Hazard (or danger) classes 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 are harmful working conditions that are present to one degree or another in most industries, firms, and organizations. But their widespread use leads to them being forgotten, both by employees and employers. Meanwhile, the Law on SOUTH requires managers to pay close attention to identifying and assessing production risks and protecting employees from them. Failure to properly account for adverse consequences may result in the need to pay compensation to injured employees. And this is the least of the likely problems.
The danger and harmfulness of work are divided into 4 options
The first, also optimal, refers to such a production process when nothing harms working people or the level of danger does not exceed established standards.
The second - acceptable - is established when workers are negatively affected, but if the work regime is observed, the body returns to normal on its own and no special medical intervention is required.
Class 3 hazardous working conditions occur in enterprises where the level of exposure to negative factors exceeds permissible standards. Well, the fourth is installed in workplaces where the likelihood of a threat to an employee’s life arises every day.
Optimal environment
In short, the work regime corresponding to this option does not in any way affect the health and normal life of workers. The workplace complies with hygienic standards, and to maintain efficiency at the enterprise it is not necessary to create a special environment.
Acceptable conditions
In this case, the situation is more complex, but not critical. There is a harmful effect on the body of employees at work, but its strength does not exceed sanitary and hygienic standards. To recover, a person just needs to follow a work regime, that is, not work more than a set number of hours and not neglect weekends and vacations. In this case, the functionality and performance of a person will not decrease.
Dangerous situation
As mentioned earlier, in this case there is a real danger for employees during the work process. Hygienic requirements in such production do not meet established standards.
Harmful working conditions subclass 3.1: what does it mean?
The first degree of harm is assigned if the health of employees is so strongly affected that the body does not have time to recover by its next shift. But at the same time, the risk of occupational diseases does not arise even in the long term. This does not mean that he will not have to seek medical help in the future; such a chance always remains. And the longer an employee works in production, the faster the probability increases. But you can reduce the risk by increasing the number of hours of rest or completely stopping the negative impact.
Harmful working conditions, 2nd degree, 3rd class
It is customary to talk about such a danger if the influence of negative factors is so strong and long-lasting that permanent changes occur in the body of workers. Occupational diseases appear over time (about 15 years after starting work at the enterprise), but they manifest themselves in a mild form. There is no loss of performance in the long term. An employee can perform his official duties even at the initial stage of an occupational illness, but regular medical monitoring of his condition is mandatory.
Harmful working conditions 3 class 3 degree
The differences from subclass 2 are that from regular negative effects in the body, occupational diseases of not only mild but also moderate severity develop. This means that over time, working capacity is seriously reduced or lost completely.
Subclass 3.4
Against the background of such dangers, severe forms of illness develop and loss of working capacity inevitably occurs. We are talking about a long period of work in the profession, perhaps with a gradual increase in negative impact, for example, from the second subclass or from the third to the fourth.
Dangerous situation
In a situation where every shift an employee is exposed to such strong negative factors that life and health are constantly in real danger (for example, in the form of an acute occupational disease), they speak of the fourth class of harm. In fact, this situation is extreme. They may be due to:
- Physical impact of moving machines and mechanisms.
- Chemical influence of poisonous and toxic substances present in production.
- Biological effects of pathogens, bacteria and microorganisms.
- Neuropsychic and physical overload.
Professions of the 3rd class of hazardous working conditions do not differ from professions with the 4th. The difference depends only on the likelihood of negative consequences occurring.
Do you want to implement Warehouse 15? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted!
Sanitary protection zones of objects and enterprises. Dimensions of zones and hazard classes of enterprises
A sanitary protection zone (SPZ) is an area around facilities and industries that have a harmful impact on the environment and human health.
The dimensions of the sanitary protection zone are determined by the regulatory document “Sanitary protection zones and sanitary classification of enterprises, structures and other objects” (SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1200-03).
The introduction of a sanitary protection zone is aimed at reducing the harmful effects of pollution from facilities and industries on the atmospheric air to hygienically established standards.
In essence, sanitary protection zones are a protective barrier that ensures the level of safety of the population during normal operation of the facility.
Characteristics of the third class and its subclasses
A clear division is presented in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and according to it, the third remains the most common. The degree of risk is determined by how severe the consequences may be for employees.
For example, it is assumed that it takes a day to restore the functional state of the body and human performance. If you have to go to the next shift less than 24 hours after the end of the previous one, it can be argued that harmful working conditions of 1st degree, 3rd class have occurred.
If you work in such an environment for a long enough time (15 years or more), you can acquire occupational diseases, which means the subclass of harmfulness will change. What it will become depends on whether the ability to work will be lost and how much the overall health will deteriorate.
Additional payment for hazardous working conditions
Now let’s look at Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states what payment for hazardous working conditions is according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Russia today. It says:
| “The minimum increase in wages for employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions is 4 percent of the tariff rate (salary) established for various types of work with normal working conditions.” |
That is, the additional payment is at least 4% of the salary. The employer has the right to pay more, and 4% is a mandatory minimum wage along with other compensation.
Types of benefits
If the 3rd hazard grid at work is established, employees are entitled to a number of special benefits and this fact does not depend on the specific subclass. The following guarantees can be considered the main ones:
- Reduction of working hours to 36 hours. Everything worked above is considered overtime and is paid separately.
- Additional week's vacation.
- Increased allowances.
- Early retirement.
- Regular medical examinations at the expense of the company.
- Issuance of personal protective equipment.
There are other benefits associated with a specific type of activity and negative impact.
Compensation payments and guarantees
Let's talk about the benefits that employees are entitled to if the production level is set to the third or higher level of harmfulness. All payments and guarantees are assigned after the SOUT commission. Based on the results of the work of the special commission, a statement and map are drawn up, which describes the current assessment of working conditions of class 3. It is this document that becomes the basis for assigning compensation.
Shorter working day
A standard week of work according to the labor code is 40 hours. But if health hazards are identified at work, shifts can be reduced to 36 hours a week. This does not mean that all employees will necessarily change their work schedule.
By agreement with management, it may remain the same, but in this case, all extra hours must be paid overtime. It is important to note that the final decision on whether to agree to work the usual 40 hours, but for additional pay, is made primarily by the employee. He cannot be fired for refusing to work overtime.
Additional leave
If the production conditions are 1st degree 3rd class or with a higher subclass, employees have the right to increased annual leave. Its duration is at least one week. If the employer provides more additional days of rest, some of them can be replaced with monetary compensation. And again, it is important to note that replacing vacation with payment is allowed only with the consent of the employee. If it is fundamentally important for him to use all available weekends, he has the right to do so.
Right to retire early
This right is granted to employees if their work activities comply with three provisions:
- Negative impacts from external factors are experienced at least 80% of the time spent at the workplace.
- The total length of service in a job where the hazard class is 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 or more is at least 12 years.
- The name of the profession corresponds to the qualification directory of managers.
If there are no contradictions, you can retire at 55 for men and at 50 for women. The right is granted to employees of the railway, geological exploration, logging industry and some other areas.
Hazardous working conditions
The general list of circumstances that have a negative impact on the health and performance of employees includes:
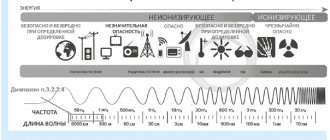
- Excessive concentration of dust in the rooms where the work process takes place.
- Poor lighting.
- Excessive noise level.
- Radioactive radiation.
- High humidity and air temperature.
- Prolonged interaction with chemical or toxic substances, bacteria.
Persons who experience the negative impact factors listed above in the workplace are entitled to special benefits and compensation, which we will discuss below.
Distribution of food rations for treatment and prophylactic purposes
Subclass of hazard (harmful working conditions) 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 and higher guarantees employees who experience negative impacts, therapeutic and preventive food from the enterprise. It includes products designed to improve health and reduce the likelihood of developing occupational diseases.
A complete list of rations is developed by the trade union and approved by the manager. It often includes milk and dairy products. They are the ones who can minimize the impact of toxins, bacteria, radiation, and chemicals. Every employee who works in hazardous conditions for at least half of their shift has the right to receive rations.
Periodic medical examinations
As mentioned earlier, due to the high risk of developing occupational diseases of varying severity, persons working in an environment corresponding to work class 3.2 and higher must undergo regular medical examinations. If it reveals changes in health status, treatment is prescribed according to one of three types:
- Outpatient – on the basis of a clinic collaborating with the enterprise.
- Inpatient - in a hospital.
- Sanatorium-resort - on the basis of a medical sanatorium collaborating with the enterprise.
The frequency of examinations depends on the type of negative impacts, but at least once a year. The list of doctors conducting a medical examination may also change, but usually it includes a therapist, neurologist, psychotherapist, narcologist, urologist/gynecologist, and surgeon. If an employee has discovered health problems, he can undergo the test unscheduled.
Additional payment for harmful effects: what to expect in connection with the new law?
08/21/201509/06/2018 17:17 Labor consultant
Despite technological equipment being improved every year, it is impossible to completely eliminate all risk factors for specialists in the workplace. This circumstance obliges employers to take measures to compensate for the harm caused to the human body. One of these measures is additional payment for hazardous working conditions.
On January 1, 2014, a new law N 426-FZ came into force, regulating the assessment of the state of the working atmosphere of employees. The concept of workplace certification (AWC) ceases to exist. Special assessment of working conditions or SOUT - this is what is now called a set of measures to identify the negative impact of labor process factors on the health of workers. However, the results of institutions that certified their workplaces before 2014 are valid for five years. The same period is set for a special assessment of working conditions.
Degree of hazardous production
If, according to the results of the SOUTH, the levels of the negative influence of production factors are higher than the permissible standard values, the working conditions are characterized as harmful. In this case, the labor code provides for a number of social guarantees for employees forced to work in unsafe workplaces. This point must be fixed in the employment contract without fail.
According to Art. 14 of the Federal Law, the degree of hazard is classified depending on the level of negative impact of the harmful component in the workplace as follows:
| Classification of working conditions | |
| Optimal working conditions | working conditions under which there is no exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors on the employee or the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions and accepted as safe for humans, and the prerequisites are created for maintaining a high level of employee performance . |
| 1 class | |
| Acceptable working conditions | working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, the levels of exposure of which do not exceed the levels established by the standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, and the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored during a regulated rest or by the beginning of the next working day (shifts). |
| 2nd grade | |
| Harmful working conditions | working conditions under which the levels of exposure to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors exceed the levels established by standards (hygienic standards) of working conditions, including: |
| 3rd grade | 3.1 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, after exposure to which the altered functional state of the employee’s body is restored, as a rule, with a longer cessation of exposure to these factors than before the start of the next working day (shift), and the risk of health damage increases; |
| 3.2 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or occupational diseases of mild severity (without loss of professional ability ), arising after prolonged exposure (fifteen years or more); | |
| 3.3 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during the period labor activity; | |
| 3.4 working conditions under which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure of which can lead to the emergence and development of severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general ability to work) during the period of work. | |
| Hazardous working conditions | working conditions in which the employee is exposed to harmful and (or) hazardous production factors, the levels of exposure to which during the entire working day (shift) or part of it can create a threat to the life of the employee, and the consequences of exposure to these factors cause a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease in period of working activity. |
| Class 4 | |
At the same time, the hazard class can be reduced by one step by providing employees with modern certified personal protective equipment.
Requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for organizations
The specifics of the work process, payment calculations and pension contributions, as well as the specifics of providing leave to employees engaged in hazardous work, are regulated by Articles 219, 92, 117, 147 of the Labor Code. Since the entry into force of the law on labor protection on January 1, 2014, corresponding changes have been made to the labor code.
First of all, the employer must include the degree of harmfulness of production, as well as compensation and guarantees in the employment contract. If this has not been done previously, after a special assessment, an additional agreement is concluded with employees, containing information about working conditions and benefits provided. The company's management must take care not only of the regular implementation of SAL, but also of timely amendments to employee employment contracts. Otherwise, the question may arise about the legality of providing certain payments and carrying out work activities.
The right to increased wages, according to Art. 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, have all employees employed in production with a hazard and/or hazard class of 3 (3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4) or 4. The minimum percentage of salary increase for such categories is 4% of the same type of work with normal conditions.
In this case, the employer has the right to increase the interest rate in accordance with the terms of the collective agreement. This amount is considered part of the salary, not compensation as such, and is therefore taxed equally.
Why should an employer pay extra?
This salary supplement is one of the social measures to support workers, designed to compensate for the damage caused to human health by harmful technological processes. Along with the additional payment, employees may be provided with other benefits: an increase in the number of days of annual leave, a reduction in the length of the working day or week, early retirement, provision of employees with dairy products and therapeutic and preventive nutrition, etc. The assignment of appropriate guarantees and compensation is made on the basis of labor legislation and the provisions of the collective agreement, the amount of payments and the right to additional benefits depend on the level of hazardous production and are indicated in the employment contract.
More information about therapeutic and preventive nutrition can be found in the article “Special nutrition when working in hazardous working conditions”
Calculation of allowance for hazardous working conditions
Government Decree No. 870 of November 20, 2008 established the minimum bonus rate for employees working in a harmful or dangerous environment; its amount is 4%. After a special assessment, it may be increased. In production, as a rule, provisions for additional payments are included in the collective agreement. When calculating the bonus, the trade union can be guided by the following scheme.
The procedure for determining the amount of additional payment
Due to the lack of modern regulatory documents regulating this area of labor relations, it is customary to use the Standard Regulations on the Assessment of Working Conditions dated October 3, 1986 as the basis for calculating the premium for harmfulness.
- Determination of the hazard class by comparing the maximum permissible values with real indicators of the hazards of production.
- Converting classes to points. According to Appendix N2 of the Model Regulations, the following points correspond to hazard class 3
| Harmful working conditions. Class 3 | ||
| Class 3.1 | Class 3.2 | Class 3.3 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
Subclass 3.4 was first mentioned in 1994 and therefore does not appear in the table. It is logical to assume that it corresponds to 4 points.
Organizations that have introduced hazard class 4 need an emergency set of measures to reduce the negative impact of production factors or reduce the time of such impact.
- Determining the time of exposure to a negative factor. The amount of the premium is determined based on the time of actual stay under the harmful influence of a particular factor.
- Establishing the amount of additional payment for harmfulness. When calculating the interest rate, the sum of all unfavorable factors is taken into account. Clause 1.6 of the Standard Regulations is usually taken as a guideline when calculating
| Working conditions | Actual sum of points according to the degree of harmfulness | Amount of additional payment as a percentage of salary |
| Heavy, harmful | 4 | |
| 2.1-4.0 | 8 | |
| 4.1-6.0 | 12 | |
| Particularly heavy, particularly harmful | 6.1-8.0 | 16 |
| 8.1-10.0 | 20 | |
| >10 | 24 |
In what cases can compensation for harm be cancelled?
A company that has implemented a set of measures to reduce the negative impact of production factors to an acceptable level is exempt from the obligation to pay surcharges for harmful effects. Such measures include, first of all, the improvement of technological equipment and the provision of employees with personal protective equipment that reduces the harmful effects of harmful components.
If, as a result of the reorganization, the harmfulness was not completely eliminated, but its class was lowered, the employer has the right to reduce the percentage of compensation contributions. Cancellation of the surcharge is also possible in the event of an increase in one or another harmfulness coefficient. The amendments made to the Federal Law in January 2014 imply an increase in the lower limit of acceptable values when assessing the harmfulness of production, as a result of which many workers in the industrial and chemical sector may lose additional accruals. At the employee’s initiative, an appeal may be filed with the inspection body with a request to review the results of the inspection.
According to Law N 426-FZ, organizations are required to provide data on the implementation of special assessments or workplace certification completed before January 2014 to the unified information system for recording inspection results by January 1, 2021.
Is compensation possible in money?
Some types of guarantees and benefits may be replaced by monetary compensation, in particular, the additional vacation discussed earlier or a food package. But given the difference in wholesale and retail prices, inflation and other economic features, choosing a therapeutic and prophylactic ration turns out to be more profitable, so it is rarely refused. Compensation is assigned once a month (if we are talking about products) or once a year (instead of vacation) upon the written application of the employee.
Do you want to implement “Store 15”? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted.
How to reduce the occupational hazard class
Some types of activities do not allow reducing the degree of harm from being in the workplace, for others it is enough to follow simple rules: provide employees with certified personal protective equipment and monitor their mandatory use during work.
In any case, the decision to change will be made by the next commission, but it cannot differ from the previous one by more than one subclass. To achieve an even more serious reduction, you will have to contact the territorial department of sanitary and epidemiological surveillance, and whether it will be positive is unknown.