Home / Labor Law / Payment and benefits / Sick pay
Back
Published: 05/12/2016
Reading time: 10 min
0
4262
Working ability is understood as a set of various signs and characteristics of a person with the help of which he can perform certain types of work. Depending on the nature of work activity, the set of these characteristics may differ for different professions.
In case of partial or complete loss of ability to work, the employee may be entitled to certain payments and compensation . It is worth considering what types of temporary disability are distinguished and what benefits an employee can count on.
- Main types of disability Possibility of further restoration of health status
- Degree of ability to work
- By type of work activity
- Disease
What is disability
The law does not define the concept of disability, but establishes the amount of benefits and the procedure for other payments if people are temporarily or permanently disabled.
There are two forms of this concept:
- Temporary – it is characterized by the loss of work skills, which are restored over time.
- Permanent – loss of labor functions indefinitely.
Degree of conservation:
- partially: the concept assumes that a person works, but he can only perform certain functions;
- completely: a person is limited in his capabilities, he cannot perform work duties, regardless of the load.
By type of performance of labor duties, incapacity for work is divided:
- professional: means that a person cannot work only in a specific area, which, according to the conditions of work, is contraindicated for him (performing work duties in a hot shop);
- general: a person cannot perform any labor functions, which is associated with an unsatisfactory state of health, a threat to the lives of people around him, for example, in the presence of a disease of viral etiology.
Most often, employers are faced with such a form as temporary disability due to a specific disease.
Care payments
Citizens who care for a disabled person are entitled to financial support in the form of a monthly allowance. Compensation payment for caring for a disabled person is made to the following citizens: an able-bodied person who does not have a disability, has not retired, is able to carry out work activities, a non-working citizen who is not officially employed in an organization, is not registered with the employment center and does not receive benefits for unemployment (that is, he must have no income).
Also, payments are due to citizens who have reached the age of 16 and live with the patient in the same locality. The Civil Code does not require living together in the same house. If several people are caring for a disabled person, a seriously ill person, or an elderly person, then the benefit will be paid to only one of them.
Please note: there may not be a family relationship between the patient and the person caring for him.
In 2021, the compensation amount is 1200 rubles. monthly. Cash payments are not made to the caregiver, but along with the patient’s pension. In addition, benefits are calculated in accordance with the regional coefficient.
Design principle
To apply for compensation, you should contact the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation with the following package of documents:
- application in two copies. The first is written on a form for people caring for them, the second for people with disabilities. If a person who needs the help of third parties is declared incompetent and cannot fill out an application on his own, then an authorized notary can do this for him. In this case, a power of attorney is attached to the applications;
- a certificate from the Pension Fund confirming that the caregiver does not receive payments;
- a certificate from the employment center confirming that the caring citizen does not receive unemployment benefits;
- a certificate from the tax office confirming that the caregiver does not have the status of an individual entrepreneur;
- if the caregiver is studying, then it is necessary to submit a certificate from the educational institution about the date of completion of studies;
- certificate of inspection report. A sample certificate is available at MSEC. Its duplicate can be made on the medical portal;
- passport, work books and copies of both persons.
Who can be denied payments?
The Pension Fund of the Russian Federation has the right to refuse to issue cash payments to a person who cares for a disabled, old or sick person for the following reasons. If the caregiver has an income. The Pension Fund evaluates the data provided with the application for compensation. If you have paid work, benefits will be denied.
If the person who plans to provide care is himself a citizen who cannot work. That is, he himself has a disability or cannot, by decision of the medical commission, provide care. If the patient for whom care was planned loses his disability status within a few days.
Causes of disability
There are many situations in which loss of labor skills occurs. These include:
- an illness that led to persistent impairment of health, but this did not arise as a result of the negative influence of working conditions;
- an illness that was discovered as a result of performing professional duties (for example, harmful working conditions);
- injury sustained at home, but not at work;
- injury resulting in serious health problems: an emergency occurred at work.
The main labor guarantee that a citizen has the right to count on is the receipt of benefits.
Main disease
A common reason for filing a disability. It occurs due to a disease that has overtaken a person. He loses his skills, and this makes it impossible for an employee of the enterprise to perform his job duties.
Depending on the situation, the disease can give rise to different consequences for a person. For example, bring him permanent or temporary disability.
Occupational disease
The definition of the concept is given in N125, in article 3. This is an ailment that is caused by the influence of production factors on an employee that are harmful to his health. As a result of the disease, the person's health deteriorated. He acquired the status of being unable to work, and not of a temporary, but of a permanent nature.
There are two types of occupational diseases:
- chronic – caused by prolonged exposure to negative factors at work;
- acute – the effect of negative factors on the employee’s condition is rapid, with pronounced consequences.
Domestic injury
The injury was not sustained at work, but at home. Depending on certain conditions, a certificate of incapacity for work issued as a result of an injury is paid.
Work injury
If the injury occurs on the employer’s premises, as well as while traveling to or from the place of work, the employer pays not only sick leave, but also compensates the employee for the inconvenience associated with the injury.
Child
Parents (mother or father) have the right to take sick leave for the child. This is necessary to provide care for the minor.
Prosthetics
The algorithm for medical measures and the issuance of sick leave are established in N255 of the Federal Law, Art. 6. A person who needs a service takes a referral from the specialist treating him. The prosthesis is selected individually and installed.
Adoption
According to Article 257 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a woman who has adopted a baby has the right to leave under the BIR.
Payment and delivery of pensions
The legislation provides for the right of a pensioner to choose the organization that delivers the pension. You can receive it in 3 ways:
- At home (the organization chosen by the person brings funds to the pensioner’s place of residence);
- At the organization's cash desk;
- To a bank account.
At the request of the person, the pension can be received by the principal. If the power of attorney is issued for more than a year, then the authorized person has the right to receive payments during the entire period of its validity. At the same time, the trustee must confirm his registration at the place of receipt of the pension every year.
In practice, most often the delivery of pensions to your home is carried out by the post office at the place of registration of the person. You can also receive payment at the post office itself by applying in person. If it is impossible to apply in person, the pension can be issued by proxy.
Important! If a person is undergoing treatment in a medical institution, the power of attorney is certified by the head of the department.
The next common method of receipt is through a bank. Payment can be received at the cash desk or on a card. The pension is credited to the account on the day it is received from the branch at the place of residence of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. The Commercial Bank does not charge any commission for this service.
The territorial body of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation contains information about organizations that have the right to deliver pensions to your home or issue them at the cash desk.
Procedure for assigning payments
In order to receive payments to disabled citizens, the following documents must be provided:
- An application from a disabled person giving consent to care for him. If a person is declared incompetent, then the application is submitted by a legal representative. The document must be accompanied by a document confirming guardianship.
- Statement from the person who will be caring for or is caring for.
- A certificate confirming that the pension has not been assigned. She is taken to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation at her place of stay.
- A certificate confirming that no unemployment benefits are being received.
- Extract from the certificate of examination of a disabled citizen.
- A conclusion that confirms that a person needs constant care.
- Passport.
- Work record book of the caregiver.
- Certificate of full-time training of the person providing care.
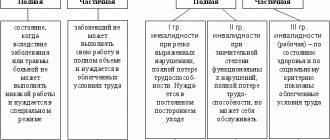
Types of disability
There is no concept of temporary disability in the legislation of the Russian Federation. The law establishes the types and forms of payment for sick leave, as well as benefits for specific categories, depending on the type of disability.
Kinds:
| TEMPORARY | PERSISTENT | ||
| partial | full | partial | full |
| full work activity cannot be carried out: a person requires a lighter version of work | The patient cannot perform any work; special care is required | 3 group | disability: 1st and 2nd group |
Disability groups are assigned depending on the degree of loss of ability to work, as well as to care for oneself independently. There are 3 groups:
- First: the ability to maintain oneself in proper condition is completely lost. A person depends on the help of family and friends. Unable to move independently. In some cases, disorientation in time and space may be noted. A person sometimes does not communicate with people, and also cannot control himself.
- Second: a person partially needs care, since the ability to self-care has not been completely lost. He can move, but with special devices. The ability to carry out professional activities has been lost, although certain types of work are available to a group 2 disabled person. He can look for a job and get one if his health condition allows it. If we are talking about a child, then with group 2 he may lose the ability to learn, or he may do it according to an individual program. Orientation in space and time can be carried out both independently and with the help of strangers.
- The third group differs from the previous ones in that it is a working group. A person orients himself in space, can move independently and communicate with other people. The ability to learn is preserved, but he needs a special regime and special help from teachers. People with this disability group cannot work in difficult and harmful working conditions, however, they perform a certain amount. In some cases, a person cannot quickly analyze the information received, since this requires a little more time compared to a healthy person.
Permanent disability
Permanent disability is characterized by a disorder of body functions. As a result of the disease, a person cannot completely recover from it. This circumstance is equivalent to the term disability, which is established by N181-FZ of 1995.
The causes of loss of health on a regular basis are:
- pathologies of a chronic nature;
- congenital anomalies;
- diseases transmitted by inheritance;
- consequences of injuries and injuries;
- poisonings that occurred at work.
Doctors, if there is an unfavorable prognosis for a person in relation to his professional activity, give a referral from a medical institution. A person goes to a clinic at his place of residence. He is sent to the ITU to receive the results of an examination based on the examination of his health.
After passing the commission, a person is assigned a disability. There are three groups: the first two are non-working, and in the third group a person can work. The extreme severity of the disease means that the citizen is unable to perform simple work. The first two groups are prohibited from working, but in some cases, depending on the state of a person’s health, a disabled person can apply for a job.
Temporary disability
Loss of performance occurs temporarily as a result of illness or injury. A person is temporarily disabled due to illness: as a result of medical manipulations, a person’s illness is reversible. The patient is given a sick leave certificate.
A sick leave certificate is a document intended to establish the following facts:
- official confirmation that an employee of the enterprise was absent from the workplace for valid reasons;
- payment of benefits;
- analysis of the reasons for the inability to work temporarily.
Who belongs to the category
Many people are interested in the question of who is considered disabled. In Russian legislation, this group is divided into the following criteria: minor children, pensioners who receive cash payments and do not work, disabled people, people who are dependent and have lost guardians. The disabled population is unable to work due to age or health conditions.
Inability to engage in work is defined in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is assigned:
- minors under 16 years of age. After which the teenager has the right to carry out work activities;
- students who study at a public institution under 18 years of age;
- students who receive higher education full-time until the age of 23;
- disabled people of the first and second groups. The third group usually does not provide such benefits;
- pensioners who are not working.
Periods of temporary incapacity for work
Periods of incapacity for work in tabular form:
| Medical | Term | Social | Duration (max/min) |
| intestinal infections | from 8 to 15 days, but not more than 30 | sick leave | for categories of diseases up to 15 days, after 4 months the decision is made by a special commission and the person is assigned disability |
| whooping cough, scarlet fever, erysipelas, pneumonia | from 10 to 40 days | sick leave | |
| viral diseases | from 8 to 30 days | sick leave | |
| worm infection | from 4 to 28 days | sick leave | |
| viral infection | from 9 to 30 days | sick leave | |
| respiratory system diseases | from 9 to 30 days | ||
| diseases of the nervous system | from 3 to 120 days | ||
| mental disorders | from 10 to 120 days | ||
| gland diseases | from 6 to 120 days | ||
| cancer | from 30 to 120 days |
The duration of temporary disability is limited. If a person goes beyond the temporary limits of sick leave, the issue of disability is resolved.
Comments on Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, judicial practice of application
In paragraph 31 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2012 No. 9 “On judicial practice in inheritance cases,” the following explanations are given.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Divorced or divorced: how to write correctly on a resume and other documents
When determining inheritance rights in accordance with Articles 1148 and 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to keep in mind the following:
Who is considered disabled?
Disabled people in these cases include:
- minors (clause 1 of Article 21 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- citizens who have reached the age that gives them the right to establish an old-age labor pension (clause 1 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 N 173-FZ “On Labor Pensions in the Russian Federation”), regardless of the assignment of an old-age pension to them. Persons who retain the right to early assignment of an old-age labor pension (Articles 27 and 28 of the said Federal Law) are not classified as disabled;
- citizens recognized in accordance with the established procedure as disabled people of groups I, II or III (regardless of the assignment of a disability pension to them);
Disability is determined as of the date of opening of the inheritance
The circumstances associated with a citizen’s incapacity for work are determined on the day the inheritance is opened. A citizen is considered disabled in cases where:
- the day of his coming of age coincides with the day of opening of the inheritance or is determined by a later calendar date;
- the day of his birth, which is associated with reaching the age that gives the right to establish an old-age labor pension, is determined by a date earlier than the day of opening of the inheritance;
- his disability was established from the date coinciding with the day of opening of the inheritance or preceding this day, indefinitely or for a period until the date coinciding with the day of opening of the inheritance, or until a later date (clauses 12 and 13 of the Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2006 N 95 “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled”);
A dependent of the testator is a person supported by him and not necessarily a relative
A person who received from the deceased for a period of at least a year before his death - regardless of family relations - full maintenance or such systematic assistance that was for him a constant and main source of livelihood, regardless of whether he received own earnings, pensions, scholarships and other payments. When assessing the evidence presented in support of being a dependent, the ratio of the assistance provided by the testator and other income of the disabled person should be assessed.
A disabled citizen - a recipient of annuity under a lifelong maintenance agreement with a dependent, concluded with the testator - the annuity payer (Article 601 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), does not inherit by law as a dependent of the testator;
A disabled and dependent grandson of the testator inherits regardless of whether he or she lives together with the testator.
Disabled dependents of the testator from among the persons specified in paragraph 2 of Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, inheriting by right of representation, who are not called to inherit as part of the corresponding queue (grandchildren of the testator and their descendants during the lifetime of their parents - heirs according to the law of the first priority), inherit on based on paragraph 1 of Article 6 and paragraph 1 of Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, that is, regardless of cohabitation with the testator.
Living together with the testator for at least a year before his death is a condition for calling to inherit only the disabled dependents of the testator, named in paragraph 2 of Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (from among the citizens who are not included in the circle of heirs specified in Articles 1142 - 1145 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
When disabled dependents are heirs of the eighth stage
Independent inheritance by disabled dependents of the testator as heirs of the eighth order is carried out, in addition to cases where there are no other heirs by law, also in cases where none of the heirs of previous orders has the right to inherit, or all of them are excluded from inheritance (Article 1117 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), or are deprived inheritance (clause 1 of Article 1119 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), either none of them accepted the inheritance, or all of them refused the inheritance.
Example of a statement of claim
Statement of claim for recognition of property rights by inheritance (at the time of the death of the testator, the plaintiff was disabled due to old age and was his dependent, which, according to Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in the absence of other heirs, by law gives the right to the disabled dependent of the testator to inherit independently as an heir of the eighth stage ).
Legislative acts protecting the rights of disabled citizens
The legislator has issued regulations that protect public health:
| NPA | Article |
| Constitution of the Russian Federation | 41: every citizen in the Russian Federation has the right to count on health protection, as well as the provision of medical care. 39: every citizen in the Russian Federation is guaranteed social security in case he loses his health |
| Code of Administrative Offenses | Art. 8.5 establishes liability for concealing information about the state of the environment, which may adversely affect public health |
| Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the protection of the health of citizens N323 Federal Law of 2013 | Art. 2 defines the basic principles related to the protection of the health of citizens Art. 24 - establishing the procedure for medical intervention |
| Criminal Code of the Russian Federation | Establishes liability for attempts on the life and health of citizens |
| N 52-FZ of 1999 | |
| N 326-FZ of 2010 | |
| N 61-FZ of 2010 | |
| N 99-FZ of 2010 |
Payment amount
The state provides 2 types of pensions for pensioners: insurance (labor) and social.
A mandatory condition for insurance is more than 5 years of experience. The social pension is intended for persons whose work experience is less than 5 years.
It is worth noting that in cases where the amount of the accrued pension is less than the established minimum subsistence level provided for in the region of residence, the pensioner has the right to a federal or social supplement, which eliminates this difference.
Factors that determine the amount of payments:
- Insurance experience. This is the sum of all work periods. A mandatory condition is the deduction of contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation throughout the working life.
- Individual pension coefficient. It is calculated based on contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the duration of work.
- The type of pension provision chosen by the citizen in the Compulsory Pension Insurance system.
- Coefficients provided by the state.
In the event of the loss of one breadwinner, a monthly fixed payment is provided, which currently amounts to 2279 rubles 47 kopecks, and 4558 rubles 94 kopecks in the event of the loss of both parents for each child.
Inheritance by disabled dependents of the testator. eighth stage
The legislator divides the dependents defined in this article into 2 categories. For your information, the first category includes dependents who are part of the second and all subsequent lines of inheritance by law, but are not called upon to inherit, due to compliance with the principle of priority (clause.
The second category includes dependents who are not heirs by law, but are fully supported by the testator and live with him for a year until the day of his death (clause 2 of Article 1148 of the Civil Code). If the above persons can be simultaneously called to inherit in order of priority and on the basis of dependency, then they receive the inheritance as representatives of the corresponding order or by right of representation.