Do they have the right to ask an employee in an early position to leave work and what should she do?
Can a woman be laid off in the early stages of pregnancy? And what should she do if she faces dismissal?
If a woman feels for sure that she is pregnant, she must go to the local clinic, undergo an examination and obtain a medical certificate . You must contact your immediate supervisor with this document.
From the moment the certificate is recorded by authorized persons of the organization, the pregnant employee can be calm - she will definitely not be laid off.
Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not make exceptions regarding the timing of pregnancy, therefore all pregnant women are entitled to state guarantees against dismissal .
Even if the decision to reduce staff was made several months before the employee learned about her position, if she receives notice and she has proof of her pregnancy, the reduction in her position will be immediately canceled.
It is very important that pregnant women receive amnesty from layoffs on the very day they are recognized as pregnant. And if medical tests show that this happened before receiving the notification, the employee should first contact the head of the organization directly, armed with Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If such an action does not help, it is necessary to apply to the court with a demand to leave her position.
Life situations
Despite the categorical statements of lawyers about the impossibility of reducing a woman at any stage of pregnancy (and during maternity leave for 3 years), Law 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not always work. That is, it does not contain clear instructions on what to do if the employer, following the letter of the law, reduced staff, provided options for other positions, but the woman did not give her written consent, wanting to remain working under the same conditions and salary.
In essence, this is a direct conflict that puts both the woman at a disadvantage (stress is harmful for the child) and the director, who cannot give the employee something that actually does not exist. Here the right remains to resolve the situation amicably, to negotiate privately.
Share with your friends:
Responsibility of the employer for illegal dismissal from work during layoffs
Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation regulates all unlawful refusals of employment, as well as facts of illegal dismissals.
According to this article, an employer who decides to take illegal dismissal actions may be punished either with a fine or correctional labor.
It also provides for punishment in the form of correctional labor for the manager for a period of up to 360 hours.
Dismissal of a pregnant woman is an action that contradicts the Labor legislation of the Russian Federation. It is necessary to think carefully before putting pressure and moral pressure on a woman in a position, demanding that she quit. The law strictly protects the rights of pregnant women, so you should not commit a crime for a small gain.
To summarize, we note that a reduction is a reduction in the number of employees due to the reduction of positions or the exclusion of any unit from the staffing table. Dismissing a pregnant woman due to a reduction in headcount or staffing is prohibited by law.
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
Dismissal is possible only if the organization is completely liquidated . If an employer dares to break the law, he will face severe punishment in the form of a fine or correctional labor.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
When companies plan to make layoffs, one of the problems they face is pregnant employees. Is it possible for a pregnant woman to be laid off when reducing staff? In this article we will look at whether it is possible to make a pregnant woman, as well as a young mother, redundant.
- Is it possible to make a reduction under the Labor Code?
- If a pregnant woman is on maternity leave
- Reduction of a young mother
- Employees with children under 14 years of age
- Single mom downsizing
- How to confirm the status of a “single mother”
- When can you fire a pregnant woman?
- conclusions
- Legislative framework (articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
Results
So, the answer to the question of whether it is possible to shorten a pregnant woman is negative.
Russian legislation is aimed at protecting motherhood and childhood, therefore working pregnant women have a special set of rights, including in terms of maintaining their right to work in the organization even if management has decided to reduce staff. However, there is only one exception to this rule: a pregnant woman can be fired if the organization completely ceases its activities through liquidation. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is it possible to make a reduction under the Labor Code?
According to the Labor Code (261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation), it is prohibited to lay off a pregnant employee. This follows from the fact that staff reductions are carried out at the initiative of the employer, which means that dismissal due to reduction will be a gross violation of legal requirements.
If the expectant mother even independently decides to be laid off, this will be a gross violation for the employer. The laid-off employee will have the right to be reinstated at work by court decision.
Even if the employee hid her pregnancy and the employer laid her off, this will not relieve her of the obligation to reinstate the employee in her position. In addition, all days from the moment of reduction to the moment of restoration will be considered forced absences.
The employer will have to pay the average salary for all these days. The judicial authorities always take the side of the pregnant woman in such cases.
Important! Retrenchment of a pregnant woman is a gross violation of her rights.
Reduction of pregnant women
Is it possible to fire a pregnant woman due to staff reduction? In general, it is impossible to lay off a pregnant employee .
Such an action contradicts Article 261 of the Labor Code, in which the first paragraph clearly states the prohibition of dismissing a pregnant woman at the initiative of the employer.
The only case when the law allows the layoff of a pregnant woman is the liquidation of a company and its deletion from the register of legal entities.
Also, under no circumstances should you put pressure on an employee to resign from her position on her own. The law very strictly protects the rights of pregnant workers, not only in terms of dismissal.
If pressure was exerted on a pregnant woman in order to force her to resign, such a case is already regulated by the Criminal Code. Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for punishment for such managers in the form of a fine equal to 18 months’ salary, or 360 hours of correctional labor.
Expert opinion
Novikov Oleg Tarasovich
Legal consultant with 7 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. Member of the Bar Association.
If a legal entity is liquidated and deleted from the state register, and there are no successors to this organization, then the pregnant woman is dismissed on a general basis. This applies to branches and divisions of large corporations.
But you cannot fire a pregnant employee by manipulating the legal structure of the company . In the event of mergers and acquisitions, the employee is required to retain her work position; reduction of the position of a pregnant woman is unacceptable.
When the term of the employment contract expires, the employer also does not have the right to dismiss the employee at his own request, even if he no longer needs her services.
A woman can write a statement demanding that she be given another job or keep her old one; the employer, according to the second part of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is obliged to do this.
This also applies to cases where a pregnant woman is still on probation. According to Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a probationary period is, in principle, not provided for pregnant women.
This means that when a woman becomes pregnant, she is automatically included in the staff, has the right to work part-time, and cannot be fired for almost a year. In addition, she cannot be forced to work overtime.
If she doesn't like any of them, we can assume that she no longer works in your organization.
Reduction of a young mother
If an employee has already given birth and her maternity leave has ended, this does not mean that she can be laid off. The ban also applies to young mothers until her child celebrates his 3rd birthday.
Even if the woman did not go on maternity leave, but continued to work. It also does not matter whether the woman took out maternity leave.
Even if a woman was on vacation for only a short time and returned to work ahead of schedule, it is prohibited to lay off her job until her child turns three years old.
In what cases can a pregnant woman be fired?
To fire a pregnant woman, one of the following conditions must be met:
- liquidation of the enterprise}
- termination of the activities of an individual entrepreneur.
The employee must be notified of the upcoming dismissal at least two months in advance. The time from the moment a pregnant woman is fired until the child turns three years old is included in continuous service. Upon termination of the employment contract and for the next two months, she will be paid the average monthly salary.
Social protection authorities provide such mothers with monthly compensation payments. Their size is similar to that established for non-working women who are on maternity leave or parental leave.
Single mom downsizing
There is no such term as “single mother”, that is, it is difficult to determine what exactly is meant by this concept. However, the law prohibits dismissing employees through layoffs if they are single mothers with children under 14 years of age.
The uncertainty of this concept leads to frequent litigation, and sometimes the court sides with the woman, and sometimes supports the employer.
It is generally accepted that a single mother is the woman whose child’s birth certificate contains a dash in the “father” column. However, the legislation establishes that a single mother is a woman who fulfills her responsibilities as a parent (established by the Family Code) individually and independently.
This statement applies both when a woman has natural children and when the children are adopted.
According to the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (No. 1 of January 28, 2014), a woman is recognized as a single mother if the child’s father does not participate in his upbringing in any way. The reasons for non-participation in this case can be different: evasion of the father’s responsibilities, death of the father, restriction or deprivation of parental rights, being in prison, incapacity, etc.
Desire of the authorities
Do they have the right to lay off a pregnant woman? The labor legislation of the Russian Federation allows the employer to terminate the employment relationship with his subordinates on his own initiative. But this right does not apply to all employees.
The exception is pregnant women. They cannot be dismissed at the initiative of the employer. The law prohibits acting in this way.
How to confirm the status of a “single mother”
In any case, it is necessary to confirm that the mother is single with certain documents, for example, a court decision on deprivation of parental rights, a death certificate, etc. The final decision on whether a woman is a single mother is made based on several circumstances at once.
You can confirm your status by contacting social security and presenting the following documents:
- Statement from a woman;
- Passport;
- Children's birth certificate;
- Certificate of family composition;
- Certificate from the Civil Registry Office No. 25;
- Confirmation of the child's citizenship;
- Certificate of employment about income;
- A working woman, or a certificate from the employment service;
- Certificate from the tax office.
Actions of a pregnant woman
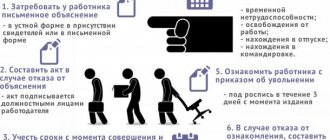
If an employee is on the dismissal list and is pregnant at that time, then, first of all, there is no need to worry, even if she already has a notice of dismissal. Do not forget that the law is on the side of the expectant mother. Necessary:
- Confirm the fact of pregnancy using a certified certificate obtained from the antenatal clinic. Every woman should register (preferably early) with an official medical institution and visit it occasionally to show that she is still pregnant.
- It is better to provide the received certificate before issuing a layoff order, before actual dismissal occurs. The main thing is to notify your management, and when this information reaches the employer, the employee should not worry. If the woman did everything correctly and on time, then the employer is obliged to take action and exclude the employee from being dismissed.
Rights of pregnant women during layoffs
Staff reduction refers to the exclusion of certain positions from the staffing table. That is, the elimination of these positions.
The rights of an expectant mother are not particularly different from the rights of other employees, with the exception of the presence of a preemptive right - the right to dismissal “last in line”, as an employee from the corresponding category of persons who have the right to remain at work.
So, what should an expectant mother know about her rights?
- 2 months before the planned layoff, the employer is obliged to notify the pregnant employee.
- The employer is obliged to offer the expectant mother all available vacancies in his organization that are suitable for the employee both in terms of qualifications and her state of health.
- The employee, in turn, has the right to refuse these vacancies if they do not suit her.
- An employer has the right to fire an expectant mother due to layoffs only in one case - upon liquidation of a company or individual entrepreneur (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Dismissal for any reason other than liquidation of the company is not legal, and can be appealed in court, which will be on the side of the expectant mother.
- Dismissal will also be considered illegal if the employer learned about the fact of pregnancy after the termination of the employment contract.
- Dismissal without substantial grounds entails criminal or administrative liability for the employer.
- If the employment contract expired during the employee’s pregnancy, then, upon her application and in the presence of a certificate of pregnancy, the employer is obliged to extend the employment contract until the end of the pregnancy. No more than once every 3 months, an employee will have to confirm her pregnancy with certificates if the employer requires it.
- Dismissal of an expectant mother is permissible due to the expiration of the employment contract during pregnancy if the contract was concluded for the duration of the work of the absent employee, and it is not possible to transfer the pregnant employee to another position suitable for her health reasons. The employer’s obligation in this case is to offer the expectant mother all available vacancies suitable for the employee in his area, and all available vacancies in other areas, provided that this is provided for in the contract.
- It is also illegal to fire an expectant mother “for lack of compliance” while she is on probation. A probationary period for an expectant mother cannot be established at all - this contradicts Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. And at the same time, it does not matter at all whether the employer knew about the employee’s pregnancy or found out only after hiring.
On a note:
The rights of the expectant mother during the reorganization of the company depend on the reorganization process itself. If the reorganization is a “liquidation”, in which the company is legally closed and after a while appears in a new form and with the same founders, then it will not be possible to challenge the dismissal in court, since in fact the liquidation still occurred.
Legislative protection of the expectant mother from layoffs is provided by Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Employer action
It is known for certain that for small companies, maintaining a pregnant employee costs a pretty penny. It is much cheaper to liquidate the company, assign it a new legal status and re-hire suitable employees. This is what unscrupulous managers take advantage of due to the legal illiteracy of pregnant women and the fact that rarely anyone dares to sue.
You can reach an amicable agreement and create a position exclusively for a pregnant employee until maternity leave, and then liquidate it. In large corporations, you can transfer a woman to another branch or structural unit.
Pregnancy is always associated with absenteeism, constant visits to doctors, and in severe cases, being kept in hospital. As a good employee for the company, the pregnant woman is lost. Recording the time of absence from the workplace, failure to complete tasks, mistakes that entail financial losses for the enterprise, will make it possible to enter comments in the work book, deprive of bonuses, pay only the official (white) salary or reduce its level.
All these actions are actually legalized harassment of a pregnant employee; it is very difficult to prove the psychological effect on her in court. Therefore, the woman herself prefers to resign due to redundancy and preserve her health and her unborn child.
What to do if a pregnant woman’s position is laid off?
If your boss threatens to fire you by hinting at your position, you can do the following:
- Remind him of the illegality of his intentions.
- Write an application to extend the term of the employment contract if this period expires. The employer is obliged to extend the period of cooperation and has no right to refuse. Please note: the updated version of the contract is valid until the end of your pregnancy.
- Do not give in to provocations and threats. Dismissal is possible solely on the basis of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation under paragraphs 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10 and 11, and the employer will also have to prove that the contract was actually violated by the employee.
- If the notice of future layoff was nevertheless signed by the expectant mother, and after signing it turned out that she was expecting a child, then presenting the pregnancy certificate to the employer before the expiration of the notice (usually 2 months) will cancel the upcoming dismissal - they do not have the right to fire the expectant mother. True, an employee should not hide the fact of her pregnancy. The fact of pregnancy hidden from the employer will become a legal obstacle to her reinstatement at work. A pregnancy certificate provided after dismissal may be regarded by the court as an abuse of right, and it will be very difficult to prove that “I myself did not know.”
If the employer does not particularly respect the law and does not intend to keep you at work or offer you another one, then you should...
- File a complaint with the State Labor Inspectorate.
- File a complaint with the Prosecutor's Office.
- File a claim in court.
Personal decision
The labor legislation of the Russian Federation protects this category of citizens in every possible way. But it does not prohibit pregnant women from quitting their jobs.
Thus, according to the law, a woman can independently submit a letter of resignation to her boss. He, in turn, does not have the right to keep the employee at work. The employment relationship must be terminated.
This scenario is the most favorable outcome for any employer. The main thing is that the girl makes the decision to quit herself. Otherwise, she can complain to the labor inspectorate and be reinstated in her position.
Where can a pregnant woman go for help when downsizing?
A company is considered liquidated if it ceases to exist as a legal entity. The liquidation of a company's branches is considered a reorganization.
What should an expectant mother do if she was laid off due to liquidation or reorganization of the company? Does it make sense to join the fight? So what should I do?
To begin with, weigh the pros and cons. Do you have enough strength and can you finish the job? Still, the baby’s health is more valuable.
The dismissal procedure must be followed in accordance with the law:
- Notice of impending dismissal 2 months in advance. Only in writing and only with your signature. Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Payment to the expectant mother of severance pay equal to the average monthly earnings (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) + preservation of the average monthly earnings for the duration of employment. This employment period can be extended to 3 months if, having managed to register with the employment center in the first 2 weeks after dismissal, you still have not found a job by the 3rd month.
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to challenge a reduction due to the liquidation of a company. If the company ceases to exist, then pregnancy no longer plays a role - the employee is fired, like all other employees. The only caveat: if the reduction procedure was violated, then you can seek compensation through the court.
What to do if the expectant mother is fired due to reorganization (only 1 branch in which the pregnant woman works is liquidated, while the company itself continues to operate)?
What the law says about this situation:
- According to Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, upon termination of the activities of a branch located in another location, the reduction of employees is carried out by the employer according to the reduction scheme during the liquidation of the company. That is, with mandatory compliance with all rights, stages of the dismissal procedure and guarantees.
- In this case (head office in one area, branch in another), the employer is not obliged to provide vacancies. Because This is not a reduction in staff, but the liquidation of a branch.
- The average monthly earnings, which is equal to the severance pay, does not consist of salary (not to be confused!), but of average earnings, which includes allowances, bonuses and other payments provided for in the contract. And maternity benefits do not apply here - this is a separate payment, the right to which remains with the expectant mother, regardless of the fact that the dismissal occurs due to the liquidation of the company.
- When maternity leave begins before dismissal, the employer pays a benefit equal to the average monthly earnings for all days at once. If the start of maternity leave falls within a month after the date of dismissal, then the employer is not obliged to pay it.
- When contacting the employment center, the expectant mother is recognized as unemployed and is dismissed due to liquidation within 1 year before she is recognized as unemployed, the social security authorities receive maternity benefits.
If the rights of the expectant mother are violated and the benefits are not paid, then she should contact the Labor Inspectorate. If the employer continues to refuse to pay benefits, you can go to court and the prosecutor's office.
Still have questions? Just call us:
Making a decision to reduce the number or staff of an enterprise is usually a forced measure for the employer. However, when resorting to it, it should be borne in mind that not all categories of employees can be dismissed on the initiative of the company’s management.
Russian legislation provides additional guarantees to pregnant women when considering the issue of terminating employment relations with them.
Illegal dismissal - is it possible to recover?
If an employer fires a pregnant woman on his own initiative, thereby violating labor laws, the woman can protect her rights and be reinstated at work in court. To do this you will need:
- Prepare evidence that she was dismissed at the initiative of the employer, for example, a work book with a corresponding entry or a copy of the dismissal order, which indicates the basis for the dismissal.
- File a claim. We will discuss the requirements that can be included in this statement below.
- Submit completed documents to the court.
Moreover, it is possible to be reinstated at work if the dismissal order and the work record book indicate the pregnant woman’s own desire as the basis for terminating the employment contract. Even if there is a letter of resignation, the court may conclude that it was written under pressure from the employer, who wanted to get rid of the pregnant employee. As evidence that the employee was actually under external pressure, under the influence of which she made the decision to quit, the court may take into account the following factors:
- the woman has no other sources of income;
- lack of job offers in other organizations.
Thus, the Moscow City Court, in its appeal ruling dated March 28, 2018 No. 33-13175/2018, based on the listed factors, decided that, by resigning, the woman acted to her detriment. Termination of the employment contract led to the following consequences:
- deprived her of the right to receive maternity benefits due to her;
- significantly reduced the amount of child care benefits (unemployed citizens receive the minimum established by law).
The woman could not consciously take such a step - this means that her employer forced her to quit, even if of her own free will. The court reinstated the woman in her position and satisfied all her demands.
Important! A woman fired during pregnancy can be reinstated at work even if at the time of her appeal to the court the pregnancy was not still present (clause 25 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2).
On what grounds do they have the right to dismiss?
You can dismiss an employee who is in a difficult position for several reasons:
- if the enterprise where she works is completely liquidated;
- if she works for an individual entrepreneur who is forced to completely stop conducting business;
- at your own request;
- by agreement of the parties;
- at the end of the fixed-term employment contract, unless the employee contacts the employer with a written application for its extension until the end of the pregnancy.
A dismissed employee should keep in mind that upon termination of employment due to a reduction in the number or staff of the enterprise, employees are provided with certain guarantees, including payment of severance pay and preservation of average earnings for a certain period. When deciding to dismiss at your own request or by agreement of the parties, no guarantees or compensation are provided.
Guarantees when working conditions change
Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the employer to make adjustments to the working conditions fixed by the contract. Basic job functions cannot be changed.
Changes may be associated with the modernization of technological processes, updating of technical equipment, and reorganization of production. The management of the enterprise is obliged to warn the staff in writing about the upcoming changes and the factors that led to them 60 days in advance.
Changing working conditions should not aggravate the situation of people relative to those fixed in labor agreements and collective agreements. If the situation at the enterprise is unfavorable, staff reductions occur, part-time work (or a week) is introduced for a period of no more than six months, and people are transferred to other jobs.
The provisions of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also apply to employees in the position. The dismissal of such women due to staff reduction is excluded. Demotion is possible only with the written consent of the pregnant woman, otherwise management is obliged to maintain her previous working conditions.
In cases where, without changing working conditions, the further activities of the enterprise are difficult or impossible, compromise decisions are made in relation to pregnant employees.
In what cases is it possible to lay off/fire a pregnant woman? If a woman does not compromise and does not agree with any of management’s proposals, the employment contract with her is terminated for the reasons specified in paragraph 7 of part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call: +7 Moscow and region.
+7 St. Petersburg and region. 8 Other regions of the Russian Federation You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of all your problems!
How to get fired from your job?
Labor legislation imperatively prohibits the dismissal of pregnant women due to a reduction in the number or staff of an enterprise. There are only 2 possible exceptions:
- if we are talking about liquidation of the company;
- if the activities of the employer-individual entrepreneur are terminated.
Women must be notified of dismissal at least 2 months before the date of termination of the employment relationship.
If a reduction in the number or staff of an enterprise is inevitable, the employer must offer the employee another position in which she can carry out work activities taking into account her state of health.
An employee can be transferred to another workplace only if she agrees to this in writing.
Thus, according to the law, the employer has only 2 options to get out of this situation:
- the introduction of a new staff position, to which the employee in the position will be registered with her consent;
- dismissal of the remaining employees, with the exception of the pregnant woman.
The employee has the right to submit a certificate confirming her position at any time before dismissal, as well as to report her condition to the employer after termination of the employment relationship, but only if she was not previously aware of this fact of pregnancy.
The responsibility for finding vacancies for which the employee can perform labor functions lies with the employer. What an employer is obliged to do when laying off an employee and what rights management has, read here.
conclusions
Retrenchment of pregnant workers is permitted by current legislation if this dismissal is carried out in connection with the liquidation of the employer's organization. In other situations, this category of employees is reliably protected by the state from dismissal initiated by management.
Generally binding rules must be observed - an appropriate order is issued, the necessary payments are made, a work book and other papers are issued that confirm the labor activity of the departing citizen.
If the employer is liquidated, all laid-off employees are provided with severance pay. In addition, pregnant women are paid targeted social benefits from the state.
Responsibility for illegal actions
For illegal actions resulting in the dismissal of an employee in this position, the employer may be subject to:
- to administrative liability under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- to criminal liability under Article 145 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- to civil liability.
In addition, if a dismissed employee goes to court with a claim for reinstatement at work, her claim will be satisfied. In addition to reinstatement at work, the woman will be paid wages for the period of forced absence, as well as compensation for moral damages in connection with illegal dismissal.
The only exception would be if a pregnant woman deliberately conceals her position. In this case, this circumstance may be regarded by the court as an abuse of law and will be grounds for refusal to satisfy the stated requirements.
External factors
Is it possible to reduce the position of a pregnant woman? In general, the employer has the right to remove this or that vacancy. But at the same time, he must transfer the pregnant woman to another job and offer her a new position.
Under certain circumstances, the boss may sever the employment relationship with the category of citizens being studied. Namely:
- if the employee whose position was temporarily filled by the pregnant woman returns to work again;
- at the end of a current fixed-term employment contract;
- when a company moves to a new location and the employee refuses to move.
Typically, all these features occur when concluding a fixed-term employment contract. Women who are hired by a company for an indefinite period are the category of personnel most protected from dismissal. And if a person is pregnant, they are protected even more.
What to do if human rights are violated?
If a pregnant employee has received a warning about her upcoming dismissal due to a reduction in the number or staff of the company, she must first inform the employer about her situation, confirming it with a corresponding certificate issued by the antenatal clinic.
If illegal dismissal has taken place, then you should as soon as possible:
- contact the labor inspectorate with a complaint about the employer’s illegal actions;
- contact the investigative body authorized to resolve issues of initiating a criminal case against the employer in connection with its violation of the rights of employees, or file a complaint with the prosecutor’s office;
- submit a claim to the court for reinstatement at work.
It is necessary to go to court within 1 month from the date the employee receives the dismissal order (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, appealing to other authorities does not stop the passage of this period.
The basis for its restoration may be, for example, the woman’s stay in a hospital and, as a result, the impossibility of protecting her rights.
An employer who decides to part ways with a pregnant employee will find it very difficult to do so.
Read all about the dismissal procedure and employee rights here.
The legislation directly prohibits terminating employment relationships with women in the position at the initiative of management, up to and including bringing the manager to criminal liability. Therefore, the head of the enterprise will have to look for compromise solutions, for example, termination of the employment contract on the initiative of the employee herself or by agreement of the parties with the payment of decent compensation.
In today's complex and unstable world, everyone is afraid of salary cuts, unemployment, and layoffs. Many employers, in an effort to make their organization more efficient, are reducing staff numbers, reorganizing the enterprise, and so on, which can affect any of the employees.
This situation is especially worrying for expectant mothers. It is important for them to know whether it is possible to dismiss a pregnant woman due to staff reduction, what rights and guarantees are provided, and how to protect themselves in the event of arbitrariness on the part of the employer.
Does pregnancy time affect contraction?
When reducing staff, the employer must first find out whether any of the employees are expecting a child.
This will avoid problems in the future. If someone finds themselves in a situation, then it is necessary to request the appropriate certificate and, on its basis, exclude the employee from the list for layoffs. The woman herself has the right to report pregnancy not only before immediate notice of layoff, but also in later periods - two months before dismissal and even after dismissal.
It happens that an employee becomes pregnant after receiving a layoff notice. But even then they won’t be able to fire her. Then the reduction procedure is suspended, for which a special order is issued. And management is looking for alternative options to reduce staff.
Due to stress or other reasons, a woman may lose her child before a court decision is made on her restoration. Even then, she does not lose the right to return to work, since the fact of unlawful dismissal remains, because at the time of dismissal the employee was expecting a child.
If a woman becomes pregnant immediately after dismissal, then the employer’s actions will be considered lawful and the court will refuse to reinstate the former employee. This is perhaps the only acceptable reduction option.
The expectant mother is almost untouchable
Dismissal of a pregnant woman due to staff reduction is possible only upon liquidation of the enterprise
And indeed it is. If a pregnant woman works under an employment contract with an indefinite term, then she belongs to one of the categories of citizens most protected from almost any dismissal. According to Article 261 of the Labor Code, initiated
Termination of a contract with a pregnant woman by an employer is unacceptable. The exception is cases of liquidation of an organization or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur.
Guarantees when working conditions change
According to Article 74 of the Labor Code, with significant changes (structural, organizational, etc.) occurring in the organization, the terms of the employment contract can be revised. That is, with significant changes taking place at the enterprise, working conditions, pay, and work hours may be changed for individual employees.
Moreover, if the threat of staff reduction or staff reduction looms over the organization, then the employer can switch to forced measures: introducing a part-time working week (day) for no more than 6 months, transferring to another position.
In this case, the administration is obliged:
- justify in detail all upcoming innovations, put them in writing and inform the employee no later than two months before the start of the changes>
- if the employee expresses her disagreement with the innovations, the employer must offer an existing vacant position, while demotion of a pregnant woman due to staff reduction is possible only with the consent of the employee herself.
If there is no alternative, dismissal occurs. However, it is impossible to lay off a pregnant woman, or one who is on maternity leave, has children under three years of age, and is raising a child on her own (single mother)!
Expert opinion
Gusev Pavel Petrovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in defense in court.
So what's going on? The employer notifies employees of upcoming changes. A woman belonging to a preferential category does not agree with these changes. The employer cannot fire her...>
Unfortunately, this point is not clearly stated in the legislation. If you follow the letter of the law, the employer is obliged to leave the “beneficiary” under the same working conditions. But will a woman want to aggravate her relationship with her employer? Maybe it's better to resign due to redundancy?
Guarantees for pregnant women under threat of dismissal
Dismissal of a pregnant woman due to staff reduction is possible with the consent of the expectant mother
In Art. 261, part 1 of the Labor Code contains a ban on the employer’s dismissal of a pregnant woman due to staff reduction or other reasons. This is in some way a labor benefit aimed at supporting motherhood and childhood.
This increased protection is aimed at preventing possible discriminatory actions by unscrupulous employers. Yes, there are also those who seek to avoid the need to provide women with maternity leave, child care, and other guarantees and benefits provided for by law.
At the same time, for a pregnant woman, finding a job is extremely difficult, since employers are reluctant to provide work to this category of applicants.
Some nuances that may arise in connection with such circumstances:
- Whether the employer knew about the pregnancy of the dismissed employee at the time of making the decision to reduce staff does not matter. This circumstance does not affect compliance with the guarantees provided by law when dismissing pregnant women at the initiative of the administration.
- The ban on dismissal or layoff of a pregnant woman does not depend on the employer’s knowledge. Even if an employee found out about her pregnancy after signing a notice of dismissal due to staff reduction, and provided the administration with a medical certificate that confirms the state of pregnancy, the employer cannot fire her.
- If the dismissal has already taken place, then after providing such a certificate the employee must be reinstated. However, before making a decision, the administration must make sure that the period of pregnancy indicated in the certificate confirms its presence on the date of dismissal due to staff reduction.
The implementation of guarantees and benefits provided by the Labor Code to employees must comply with the general legal principle of the impossibility of abuse of their rights by employees. That is, if at the time of dismissal from a pregnant woman’s job she knew about her pregnancy, but hid this fact from the administration, the employer formally has the right to refuse to reinstate her at work.
The question of whether layoff notices are given to pregnant women has a negative answer, since a pregnant woman cannot be fired due to staff reduction.
Is it permissible to dismiss an employee who is pregnant during a staff reduction?
A pregnant woman can be fired if the employer’s organization is liquidated and the work activities of all its employees are stopped, that is, officially terminated.
As part of this procedure, all citizens employed at this enterprise are subject to layoffs. The head of the liquidated organization is also dismissed on the same basis - how to dismiss a director during liquidation. Working women expecting children are no exception in this case. It does not matter how pregnant the pregnant woman is - early or late.
As established by Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on personal initiative, the employer does not have the right to terminate the employment relationship with a pregnant employee. However, liquidation of a company is an exception to this rule. If a company is liquidated, the employment agreement concluded with its pregnant employee can be terminated at the initiative of the management of this company on the most general grounds.
It is important that it is possible to lay off a woman who is expecting a child only if the employer finally and completely ceases its business activities. Reorganization of a company by merging its branches and other events of this kind cannot be grounds for laying off a pregnant employee.
When legally dismissing a pregnant employee, the management of the liquidated company must comply with all the rules governing the procedure for such a reduction:
- Timely notification of all employees about the planned liquidation of the company and upcoming dismissal.
- Correct execution of all necessary documentation accompanying the reduction procedure.
- Timely and complete settlement with dismissed employees, transfer of all due payments.
How to fire a pregnant woman if her position is being reduced?
If a pregnant employee is laid off (dismissed) due to the liquidation of the organization, the management of this company must follow a certain procedure for such dismissal. This procedure applies both to a pregnant employee and to any other employee employed at a liquidated enterprise (since the general grounds apply).
The order of reduction is as follows:
| Stage 1. | Informing the employee about the upcoming layoff due to the liquidation (closure) of the company. |
The notification procedure is regulated by Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employer sends personal written notice of appropriate content to each employee dismissed for this reason (including a pregnant employee). This must be done 2 (two) months before the planned date of the intended disposal (no later). Reading of this notice must be confirmed by the personal signature of the laid-off employee.
An employer has the right to dismiss an employee before the end of the above two-month period if the employee has given his written permission to do so. If such an agreement is reached, the employer must pay appropriate compensation.
This compensation is determined as the average daily earnings of this employee, calculated in proportion to the number of days remaining until the end of the above-mentioned two-month period. This rule is stipulated by part 3 of article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
| Stage 2. | The employer issues a dismissal order in connection with the reduction. |
Expert opinion
Novikov Oleg Tarasovich
Legal consultant with 7 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. Member of the Bar Association.
On the employee’s last day of work, the employer issues an administrative act that regulates the employee’s departure due to layoffs due to the liquidation of the company.
As a rule, such paper is drawn up by management using the T-8 (T-8a) template. The dismissed employee must personally familiarize herself with this document, confirming this fact with her signature.
| Stage 3. | Carrying out the necessary calculations (payments). |
If the layoff of a pregnant woman is caused by the liquidation (closing) of an organization, such an employee has the right to receive certain cash payments from the employer. These include wages due, unused vacation pay, and severance pay.
All these compensations are considered mandatory in this case. They are paid to the recipient directly on the day of his departure (Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
| Stage 4. | The employer provides the dismissed (redundant) employee with accompanying documentation. |
Such papers are transferred to the retiring employee along with any monetary payments due. These are documents that contain information about an individual’s work activity with a given employer. We are talking about the work book of a pregnant employee, a 2-NDFL certificate, as well as other papers (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the relevant data must be entered into the work book of the retiring employee. Additional documentation about work activity is provided to the employee being laid off upon her written request.
The correct basis for such dismissal is clause 1 of part 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, that is, the dismissal of an employee due to the liquidation of the organization. This wording should be reflected in the work book of the retiring employee.
What payments are due?
As stipulated by the requirements of Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, all necessary mutual settlements are made with the retiring employee directly on the day of dismissal. This day is clearly stated in the employer’s administrative act on the layoff of a particular employee.
If a pregnant woman is laid off from her job due to liquidation, these requirements must also be met.
The dismissed employee is entitled to the following payments from the employer:
- The accrued amount of her salary payable at the time of departure.
- The amount of unused vacation pay (if any) can be calculated using the online calculator.
- The amount of severance pay due to a woman in connection with a layoff.
If a laid-off employee considers the payments received insufficient, she can contact the management of the employer company to resolve the issue of increasing the amounts due. However, the employer has the right to refuse such a request.
Will the dismissed person receive benefits under the BiR?
In addition to the payments due to a pregnant employee from the employer upon layoff, she also has the right to receive certain compensation from the state.
We are talking about a social target benefit assigned to such an employee in connection with her pregnancy and upcoming birth.
To legally receive maternity benefits, a woman must contact her local social security department with the following documents:
- Application with the required content.
- Certificate of incapacity for work (completed).
- A certificate confirming that the applicant has unemployed status (at the time of application). Issued through the Employment Center.
- A special extract made from the applicant’s work record book (certified by a notary).
When a son (daughter) is born, the woman will also receive a special allowance, which is accrued to her for child care (it is paid until this child turns 1.5 years old).