Home / Labor Law / Dismissal and layoffs / Retrenchment
Back
Published: 05/06/2016
Reading time: 6 min
0
4449
The norms of the current labor legislation provide for a woman’s right to paid leave, which includes the last months of pregnancy and the first one and a half or three years of the child’s life.
Such leave is commonly referred to as maternity leave. Meanwhile, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain the concept of “maternity leave”; instead, the concept of “maternity leave” appears. The procedure for granting such leave is regulated by Article 255 of the Labor Code. Article 256 of the same document provides for the young mother to retain her job throughout the entire vacation period.
But this does not mean that a woman who has gone on maternity leave is completely insured against losing her position . Let's figure out in what cases a maternity leaver may lose her job.
- Under the protection of the law
- Liquidation of an enterprise and an employee on maternity leave
- What payments can you expect?
- Dismissal after maternity leave: are payments due?
Is it possible to fire a woman who is on maternity leave?
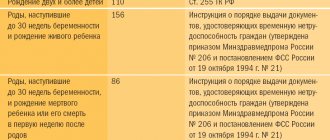
Maternity leave is called leave to care for a child; its duration is up to 3 years. The period for providing monthly benefits is limited to up to 1.5 years in accordance with Law No. 81-FZ of May 19, 1995 “On state benefits for citizens with children.”
It is precisely one and a half years out of three provided as part of maternity leave that are counted towards the insurance period for the purpose of a future pension.
Leave to care for a child until he reaches the age of 3 years is a state guarantee for every woman who gives birth, as well as:
- the child's father;
- grandmother;
- grandfather;
- other relatives or guardians who actually care for the child.
Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation guarantees the retention of a position and average monthly earnings, and this period is also counted in the total length of service and work experience in the specialty. Although the legislation of the Russian Federation does not provide for an official extension of maternity leave, it is possible to extend it in the following ways:
- go on regular leave by agreement with the employer immediately after maternity leave;
- become pregnant with another child and thereby extend maternity leave to 6 years;
- issue a sick leave certificate for medical reasons if the child needs medical care and care.
The law prohibits an employer from laying off employees and employees on maternity leave on their own initiative, including through layoffs. The only exception is the liquidation of an organization or termination of the activities of an individual entrepreneur. In all other cases, being registered with an organization during the period of child care is a guaranteed right (read about the legal grounds for layoffs and how to reduce the risk of dismissal here)
An employee on maternity leave can, at her own request, go to work part-time, remotely, and also receive child care benefits. In this case, it is impossible to dismiss her due to reduction while she is on maternity leave, even though she works part-time. Find out which employees cannot be laid off according to the law, and who has a preferential right.
Also, a woman on maternity leave can go back to full-time work, interrupting her maternity leave and thereby losing her right to benefits.
However, it is still impossible to fire an employee with a child under 3 years old, even if she returns to work (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
There are exceptions in this case:
- failure or improper performance by the employee of her duties;
- showing up at work while intoxicated;
- disclosure of trade secrets;
- identification of facts of theft, misappropriation of money;
- falsification of documents;
- systematic violation of the work regime;
- gross violations of official duties.
If such facts are established, the mother of a small child may be fired.
In what cases is dismissal illegal?
Can they legally be laid off while on maternity leave? Unfortunately, this issue is relevant in the modern world and requires special attention in each specific case.
When reorganizing a company
During maternity leave, significant changes may occur in the company in which the young mother worked.
They may be caused by a change in the organizational form of the enterprise:
- connection of several divisions;
- merger;
- selection;
- separation;
- transformation.
Such an inversion often introduces organizational changes, adjustments to job responsibilities, composition and size of the workforce. At the same time, the reduction of maternity leave while reducing the number of staff is illegal and protected by law.
In addition, the reorganization of an enterprise is not a basis for terminating a trade agreement with employees, except in the case where the hired persons themselves refuse to work in the new organization. Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation strictly prohibits the termination of employment contracts with women with children under three years of age.
Attention: It is mandatory to make an entry in the work book about the reorganization of the legal entity with reference to the corresponding decision of the director (Rostrud letter No. 1553-6 dated September 5, 2006).
Other cases
Also, the employment relationship can be terminated with a young mother if she herself expresses a desire to quit. In this case, the employee must write a written application addressed to the organization’s management, who must affix her visa.
On the last working day, the employee must be given a paycheck for the time worked and unused vacation, as well as a work book.
Also among the legitimate reasons for dismissal may also be:
- expiration of the term of validity of an urgent TD;
- confirmation of the employee’s inability to work, which is proven by medical certificates and reports;
- subject to administrative or criminal punishment, excluding the opportunity to engage in a specific type of activity if it is part of the employee’s job duties.
There are no other cases provided for by law and dismissal actions will be considered illegal.
When and how they can be fired during staff reduction: procedure
When an employer decides to reduce staff, then in relation to a maternity leaver, he has two options to resolve the issue:
- transfer her to another position, but only with the written consent of the employee (it is possible to introduce a new staff position);
- do not reduce the position of a maternity leaver before she returns to work.
Dismissal of an employee is not allowed even if the employer did not know about her pregnancy at the time the decision to lay off was made. If she is provided with a certificate of pregnancy confirming this fact as of the date of dismissal, an order for reinstatement must be issued.
You can dismiss an employee on maternity leave only after she returns from maternity leave and the child turns 3 years old.
Notice of layoffs can be sent to a woman in advance so that she knows that after leaving maternity leave her job will be reduced and she will have to look for a new job.
When is it possible to reduce a maternity position?
A reduction in the rate of an employee on maternity leave is possible only if there are good reasons:
- liquidation of the enterprise;
- bankruptcy of the company;
- termination of business activity.
If these grounds exist, there is a certain algorithm of actions, which we will consider below.
Upon liquidation of an enterprise
Liquidation of a company involves the absolute termination of economic or other activities and its exclusion from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Thus, the organization loses its entire staff along with management.
Dismissal of a maternity worker occurs only according to a procedure clearly established by the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and with payment of the required compensation.
Under such circumstances, two to three months before the withdrawal of a staff unit, it is necessary to take the following actions:
- notify the employee of the upcoming dismissal in writing;
- familiarize yourself with the order with a personal signature;
- enter information about liquidation in the work book.
On the last working day, it is necessary to make all required compensation payments, issue a certificate of income and the necessary papers to further receive payments from the state.
A mother on maternity leave can terminate the employment agreement on her own initiative, without waiting for the liquidation process of the enterprise. In such circumstances, she may demand compensatory monetary compensation from the moment of dismissal until the final cessation of the company's activities.
After the employee returns from maternity leave
After the end of maternity leave, a woman is obliged to begin fulfilling her official duties; guarantees from the state for maintaining the position in this case have already lost force. On the first day of work, the employer can begin processing dismissal on a general basis.
But if the employee interrupts such a vacation ahead of schedule, and the baby is not yet 3 years old, then the employer cannot lay her off or fire her on his own initiative; this would be illegal.
Notification of a reduction in the employee's rate in the staffing table
A notice of reduction is a document, the text of which indicates information about the reduction of a position in an organization. It can be given to a maternity leaver with an offer to take a new position. Even if the employee received such a notice and this fact is confirmed, she cannot be fired due to a reduction in her position. With written consent, an employee can be transferred to another position.
Notice of layoffs must be provided in writing - it can be delivered to the organization in person or sent by registered mail.
The notification must be drawn up in two copies:
- one is given to the employee;
- the second with the recipient’s signature remains in the personnel department.
What to do if management insists on layoffs?
Contacting the labor protection service
If the employer has laid off a woman on maternity leave, but the company continues to operate (i.e. the case does not fall within those specified in the law), the woman has the right to complain to the labor inspectorate.
The complaint must be drawn up by hand or typed on a computer and submitted to the inspector when visiting the government agency. It is advisable to attach supporting documents to the document (for example, a copy of the layoff notice or dismissal order).
Attention! If there are no such documents, then the inspector must still accept the application - their absence cannot be a reason for refusal.
After receiving the application, the inspector must conduct an unscheduled inspection. If he identifies violations, he will have to issue an order to eliminate them (in this case, reinstate the employee in her place). The labor inspectorate has no right to collect funds.
Arbitrage practice
The employee has the right to file a claim in court to restore her labor rights. However, in this case, she needs to remember that the law establishes a limitation period of 1 month from the date of dismissal or receipt of the work book. If you miss it, you will need to prove that the deadline was missed for a good reason.
Judicial practice shows that in labor disputes in such a situation, the court almost always sides with the employee.
In this situation, you need to remember that the law, as such, prohibits dismissing a maternity leaver due to reduction.
If the employer nevertheless took the risk of laying off such an employee, and the woman left a notice of layoff in her hands, the court will order her to be returned to her position and pay the average salary for the missed days without taking into account her length of service.
Who is responsible for the dismissal of a maternity leaver?
The law protects a woman on maternity leave from illegal actions of her employer. It is strictly prohibited to dismiss a maternity leaver on the employer’s own initiative (except in the event of liquidation of the company or the employee’s wishes stated in writing).
There are situations when an employer tries to force an employee out of the organization by exerting psychological pressure and insisting on filing an application for resignation at will (read about an application for early dismissal due to staff reduction and the nuances of the procedure here). An employee on maternity leave has the right to complain to the State Labor Inspectorate and file a claim in court.
If the claim is satisfied by the court, the employer will be obliged to reinstate the employee at work, as well as pay lost wages for the period of forced absence and compensation for moral damage.
The demand for reinstatement and payment of lost earnings is subject to immediate execution.
- The State Labor Inspectorate can fine the employer: liability for illegal dismissal is provided for in Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine on the company itself or its director personally.
- The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation also contains rules regulating liability for illegal dismissal. Article 145 provides for liability for the director in the form of a fine or compulsory labor.
Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Unreasonable refusal to hire or unjustified dismissal of a pregnant woman or a woman with children under three years of age
Unjustified refusal to hire or unjustified dismissal of a woman on the grounds of her pregnancy, as well as unjustified refusal to hire or unjustified dismissal from work of a woman who has children under three years of age, for these reasons -
shall be punishable by a fine in the amount of up to two hundred thousand rubles, or in the amount of the wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to eighteen months, or by compulsory labor for a period of up to three hundred and sixty hours.
What an employer is obliged to do when laying off an employee and what rights management has can be found here.
Normative base
In accordance with Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a woman on maternity leave must retain her position, as well as the responsibilities specified in the cooperation agreement. This is carried out regardless of what production processes occur in the company, as well as what economic problems arise.
Moreover, in accordance with the stipulated article, the employee can terminate maternity leave early and begin performing previously assigned duties in full or on a shortened working day.
Moreover, in some cases, cooperation is allowed not only on a part-time basis, but also on performing direct duties at home.
Also, according to the norms enshrined in Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, even with early departure from maternity leave, it is almost impossible to fire a woman due to a job reduction until her child reaches the age of 3 years. If the employee is a single mother or is raising a disabled child, then until the child turns 14 and 18 years old, respectively.
However, given that the economic situation of companies can change dramatically, as well as the fact that the employee may not be an exemplary employee, the law allows, as an exception, the dismissal of a woman on maternity leave. This is possible in the event of liquidation of the institution, in the manner prescribed by law, and a similar reduction, that is, with the payment of benefits and all payments guaranteed by law (for unused vacations, average monthly earnings for 3 months, the remaining amount of benefits).
What payments are due?
If a woman on maternity leave is laid off, the law guarantees that she will receive payments required upon dismissal on a general basis, including after 3 years of maternity leave, the calculation is made as follows: severance pay in the amount of the average monthly salary for the position held, as well as payments in the amount of the average monthly salary for the period of employment (limited to two, less often - three, months from the date of dismissal).
An employee dismissed due to layoff has the right to a payment in the amount of three monthly earnings if she contacts the employment service and registers no later than two weeks from the date of dismissal. If a maternity leaver registers with the employment center after being laid off, she is entitled to unemployment benefits. But then she loses the right to monthly child care benefits.
As noted above, while receiving child benefits, a woman cannot be fired due to a reduction in position or number of employees.
If a woman was laid off illegally and she did not challenge it in court, the payment of child benefits will be carried out by the social security authority.
The rights of an employee on maternity leave are reliably protected by law, so it is important to know about them and not be afraid to use them. Women on maternity leave should remember that they cannot be fired due to staff reduction in the organization. After returning to work, they can count on all redundancy payments and assistance from the central employment center in finding employment.
Can they be removed from office when moving from one maternity leave to another?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that while an employee is on maternity leave or child care leave, she retains her job and is paid benefits.
There are times when, while on maternity leave to care for one child, a woman learns about a new pregnancy. Then the employee is entitled to another maternity leave, but the Labor Code prohibits taking two leaves at the same time.
To get out of this situation, they usually interrupt maternity leave for the first child and replace it with labor and labor leave, after which the employee goes on another maternity leave, but this time for two children. To do this, the woman should write a corresponding statement.
The guarantees of job security in this case are the same as during the first pregnancy.
Cases from judicial practice
Russia does not have a precedent system of law . This, however, does not mean that the judge will not pay attention to the decision of another court when considering a similar case.
Therefore, even if the Labor Code does not explain some aspects of the dismissal of mothers during liquidation, their importance has already been established by the judicial system:
- You must notify in person and against signature: only a personal signature and affixed one will certify the fact of timely notification.
- A notification sent by mail without a list of attachments is not evidence of notification, because no one can accurately confirm the contents of the envelope (St. Petersburg court).
- The fact that a letter was sent is not proof of notification. If the letter is not served, then the woman cannot be fired (Omsk Regional Court).
- If a woman refuses to receive a notice and sign for it, this fact must be certified in writing. In this case, it is necessary to find 2 witnesses. For example, neighbors.
If a pregnant woman or mother is laid off before her child’s 3rd birthday, she retains her average earnings for up to three months while looking for a new job (for the same women who worked in the Far North - up to 6 months).
Downsizing after maternity leave
An employee cannot be laid off during any vacation. This point also applies to the entire period of maternity leave. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 191-193), leaving maternity leave will be required the next day after the child turns three years old. It is on this day, that is, on the first working day, that a reduction can occur. In order to understand what payments will be in the future after the reduction, you will need to calculate the average earnings. Payouts on the exchange also depend on average monthly earnings.
Notification of a maternity leaver about future dismissal is carried out according to standard regulations in accordance with Article 180. The notice must be given to the employee in any convenient way, including by mail. The fact of receipt of the notification is the day from which two mandatory months are counted.
What period to take to calculate redundancy benefits when leaving maternity leave?
The first thing I want to say is that they have no right to lay you off (well, unless in connection with the liquidation of the organization). The second period for calculation: as a general rule, this is 12 months before the date of reduction. Sick leave and vacations are excluded from this period, namely:
When calculating average earnings, the calculation period does not include the time when the employee: received temporary disability or maternity benefits; had the right to average earnings, according to Russian law, among other things, on vacation or a business trip (the only exception: the employee is entitled to average earnings during breaks to feed the child, but these intervals are not excluded from the billing period); did not work due to downtime due to the fault of the employer or for reasons beyond the control of management or staff; was unable to work due to a strike in which he did not take part; received additional paid days off to care for disabled children and people with disabilities since childhood; was released from work for other reasons in accordance with Russian legislation.
This is interesting: How many certificates were issued in 2021 under the Tyumen young family program
We tell you as fully as possible about the nuances of layoffs and layoffs after maternity leave.
In any case of termination of the employment relationship with a woman after maternity leave, the company issues a dismissal order. The document must indicate the reason for dismissal (article of the labor code), as well as the end date of work. Based on this order, an entry is made in the work book.
Dismissal of an employee by agreement of the parties after maternity leave is possible only if both parties (employer and employee) agree to such dismissal. For this purpose, a dismissal agreement must be drawn up. Moreover, it does not matter at all who is the initiator of such an agreement.