Jurisdiction means which court will consider the claim, and is determined by the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. The jurisdiction of labor disputes is regulated by Chapter 3, Articles 23-32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. There are such types of jurisdiction as generic, territorial, general territorial, alternative territorial, etc. Generic jurisdiction establishes what type of court is appointed to consider a case depending on its category. In particular, cases that do not arise from labor relations are dealt with in magistrates' courts. Claims for reinstatement and resolution of individual labor disputes are filed in district courts of general jurisdiction (read about judicial practice in labor disputes here). Territorial jurisdiction determines the court to consider the case depending on the location of the plaintiff and defendant.
Jurisdiction of labor disputes
This is a legal concept indicating the competence of courts to decide this category of cases. From the point of view of a citizen, it determines exactly where he should go if his rights under the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are violated. The following varieties exist:
- Generic. Designates the category of the court obligated to ensure the consideration of the case;
- Territorial. Indicates the area over which the jurisdiction of the judicial authority has extended.
The correct determination of jurisdiction makes it possible to establish a court that can resolve certain disagreements between the defendant and the plaintiff.
Most of the disputes affecting the field of labor law are referred to district courts. The exception is cases in which the legality of a strike and the damage caused by it is considered. Citizens turn to the magistrate if they have accrued wages for which there is arrears, as well as in connection with the collection of other amounts that must be paid to the employee.
To begin legal proceedings, you must go to the district court. The difficulty is in correctly determining the location of the defendant, since territorial affiliation is established at the physical address of the employer. The plaintiff retains the opportunity to file a lawsuit within three months after the violation was committed. If the dispute concerns dismissal, then the filing period is limited to one month.
Regulatory regulation of the issue
According to the definition of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2017 No. 75-KG17-4, the decision on the addressee of the statement of claim is made by the petitioning party. Thus, the employee has the right to independently indicate the authority to which the request will be sent, regardless of the provisions present in the employment agreement. In this case, the general rules for filing an application are determined by Art. 29 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
Expert commentary
Gorchakov Vladimir
Lawyer
Art. 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation establishes that parties having claims against each other have the right to change jurisdiction by agreement. This rule applies until the claim has been accepted by the authority for consideration. At the same time, jurisdiction under Art. 26, 27, 30 of the Code of Civil Procedure cannot be changed even by agreement of the parties.
Federal Law No. 272-FZ dated 07/03/16 Art. 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure was supplemented with provisions according to which claims related to the restoration of labor rights can be considered by the court at the place of residence of the applicant. Also, part 9 of this article provides that statements of claim arising from agreements in which the place of execution is indicated may be submitted at the specified location.
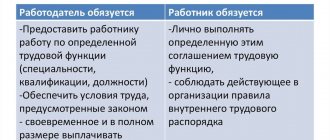
According to labor legislation, a contract concluded by an employer with a subordinate, as well as a collective agreement with other internal documentation of the organization, cannot contain rules according to which an employee is impaired in guarantees and freedoms. This is evidenced, in particular, by Art. 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which these provisions are not subject to application. Thus, the papers signed by the employee can only regulate the relationship between the latter and management during the work process.
Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - Regulation of labor relations and other directly related relations in a contractual manner
In accordance with labor legislation, the regulation of labor relations and other relations directly related to them can be carried out by concluding, amending, and supplementing collective agreements, agreements, and employment contracts by employees and employers. Collective agreements, agreements, and employment contracts cannot contain conditions that limit the rights or reduce the level of guarantees of employees in comparison with those established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms. If such conditions are included in a collective agreement, agreement or employment contract, then they are not subject to application.
Types of jurisdiction
Each jurisdiction for labor disputes that arise is a special case of jurisdiction. From the point of view of procedural law, this is a mechanism that distributes cases and streamlines the work of the judicial system. In practice, consideration of these types is carried out jointly within the framework of each type of proceeding, otherwise the process becomes meaningless.
Wage collection cases
Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the principle of calculating wages. This is a reward for work performed by an employee within the scope of his qualifications. This concept includes incentive payments and compensation. If an employee needs protection in order to restore his right to wages, he, according to Art. 24 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, you should contact the district court.
In 2021, citizens received the right to file a claim both at the location of the employer and at their own place of registration (Part 6.4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). There is an opportunity to apply to the magistrate with an application to draw up a court order, provided that the declared amount does not exceed 50 thousand rubles (clause 1.5, clause 1, article 23 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). In this case, the employee is not required to pay expenses and fees.
Individual labor disputes
These include disagreements that are not subject to standard regulation that have arisen between the employee and the company. Such cases concern issues related to the application of the provisions of legal acts that determine the procedure for implementing labor relations, or if there is an unjustified refusal to hire, or damage to property by an employee.
Jurisdiction is determined according to the general rules, but if the case concerns state secrets (for example, during employment in the intelligence services), then the consideration is transferred to the region. Features of determining the territorial affiliation of a court in accordance with Art. 29 Code of Civil Procedure in various situations:
- The location of the defendant is unknown or he lives outside the Russian Federation. The location of the property or last known place of residence is taken into account;
- The violation was committed by a branch or representative office of the company. It is possible to open a trial at their address;
- Claim for compensation for injury to health or death of the breadwinner. The plaintiff has the right to go to court at his own registration or the address at which he suffered damage;
- A dispute about the restoration of labor rights and compensation for losses incurred due to a conviction contrary to current legislation, as well as in connection with an unlawful conviction in a criminal trial, the use of preventive measures, and administrative punishment. Part 6 art. 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure indicates that the plaintiff may file an application at his place of residence in such a case.
It is important to know! If the employment contract specifies the place of its execution, legal proceedings can be conducted in accordance with the given data. Article 32 provides for the possibility of an agreement whereby the parties independently choose where to initiate proceedings.
Reinstatement
In this case, jurisdiction over labor disputes that arise is carried out at the location of the employer. In paragraph 2 of Art. 54 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that a legal entity is located at the place of state. registration - the address is given in the company documents.
The plaintiff can change jurisdiction according to his registration, which is provided for in Art. 29 Labor Code. This is due to the fact that many modern companies have opened representative offices throughout the country - it would be difficult for citizens to attend meetings held thousands of kilometers from their place of residence.
At the request of the plaintiff, the case is considered at the address of the branch/representative office of the company that provided the workplace. To do this, they must be present in the legal documentation. persons (Article 55 of the Civil Code), which is established by the judicial authority before the start of the consideration. Judges often return applications despite justification, which forces citizens to appeal to higher courts.
Where to file a claim
If the defendant is an organization (legal entity), the employee files the claim in the district court at the location of the defendant. If a labor dispute has arisen with an individual entrepreneur employer, the application is submitted at the defendant’s place of residence. If the claim is for reinstatement at a workplace that is located in a branch or other division of the employer, the plaintiff chooses the district court located at the location of the branch or main production. The choice between several courts that have jurisdiction over the case belongs to the plaintiff.
In order to properly file claims, you need to remember in which court labor disputes are heard. Jurisdiction is determined taking into account the type of branch of law to which the claim relates, the cost of the claim, and the place of residence of the plaintiff and defendant. The procedure for determining the jurisdiction and jurisdiction of labor disputes is established by codes. A claim filed in the wrong court will not be considered. Arbitration courts do not consider claims in labor disputes. The exception is when several employees file a claim against one employer, and each has different claims against their superiors. In this case, a class action lawsuit is filed. Courts of general jurisdiction do not consider class actions in labor disputes, so you need to apply to labor arbitration. The statement of claim is filed with the district court at the place of registration of the defendant, at the place of registration of the plaintiff, at the location of the enterprise or its branch.
Nuances
If the plaintiff files a claim against several organizations located in different places, but related to his claim, he has the right to choose which district court to appeal to. This is often used by those who are inconvenient to go on long trips to resolve their affairs.
Attention! The Civil Code provides for the opportunity to submit an application at the place of work. In this case, the jurisdiction of the labor dispute changes - if desired, the employee can file a claim using the address of the enterprise where he worked.
Innovations in 2021: features of case consideration
At the end of November 2021, the President of the Russian Federation signed Federal Law No. 451-FZ. The document makes adjustments to the existing legal regulations, including the Civil Procedure Code of Russia (Article 10 of Federal Law No. 451). Chapter 3 has been amended, but the amendments have not yet entered into force. This event is associated with the work of new cassation and appeal courts. The latter are provided for in Art. 21 of the previously mentioned law. The courts will review previously made decisions on labor disputes related to state secrets.
It is worth noting that the adopted federal law does not in any way affect the provisions of Articles 23-27 and, thus, does not change the jurisdiction of the cases under consideration. Thus, there were no adjustments to legislation aimed at resolving labor conflicts between employers and employees considered by courts of general jurisdiction.
After the amendments come into force, the procedure for citizens’ applications will change. Now the plaintiff will have to submit documentation at the legal address of the organization, and not at its location. Similar adjustments have been made to the articles on alternative and exclusive jurisdiction and on the connection of cases.
Article 33 of the Code of Civil Procedure, which regulates the transfer of a claim to another instance, will change taking into account the following additions:
- The current rules require the consideration of disputes by authorized bodies up to the adoption of appropriate decisions when factors appear that change the jurisdiction of the case. The latest adjustments will lead to the fact that the court will be obliged to transfer documents according to jurisdiction (the Supreme Court of the constituent entities and the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation);
- clarification when challenging judges. Cassation bodies of general jurisdiction redirect cases to other authorities. In case of withdrawal from new vessels, the transfer of documentation is handled by the RF Armed Forces.
In addition to the above innovations, the Code of Civil Procedure is supplemented by Art. 33.1. According to this article, a conflict with petitions in various branches of law (civil, administrative), if it is impossible to separate them, is considered in one proceeding. The authority carries out activities according to the rules of civil proceedings. If the plaintiff violated jurisdiction when submitting papers for consideration, then the application may be returned in that part that is not within the jurisdiction of the authority.
Time limits for consideration of labor disputes
In case of illegal dismissal or premature termination of an employment contract, the limitation period is 1 month - this is provided for in Art. 392 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If an employer fails to pay wages, the employee has one year to file a claim.
If an employee does not go to court on time, he still retains the right to defense, but judges must recognize the reasons for missing deadlines as valid. In Art. 154 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation also specifies the following restrictions for filing an application:
- restoration of the workplace – 30 days;
- other labor disputes – 2 months.
If difficulties arise during the consideration of the case, the deadline may be extended by a court decision.
General provisions on the jurisdiction of labor conflicts
Basic provisions on the jurisdiction and jurisdiction of labor disputes are established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, based on the meaning of Art.
382 and 398 of which jurisdiction depends on what type it is - collective or individual. The first are resolved not by state bodies, but by a specially organized conciliation commission. It is also formed from representatives of the employer and employees hired by him on an equal basis (Article 402 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the dispute is not resolved by the commission, the case is transferred to an independent specialist, whose candidacy is approved by both parties - a mediator and (or) labor arbitration (Articles 403–404 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). More details about collective labor disputes are described here. Conflicts between a specific worker and his employer, according to Art. 382 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, are subject to the jurisdiction of courts and labor dispute commissions. However, a number of cases, for example disputes about discrimination against workers, fall under the exclusive jurisdiction of the courts.
However, these are only general provisions on jurisdiction. In practice, it depends on several other factors.
What to do if the defendant’s place of residence is unknown
Territorial jurisdiction is determined by the location of the defendant. If the defendant is an individual, jurisdiction is determined by his place of residence. According to Article 20 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the place of residence is considered to be the place where the citizen permanently or most often lives, where the citizen is registered and lives as an owner, tenant, on other grounds provided by law. If the defendant’s place of residence is unknown, or such a place does not exist on the territory of the Russian Federation, the statement of claim is filed at the location of the property or at the last known place of residence of the defendant. When filing a claim, the plaintiff must indicate the defendant's place of residence.
If it is unknown, the court initiates a search for the defendant in case of consideration of cases on:
- protecting the interests of public entities;
- collection of alimony;
- compensation for harm resulting from injury;
- death of the breadwinner.
In all other cases, the search is carried out by law enforcement agencies.
Which court should you file a claim in labor disputes?
By virtue of clause 1, part 1, art. 22 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and Art. 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such disputes are subject to the jurisdiction of courts of general jurisdiction.
As a general rule, a claim is filed at the location of the organization, which, by virtue of Part 2 of Art. 54 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is determined by the place of its state registration on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Based on these legal norms, a statement of claim in a labor dispute, namely the employee’s claim, as a general rule, must be filed with the district (city) court at the place of the employer’s legal address.
One of the exceptions is the situation when the employee who intends to go to court works or worked not in the parent organization, but in its branch or representative office. In this case, the employee can file a claim with the court at the location of the branch or representative office (Clause 2 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Also, for the restoration of labor rights, the plaintiff can apply to the court at his place of residence. This opportunity is provided by clause 6.3 of Art. 29 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
In addition, a claim arising from an employment contract, which specifies the place of its execution, can be filed with the court at the place of execution of the contract (Clause 9, Article 29 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation). A similar situation may arise when the contract specifies a specific place for the employee to perform his duties.
Part 10 art. 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation gives the plaintiff the right to choose between several courts, which, according to this article, have jurisdiction over the case.
An exception to all these rules is contractual jurisdiction, that is, determined by the parties at the conclusion of the contract. This means that the parties, when concluding it, agreed that the disputes that arose would be resolved in a certain court, for example, in the Voskresensky City Court. In this case, the labor claim is filed in the court specified in the contract.
However, the condition of contractual jurisdiction included in the contract has its own characteristics and is not always legal. In what cases, you will find out from one of the following articles in the labor section of the blog.
Based on all of the above, it becomes clear that before going to court for a labor dispute, you should study your contract with the employer for jurisdiction.
Is it permissible to go to court at the location of the employer?
In accordance with the general procedure, the jurisdiction of a particular dispute should always be determined by the person who decided to apply to a judicial institution. In most cases, the claim is brought at the immediate place of residence of the defendant.
He competently draws up a statement of claim, attaches pre-prepared documentary evidence to it and applies to the court. Next, after accepting all incoming papers, the court makes a decision to set a date for the first consideration of the labor conflict.
But, if a citizen makes a claim specifically against an organization, he, as a rule, has questions about the correct determination of jurisdiction. In this case, the standard rule is used, namely, going to court at the immediate location of the organization in which the employee works. The company's address must be indicated accurately in the claim, without any errors or omissions.
In addition, the provisions of Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation establish that, if there is such a desire, the parties to a professional relationship have the right to independently determine the jurisdiction of the conflict that has arisen between them. For this purpose, for example, the previously established territorial jurisdiction of the dispute may be deliberately changed. In order for all the necessary changes to be made officially, the parties to the employment relationship should enter into an appropriate agreement between themselves. This document sets out all the important provisions of the future procedure for resolving professional conflicts. Once drafted, the completed agreement must be signed by both parties to the employment relationship.
The current legislative norms also determined a list of special types of labor disputes, the jurisdiction of which is determined by the place of residence of the plaintiff. In most cases, such disputes will be special conflicts, the subject of which is directly related to various monetary issues. In addition, this category also includes disputes regarding the restoration of certain labor rights of an employee that were violated by the employer. In the event of such conflicts, the plaintiff will be able to apply to the judicial institution at the place of his own registration or based on his current place of residence.
Tribal and territorial jurisdiction for a claim for reinstatement at work
Therefore, the problem arises of delimiting the jurisdiction of cases between district courts and magistrates in cases where the plaintiff combines in one application both a demand for reinstatement and another related claim within the jurisdiction of the magistrate.
At the same time, the plaintiff may choose the place for consideration of his request for reinstatement at work, provided that he was dismissed from a branch (representative office) of the organization with which the employment contract was concluded.
What does the Civil Code say?
The Code of Civil Relations regulates the procedure for resolving labor disputes. Firstly, they must be based on a conflict between the staff and the employer. Secondly, they must have a legal basis. Thus, if two factors are met, in accordance with the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the district court will consider the dispute. The only exceptions are those cases that are separately identified by decisions of the magistrate's court.
Class action lawsuits
Collective disputes (Article 22 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation) can and should be considered in a court of general jurisdiction. This is due to the fact that the article does not clearly indicate which court - district or magistrate - has jurisdiction over this issue. However, Art. 23 clearly states that the magistrate’s court cannot hear cases involving collective disputes. In addition, the Civil Procedure Code also stipulates that such disputes are considered exclusively within the framework of lawsuit proceedings.
However, the court may reject the claim and not consider the case if:
- the procedure for filing a claim established at the federal level was not followed
- no attempts at pre-trial settlement of the dispute
Regarding independent settlement, it is worth noting: it is mandatory only because the trial will actually do the same thing, but it will be imperative. As for other cases, the court accepts the case for consideration.
Thus, if you determine in time the procedure and jurisdiction of a particular dispute, you can save time on consultations and the process as such. However, constant changes in legislation cannot force one to always act according to one scenario, which implies the use of laws solely in accordance with their content.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Where to write depending on the situation
In addition to the rules for contacting judicial authorities upon fact:
- registration of the defendant;
- the plaintiff's residence;
- location of subsidiaries;
There is also situational jurisdiction. This means that the choice of court occurs according to their authority. After all, some materials cannot be considered by the magistrate court, but only by the district court and vice versa. As a rule, at least a district or magistrate court is located in a certain territory to resolve conflict situations. At the same time, the difference compared to territorial distribution is that the plaintiff is deprived of freedom of choice. (that is, if his situation requires the case to be heard in the district court, that is where he should go).
In the case of disputes between an employer and an employee, the magistrate can only issue an order regarding non-payment of already accrued funds:
- if the salary is accrued but not issued to the employee;
- if vacation pay is accrued but not given to the employee;
- if the dismissal payment is accrued but not issued to the employee;
- if compensation for the delay of money from the employer is accrued but not paid;
- any other funds have been accrued to employees but not paid.
For all other issues regarding labor disputes (some of them were noted above in the text), you can only contact district judicial authorities (or city ones, depending on the territorial structure of the settlement). In cities of federal significance (Moscow, Sevastopol and St. Petersburg), the jurisdiction of the courts only includes verification of already adopted court decisions.