Home / Labor Law / Labor Code
Back
Published: 07/18/2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
1229
Working time is one of the most important working conditions and its unique measure, which is used in slightly different meanings in different branches of science. As for the sphere of labor, the definition of working time and its possible duration are enshrined at the legislative level, namely in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
with the requirements of current labor legislation is an important constitutional guarantee of every employee. Therefore, it is worth considering this concept in more detail, as well as its available types and forms.
- Legislative regulation and concept
- Main types Normal duration
- Shortened working hours
- Part-time work
Classification of types of working time according to Labor Code
Working time should be understood as periods of working activity:
- with a standard duration of 8 hours;
- within the framework of reduced working hours;
- not completing the full scope of work;
- overtime work performed outside the standard;
- irregular working hours established by local regulations of the organization.
The Labor Code also includes other periods in the concept of working time, for example:
- breaks for rest and meals (lunch), when the employee cannot leave the place of work (in accordance with Article 108 of the Labor Code);
- breaks provided for in Article 109 of the Labor Code, which must be provided under certain conditions (working in the cold season in the open air or in unheated rooms) for rest and heating;
- time of separation from work for a woman breastfeeding.
Let us note that the employer is obliged to pay for the working time of each employee, including all overtime hours in excess of the normal shift duration and shortcomings caused by the employer.
Night work
If an employee’s shift occurs at night, the employer must reduce it by one hour without the need to work off. According to the law, today night time is considered to be the time period from 22:00 to 6:00. Hours worked during this period must be paid at an increased rate.
However, in cases where a reduced length of time is introduced for an employee, a reduction in the night shift is not provided. A similar rule also applies to employees for whom there are no other working hours.
The length of the working day at night can also be compared with the duration of the working day during the day; it is also allowed for shift work and in case of production necessity.
However, it is worth noting that night work is not permitted for all groups of people. In particular, the following are not allowed:
- Pregnant women.
- Persons with disabilities.
- A person under 18 years of age (with the exception of cases when a minor is involved in working on a work of art).
In some cases, the following may be involved in night work:
- Women raising three or more children.
- Employees raising children under five years of age on their own, without the help of a spouse.
- Guardians of children under five years of age.
- Employees caring for a sick family member (moreover, the latter’s health status must be officially confirmed by a medical certificate).
However, in these cases, consent to work at night must be in writing. The employee has the right to be notified of the specifics of the work and can terminate the contract if the need arises.
Features of the work schedule at night in cases when it comes to concerts, theater organizations, and the media are negotiated separately in accordance with regulatory agreements, commissions for regulating business relations, as well as collective agreements.
Standard working hours 2020
Labor legislation establishes a standard working time, which represents the number of hours in a certain calendar period of time spent on work under an employment contract. This norm is determined based on the following parameters:
- sufficient to prevent people from becoming overworked;
- promotes employee health protection, improved performance and productivity;
- allows you to improve your skills without leaving work.
The legislation limits the duration of working hours per week to the following figures:
| Category of workers | Maximum length of the working week in hours |
| The bulk of workers, excluding the categories below | 40 |
| Partners under an employment contract | 20 |
| Students working during holidays aged: | |
| up to 15 years old from 15 to 16 years old from 16 to 18 years old | 24 24 35 |
| Students working during the academic year aged: | |
| from 14 to 16 years old from 16 to 18 years old | 12 17,5 |
| Disabled people of groups 1 and 2 | 35 |
| Workers working in harmful and dangerous production | 36 |
| Medical workers | 24-36 (depending on the category in accordance with Decree No. 101 dated 02/14/2003) |
| Teaching staff | 36 or lower depending on the categories determined by Order of the Ministry of Education and Science dated December 24, 2010 No. 2075 |
| Women working in the Far North and equivalent areas | 36 |
| Women working in rural areas | 36 |
Thus, the working week may have strictly established working days and days off, or a shift schedule with days off. An increase in the standard working hours is not allowed.
Working outside normal working hours
Normal working hours (40-hour work week) should generally not be exceeded. However, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal laws may establish exceptions to this rule when an employee, at the initiative of the employer, can perform work outside the normal working hours. In Art. 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for two such cases: overtime work and work on irregular working hours.
Overtime work is determined by Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as work performed by an employee on the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period.
Involvement in overtime work is carried out by the employer only with the written consent of the employee in cases expressly provided for in Part 2 of Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as, for example, if a replacement employee fails to appear, if the work does not allow a break). Part 3 Art. 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for cases of involving an employee in overtime work without his consent (for example, when performing work necessary to prevent a disaster, industrial accident or eliminating their consequences; when performing socially necessary work to eliminate unforeseen circumstances that disrupt the normal functioning of centralized hot water supply systems, cold water supply and (or) water disposal, gas supply systems, heat supply, lighting, transport, communications and in other cases).
In other cases, involvement in overtime work is permitted with the written consent of the employee and taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
It is not allowed to involve pregnant women and workers under the age of 18 in overtime work, and the involvement of disabled people and women with children under three years of age is permitted with their written consent under the following conditions: firstly, such work is not prohibited to them due to their condition health in accordance with a medical report and, secondly, they are aware of their right to refuse overtime work.
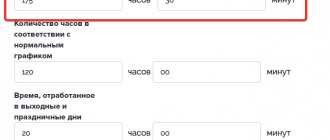
Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a maximum number of hours of overtime work for each employee: no more than four hours for two days in a row and 120 hours per year.
Work beyond the established working hours cannot be overtime if it is performed by an employee with irregular working hours.
Overtime work must be properly documented (by order or instruction of the employer and the written consent of the employee in cases established by law) and taken into account by the employer. The amount and forms of compensation for overtime are established by Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: overtime work is paid for the first two hours of work at least one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at least double the rate. Specific amounts of payment for overtime work may be determined by a collective agreement, local regulations or an employment contract. At the request of the employee, overtime work, instead of increased pay, can be compensated by providing additional rest time, but not less than the time worked overtime.
Irregular working hours are a special work regime, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the established working hours (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Irregular working hours are usually established for workers whose work cannot be accurately recorded in time. In accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 11, 2002 N 884 “On approval of the Rules for the provision of annual additional paid leave to employees with irregular working hours in federal government institutions”, the list of positions of employees with irregular working hours includes management, technical and business personnel and others workers whose work during the working day cannot be accurately recorded; who distribute working time at their own discretion; whose working time, due to the nature of the work, is divided into parts of indefinite duration.
Overtime work and work on irregular working hours have significant differences.
Working hours
The work schedule (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is established by the regulations of the organization as a whole for all employees. An individual approach may be taken for individual employees.
The general concept of a work regime implies a reasonable combination of periods of work and rest within a calendar period. This:
- 5 working days and 2 days off per week;
- 6 working days and 1 day off per week;
- special work modes (with part-time work, irregular working hours, flexible hours, dividing work time into parts);
- Shift work on a rotating schedule.
Parameters that determine working hours:
- duration of work per week (in hours);
- time period allotted for a day or shift;
- daily work start and finish schedule;
- establishing periods allotted for rest and eating;
- other parameters depending on the specifics of the organization.
Normal operation
The normal work schedule (in practice considered a single shift) is established taking into account working hours and can be daily, weekly or cumulative.
Any work performed in excess of the daily work schedule is overtime work (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When recording working hours in aggregate, a total of a longer period of work is assumed, in particular, for a month, quarter or year. The main task of the summarized recording of working time is the correspondence of the working day norm to the duration of working time for the entire accounting period. This method of setting working hours is usually used when organizing work on a rotational basis, transport, communication services and others. Note that the summarized recording of working hours does not provide for restrictions on the duration of the work shift, but as a rule, it is 8-12 hours.
Rules for irregular work
The Labor Code in Article 101 defines an irregular working day as a special regime established for individual employees when the employer has the right to involve them in work functions outside the normal working hours. However, such processing should be episodic.
The nature of work involving irregular working hours is necessarily fixed by the employer’s regulations, collective and labor agreements. The employer has the right to engage an employee to work outside the established working hours only to perform the functions established by the employment contract.
If an employee is hired to work with an established schedule on a part-time basis, then non-standardization cannot be applied to him.
As compensation, citizens who have irregular working hours are provided with additional paid leave every year. Overtime hours are not taken into account and are not paid for. However, the employer does not have the right to demand that work be carried out on days that are scheduled days off for the employee.
Essential Basics
Working time is the period during which an employee, according to the employment contract, performs his duties and obeys internal regulations.
Whether an employee receives the right to rest depends on correctly chosen and established working hours.
Within the framework of the topic “Working time” it is important to know the following concepts:
| Work week | This is the legally established distribution of working hours during the calendar week (from Monday to Sunday inclusive) |
| Labor day | This is the period within one calendar day when the employee is at the workplace and performs his duties. |
| Work shift | This is working time that is used during the day, taking into account the standards established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as according to the work schedule |
| Schedule | This is the calendar time schedule at which the employee will perform his work |
| Production calendar | This is a special calendar compiled by the government of the Russian Federation, which displays all working days and weekends assigned for a given period (calendar year), taking into account public holidays |
What you need to know
The employer or his authorized person must distribute and record working time. The distribution of working hours is carried out on the basis of a “mode”.
According to Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the working regime is the distribution of time norms within the work week.
The length of the work week can be 5 or 6 days. This may include shift work or daily work. It can also consist of all three types of time, which will be discussed below.
Everything related to the work week and time distribution must be specified in the collective agreement concluded between the employer and employees.
When concluding a contract with a new employee, it is important that he is familiar with the internal regulations, which are drawn up on the basis of the distribution of working hours.
If an individual regime is determined for an employee, this information must be specified in the employment contract.
Another measurement value in the mode is “working day”. Its accounting has several types:
| Daily | This is a recording of working hours with daily exits during the work week and 1-2 days off |
| Summarized time tracking | This is an accounting of working time for the period as a whole with its uneven distribution across shifts |
| Flexible accounting | This is accounting in which individual employees of an organization have the right to independently determine the period and time of their work tasks. |
| Irregular day schedule | Accounting in which the number of working hours per week exceeds the norm established by law (40 hours) |
| Divided working time | — |
| Multi-shift | Accounting for working hours when the company has several shifts of employees, each of which starts in its own time period |
Working hours can be set for each employee separately or for the organization as a whole.
Scheduling
Drawing up a working time schedule is an important and responsible process in an enterprise.
It allows you to solve a number of issues and tasks, the main of which is the distribution and recording of working time, as well as the determination and implementation of assigned tasks by the employee.
There is an approved form for filling out a monthly working time schedule. You can see an example of it below.
After drawing up the schedule, each employee should become familiar with it. After this, it is posted in a certain place where it will be available for employees to clarify the information.
All employees included in the staff must be entered in the table. As a rule, working time should be distributed evenly between them, except in cases where an individual schedule is determined for the employee.
It should display all working days and weekends. It should be compiled in such a way that all members of the work team can easily understand the symbols.
There are several methods for drawing up a work schedule, depending on the internal routine of the enterprise:
| Linear | It is used if the load is distributed evenly between employees, it can be completed in 8 hours of working time. In this case, all employees come to work at the same time |
| Belt (stepped) | They are used if the team needs to be divided into groups that will leave at different periods of working time |
| Final accounting | Opening hours |
| Two-brigade | In this case, the enterprise forms two teams with an equal number of people, they work alternately (every other day). Working time per shift is up to 12 hours |
| Combined | Used if the entire work team is divided into groups working according to their own schedule |
Essentially, a schedule is a working time plan. But to keep records of it, a document similar in form, but different in essence, is used - a time sheet.
It is also compiled in a table, contains information about employees and includes the entire list of staff. But it displays the actual working hours of employees.
It is the time sheet that is used to calculate wages and other financial transactions related to wages. Below is a sample of such a document.
Keeping a schedule and time sheet must be approached extremely responsibly. These documents must display truthful information.
It is important to maintain them throughout the reporting period. After this, they can be sent to the archive.
How sick leave is calculated in 2021, see the article: how sick leave is calculated. Can a pregnant woman be fired from her job while on maternity leave? Read here.
If the enterprise is visited by tax authorities, they can be checked, like all primary documentation. If any violations are detected, the person completing them will be held liable.
The presence and correct schedule may be of interest not only to the tax audit, but also to labor protection authorities.
They may be the basis for protecting the rights of the organization in the event of litigation regarding dismissal.
Normative base
The establishment of working hours is part of labor relations, which in turn are regulated by the laws of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, it is important to know the regulatory framework in order to act within the law. All labor relations are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Regarding working time, the following articles are used:
| Ch. 15 | Art. 91— |
| Ch. 16 | Art. 100-105 |
| Ch. 17 | Art. 106—107 |
| Ch. 18 | Art. 108—113 |
| Ch. 19 | Art. 114—128 |
But besides this, other regulations are also used:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Law of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 1992 N 2490-1 (as amended on June 29, 2004).
- Law of the Russian Federation on vacations.
- Federal Law of the Russian Government No. 197.
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia, dated January 5, 2004 No. 1.
When drawing up a working time schedule, an authorized person or employer must take into account all the norms prescribed in these acts.
Recording working hours according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2021
Employers, regardless of their organizational and legal form, are required to keep a timesheet of working time worked by each employee for a certain period of time (Article 91 of the Labor Code). Accounting means recording the duration of hours actually spent on the performance of labor functions, as well as periods of rest and other distractions.
For these purposes, responsible persons appointed by the head of the organization maintain time sheets. Only with proper and complete documentation is it possible to avoid claims and disputes from employees and regulatory structures.
The timesheet is the basis for calculating wages for each employee.
Legislative regulation and concept
Section IV of Part 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the issues of regulating the working time of employees.
In particular, according to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working time is the period during which an employee is obliged to perform his labor functions established for him by the internal local acts of the company and the employment contract.
Working time also includes some other periods defined by the Labor Code.
Russian Federation, federal laws and other legal acts. In particular, these may include periods of downtime, as well as various paid breaks for lunch and rest, which are one of the labor guarantees of employees.
In addition to the definition of working time, Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also provides its maximum permissible duration for one week, which is 40 hours. But for some categories of workers this duration is equal to less time. In addition, the same article places an obligation on the employer to keep records of the time worked by each employee.
Legal regulation of working hours has several goals, namely:
- its more productive use;
- protecting the health of the employee, maintaining his long-term ability to work and work activity;
- improving the level of professional training of the subordinate.
Therefore, the employer must comply with the statutory maximum hours and other important requirements regarding working hours. Otherwise he may be punished.
What is rest time according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
By rest time, labor legislation understands periods when an employee is released from work duties and has the right to use them at his own discretion. These are the following breaks:
- during the work shift (lunch, special: provided within the framework of the law to nursing women, workers in cold working conditions for heating, air traffic controllers);
- between shifts;
- weekend;
- holidays recognized as non-working days by labor legislation;
- vacations: annual paid and additional.
Irregular working hours
From the point of view of labor law, irregular working hours are recognized as time exceeding 8 hours.
Irregular time refers to the time when an employee is involved occasionally to carry out some important or urgent work.
For performing work in difficult conditions (on weekends, on holidays, at night, when combining positions), the employee is entitled to additional payments provided for in Article 149 of the Labor Code
, as well as legal acts drawn up at the enterprise (collective agreement, additional agreements, employment contract ).
Lunch rules
The employer is obliged to provide employees with breaks for meals and rest during the working day or shift. Its duration is not included in the calculation of working time.
The minimum and maximum thresholds for the time allotted for lunch are established by law:
- at least 30 minutes;
- no more than two hours.
The parameters for the start and end of the break, as well as its duration, are fixed in the internal labor regulations and are prescribed in the employment contract.
During the lunch break, the employee has the right to leave the workplace and use it at his own discretion. If the technological process and regulations of the organization do not allow the employee to leave the place of work, then the periods allotted to him for rest and lunch are subject to accounting as working hours.
Shortened working hours
Short-time working hours are working hours less than the usual eight hours, but are fully paid.
Shortened working hours are established for certain groups of workers.
This category includes:
- workers under 16 years of age – work no more than 24 hours a week;
- persons from 16 to 18 years old – a working week of no more than 35 hours;
- disabled people of group I or II – work no more than 35 hours;
- workers employed in hazardous industries and industries with hazardous working conditions.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 92)
, federal laws may establish reduced working hours for certain categories of workers (teaching, medical and others).
The duration of work of a particular employee is regulated by the provisions of the employment contract on the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, taking into account the results of an assessment of working conditions.
Payment for reduced working hours is calculated as for fully worked hours.
You may be interested in the mental map “How much should we work?”, which indicates what points should be spelled out in the employment contract regarding working hours
Or look HERE what else needs to be included in an employment contract
Part-time work according to the labor code
The Labor Code (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) allows employers to use part-time work when the working week is less than 40 hours. This regime may include:
- reducing the working day or shift by a certain number of hours daily;
- reduction of working days in a week when using the normal duration of a work shift;
- a combination of the above factors, when the number of working days per week and the duration of the shift are reduced by a certain number of hours.
In the case of part-time work, remuneration is made depending on the time actually worked or the amount of work completed. It should be noted that in this case the number of days of annual paid leave is not reduced. The calculation of total length of service does not depend on the use of a shortened working day, because the fact of working in this mode is not reflected in the work book.
The establishment of part-time work is carried out at the initiative of the employee; only in exceptional cases it is permissible to do this at the initiative of the employer, but in this case for no more than six months. Since the application of the regime is a significant change in the terms of the employment contract, the employee must be notified two months before the effective date when transferring to it.
An employee may appeal to the employer with a request to establish a part-time working day, citing circumstances. At the same time, Article 2 of the Labor Code states that it has no right to refuse if the applicant:
- pregnant woman;
- the mother of a child who is on leave to care for him;
- parent or guardian of a disabled minor child;
- provides care for a sick relative, confirming this fact with documents.
Innovations in labor legislation affected this article in terms of establishing a convenient work schedule for the above categories until the time when circumstances apply. For example, if a woman is caring for a disabled minor child, then when he reaches adulthood, the rule of unconditional provision of part-time work ceases. In the future, you can ask for it, but at the discretion of the employer.
Working time concept
The legal definition of the concept of “working time” is given in Art.
91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Working time is the time during which the employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to working time (for example, breaks for heating and rest provided to employees working in the cold season in the open air or in closed unheated rooms; breaks for feeding a child provided to women with children under 1.5 years of age; periods of downtime not through the fault of the employee , and etc.).
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year) depending on the established duration of working time per week is determined by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor (Ministry of Health and Social Affairs development of the Russian Federation).
The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week.
Types of working time
The classification of working time by type depends on:
- duration of working hours per calendar week;
- order of establishment;
- legal consequences of the use of certain types of working time.
These three types are the so-called “standard working hours”.
Depending on duration:
- normal working hours;
- reduced working hours;
- part-time work;
- work outside the established working hours (overtime - Article 99 of the Code; irregular working hours - Article 101 of the Code).
Normal working hours
Normal working hours are the standard working hours established by law, which must be observed by the parties to the employment contract (employee and employer), regardless of the form of ownership of the organization where the labor relationship is carried out. ILO Convention No. 47 on the reduction of working hours to 40 hours per week, art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes normal working hours of no more than 40 hours per week.
The legal consequence of establishing normal working hours for an employee:
- payment of his wages in full and not lower than the minimum wage established by federal law.
Legally significant circumstance determining the normal working hours:
- the number of hours worked per calendar week, which is confirmed by:
- documents establishing the employee’s working time at 40 hours per week;
- time recording data confirming working 40 hours per week.
Shortened working hours
Short-time working hours are less than normal working hours established by law, but with full pay.
In Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that reduced working hours are established:
- for workers under the age of sixteen - no more than 24 hours a week;
- for workers aged sixteen to eighteen years - no more than 35 hours per week;
- for employees who are disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 hours per week;
- for workers whose working conditions at their workplaces, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as hazardous working conditions of the 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions - no more than 36 hours per week.
Comment:
Federal Law No. 426-FZ of December 28, 2013 introduced the employer’s obligation to conduct a special assessment of working conditions, which replaced workplace certification. The purpose of carrying out an SOUT is to identify dangerous and harmful production factors that operate in the workplaces of enterprises and organizations. Based on the results, classes of working conditions at workplaces are established in accordance with regulatory documents.
SOUT is carried out by specialized organizations, for example, ANO USC "Harmony".
The length of working time for a particular employee is established by an employment contract on the basis of an industry (inter-industry) agreement and a collective agreement, taking into account the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
The length of working time of persons under the age of eighteen who are receiving general education or secondary vocational education and who combine education with work during the academic year cannot exceed half of the norms established by Part 1 of Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for persons of the appropriate age.
Federal legislation may establish reduced working hours for other categories of workers (teaching, medical and other workers).
Comment!
Norms Art. 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the duration of daily work, does not limit the effect of the provisions of Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which determines the total working hours per week. Norms for working hours and the duration of daily work are applied independently if there are grounds specified in the law.
Thus, under no circumstances can an employee between the ages of 16 and 18 be assigned a working time schedule, for example, “two in two” with an 8-hour working day.
Establishing a shorter working day for minors (as well as other categories of workers specified in the law) is not a right, but an obligation of the employer.
The establishment of shortened working hours at the expense of the employer’s own funds improves the position of the employee compared to the law. In this connection, on the basis of Art. 8, 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, local regulations may establish reduced working hours for other categories of workers that are not listed in federal legislation. But the costs associated with this reduction must be borne by the employer.
Legal consequences of establishing reduced working hours:
- retention by the employee of all benefits and advantages provided for by law, including the right to receive wages in full and not lower than the minimum wage established by federal law.
Thus, despite the reduction in the number of working hours per week, the reduced working hours do not limit the rights of workers, including the right to receive full wages. That is, working under reduced working hours in terms of the benefits provided does not differ from work with normal working hours; in fact, employees with reduced working hours are paid additionally for hours not worked to normal working hours. This additional payment is included in the wages of employees with reduced working hours.
Legally significant circumstances characterizing reduced working hours:
- establishment of working hours in accordance with current legislation of less than 40 hours per calendar week;
- compliance with the established duration of reduced working hours;
- preservation of benefits provided for by law for employees with reduced working hours, including the right to receive wages in the same amount as employees with normal working hours.
Part-time work
The term " part-time work " covers:
- part-time;
- part-time work week.
Part-time work, like short-time work, is set at less than 40 hours per week. As a general rule, the employer does not have the right to unilaterally introduce part-time work, for example, in the absence of work volume. The lack of consent of employees or their authorized representatives to introduce part-time working hours makes it possible to demand payment for hours not worked through no fault of the employee as idle time.
Thus, part-time work is introduced by agreement between the employer and employee, concluded in writing.
IMPORTANT! The absence of written documents deprives the parties to the employment contract of the right, in the event of a dispute, to refer to witness testimony to confirm the terms of the part-time agreement.
According to Part 2 of Art. 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to establish a part-time working day (shift) or a part-time working week at the request of:
- pregnant woman;
- one of the parents (guardian, trustee) with a child under the age of 14 years (disabled child under the age of 18);
- a person caring for a sick family member in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
In this case, part-time working time is established no more than for the period of existence of the circumstances that were the basis for the mandatory establishment of part-time working time, and the regime of working time and rest time is established in accordance with the wishes of the employee, taking into account the conditions of production (work) for a given employer.
When working part-time, the employee is paid in proportion to the time he worked or depending on the amount of work he performed.
Part-time work does not entail for employees any restrictions on the duration of annual basic paid leave, calculation of length of service and other labor rights.
Legally significant circumstances characterizing part-time work:
- the presence of a voluntary expression of the employee’s will to establish part-time work;
- reducing the number of working hours in each calendar week (the number of hours worked during a calendar week is reduced by reducing daily work or the number of working days during a calendar week);
- payment of wages in proportion to the time worked or the amount of work performed (the main difference between part-time work and reduced working time).
Working outside the established working hours
The employer has the right, in the manner established by this Code, to engage an employee to work beyond the working hours established for this employee in accordance with the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations, an employment contract:
- for overtime work (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the employee works on irregular working hours (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Work outside normal working hours is an independent type of working time.
More details
It should be noted that work outside the normal working hours for an employee is an additional type in relation to the considered types of working hours. This type of working time does not coincide with any of the types considered, and exists in parallel with one of the main types of working time, that is, with normal working hours, reduced working hours or part-time working hours.
Persons working under normal working hours may be required to work more than 40 hours per calendar week; workers with reduced working hours may also perform work outside their assigned working hours.
Legally significant circumstances characterizing work outside normal working hours:
- fulfilling an auxiliary role in relation to the main types of working time (this circumstance is confirmed by data recording the working time of an employee who has worked in excess of the standard hours established for him);
- a circumstance characterizing work outside the standard hours established for an employee is the involvement in this work on the basis of the voluntary expression of the will of the employee or an order of an authorized representative of the employer issued in accordance with the current legislation (this circumstance is confirmed by a written statement of the employee, concluded with him by an agreement on the performance of work for within the limits of the established hours, as well as by order of the authorized representative of the employer);
- Working time outside the normal hours established for the employee is characterized by the employer's obligation to pay additionally in accordance with the law and the agreement concluded with the employee.
The main document confirming the accounting of working time actually worked by each employee is the Time Sheet .
Practice shows the following types of working time recording:
- daily (when the employee has the same working hours every day);
- weekly (when the duration of daily work may vary by agreement between the employee and the employer, but the weekly final result must be within the law, i.e. no more than 40 hours per week);
- summarized (when the length of working time per day, per week may be different, but overtime on some days is compensated by underwork on others, however, during the accounting period (month, quarter, year) the employee must work the established standard hours).
0
1.64
Payment for processing
Work beyond the established working hours and on weekends must be paid in accordance with Article 153 of the Labor Code at a double rate. This rule applies to any remuneration system.
It is acceptable to provide a day of rest (time off). In this case, the employee may be given a choice: time off or double tariff. In the first case, the day off worked is paid in the usual manner (single payment).
Double payment is calculated without taking into account bonuses, compensation and other incentive payments.
Nuances
Any of the working hours used must reasonably combine periods of work and rest, which will not only preserve the efficiency of employees during the shift, but also ultimately increase their productivity. Of course, each of them has its own nuances. Therefore, it is established depending on the characteristics of a particular organization and on the basis of local regulations.
Important conditions are compliance with labor laws and preventing violations of workers' rights.