
4. The work book contains information about the employee, the work he performs, transfer to another permanent job and the dismissal of the employee, as well as the grounds for termination of the employment contract and information about rewards for success in work.
5. Information about penalties is not entered into the work book, except in cases where the disciplinary sanction is dismissal.
6. Work books are kept in the state language of the Russian Federation, and on the territory of a republic within the Russian Federation that has established its own state language, registration of work books can, along with the state language of the Russian Federation, be carried out in the state language of this republic.
7. The employer is obliged, upon a written application from the employee, no later than three working days from the date of its submission, to give the employee a copy of the work book or an extract from the work book certified in the prescribed manner.
II. Maintaining work records
8. The registration of a work book for an employee hired for the first time is carried out by the employer in the presence of the employee no later than a week from the date of hiring.
9. When registering the work book, the following information about the employee is entered:
a) last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth (day, month, year) - on the basis of a passport or other identity document;
b) education, profession, specialty - on the basis of documents on education, qualifications or the presence of special knowledge (when applying for a job that requires special knowledge or special training).
10. All entries about the work performed, transfer to another permanent job, qualifications, dismissal, as well as awards made by the employer, are entered into the work book on the basis of the relevant order (instruction) of the employer no later than a week, and in case of dismissal - on the day of dismissal and must correspond exactly to the text of the order (instruction).
11. All entries in the work book are made without any abbreviations and have their own serial number within the appropriate section.
12. The employer is obliged to familiarize the owner with each entry made in the work book about work performed, transfer to another permanent job and dismissal, against signature in his personal card, which repeats the entry made in the work book.
The form of the personal card is approved by the Federal State Statistics Service.
13. The work book is filled out in the manner approved by the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation.
14. Entries in the work book about the reasons for termination of the employment contract are made in strict accordance with the wording of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law.
15. Upon termination of an employment contract on the grounds provided for in Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (except for cases of termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employer and due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties (clauses 4 and 10 of this article), an entry is made in the work book about dismissal (termination of employment contract) with reference to the relevant paragraph of part one of this article.
16. When terminating an employment contract at the initiative of the employer, an entry about dismissal (termination of the employment contract) is made in the work book with reference to the corresponding paragraph of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
17. When an employment contract is terminated due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties, an entry is made in the work book about the grounds for termination of the employment contract with reference to the relevant paragraph of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
18. When terminating an employment contract on other grounds provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal laws, an entry about dismissal (termination of the employment contract) is made in the work book with reference to the relevant article, paragraph of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law.
19. Upon termination of an employment contract with an employee who, in accordance with a court verdict, has been deprived of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities and has not served his sentence, an entry is made in the work book about on what basis, for what period and what position he was deprived of. the right to occupy (what activities one is deprived of the right to engage in).
20. Information about part-time work (about dismissal from this job), at the request of the employee, is entered at the place of main work in the work book on the basis of a document confirming part-time work.
21. The following entry is also made in the work book at the place of work, indicating the relevant documents:
a) on the time of military service in accordance with the Federal Law “On Military Duty and Military Service”, as well as on the time of service in internal affairs bodies, the State Fire Service of the Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergencies and Disaster Relief, institutions and the authorities of the penal system, tax police authorities, authorities for control over the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities;
b) about the time of training in courses and schools for advanced training, retraining and training.
22. Relevant entries made in the work book of persons released from work (position) in connection with an illegal conviction or removed from office in connection with illegal prosecution, established respectively by an acquittal or a resolution (ruling) on the termination of a criminal case in absence the events of the crime, due to the absence of corpus delicti in the act or the lack of proof of their participation in the commission of the crime, are recognized as invalid. The employer, upon a written application from the employee, issues him a duplicate work book without the entry declared invalid. A duplicate of the work book is issued to the specified persons in the manner established by these Rules.
In the work books of persons who have served correctional labor without imprisonment, an entry is made at the place of work stating that the time worked during this period is not counted towards continuous work experience. This entry is made in the work books at the end of the actual term of serving the sentence, which is established according to certificates from the internal affairs bodies.
When a convicted person is dismissed from work in the prescribed manner and he is accepted into a new place of work, the corresponding entries are made in the work book in the organization to which he was hired or sent.
23. When continuous work experience is restored in accordance with the established procedure, an entry on the restoration of continuous work experience is made in the employee’s work book at the last place of work indicating the corresponding document.
24. The following information about awards (incentives) for labor merits is entered into the work book:
a) on the awarding of state awards, including the conferment of state honorary titles, on the basis of relevant decrees and other decisions;
b) on awarding certificates of honor, conferring titles and awarding badges, badges, diplomas, certificates of honor by employers;
c) on other types of incentives provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as collective agreements, internal labor regulations, charters and regulations on discipline.
25. Entries on bonuses provided for by the remuneration system or paid on a regular basis are not entered into work books.
III. Making changes and corrections to the work book. Duplicate work book
26. Changes in records about the last name, first name, patronymic and date of birth, as well as about the education, profession and specialty of the employee are made by the employer at the last place of work on the basis of a passport, birth certificate, marriage, divorce, change of last name, first name, patronymic and other documents.
27. If an incorrect or inaccurate entry in the work book is identified, it is corrected at the place of work where the corresponding entry was made, or by the employer at the new place of work on the basis of an official document of the employer who made the error. In this case, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the necessary assistance when applying.
28. If an organization that made an incorrect or inaccurate entry is reorganized, the correction is made by its legal successor, and in the event of liquidation of the organization, by the employer at the new place of work on the basis of the relevant document.
If an incorrect or inaccurate entry in the work book was made by the employer - an individual who is an individual entrepreneur, and his activities are terminated in the prescribed manner, the correction is made by the employer at the new place of work on the basis of the relevant document.
29. Corrected information must fully comply with the document on the basis of which it was corrected. In the event of the loss of such a document or its discrepancy with the work actually performed, correction of information about the work is carried out on the basis of other documents confirming the performance of work not specified in the work book.
Witness testimony cannot serve as a basis for correcting previously made entries, with the exception of entries in respect of which there is a court decision, as well as the cases provided for in paragraph 34 of these Rules.
30. In sections of the work book containing information about work or information about awards, crossing out inaccurate or incorrect entries is not allowed.
Changing entries is made by invalidating them and making correct entries.
The same procedure is used to change the record of an employee’s dismissal (transfer to another permanent job) if the dismissal (transfer) is declared illegal.
31. A person who has lost his work book must immediately notify the employer at his last place of work. The employer issues a duplicate work book to the employee no later than 15 days from the date the employee submits the application.
32. When preparing a duplicate work book, carried out in accordance with these Rules, the following are entered into it:
a) information about the employee’s total and (or) continuous work experience before joining this employer, confirmed by relevant documents;
b) information about work and rewards (incentives) that were entered into the work book at the last place of work.
The total length of service is recorded in total, that is, the total number of years, months, days of work is indicated without specifying the employer, periods of work and positions of the employee.
If the documents on the basis of which entries were made in the work book do not contain complete information about work in the past, only the information available in these documents is entered into the duplicate work book.
33. If there is an entry in the work book about dismissal or transfer to another job that has been declared invalid, the employee, upon his written application, is issued a duplicate work book at his last place of work, into which all entries made in the work book are transferred, with the exception of the entry declared invalid.
The work book is drawn up in the prescribed manner and returned to its owner.
A duplicate of the work book is issued in the same manner if the work book (insert) has become unusable (burnt, torn, stained, etc.).
34. In the event of a massive loss by an employer of the work records of employees as a result of emergency situations (ecological and man-made disasters, natural disasters, mass riots and other emergency circumstances), the length of service of these employees is established by the length of service commission created by the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The composition of such a commission includes representatives of employers, trade unions or other representative bodies authorized by employees, as well as other interested organizations.
Establishment of the fact of work, information about the profession (position) and periods of work for a given employer is carried out by the commission on the basis of documents available to the employee (certificate, union card, trade union member registration card, pay book, etc.), and in the event of their absence - based on the testimony of two or more witnesses who know the employee through joint activities with him or her at the same employer or in the same system.
If the employee had already worked for this employer before joining, the commission takes measures to obtain documents confirming this fact.
Based on the results of the commission’s work, a report is drawn up, which indicates the periods of work, profession (position) and length of service of the employee.
The employer, based on the commission’s act, issues the employee a duplicate work book.
If the documents have not been preserved, work experience, including that established on the basis of witness testimony, can be confirmed in court.
IV. Issuance of a work book upon dismissal (termination of an employment contract)
35. When dismissing an employee (terminating an employment contract), all entries made in his work book during his work with this employer are certified by the signature of the employer or the person responsible for maintaining work books, the seal of the employer and the signature of the employee himself (except for the cases specified in paragraph 36 of these Rules).
If the work book was filled out in the state language of the Russian Federation and in the state language of the republic within the Russian Federation, both texts are certified.
The employer is obliged to issue the employee on the day of dismissal (the last day of work) his work book with a record of dismissal included in it.
If there is a delay in issuing a work book to an employee due to the fault of the employer, or if the reason for the employee’s dismissal is entered into the work book incorrectly or does not comply with federal law, the employer is obliged to compensate the employee for the earnings he did not receive during the entire delay. In this case, the day of dismissal (termination of the employment contract) is considered the day the work book is issued. On the new day of dismissal of the employee (termination of the employment contract), an order (instruction) of the employer is issued, and an entry is made in the work book. A previously made entry about the day of dismissal is invalid in the manner prescribed by these Rules.
36. If on the day of dismissal of an employee (termination of an employment contract) it is impossible to issue a work book due to the employee’s absence or his refusal to receive the work book in hand, the employer sends the employee a notice of the need to appear for the work book or agree to send it by mail. Sending a work book by mail to the address specified by the employee is permitted only with his consent.
From the date of sending this notification, the employer is released from liability for the delay in issuing a work book to the employee.
37. In the event of the death of an employee, the work book, after making an appropriate entry in it about the termination of the employment contract, is handed over to one of his relatives against signature or sent by mail upon the written application of one of the relatives.
V. Insert in the work book
38. If all the pages of one of the sections are filled out in the work book, an insert is sewn into the work book, which is drawn up and maintained by the employer in the same order as the work book.
The insert without a work book is invalid.
39. When each insert is issued, a stamp is placed in the work book with the inscription “Insert issued” and the series and number of the insert are indicated.
VI. Accounting and storage of work books
40. In order to record work books, as well as work book forms and inserts in it, employers maintain:
a) a receipt and expenditure book for recording the forms of the work book and the insert in it;
b) a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them.
The forms of these books are approved by the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation.
41. In the receipt and expenditure book for accounting of work book forms and the insert in it, which is maintained by the accounting department of the organization, information is entered on all operations related to the receipt and expenditure of work book forms and the insert in it, indicating the series and number of each form.
In the book of accounting for the movement of work books and inserts in them, which is maintained by the personnel service or other division of the organization that processes the hiring and dismissal of workers, all work books accepted from employees upon entering work are registered, as well as work books and inserts in them, indicating the series and numbers issued to employees again.
Upon receipt of a work book in connection with dismissal, the employee signs on the personal card and in the book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them.
The receipt and expenditure book for recording the forms of the work book and the inserts in it and the book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them must be numbered, laced, certified by the signature of the head of the organization, and also sealed with a wax seal or sealed.
42. Forms of the work book and its insert are stored in the organization as documents of strict accountability and are issued to the person responsible for maintaining work books at his request.
At the end of each month, the person responsible for maintaining work books is obliged to submit to the organization’s accounting department a report on the availability of work book forms and the inserts in them and on the amounts received for issued work books and inserts in them, with the attachment of the receipt order of the organization’s cash desk. Work book forms and the insert in it that are damaged when filling out are subject to destruction and the corresponding act is drawn up.
43. Work books and duplicates of work books not received by employees upon dismissal or in the event of the death of an employee by his immediate relatives are stored until required by the employer (in an organization or by an individual who is an individual entrepreneur) in accordance with the requirements for their storage established by law Russian Federation on archival matters.
44. The employer is obliged to constantly have in stock the required number of work book forms and inserts into it.
VII. Responsibility for compliance with the procedure for maintaining work books
45. Responsibility for organizing the work of maintaining, storing, recording and issuing work books and inserts in them rests with the employer.
Responsibility for maintaining, storing, recording and issuing work books lies with a specially authorized person appointed by order (instruction) of the employer.
For violation of the procedure for maintaining, recording, storing and issuing work books established by these Rules, officials bear responsibility established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
VIII. Production of work book forms and provision of them to employers
46. The production of work book forms and the insert in it and the provision of them to employers on a paid basis are carried out in the manner approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The forms of the work book and its insert have the appropriate degree of protection.
47. When issuing a work book or an insert to it to an employee, the employer charges him a fee, the amount of which is determined by the amount of expenses for their acquisition, except for the cases provided for in paragraphs 34 and 48 of these Rules.
48. If the initial filling of the work book or the insert in it is incorrect, as well as if they are damaged through no fault of the employee, the cost of the damaged form is paid by the employer.
- Back
- Forward
What the current legislation says regarding electronic work books
The need to switch to the ETC was approved by Law No. 439-FZ dated December 16, 2019 on amendments to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This regulation comes into force on January 1, 2021. The transition to the electronic format of labor documents is mandatory, but it will happen gradually. For citizens who will start working for the first time no earlier than 01/01/2021, work books will be issued exclusively in electronic form, while other workers have a choice.
Until June 30, 2021, the employer must notify each employee personally of the upcoming innovations by sending him a written notice. From 2021, employers will have to generate and submit to the Pension Fund a new personalized SZV-TD report, which will contain information about personnel changes for each employee (new Article 66.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 1 of Law No. 436-FZ of December 16, 2019). You will also have to make changes to local regulations related to maintaining work records.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- What should an employee do if the employer has lost his work book?
- Work book for transfer to another position: sample 2021
- Work book certified by the employer for the bank: sample 2021
- Validity period for a copy of a work book for a bank
- Information about disciplinary sanctions in the work book
- The employee does not want an electronic work record book
- Example and procedure for filling out an electronic work book
It should be noted that each employee has the right to independently decide in what format his work record book will be kept (paper or electronic). If an employee decides to keep a paper book or refuse to maintain it, he must write a corresponding statement. If such an application is not received from the employee, the employer will continue to maintain a paper book along with its electronic version.
How to prepare for changes as HR workers
Expert opinion
Lebedev Sergey Fedorovich
Practitioner lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in defense in court.
Firstly, prepare in advance for changes in local regulations, prepare a draft change in the internal labor regulations/collective agreement/other internal regulations of the organization.
We plan to prepare a draft with changes to the internal labor regulations, as well as an order for making changes and familiarization sheets with the labor regulations in advance, in October 2021, since when making changes to the local regulations of the company, everyone is required to familiarize themselves with them employee.
Secondly, prepare, by the end of 2021, information letters/draft orders/notifications or other ways of conveying information to employees in advance that electronic recording of data on labor activity is being introduced. Employees need to be informed that if they would like to keep their work record books in paper form, they must submit an application to the personnel service (or to the person responsible for storing work records) before the end of 2021.
We plan to send out a corporate mailing in the form of an information letter for general information, and more formal documents - notification to each employee no later than October 31, 2020. Additional agreements to employment contracts are not required, since electronic data on labor activity does not entail changes in the essential and mandatory terms of the employment contract.
Thirdly, if the employment contract form specifies a list of documents for employment, then this form must be changed and used from 2021.
We do not prescribe this list in employment contracts, but refer to the internal labor regulations.
Fourthly, for those whose applications will not be received, you need to organize the issuance of work documents on the first working day of 2021: sign in journals, draw up a register whose work records are stored in paper form according to applications.
Fifthly, take care of the technical support for transferring data to the Pension Fund.
When this bill is approved in the first years of its existence, improvements and significant changes are possible. During the transition period after its introduction, we would recommend ensuring that the employer keeps workers’ work books so that they do not have to be collected again in the event of any amendments to the law.
This is important to know: How to fill out a work book correctly: sample 2021
Examples of using ETC
If hired for the first time since January 1, 2021, a paper work book will not be created.
Let's consider several possible situations from practice.
The employee gets a job after the law comes into force (from 01/01/2020 to 01/01/2021).
You must be guided by the previous rules: an employee without work experience must have a paper work book, an employee with work experience and a previously issued work book must have all the relevant entries about his work activity entered into it.
Example 2.
An employee who has work experience and a previously issued work book gets a job after the transition period (after 01/01/2021).
From 2021, providing a work book for applying for a job is not mandatory, but at the request of the employee, the corresponding entry must be made in the work book, and the book must be kept by the employer.
This is important to know: Application for a copy of the work record: sample 2021
Example 3.
An employee without work experience gets a job after the transition period (after 01/01/2021).
From 2021, according to the bill, there should be a complete transition to electronic work books. Therefore, we assume that a paper work record book is not required. However, the bill currently does not provide any clarification as to whether an employee has filed a corresponding application and insists on maintaining a paper work record book. Presumably, in 2021 there will be clarifications from the Ministry that will bring more clarity to their implementation.
Example 4.
An employee came with a paper work record in 2021. Can he keep it?
By this point, local regulations (in the Internal Labor Regulations) will already have to indicate all the innovations regarding the electronic format for storing data on labor activity. You will need to act in accordance with these rules.
It is recommended to talk with the employee when applying for a job and then make a decision whether to write an application for maintaining a paper work record or not. In 2021, we still accept paper labor documents without fail.
Pros and cons of electronic work books
no costs for work books;
solving the problem of remote employment;
removal of responsibility for storing work books (if you do not write a corresponding statement, the book will be handed over to you, and the employer will not be obliged to keep it);
the impossibility of loss of employment by either the employee or the employer;
absence of employees with multiple jobs, no need to restore employment;
eliminating errors in information;
speed of data provision, speed of exchange of information about the work experience of the employer and the Pension Fund;
availability of data at any time for the employee (you can get the SZI-TD form right here and now in the personal account of the Pension Fund and State Services, if certification is necessary - from the employer, at the MFC and in any territorial body of the Pension Fund).
the employer’s lack of confidence that the employee is getting a job at his main place of work and has already been fired from his previous job (since now there is no need to pick up the work book upon dismissal and there is no “material evidence” of the fact of leaving);
the need to maintain registers of paper and electronic work books, depending on the applications of employees, to organize the storage of applications for paper work books;
the need to carry out large-scale additional work - notifying employees about new legislation and the need to choose between a paper and electronic work book, changing local regulations governing the activities of the organization, agreements and collective bargaining agreements;
the employer stores data electronically for only 3 years after the employee’s dismissal;
the “electronic labor” will not contain information about awards;
on the day of dismissal, the employer, instead of the labor record, is obliged to issue information about the employee’s work activity with the seal of the organization. If on the day of dismissal it is impossible to issue information about work activity due to the employee’s absence or refusal to receive it, the employer is obliged to send by registered mail with notification information about work activity on paper, duly certified - that is, the paper work is not canceled.
Translation of other personnel documents into electronic form
On October 28, 2021, news appeared on the official website of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation about the approval by the tripartite commission for regulating social and labor relations of a bill on conducting an experiment on converting personnel documents into electronic form. The experiment is aimed at testing the mechanisms for maintaining electronic personnel document flow. At the same time, legal entities participating in the experiment independently determine the types of documents in respect of which the experiment will be conducted, as well as the type of electronic signature used in the work (with the exception of an employment contract, a contract of liability and a student agreement, when concluding which the employer is obliged to use an enhanced qualified electronic signature). signature), and employees of organizations participating in the experiments can refuse to maintain their documents relating to labor relations with the employer in electronic form by writing a written refusal.
The costs of electronic document management (including expenses for electronic signatures) are borne by the employer. The period of the experiment is from January 1 to December 31, 2021. According to the bill, no more than 10 legal entities should take part in the experiment; according to the news of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, 37 large companies have already expressed their desire.
Order on electronic work books
Employers can issue an order to introduce electronic work books as early as January 2021. The unified form of the document has not been approved; it can be drawn up in a free format. The order must include: record which employee will perform the following functions:
Prepare the SZV-TD report for the Pension Fund and information in the SZI-TD form issued to employees.
Notify staff about innovations in relation to work books.
Collect statements written by employees of the organization.