Specialty clothing, footwear and personal protective equipment (PPE) are used in many industries. A set of equipment designed taking into account working conditions makes work safe and comfortable.
What requirements for workwear are important to comply with, who is entitled to free equipment, and how to properly care for things? It is important to know the answers to these questions, both for business managers and HR officers and procurement department specialists.
Let’s define the concepts: is workwear PPE or not?
Special clothing is needed not only for representatives of dangerous professions, but also to maintain the appearance of the organization. By definition, workwear is a custom-made uniform that is worn over regular clothing and sometimes over the naked body. Protective equipment helps protect workers from exposure to harmful factors and mechanical shocks. For some specialists, reflective stripes are applied to the workwear, which help the worker to be seen in the dark.
Labor protection, workwear
Note !
Any protective clothing is workwear, but not every workwear can be considered PPE. This includes the uniform that employees wear to maintain the appearance of the company: cleaners in hotels, restaurants, flight attendants, and the like.
Types and features of storage of workwear
The issuance of workwear can be regulated not only by the nature of hazardous production, climatic conditions, seasonality of work, but also by the level of protection provided. Based on the latter, the following classifications (types) of special kits are distinguished:
- Protection from dirt;
- Personal hygienic protective equipment;
- Against mechanical impact;
- Thermal insulation kits;
- Prevents exposure to toxic fumes.
The protective equipment provided at the workplace, provided for by labor safety regulations, must be stored in accordance with the established rules and conditions:
- Separate from the employee's personal belongings;
- In a special dressing room and in a separate cubicle for each employee.
In case of untimely provision of an employee with a set of clothing necessary for work in hazardous production conditions, the employer pays the subordinate 65% of earnings if the former was removed from work for the specified reasons and was declared idle.
Ensuring the proper sanitary and hygienic condition of workwear is the responsibility of the employer. To comply with the stipulated rule, employers, as a rule, cooperate with specialized dry cleaning institutions that have permission from Rospotrebnadzor and carry out washing of special kits according to the schedule approved with the employer.
While washing the previous special kit, the employee must be provided with another similar means of protection in satisfactory sanitary condition.
Primary requirements
Issuance of PPE: what guides the employer
Legislation puts forward its own requirements for workwear, safety shoes and personal protective equipment for working on construction sites, with electrical installations, in the chemical industry, etc. First of all, it should be useful, and the employee should feel comfortable in it.
To personal protective equipment
PPE should not interfere with the performance of work, nor should it negatively affect the quality of work. If PPE is divided into several parts (separately for the torso and the area below the waist, for example), then their joint use should not interfere with each other. When workers are issued personal protective equipment, they must be given instructions on use, maintenance and storage. Tests and special inspections are regularly carried out to determine suitability for further use. If overalls, for example, are worn out or torn, they must be replaced with new ones.
To workwear
Some of the requirements duplicate the requirements for personal protective equipment: convenience, unhindered use, quality. Workers are subject to storage and care requirements for protective clothing. The employee is required to perform laundry, cleaning and disinfection. If clothing belongs to PPE, then additional requirements may be imposed on it (additional cleaning of hazardous substances). In addition, staff must be able to properly handle clothing.
Medical staff in clothes
Note! Extension of the wearing period of workwear according to the Order of the Ministry of Labor allows for an extension of the operational life if the PPE and workwear maintain their quality condition.
For safety shoes
Requirements for footwear for labor protection:
- Firstly, safety shoes must be the right size;
- Secondly, match the working environment: adhesion of the sole to the coating on the working terrain (concrete, sand, earth, tiled areas);
- Thirdly, comply with hygiene standards and be environmentally friendly;
Workers can buy their own shoes in specialized shoe stores. Honest manufacturers conduct tests before releasing models for sale. Large enterprises provide regular cleaning and bulk orders for employees.
Fabrics used for sewing workwear:
- Alova -100% polyester , density 200 g/m2, water resistance of at least 8000 mm water column. This is a modern multilayer material combining textile layers and membrane films. The membrane functions as a waterproof and, at the same time, vapor-conducting layer. The outer textile layer of Alova fabric provides the strength, thickness and visual appeal of the membrane. Alova fabric (Alova, membrane ) is velvety to the touch, products made from it are always reliable and comfortable to wear.
- Calico -100% cotton . Calico perfectly absorbs moisture, has high breathability and is considered a good hygienic and highly environmentally friendly material.
- Duspo -100% polyester . Lightweight, pleasant to the touch fabric with excellent windproof and water-repellent properties. Thanks to the “milky” impregnation, the fabric dries quickly and prevents the migration of insulation.
- Locker classic - 100% nylon , 105 g/m2, water-repellent finish, strength, comfort to wear, color fastness, moisture protection. High-quality Korean fabric designed for workwear, sportswear and casual wear.
- Moleskine -100% cotton . Fire-retardant, dust-proof fabric that protects from general industrial pollution and mechanical impacts, from elevated temperatures and thermal radiation, and from non-toxic dust.
- New file - 100% polyester . Beautiful, modern material that retains the shape of the finished product well. Waterproof, retains stable color even after repeated washing and ironing.
- Oxford -100% polyester . The fabric is highly durable and has a waterproof polyurethane coating that prevents dirt from penetrating between the fibers.
- Panacea -35% viscose , 65% polyester , 150 g/m2. Plain weave fabric, protection from mechanical influences , high hygroscopicity and breathability, provides protection from moisture, absence of pilling on the surface of the fabric during use, color fastness.
- Tent fabric - 100% cotton , density 270 g/m2. Thick durable fabric with water-repellent impregnation.
- Twill - 100% cotton , density 280 g/m2. Cotton fabric with water-repellent impregnation is widely used in the manufacture of workwear Twill is a dense fabric with increased resistance to mechanical stress, strong and durable, plastic and shape-resistant.
- Satori -50% cotton , 50% polyester , density 145 g/m2. casual suit made from SATORI fabric can be autoclaved; the white color will retain its purity and freshness even when bleached with chlorine-containing substances, which is especially valuable for medical institutions.
- Sisu -35% cotton, 65% polyester , density 139 g/m2. It has good strength characteristics, does not peel, is easy to wash, and retains its quality after repeated washing.
- Blended -50% cotton, 50% or 65% cotton, 35% polyester , density 210 g/m2. The optimal ratio of cotton and polyester mixed in yarn ensures good air exchange and high resistance to mechanical abrasion. High performance qualities have made this material the most common in the production of workwear. The fabric is water-repellent.
- Taslan -100% nylon Fabric resistant to friction and repeated bending. Has good air permeability. Dries quickly. Has water-repellent and "milky" finishes.
- Twill - 35% cotton, 65% polyester , density 210 g/m2. Polyester makes the twill very durable and resistant to mechanical stress, and the cotton content makes it highly breathable and moisture-permeable, thereby creating a comfortable environment for the body. In addition, twill does not cause an allergic reaction, which is very important, given the characteristics of various industries.
- Tisi -35% cotton, 65% polyester . It comes in different densities: 120, 130 and 160 g/m2. It has good hygienic and strength characteristics, is easy to wash, wrinkles little, and does not peel. Tisi fabric is optimal in price and quality.
- Tomboy -33% cotton , 67% polyester , density 245 g/m2. The high wear resistance and strength of Tomboy fabric (manufactured by Carrington) guarantees long service life. Resistance to frequent industrial washing (at 85°C) ensures minimal shrinkage of the product, color fastness and absence of pilling. The “easy care” finish allows you to avoid ironing clothes after drying them flat.
Providing workers with special clothing
Employers, concluding an agreement with applicants, undertake to provide them with a uniform, if required. You can discuss the availability and form of workwear before drawing up a contract. If the organization’s charter stipulates the need for special clothing, then the employee undertakes to perform work in personal protective equipment. Failure to comply can result in a reprimand, fine and suspension from work.
Who should
Rules for the use of personal protective equipment
Firms can be divided into 2 groups: some are obliged to supply workers with special clothing, while others do this at their own discretion. What are the requirements for workwear regarding the provision of:
- Signal clothing: road workers, traffic police, police, janitors and other representatives of uniforms with reflectors.
- Warm uniform: builders, installers, traffic police, welders, electricians and the like.
- Pass-through protective clothing: for workers in hazardous and food production facilities and unfavorable temperatures.
Note! Sometimes different types of workwear can be used together. For example, to do metalworking or carry out construction work outdoors in winter, wear a warning light over warm clothing.
Hotel uniform
Also, uniforms are required for a number of civil servants, as well as for medical workers in order to protect hygiene. There is a difference between branded clothing and workwear. The brand name is issued by representatives of the enterprise; individual ordering of tailoring and design development is carried out through a contract with a tailoring organization. Workwear can be bought online and in specialized stores.
Issue norms
The procedure and norms that are intended to be responsible for issuance are developed and approved within the organization with the help of an order from the chief executive. In the rules, managers indicate hygiene requirements for issued clothing. It is allowed to deduct part of the salary for branded clothing. Free PPE, designed to protect the body, is issued without charging the employee, since performing work without it is contrary to GOSTs and SNIPs.
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCIES
4.1. In the event of an emergency, you should: - immediately turn off the source that caused the emergency; — stop all work not related to the liquidation of the accident; — take first aid measures (if there are victims); — take measures to prevent the development of an emergency situation and the impact of traumatic factors on other persons; — ensure the removal of people from the danger zone if there is a danger to their health and life; - Report the incident to the work manager. 4.2. Work can be resumed only after the causes that led to the emergency have been eliminated. 4.3. An employee who discovers a fire is obliged to: - call the fire brigade by calling 101, indicating the address of the facility and what exactly is burning; — turn off electrical equipment, take measures to ensure safety and evacuate people; - inform the work manager; — begin to extinguish the fire using available fire extinguishing means; — organize a meeting of fire rescue units. 4.4. The use of water or foam fire extinguishers to extinguish live electrical equipment is unacceptable. Carbon dioxide and powder fire extinguishers are used for these purposes. 4.5. Flammed fuels and lubricants should be extinguished with a powder fire extinguisher, covered with sand, earth, or covered with felt (tarpaulin, etc.). Do not extinguish burning fuel with water. 4.6. In the event of an accident at work, it is necessary to: - quickly take measures to prevent the impact of traumatic factors on the victim, provide first aid to the victim, call medical workers to the scene of the incident by calling 103 or deliver the victim to the nearest medical facility; — report the incident to the work manager; - ensure the safety of the situation at the scene of the incident before the start of the investigation, and if this is not possible (there is a threat to the life and health of others, stopping continuous production) - record the situation by drawing up a diagram, protocol, photography or other method. 4.7. In all cases of injury or sudden illness, it is necessary to call medical workers to the scene of the incident, and if this is not possible, take the victim to the nearest medical facility.
Accounting for the issuance of workwear at the enterprise
Standards for issuing workwear by profession
There is an average amount that an organization allocates for each employee for PPE. For ordinary industrial production it is 7 thousand per year, for others it can reach 24 and even 50 thousand.
Note! Since the amounts for enterprises are quite large (especially if there are many employees), records are kept of the uniforms issued and the minimum and maximum acceptable periods of wear are established.
A special responsible employee is appointed for control. In case of premature loss due to the fault of the employee (lost, torn), the company has the right to recover the cost of the new uniform from the employee. Poor calculation of the terms of use threatens unnecessary costs for clothing, or, conversely, a shortage of personal protective equipment and stagnation of the production or construction process.
Minimum set of workwear for representatives of different professions
Regulatory acts reflecting the procedure for providing workwear contain an important clause, according to which not only representatives of dangerous and hazardous professions, but also librarians can apply for personal protective equipment.
The right to a special kit arises for an employee if, during his work activity, one or a combination of the following factors occur:
- Performing work using lifting equipment;
- Work that carries a potential risk of injury to the legs;
- Work involving high noise;
- Activities that involve being outdoors (in the external environment);
- Work that requires prolonged exposure to the cold or is performed during the winter season;
- Work of a seasonal nature, during which high activity of blood-sucking insects remains.
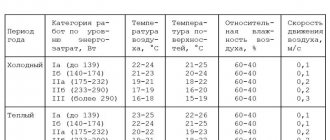
Workwear regulated by labor safety standards depends not only on the specific task performed by the employee, but also on the conditions of the region. Persons working in harsh climatic conditions are provided with warmer sets compared to the basic ones.
In relation to special kits, the technical regulations applied for certification of clothing of the specified type apply.
Below is the minimum amount of workwear that is provided to workers of general professions:
- The fitter:
- 12 pairs of gloves with polymer coating;
- Professional suit that protects against aggressive external production factors;
- Glasses;
- Gloves with a coating reinforced with a dotted rubberized layer;
- Lubrication station mechanic:
- Respiratory protection;
- Glasses;
- Professional protective suit;
- Gloves with a polymer layer;
- Rubber boots;
- Stoker:
- Polymer coated gloves;
- Respiratory protection;
- Glasses;
- Rubber boots with reinforced toe;
- A suit that protects against professional negative factors;
- Librarian:
- A robe that provides protection against pollution at work;
- Protective suit against industrial pollution.
If, along with special clothing, an employee is also given shoes, they must be able to withstand high impact and mechanical loads and have a reinforced toe cap.
Workers performing work in conditions of high humidity are provided with high-top shoes with thick rubberized soles.
Work in conditions of electromagnetic fields is carried out by employees wearing shielded shoes made of conductive materials and with the obligatory provision of a grounding function.
What document should I fill out when issuing workwear to employees?
There are groups of documents within the organization that reflect receipt and issue. This is a card for issuing workwear, where the recipients sign, indicate the date of issue and the set.
Sheet MB-7
Another document is the issuance record sheet in form MB-7, which is maintained by an accountant. A more extensive document containing information about the list of issued protective clothing and costs, as well as accounting entries.
Reference! The accountant also records the issuance of workwear with postings.
Order on write-off of workwear
Clothes are written off not simply through accounting. To write off, it is necessary to assemble an entire commission and approve property that is unsuitable for work. After this, an order is issued and the property is officially written off.
Reference! Only those items that are unsuitable for subsequent use and cannot be repaired are subject to write-off.
The reason for the write-off must be identified: damage to property due to someone else’s fault, wear and tear, and so on.
Legislative regulation
The highest level of documents are federal laws, and the most important in the field of issuing workwear and personal protective equipment are the Labor Code (Article 221), Order No. 290n. They contain rules for the manufacture and issuance of special clothing.
Order to write off special clothing, sample
Some of the regulatory documents are necessary to list the list of mandatory professions that require PPE. Also, maintaining proper condition for the special uniform: washing, cleaning and storage. The employer is obliged to provide uniforms for each separate period of work. Otherwise, employees have the right to complain and supervisory authorities to impose penalties.
Working clothes and personal protective equipment are work attributes that most workers encounter in the process of building their working career. This does not include a dress code. Neglecting the rules for wearing protective clothing can cause damage to health, injury and disfigurement.
Why do you need sanitary clothing?
Before considering the question of how often sanitary clothing should be changed according to the requirements of Russian legislation, it is initially recommended that you familiarize yourself with the goals being pursued.
To ensure sanitary and epidemiological well-being at established facilities, the work of which is directly related not only to the production, but also to the circulation of food products and medications (in pharmacies, hospitals), federal legislation establishes requirements for sanitary clothing for each officially employed employee:
- food industry enterprises;
- companies from the catering and trade sectors in particular;
- the field of medicine.
PPE provides maximum protection against negative impacts
Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be made from high-quality safe material. When used, you can achieve the maximum level of employee safety in case of possible exposure to hazardous factors and components, in particular:
- various mechanical impacts and industrial pollution in general;
- increased or decreased temperature conditions;
- exposure to electric current;
- high level of exposure to biological components: microorganisms, insects, etc.
In the process of production and circulation of food products, it is customary to classify the following as generally accepted industrial pollution according to federal legislation:
- water and all kinds of solutions containing non-toxic components and substances - liquid types of food products, various types of drinks, broths, etc.;
- a non-toxic type of dust (for example, flour), which arises from vegetable or animal oils, from existing microorganisms (we are talking about their content in manufactured food products, including conditional pathogenic organisms that have a high level of probability of causing an infectious disease, which entails risks causing harm to the human body through direct contact, including ingestion). In this case, hygiene control is additionally ensured.
Reference! Personal protective equipment must provide the maximum level of protection from elevated temperatures (relevant in the case of operating production mechanisms and equipment with increased heat generation rates), as well as from possible exposure to electric current during the performance of job duties and from sliding on a slippery surface.
The norms of federal legislation do not establish a specific list of work clothes (sanitary and special in particular) for officially employed staff who are employed not only in the food sector, but also in medicine. The mandatory wearing of sanitary clothing is regulated, which includes:
- specialized replacement shoes – the required option depends on the field of activity;
- headdress - SanPiN requirements require the use of a cap;
- apron, dress, robe.
Compliance with these features allows us to eliminate the likelihood of making mistakes with all the ensuing consequences.