The role of labor protection in the activities of individual entrepreneurs
Carrying out such events in the workplace is necessary to protect the life and health of employees and manage professional risks.
The right strategy allows a businessman to reduce the risk of injury and prevent financial payments due in the event of harm to health in the course of work. This also includes the manager’s business reputation and social responsibility.
By law, an entrepreneur is obliged to:
- Supervise the conduct of initial training.
- Issue certified tools for work.
- Equip workplaces.
- Provide training and send employees to courses.
- Maintain local documents.
That is, the businessman creates all the conditions to preserve the life and health of his employees. Regardless of what type of activity the entrepreneur has, there must be a magazine on workplace safety. If you constantly provide training in the office or warehouse, the employee will acquire the necessary knowledge. They will help hold you accountable for following the rules. And if the established procedure is not followed, the employer may make a reprimand or fire the employee.
On video: How to prepare a package of occupational safety documents in a day
Legislative changes
The lists of inspected employers have been updated
The lists of employers with high and significant risk categories have been updated. You can check your company in the lists on the official website of Rostrud. The data was presented by region and is current as of July 2021.
The frequency of scheduled inspections depends on the risk category. GIT comes once every two years to high-risk enterprises, and once every three years to significant-risk enterprises.
Let us remind you that from April 14, 2021, a moratorium on scheduled inspections of enterprises was introduced. An exception was made for high and extremely high risk categories. For small and medium-sized businesses, the ban on inspections applies without conditions.
Employers will have new responsibilities for coronavirus prevention
Document: Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of Russia dated July 13, 2020 No. 20 “On measures to prevent influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, including the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in the 2020-2021 epidemic season”
From August 9, 2021, employers will need to take additional measures to prevent coronavirus infection. Thus, the chief sanitary doctor obliged the managers:
— ensure monitoring of workers’ body temperature before admitting them to workplaces and during the working day using devices for measuring body temperature in a non-contact or contact manner. If an employee has a fever, he must be removed from work;
— ensure immunization of employees against influenza;
— prevent hypothermia for employees who work outdoors in winter, organize rooms for heating and eating, and maintain optimal temperature conditions in the premises;
— provide employees who work with the public with medical masks, respirators and gloves.
The Ministry of Health canceled mandatory medical examinations for office employees
Document: Order of the Ministry of Labor, Ministry of Health dated 04/03/2020 No. 187n/268n “On amending Appendix No. 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) hazardous industrial factors and work during which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the Procedure for conducting mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers engaged in heavy work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions"
Effective: May 24, 2021
From May 24, employees who spend more than 50 percent of their working time at computers will no longer need to undergo a mandatory medical examination. An employee will be tested only if the maximum permissible level of broadband electromagnetic fields in the workplace is exceeded.
Approved a new list of standards and codes of practice
Document: Government Decree No. 985 dated 04.07.2020 “On approval of the list of national standards and codes of practice (parts of such standards and codes of practice), as a result of which, on a mandatory basis, compliance with the requirements of the Federal Law “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures” is ensured and on the recognition as invalid of certain acts of the Government of the Russian Federation"
The number of mandatory requirements for the safety of buildings and structures has been reduced. Redundant and duplicative requirements were not included in the new list of standards and codes of practice, which will come into force on August 1, 2021.
The new list has more positions compared to the expired Government Resolution No. 1521 of December 26, 2014. It included 78 documents instead of the previous 76. But according to the Government, the number of mandatory requirements was reduced from 10 thousand to 7 thousand.
The new list does not apply to projects that started before August 1. Thus, developers and designers were spared the need to undergo state examination again.
Important papers
Occupational safety documentation must also be available. The rules of conduct are the same for all types of activities.
List of required documents:
- safety briefing log;
- on electrical safety;
- registration of accidents;
- issuance of special clothing;
- laws and regulations;
- workplace certification documents;
- initial training program.
How to make a safety magazine? To do this, you can use the resources for free, and then print it in A3 format. After that, they are fastened with a stapler. Excess edges are trimmed and pages are numbered. The finished document is sealed. You can buy a safety magazine at the store in book form. All types of documentation required for any type of activity are presented there.
On video: Types of briefings
Individual entrepreneur without employees and OT
The article highlights the basic principles of organizing labor protection management in small individual enterprises. You will learn how to launch a labor protection system in a small enterprise step by step, how labor protection is organized for individual entrepreneurs who use hired labor, as well as those who do without it. Occupational safety for individual entrepreneurs who hire workers is no different from occupational safety in small enterprises. Therefore, in the future we will talk about small enterprises. The legislation regulating the relations of citizens of the Russian Federation in the field of labor protection divides them into 2 categories: employers and employees. Workers are the people who do these jobs. Each party is assigned a specific range of labor protection responsibilities.
Document preparation
The storage period for the safety log is not limited to a certain period. It should always be archived. Every employer is required to have a safety log in 2017, otherwise it may result in a fine.
Does an entrepreneur need a safety magazine? Yes, if the individual entrepreneur has staff. Control over its management is exercised by the head of the department. After this, the head of the department monitors the entry of data. His task is to do this at least once a month with comments on the form of maintaining and filling out.
The director checks the journal once every three months. Everyone who carried out the inspection must sign the safety log. The date of correction of errors must be indicated.
The occupational safety log is kept by the responsible person appointed by order. All pages in it are numbered, stitched, stamped and signed by the manager. Where can I buy a safety magazine? It is sold in regular office supply stores. Some businessmen order them from a printing house. Is a safety magazine necessary?
Yes, to provide instructions:
- Induction training is required when an employee is hired for a specific position or when it changes. Conducted with newcomers, business travelers, and students.
- Initial briefing is carried out by the supervisor. Practical training in the workplace is also used. The employee learns about hazardous factors and risk reduction during work activities. You can train one or several employees at the same time.
- Targeted instruction for admission to certain types of one-time work.
- Extraordinary briefing, if there is a need for it. The purpose of the inspection is included in the document. This includes updating safety documents and new equipment. It will be needed if the employee has violated the requirements or has not worked for more than one month.
- During repeated briefing, the initial one is reinforced. It is carried out every six months.
The safety log is filled out in accordance with all the rules, after which the employee signs. The form of the safety log is determined by GOST. Now you can not only buy it in the store, but also download it for free. The website contains all the necessary forms, regardless of what the entrepreneur does.
How many times a year is training required? The introductory test does not require more than once. Primary – several times a year. Unscheduled and targeted training as needed. How often briefings are carried out is decided by the manager or person in charge.
The cover page of the safety magazine should include:
- Name of the organization;
- the date the document was started and completed.
It is important to know how to fill out and what lines are in the document.
The manager must enter:
- The date on which the employee was instructed.
- Personal data of the employee, position and profession, length of service.
- Instruction number, type of instruction.
- Who gave the instructions?
Signatures of both parties are required. When issuing a permit, the full name of the person who issued it and who received it and for what work is noted. It is dated and signed by both parties.
On video: Basics of industrial safety
Training and instructions on labor protection for individual entrepreneurs
An individual entrepreneur who will have or already has hired employees must undergo labor safety training at a training center. This is the requirement of paragraph 2.3.2 of the Procedure for training and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations, approved. Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29.
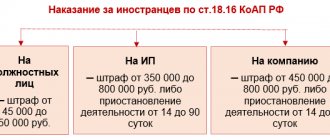
Only after this the individual entrepreneur will be able to provide instructions and training for his employees. If the introductory briefing is carried out by an untrained individual entrepreneur or another employee, a fine is possible under Part 3 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation . It is 25,000 rubles for individual entrepreneurs, and this is a significant amount for small businesses. Why you will be fined - read in our detailed material Types of liability for violation of labor protection requirements.
If the individual entrepreneur does not have the opportunity to create his own commission for testing knowledge, do occupational safety training, but entrust the training of all employees to the training center. The frequency of occupational safety training for specialists and managers is at least once a year, and for workers, follow the occupational safety rules, or set them yourself. If there is no guidance in the rules, do not forget that first aid training for workers is carried out every year, so provide training as well.
What the law says
Regulatory documents provide for activities, the number of which depends on the number of employees. If there are less than 50 employees, they are conducted by the manager. Up to 100 people - a labor protection specialist is included in the staff. More than this number of people, it is necessary to organize a corresponding department.
The occupational safety and health logbook is filled out on regular A4 sheets. All data is entered into lines. The recording can continue for several lines. Be sure to put lines in empty cells. The filling sample shows that the presence of a dash in the empty lines will prevent you from receiving a fine from regulatory authorities.
Help for checking safety logs includes the purpose and methods of control. Based on this, conclusions are drawn about the correctness of filling out the document according to the form, and comments are made. An extract from the safety journal shows whether the document was drawn up correctly, all data is entered into the book, and whether there are signatures.
It is important that workers undergo training in a specialized organization that has a license. Deviation from the established rules provides for a fine for the manager. However, this does not apply to entrepreneurs who do not have employees. It is believed that the employer will not harm his health.
Even though the business owner will have to spend some money, it is cheaper than paying a fine of 5 thousand rubles.
Organization of labor protection in a small enterprise
Of course, the organization of occupational safety management in small and large enterprises is different. At the same time, the requirements are not weakened, but management links are simply lost. For example, 3-stage OT status monitoring is replaced by 2-stage. Features of the OT service depend on:
• number of employed workers; • areas of activity of the enterprise (this affects the lists of types of work, equipment operated, etc.).
If a small enterprise employs 50 or more people, a separate OT service must be created. This mainly applies to:
• transport, manufacturing and construction small enterprises with a staff of up to 100 people; • scientific, technical or agricultural enterprises employing up to 60 people.
If there are fewer workers, the organization of labor protection in a small enterprise is carried out by:
• employer (company manager, individual entrepreneur) personally; • authorized employee (a separate position of safety engineer or part-time position is being introduced); • third-party accredited specialists or organizations under contract.
A special standard is devoted to the organization of labor protection in small enterprises - GOST R 12.0.009-2009. Labor inspectors, employees of the fire service, Energy Supervision and other departments are always ready to provide employers with a complete list of occupational safety documentation required by each specific enterprise.
Areas of activity
Entrepreneurs involved in construction must have a construction safety log. The document form is standard, briefings are carried out and registered in the same way as at other enterprises. That is, the type, date, personal data of the instructed employee are indicated, and signatures are placed. The general contractor is held liable for failure to comply with safety regulations.
Construction safety journals are divided into several types. This includes a document for entering data on workplace training, construction supervision, and induction training.
Similar rules also apply to modern carpentry. Upon arrival of an employee to the carpentry shop, the equipment and voltage are checked, and the employee must undergo all types of instructions.
An entrepreneur engaged in transportation is required to keep a driver safety log. This includes records of induction, pre-trip, special and seasonal training. In a car service center, instructions are developed for employees for all workers according to their specialization. Document forms are standard for filling out.
The pharmaceutical business is directly related to safety. Therefore, labor protection in a pharmacy is an important component of the full-fledged work of an entrepreneur.
Organization of labor protection in a small enterprise step by step
To organize an effective labor protection system in a small enterprise, you need to step by step:
1. Create an OT service or appoint a person to perform its duties. This is formalized by order.
2. By order, appoint responsible persons (for fire safety, electrical safety, high-risk work, etc.).
3. Develop and approve by orders regulations on the occupational safety service, training, organization of hazardous work, monitoring the condition of occupational safety, development of instructions, fire safety, etc.
4. Create lists of professions and types of work for which there should be safety instructions. Develop and approve these instructions.
5. Draw up and approve programs for introductory briefings and classes on the fire-technical minimum.
6. Conduct training for all employees: workers and engineers.
7. Perform a special assessment of working conditions.
8. Organize and conduct medical examinations.
9. Create a commission on occupational safety.
10. Invite employees to select occupational safety representatives and train them.
11. Develop, approve and place evacuation plans in places accessible to employees.
12. Create and organize journaling:
• induction training; • briefings at workplaces; • accounting and verification of fire extinguishers; • checking tools and devices; • accounting of NS and PP; • inspections; • recording cases of domestic injuries; • issuing instructions; • issuance of personal protective equipment; • others.
13. Organize sanitary services.
14. Organize the issuance of personal protective equipment, means for removing contaminants, and milk (if necessary).
15. Get visual propaganda: instructions, diagrams, posters, stands.
Further organization of labor protection management in small enterprises depends on the specifics of their activities. Let us note that labor protection should not just be properly organized in “paper” form, but work in practice every day. Instructions must be conducted, operational control carried out, planned activities implemented, unscheduled inspections organized, etc.
The costs of labor protection for individual entrepreneurs and small businesses can be significantly reduced at the production planning stage. To do this you need:
• Choose office, warehouse, industrial, and retail premises that have already been put into operation (there are commissioning certificates, acceptance certificates by state commissions, etc.), have passed special inspections, are equipped with warning systems, fire extinguishing systems, and have suitable sanitary and living conditions.
• Plan a special assessment of working conditions. It can be done in stages, attracting funds from the Social Insurance Fund. It must be remembered that when moving production or office, the special assessment will have to be carried out again. But for homeworkers and workers who work remotely, it is not carried out at all.
• Organize the purchase of workwear, personal protective equipment, and detergents in bulk.
• Conduct training for workers in special centers in groups, rather than individually, so that discounts can be claimed.
• Purchase foreign-made equipment that has already passed all the necessary checks, examinations and is equipped with the appropriate certificates.
• Try to stipulate in equipment rental agreements that the lessor is responsible for its verification and routine inspection.
Labor protection for individual entrepreneurs
Labor protection for individual entrepreneurs who hire workers is no different from labor protection in small enterprises: appropriate orders are created step by step, responsible persons are appointed, instructions are developed, training is conducted, medical examinations are organized, special assessments of working conditions are carried out, etc. In some cases, concerns about labor protection It is more profitable and convenient for a manager to entrust the work to a specially trained person than to do it himself.
Individual entrepreneurs are not recommended to store labor safety documentation at home. It may be required at any time when performing production tasks. In addition, during the inspection, inspectors will not have suspicions about the timeliness of its execution.
Labor protection for individual entrepreneurs without employees
Labor protection for individual entrepreneurs who do not use hired labor, but work for themselves, is significantly simplified. Since such an individual entrepreneur is not an employer (he cannot enter into an employment contract with himself), he does not need to conduct a special assessment of working conditions, there is no one to send for training, a medical examination, or insure against health insurance and health insurance. Based on this, sometimes the incorrect conclusion is made that labor protection for individual entrepreneurs “does not work.” This is wrong. For clarity, we can draw an analogy with traffic regulations, the requirements of which the driver must comply with regardless of whether he is performing a production task or driving his mother-in-law to the dacha.
An approximate list of labor protection measures for individual entrepreneurs who do not use hired labor includes:
• training in fire safety measures, fire safety training; • training in electrical safety for at least group I (this is regular instruction in an authorized organization); • OT training within the general course; • if the individual entrepreneur uses equipment, then training in safety measures during its operation; • verification or examination of this equipment; • development of instructions for the safe conduct of work performed by an individual entrepreneur (even if it is work on a computer), regular repetition of their requirements; • if the individual entrepreneur serves the population - undergoing a medical examination, issuing a health certificate; • maintenance of fire extinguishers, protective equipment.
Note: Useful materials on fire safety are presented on the official website of the Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations “To help small businesses”.
You need to understand that labor protection for an individual entrepreneur who does not use hired labor is concern for one’s own health and the health of clients. To do this, it is advisable to use the practical experience accumulated by safety specialists - study instructions, use flushing agents, PPE, master safe working methods, maintain equipment in good working order, use safe materials.
When the inspection bodies (Rosenergonadzor, SES, firefighters, metrologists and other services) “get” to a specific individual entrepreneur is a question that only they themselves can answer. The legislation allows scheduled labor safety inspections of individual entrepreneurs to be carried out no earlier than 3 years after their registration. Fines for failure to comply with occupational safety requirements are on average 10 times higher than the costs of them. Preserved health and nerves are priceless.
From this article you learned how labor protection management is organized in small enterprises, depending on the number of personnel and the direction of their activities, what is necessary for the effective operation of this system, how labor protection is organized for individual entrepreneurs who have employees, and why labor protection is needed for Individual entrepreneurs who do not use hired labor.
Please rate the site or material!
Who should be responsible for scheduling employees in the department? Should there be employee signatures, etc.? The same applies to the report card for work; who should calculate the standard hours for doctors and nurses who are on duty? Who should keep time cards, etc.? This is currently being done by senior nurses. And when should payslips be issued: before receiving wages or after?
The form of the work schedule is not established by labor legislation, but within the meaning of this document it must reflect the surnames, first names, patronymics of employees, their positions, working days and days of rest, indicating the calendar date, start and end times of work. Employees must be familiarized with the work schedule upon signature. The paintings can be placed both in the schedule itself and in a separate document. The work schedule must be approved by order of the head of the institution for a month, quarter or any other period of time.
Drawing up and maintaining a work schedule, timesheets and work time cards, as well as other personnel documents must be carried out by employees whose job responsibilities include performing such work in accordance with their labor function established by the employment contract and specified in the job description. As a rule, the preparation and maintenance of these documents is carried out by HR specialists or heads of the institution.
If your employment contract or job description does not provide for your obligation to draw up and maintain the above personnel documents, you have the right to refuse to do so.
Payslips are issued either before or simultaneously with the payment of wages.
Legal basis:
Part 1 of Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that employers, with the exception of employers - individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs, adopt local regulations containing labor law norms (hereinafter referred to as local regulations), within their competence in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, and agreements.
According to paragraph 1 of part 2 of Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee is obliged to conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract.
By virtue of Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is prohibited to require an employee to perform work not stipulated by an employment contract, except in cases provided for by the Code and other federal laws.
Clause 9 of Part 2 of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that the employer is obliged to familiarize employees, upon signature, with the adopted local regulations directly related to their work activities
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when paying wages, the employer is obliged to notify in writing each employee:
1) on the components of the salary due to him for the relevant period;
2) on the amount of other amounts accrued to the employee, including monetary compensation for the employer’s violation of the established deadline for payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee;
3) about the amount and grounds for deductions made;
4) about the total amount of money to be paid.
Information portal of Rostrud “Onlineinspection.RF”, May 2016
Managers often have doubts about whether they really need to undergo occupational safety training. And it happens that the general director of a company is generally surprised when he hears that “labor must be protected,” and especially since this still needs to be learned.
Key issues:
- Who decided that a manager should study labor protection?
- What benefits does such training give to the head of an organization?
- How to distribute labor protection responsibilities among company employees?
- What is more profitable - to study or not to study?
- What should a labor safety specialist do if a manager refuses to undergo training?
Who decided that a manager should study labor protection?
Managers often have doubts about whether they really need to undergo occupational safety training. And it happens that the general director of a company is generally surprised when he hears that “labor must be protected,” and especially since this still needs to be learned.
However, undergoing labor safety training is the responsibility of organizational leaders, directly established by law. Namely, the Labor Code (Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia and the Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/291.
One cannot but agree that in a busy work schedule it is difficult for a manager to allocate time for training, which lasts on average 40 hours. And often it is not possible to convince the director to sit at his desk. Let's see what is more profitable for a leader: to study or not to study?
Elena KAZANOK, leading HR specialist at Legal (Moscow) warns
All employees, including heads of organizations, undergo regular testing of knowledge on labor protection at least once every three years. This is controlled by the Federal Labor Inspectorate. The state labor inspector has the right to issue an order to remove the head of an organization from work if he has not completed training, instruction or testing of knowledge on labor protection (Article 357 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the manager does not comply with the inspector’s request, he may be fined, and in the worst case, disqualified.
What does occupational safety training give to the head of an organization?
Having completed mandatory labor protection training, the manager will be able to:
- avoid fines during inspections by various regulatory authorities and save the company money;
- get a guide in a complex area of legislation and select a reliable specialist to whom you can delegate authority over labor protection in the organization;
- competently distribute labor safety responsibilities in the company and be confident about the safety of your employees.
Example:
The director of Cyclone LLC hired an employee who did not have access to such work to work on a day off at a transformer substation. A subordinate entered the substation room to repair a failed unit. He was sure that the power was out, but it turned out that this was not the case. During the repair process, the worker was electrocuted by the transit cable and died on the spot.
Relatives of the deceased employee, considering the employer responsible for the death, demanded compensation. In court, the manager stated that he did not know where the transit cable was located. However, he was found guilty. As a result, the employer was charged 230,000 rubles for the death of the employee. If the manager had undergone mandatory training in labor safety and provided the necessary instructions to the employee, the accident could have been avoided.
To whom can the CEO delegate authority over labor protection?
There are several typical situations when the CEO delegates his labor protection responsibilities to another employee.
Situation 1. An organization with more than 50 employees introduces the position of occupational safety specialist. He must have experience in the field of labor protection or higher education in the specialty "Technosphere Safety", or higher education and additional vocational education in the field of labor protection.
If the number of employees is more than 100 people, then it is better to organize a labor protection service. Its head must have at least five years of experience in the field of labor protection and higher education in the field of “Technosphere Safety” or higher education and additional vocational education in the field of labor protection.
In cases where there are harmful and dangerous factors at work, it is advisable to introduce a labor protection specialist with a workforce of less than 50 people.
Situation 2. The occupational safety service or the position of occupational safety specialist has not been introduced because there is no hazardous production and the number of employees is less than 50 people. Then any employee can be entrusted with occupational safety and health. Usually the choice falls on the personnel officer, less often on the accountant. In any case, the decision remains with the employer.
The selected employee must be sent for occupational safety training. After this, he will be able to fully and legally fulfill his duties.
Situation 3. In an organization with up to 50 people, the employer deals with occupational safety issues independently. More often, this option is possible in micro-enterprises with up to 15 people.
Situation 4. In organizations with up to 50 people, occupational safety issues can be outsourced to a specialized organization. It must have state accreditation to provide labor protection services.
In any case, the head of the organization bears responsibility for labor safety violations identified, for example, by a labor inspector. Therefore, it will be useful for him to have knowledge in occupational safety issues. And without training this is impossible.
How to distribute labor protection responsibilities among company employees
In large companies where there is a specialist or even an entire labor protection service, department heads, along with their main responsibilities, are also responsible for labor protection in their departments.
The distribution of responsibilities for labor protection can be presented in the form of a table and enshrined in a collective agreement or other local regulation.
Table. Distribution of labor protection responsibilities in the company
| Responsible executor | Main responsibilities for labor protection |
| CEO | – ensuring safe working conditions for workers; – monitoring the state of labor protection in the organization |
| Head of Labor Safety Service | – monitoring compliance with labor safety standards throughout the organization; – development of regulatory documents on labor protection; – conducting introductory training; – organization of labor protection training; – organization of workplace certification; – compiling a list of workers who need to be given PPE and undergo a medical examination. |
| Head of HR department | – organization of preliminary and periodic medical examinations; – registration of benefits and compensation to employees for harmful working conditions. |
| Head of administrative and economic department | – purchase and distribution of personal protective equipment to employees; – maintaining personal personal protective equipment records. |
| Heads of structural divisions | – carrying out initial and repeated briefings at workplaces; – training in safe working methods; – ensuring safety when working with equipment and tools; – control over the use of protective equipment, etc. |
What is more profitable - to study or not to study?
Speaking about occupational safety training, one cannot fail to mention the banal truth: lack of training is a violation of labor protection legislation. The penalties for this are:
- for officials who do not fulfill labor protection duties - from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- for organizations - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles or suspension of activities for up to 90 days (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If an official violates the law again, he will be disqualified for a period of one to three years (Part 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
For comparison, in Moscow the cost of training a manager in occupational safety at a training center ranges from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles.
If such a method of monitoring labor conditions as workplace certification were used by the manager, unforeseen expenses could be avoided.
Example1
In a small organization with 14 employees, engaged in small wholesale trade, the labor inspectorate conducted an inspection and found that the premises occupied by the company were not certified for working conditions. The labor inspector issued a fine. Moreover, both the organization and its manager responsible for labor protection had to pay.
As a result, the organization lost 40,000 rubles, and its leader parted with 4,000 rubles (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Safety violations are also mentioned in the Criminal Code. If an employee is injured due to non-compliance with labor safety standards, then the person responsible for safety regulations will at a minimum be fined in the amount of up to 200,000 rubles, or, at a maximum, imprisoned for up to one year (Part 1 of Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The death of a person due to a violation of safety rules entails imprisonment for up to three years (Part 2 of Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Example2
The deputy production manager of the chemical enterprise "Sintez-PSZH" (Dzerzhinsky, Nizhny Novgorod region) instructed workers to inspect the filter elements in the cabin of the decomposition department. However, no instructions were provided before the start of work, the employees were not given special clothing, and the equipment was not properly prepared.
As a result of violations during work, a chemical outbreak occurred on June 6, 2012, and two workers were killed and four were seriously injured.
The deputy production manager was sentenced to 1.5 years in prison.
Where to study
If you decide to undergo occupational safety training, you need to contact an accredited organization.
You can obtain the necessary information from the labor inspectorate or the department that deals with labor and employment issues in your region. For example, in the Moscow region, a certificate can be provided by the Committee on Labor and Employment (website ktzn.mosreg.ru or hotline).
You can also find information about training organizations yourself on the website rao.rosminzdrav.ru.
What should an occupational safety specialist do if a manager refuses to undergo training?
First, encourage him to read this article. Perhaps the CEO just needs another reminder of something he has been constantly putting on the back burner.
Secondly, think about what your boss is interested in and how this can be linked to occupational safety training. For example:
- If the manager is focused on the constant development of his business, hint to him that during occupational safety training it is quite possible to make useful acquaintances with the heads of other organizations.
- Is your manager a fan of computer technology and easily masters new programs? Tell him about the interactive occupational safety training that some training centers offer. Computer programs allow you to consider algorithms for solving difficult situations that may arise in an organization.
- Is your manager constantly traveling on business and rarely coming to work? Consider distance learning on occupational safety and health. The boss will be able to study at a time convenient for him in any place where there is Internet access.
Remember the main thing:
- Occupational safety training is not a whim, but a legal requirement.
- A manager who knows how to protect the health and lives of his employees has the opportunity to avoid unnecessary workers' compensation costs for work-related injuries.
- Having acquired knowledge of labor protection, the manager will be able to effectively distribute responsibilities in this area among his employees.
- It is more profitable to undergo occupational safety training than to pay fines out of your own pocket at each inspection.
- To prevent training from being a boring task, you can conduct it interactively, remotely, and make useful contacts during full-time training.
"Occupational Safety and Health"