Concept and composition of salary
Remuneration is one of the main conditions of labor relations between the employee and the employer. This concept includes:
- calculation rules;
- size;
- payment terms;
- components.
Based on Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the most important information about payment (size, salary allowances) must be included in the employment contract, and additional information (for example, specific terms, calculation rules, etc.) should not change the position of the employee for the worse compared with the law.
You can find the correct employment contract in ConsultantPlus. Get free trial access to the system and proceed to the sample.
From the definition enshrined in Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it follows that salary means employee remuneration, taking into account:
- specific qualifications;
- complexity of conditions;
- workload.
This concept also includes:
- compensation payments;
- incentive payments (including various salary supplements and bonuses).
It is necessary to dwell on the composition of payments in more detail. For a simpler understanding, we will show the important components of the salary with examples in the table.
| What is included in the salary | ||
| Main part | Incentive payments | Compensation payments |
| Salary (tariff rate) | Prize | Additional payment for traveling nature of work |
| Bonus for experience | Allowance for work in special climatic conditions (heat, frost, high humidity, etc.) | |
| Additional pay for performing management functions | Additional payment for irregular working hours | |
| Financial incentives or rewarding with a valuable gift for a holiday (anniversary) | Premium for “harmfulness”, i.e. for the negative impact of production factors[u1] | |
What is the tariff rate?
Tariff rate
also implies a fixed payment, but not for the billing period, but for a specific time unit (day or hour).
In other words, in this case the official receives a salary for the amount of time worked.
How is the salary (monthly rate) calculated under such a system of monetary valuation of labor? The formula is simple: the tariff rate is multiplied by the number of time units worked
.
Example 1.
The employee's rate is 150 rubles, and he has 180 working hours per month. Then the salary will be 150 * 180 = 27,000 rubles.
The conditions for receiving payments at the tariff rate are similar to those in the case of a salary (performance of duties, presence at the workplace and adherence to the schedule).
What is good about TS? Its main advantage is commensurate wages. A citizen receives as much money as he really
worked (i.e. spent in continuous work activity).
What is included in the main (net) part of the salary?
The main part of the salary includes only the salary (tariff rate). This is a fixed part of the salary. It is reflected in the employment contract and the employer’s staffing table. The introduction of other payments to the salary (based on the law or at the will of the parties to the employment agreement) is additional, but in some cases the salary can only be a fixed salary. The opposite situation, when the salary consists only of additional payments without a salary (tariff rate), is not provided for by law.
Consequently, salary refers to the minimum amount of money that an employee has the right to claim when performing a certain job function for a specified period of time.
To set the salary level, the most important indicator is the qualifications of the employee. Its concept includes:
- having a certain level of education;
- previous practice of carrying out the relevant work;
- qualification category (if available).
Two other indicators - complexity and volume of work - are no less important, since qualifications are closely related to them. It is this that presupposes the possibility of performing a labor function with a certain level of complexity and volume. It is important not to confuse this level with personal indicators (for example, resistance to stress, independent decision-making). As a rule, personal indicators have a greater influence on the level of the position held than on the salary.
What is the meaning of the term “wages” in the Labor Code?
In Art. 129 of the Labor Code provides the basic concepts that are further used in chapters 20, 21. According to
Art. 129 of the Labor Code, wages mean payment to employees. The amount of wages, according to the official definition, depends on the qualifications of the employee, the complexity of the tasks he performs, and the quantitative and qualitative indicators of his work.
Salaries are paid to employees for fulfilling labor standards that are established by law (Articles 159-162). This is the amount of labor that the employee must provide to the employer. The most common universal measure of the quantity of labor is working time. But the employer can also adhere to other quantitative characteristics, in particular, daily output.
Remuneration taking into account the quantitative measurement of labor means that the employee is paid for all work . So, if an employee is hired to work overtime, then he receives a salary not only for labor functions within the labor standard, but also for his overtime work. In the opposite situation: if an employee has worked for an incomplete period, then he is paid only for the time he actually worked.
The quality of work is another important criterion for determining the size of wages. It characterizes tension, complexity, responsibility and independence in performing work.
Often, understanding the quality of work is understood as the conscientious performance of his duties by an employee and the absence of defects in his work. The fact that an employee must perform his work efficiently is assumed even at the time his salary is established.
The concept of labor quality is closely related to such a characteristic as complexity (the level of tasks performed). The complexity of the work can be judged by the name of the specialty, category (for example, doctor of the first or highest category) or by the degree of responsibility and independence of the work performed (junior researcher, senior researcher, etc.).
The required qualifications of the employee also depend on the complexity of the tasks performed. The latter is taken into account when setting the salary amount only when it is necessary to perform the assigned work.
For example, it is not taken into account if a highly qualified employee is hired to perform low-skilled work (an employee with an engineering degree is employed as a sales consultant).
The last criterion for determining wages is called working conditions by the legislator . Although this criterion is important, it is usually rarely used when setting the basic salary, but is used when setting the amount of compensatory additional payments and allowances.
Incentive payments and salary supplements
For the most part, incentive payments are made through bonuses (we will focus on this in a separate subsection). But there are other ways.
For example, appropriate additional payments and bonuses are intended to encourage the employee to various achievements related to work through certain material incentives.
Let us give an example of one of the types of such payments: an allowance for length of service at one enterprise. In particular, it aims to:
- reward an employee for a long period of work in a particular organization;
- encourage him to continue working in this organization;
- to orient other employees to the fact that long work experience at this enterprise provides certain material benefits, and to deter them from looking for another job.
Another similar bonus may be established for the employee for regular professional development, acquisition of additional skills, and in other cases.
The procedure for such payments varies. For example, a payment or gift could be:
- one-time (for a professional holiday, anniversary) or periodic (based on the results of fulfilling the quarterly plan, etc.);
- set at a fixed amount or calculated as a percentage of the salary.
Based on Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such subtleties are reflected in employment contracts, collective agreements, and local regulations.
IMPORTANT! If the employee’s salary includes not only salary, but also other payments, then personal income tax must be withheld from all these payments and insurance premiums must be paid.
Bonuses
Quite often you can hear the phrase “net salary without bonuses.” It is not entirely correct, because the bonus, regardless of the basis for the payment, is included in the salary. Bonuses in themselves are one of the forms of material incentives for employees who perform their work efficiently (Part 1 of Article 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Specific criteria for receiving a bonus are usually prescribed in a local act of the organization (for example, in the bonus rules). Such an act should include:
- lists of employee positions for which it applies;
- specific conditions, calculation procedure and bonus amounts;
- periods and terms for calculating the bonus (for example: the quarterly bonus is calculated and paid no later than the next salary payment date following the bonus period).
The letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated September 21, 2016 No. 14-1/-911 emphasizes that the bonus period should be longer than half a month, and the bonuses themselves are paid based on the results of an assessment of relevant indicators and achievements in work activity.
From another conclusion of the Ministry of Labor, reflected in the said letter, it follows that it is possible to reflect in a local act:
- specific dates for bonus payments;
- specific months or other bonus payment periods.
Choosing any of these options will not be considered a violation of labor laws.
For information on how bonuses affect the payment of vacation pay, read the article “Are bonuses taken into account when calculating vacation pay?”
Additional payments of a compensatory nature
This part of the salary should be distinguished from compensation for costs associated with the performance of labor duties and guaranteed by law (Article 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These include, in particular, payments:
- for business trips;
- for transfer to work in another area;
- in case of downtime due to the fault of the employer;
- for delay in issuing a work book, etc.
The number of “salary” compensations includes, for example:
- payments for special working conditions;
- compensation for work in certain areas with an unfavorable climate;
- when combining positions;
- for overtime work, etc.
Let's look at some of them in more detail.
For example, according to Art. 146 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees who work in conditions recognized as dangerous or harmful to health are entitled to a higher level of remuneration compared to other employees. The list of factors that have a negative impact on the human body was approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n.
Read about some of the nuances of harmful working conditions here .
Certain areas for which work in which a compensation bonus is awarded include:
- regions of the Far North;
- areas equated to the northern regions;
- other areas with special climatic conditions.
When determining the coefficient of the corresponding additional payment to wages, it is necessary to take into account the legislation:
- federal (norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Law of the Russian Federation dated February 19, 1993 No. 4520-1);
- regional (increased rates of coefficients may be established);
- THE USSR.
IMPORTANT! Many Soviet norms and regulations continue to apply in this area.
For more information about bonuses for work in certain areas, read the article “What benefits are available to workers in the Far North?”
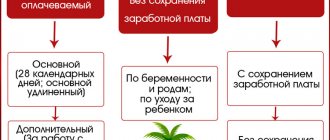
Types and forms of remuneration
Let us briefly consider the forms and systems of remuneration.
The types of remuneration include its classification into basic and additional.
The main forms of remuneration include:
- remuneration for hours worked;
- payment at various rates and prices;
- allowances for the quality and timeliness of performance of job duties;
- increased pay for working on holidays and weekends.
Additional types include:
- payment for rest time;
- benefits for dismissal of employees, etc.
IMPORTANT! One of the basic principles of labor law is to ensure payment of wages not lower than the minimum wage (Article 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Find its size for 2021 and previous years in this article.
There are 2 main types of wages: time-based and piece-rate.
Time wages are based on the number of hours worked and are not related to actual work results.
Based on Part 1 of Art. 150 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work with time-based wages, involving the performance of duties of various qualifications, is subject to payment according to a higher qualification.
For minor workers, wages are calculated taking into account their reduced working time. If desired, the employer has the right to pay additional payments to such employees.
Piecework payment depends directly on the results of work, but is not related to the time spent on it.
If an employee performs work of various qualifications on a piecework basis, then his salary is calculated according to the corresponding prices for the work performed.
Read about the salary calculation procedure here .
In some cases, employers use a tariff-free wage system. For a description of such a remuneration system, see ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ legal reference system, get a trial demo access for free.
Coefficients for calculating official salaries
This conclusion follows from paragraphs 13, 18 of the Methodological Recommendations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated October 22, 2007 No. 663, paragraphs 2(1), 3 of the Regulations approved by Government Decree No. 583 dated August 5, 2008.
Salary (official salary) is a fixed amount of remuneration for an employee for the performance of labor (official) duties of a certain complexity for a calendar month, excluding compensation, incentives and social payments. The salary, taking into account the actual time worked, together with the mentioned payments, constitutes the salary (wages) of the employee (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
A fixed-term employment contract is concluded, in particular, for the duration of the performance of the duties of an absent employee, who, in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations, and an employment contract, retains his place of work (para. 2 part 1 article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Information on the amount of wages is contained in the staffing table, internal, local regulations, which determine official salaries in relation to each staffing unit of a position, indicating its rank, class, category, qualifications.
Which document provides for a salary bracket? How can this be displayed in the organization’s local documents? 2.
Formation of a system of professional qualification groups (PQG) and corresponding qualification levels.
A conscript was hired to perform the duties of an absent employee. How can he legally set a lower salary?
Any of these approaches, being adapted to the conditions of a particular organization, may be acceptable for practical use.
The staffing table of the enterprise provides for wage levels and allows you to set up to five different salaries for each position. An employee who has a maximum salary for his position is temporarily absent (for example, on parental leave or on long-term treatment). During his absence, another employee without work experience at this enterprise is hired.
Let's look at examples of the procedure for calculating the average monthly number of core personnel and the salary of a manager (conditional data are used in the examples).
In situations where an employee performs work duties at night, he is also entitled to additional payment for each hour of additional work. The calculation of the increasing coefficient recommended by the Labor Code is 20% of the hourly salary during the daytime. To calculate the amount of an employee's hourly salary, the amount of his monthly salary must be divided by the number of hours worked. Also, an employee of government agencies is entitled to payment for work on weekends and holidays in the amount of at least one daily rate in addition to the salary, if such additional payment does not exceed the fixed monthly number of working hours. And, if work on weekends is carried out in excess of the monthly working time norm, then it is paid in the amount of no less than 200% of the daily salary.
The government has the right to set basic salaries and wage rates under the PKG. In this case, set the salary no lower than these basic amounts (Article 144 of the Labor Code).
The state allows heads of government agencies to bonus staff very generously, almost double the salary (200% more), but the employer himself decides on the size of the coefficient for each employee based on the size of the wage fund.
When registering an employee at a new place of work, a certain remuneration scheme is established between the employer and the employee, a mandatory part of which in the lion's share of cases is the official salary.
The salary schedules for both groups may indicate a salary range, called a salary range. Commercial agent, dispatcher, dispatch service operator, personnel inspector, manager's secretary, technician, merchandiser.
The employee’s salary is established by the employment contract in accordance with the current employer’s remuneration systems.
If there is no collective agreement, such provisions should be agreed upon with the trade union or other employee representative. If there are none, the employer independently, in an order or directive, sets the amount of wages, bonuses, allowances, additional wages, etc.
Naturally, this does not mean that the employer can, at his own discretion, change the amount of salary on a monthly basis, depending on the quality of the employee’s work, since any change in the amount of remuneration, according to Art. That is, each employee must have a fixed salary, but this method allows several employees occupying the same position to be given different salary amounts.
Reprinting articles and consultations from our website on other websites or printed publications is permitted with the consent of the website editors (usually free of charge or by barter in exchange for placing an advertising block on our products).
An employee’s earnings under a commission system of remuneration are determined in the form of a fixed (percentage) income from sales volume.
For more information on employers' need to comply with industry agreements, see How to Apply Industry Agreements.
Results
The wage clause is mandatory to be included in the employment agreement between the employee and the employer.
The salary includes the main part (salary) and additional incentive and compensation payments. The salary must take into account the specific qualifications of the employee, the complexity of the working conditions and its volume. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
You can also improve your professional level by:
The assignment of workers to the appropriate qualification level, as well as the tariffication of work and the assignment of a tariff category to an employee in accordance with Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is carried out taking into account the unified tariff and qualification directory of positions, specialists and employees.
These payments are distributed among the institutions under their jurisdiction and are used until the end of the financial year. The percentage of centralized budget allocations is determined depending on the size of the wage fund, the planned amount for incentive payments, taking into account the activities of institutions, the volume of work, their complexity and social significance.
The procedure for increasing an employee's salary depends on the reasons for the increase. The detailed procedure for increasing the salary is presented in situation No. 5 in the full answer.
An employee working in an institution at one or more rates (registered in the institution as an internal part-time worker) is counted in the payroll of the institution's main staff as one person (a whole unit) (clause 6 of Procedure No. 167n).
Therefore, the following situation has currently developed. The federal minimum wage is set at 7,500 rubles. per month (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 1 of the Law of June 19, 2000 No. 82-FZ).
In a federal budgetary institution, the size of salaries (rates) is determined by the head according to the remuneration system established by him, developed taking into account the approximate provisions on remuneration approved by the founder. The amount of salaries (rates) and positions of employees are established in accordance with their membership in professional qualification groups - PKG.
If an increasing coefficient is established, the amount of upcoming payments is determined by mathematically multiplying the salary by the coefficient.