Wage
The minimum wage was increased to 9,489 rubles
The minimum wage (minimum wage) from January 1, 2018 from 7,800 rubles was increased to 9,489 rubles (Federal Law of December 28, 2021 No. 421-FZ “On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation in terms of increasing the minimum wage to subsistence level of the working-age population"). This amount is 1,689 rubles more. (9489 rub. – 7800 rub.).
The calculation of many payments depends on the new minimum wage, including temporary disability benefits, maternity benefits, child care benefits for up to 1.5 years, as well as numerous social benefits, the amount of which is tied to the minimum wage. See “Minimum wage rate from January 1, 2021.” In this article we will also talk about the new amounts of payments calculated from the new minimum wage.
The minimum wage is established simultaneously throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation by federal law and is mandatory for all organizations and individual entrepreneurs using hired labor. The amount of the minimum wage is regulated by Art. 1 of Federal Law No. 82-FZ of June 19, 2000 “On the minimum wage.”
The minimum wage will be gradually equalized to the subsistence level
From 2021, a gradual increase in the minimum wage to the subsistence level will begin.
The subsistence minimum is the minimum level of income that is considered necessary to ensure a certain standard of living in Russia. This is the cost of a conditional consumer basket.
The cost of living is usually established based on the results of the past period, which is why the formulation “per quarter” is used. For the second quarter of 2021, the cost of living in Russia as a whole is set at the following levels: per capita 10,329 rubles, for the working population - 11,163 rubles, pensioners - 8,506 rubles, children - 10,160 rubles.
It is planned to increase the minimum wage in two stages:
- from January 1, 2021;
- from January 1, 2021.
As a result, from January 1, 2021, the minimum wage is equal to the subsistence level. Moreover, they will take the value for the second quarter of the previous year.
From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage will increase to 9,489 rubles - this is 85 percent of the subsistence level of the working population for the second quarter of 2021. It will reach one hundred percent from January 1, 2021. It is expected that in 2021 the minimum wage will be 11,598 rubles, in 2021 - 11,946 rubles. Thus, the minimum wage for 2018–2020 will increase by 53 percent.
From January 1, 2021, wages need to be increased
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a guaranteed minimum wage to which an employee has the right to claim. In accordance with Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked the required working hours during this period cannot be lower than the minimum wage
From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage will be increased to 85% of the subsistence level and will be 9,489 rubles per month. Accordingly, from January 1, 2021, an employer paying its employees the minimum wage is obliged to increase it to new values.
Sometimes the employer is also not required to adhere to the minimum wage. This is, for example, part-time work (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and part-time work (Article 284 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In relation to such employees, the employer is not obliged to draw up any additional agreements in connection with an increase in the minimum wage.
In all other cases that are not directly specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employers cannot pay their employees wages below the minimum wage. Otherwise, they may be held accountable under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The fine for paying wages below the minimum wage for legal entities ranges from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. Repeated violation will increase the fine to 70,000 rubles.
Wage indexation from 2021: mandatory or not?
Many HR specialists have heard that starting from 2021, employers will be required to annually index the wages of their employees. Is it true?
Indeed, there is a bill in the State Duma that would provide for the indexation of earnings once a year in connection with rising consumer prices for goods and services. The indexation amount must not be lower than the inflation rate in a particular region. However, this bill has not yet been approved.
However, despite this, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, ensuring an increase in the level of real wages already includes wage indexation in connection with rising consumer prices for goods and services. State bodies, local governments, state and municipal institutions index salaries in the manner established by labor legislation. The government has planned to index the wages of employees of federal government institutions by 4 percent: in 2021 - from January 1, in 2021 and 2021 - from October 1. Funds are provided in the federal budget.
At the same time, commercial companies and individual entrepreneurs index salaries based on collective agreements, agreements, and local regulations. If such documents do not say anything about mandatory indexation since 2018, the employer is not obliged to index earnings.
Keep in mind that the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its Ruling dated November 19, 2015 No. 2618-O noted that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not allow an employer not related to the public sector to evade salary indexation. Indexation is aimed at ensuring an increase in the level of real salary content and its purchasing power. By its legal nature, indexation is a state guarantee of remuneration for workers and must be provided to all persons working under an employment contract. Thus, the employer should not shy away from increasing wages.
However, the legislation does not establish the exact amount of indexation. Therefore, the indexation amount is determined at the discretion of the employer, taking into account the opinion of the trade union. The employer is not required to apply the official inflation rate.
Indexation for public sector employees from January 1, 2021
Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2017 No. 2716-r provides for an increase in wages for public sector employees. According to the order, from January 1, 2021, wages of workers in the public sector of the economy employed in federal institutions will be increased by 4%.
This increase applies to all federal institutions - autonomous, budgetary and state-owned. Such institutions are taken away, including institutions of the social sphere and science, forestry, hydrometeorological service, veterinary medicine, employment services and others.
The basis of the working relationship
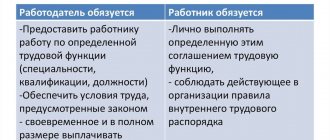
An employment contract is part of the system of legal documentation of an enterprise, which regulates the professional relations of the subjects - the subordinate and the employer. The regulatory framework at the federal level (primarily the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the internal documents of the organization itself regarding the performance of labor functions by an employee on the basis of a contract form a single set of legal documents. In this system, the employment contract occupies a central position, since it:
- regulates the relationships and obligations of the parties, their functionality, rights, responsibilities;
- establishes legal and socio-economic guarantees;
- includes mandatory terms of the employment contract .
Usually, when hiring personnel for vacancies, preparations for concluding and drawing up an employment contract are carried out by the personnel service.
The contract in question, in accordance with the provisions of Art. 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is concluded in writing, at least in 2 copies and certified by the signatures of the parties. One copy is given to the employee, and the other copy is placed in the employee’s personal file and kept in a separate folder by the employer.
In case of violations with the execution of the employment agreement in parts 3 and 4 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes administrative measures. Up to large fines for the enterprise - up to 100,000 rubles. Therefore, the employer, whether a legal entity or an individual, is obliged to control:
- the correctness of the procedure for concluding the main labor agreement (and its very existence!);
- compliance of its content with the requirements established by law (as the mandatory conditions of the employment contract are defined in it).
Thus, the document must include the mandatory information established by the Labor Code and all other legally significant positions that the parties agreed upon in the process of preparing for signing.
Special assessment of working conditions
Employers must complete a special assessment of working conditions by the end of 2018. According to Part 6 of Article 27 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions,” all employers must, as a matter of priority, conduct a special assessment in workplaces with dangerous and harmful production factors. At all other workplaces, including office ones, it is allowed to conduct a special assessment in stages. However, the last stage must be completed no later than December 31, 2021. Thus, all companies and individual entrepreneurs that have hired employees are required to conduct a special assessment in 2021, and based on its results, indicate the class of working conditions in employment contracts
Is a contract invalid if it does not contain mandatory conditions?
Missing mandatory clauses of the 2021 employment contract do not make it invalid. The missing information is entered directly into the text of the contract, and the missing conditions are stated in the annexes to the contract, which will become its integral parts. Even if there are no separate provisions in the contract, the parties must still fulfill their obligations in accordance with the provisions prescribed by law.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Checks
From 2021, labor inspectors will begin coming to inspections with questionnaires
From January 1, 2021, checklists will be used during routine inspections of employers. The questionnaires contain a closed list of questions for the company. Note that at first the new rules will only affect companies that have been assigned a moderate risk class by Rostrud. And from July 1, 2021, this procedure will be extended to all employers. Reason: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 8, 2017 No. 1084. Anyone can get acquainted with the questions and understand what exactly interests the inspectors. And the “Electronic Inspector” on the online inspection.rf website will allow you to undergo a virtual check and understand your weaknesses (Order of Rostrud dated November 10, 2017 No. 655).
What's new
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 27, 2021 No. 858 introduced a standard form of employment contract for small businesses (Article 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is valid from January 1, 2021 simultaneously with the corresponding changes to the Labor Code.
For more information about this, see “Standard employment contract: who, why and when can conclude it.”
This averaged document is intended to:
- optimize HR records management for small business owners;
- introduce common standards for documentation on issues of legal regulation of labor activities.
This one is on our website.
Since 2017, the employer is not required to adopt internal regulations on certain labor issues. They will be replaced by the specified standard labor agreements, which already include all the mandatory terms of the employment contract and a number of additional conditions, issues of remuneration, social protection, etc.
Note that the innovation affects enterprises and merchants:
- with no more than 15 employees;
- with an annual volume of financial revenues not exceeding 120 million rubles.
For personnel hired after January 1, 2021, the new contract format is mandatory. And for previously hired employees, you will have to adjust the contracts with them through additional services. agreements.
For more information about this, see “Local regulations from 2021: changes to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.”
We also note that the conclusion of employment contracts with state and municipal employees is regulated by special federal laws. Therefore, the mandatory terms of an employment contract in 2021 may have their own characteristics for them.
The employment contract must comply with the requirements of Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. All its conditions can be divided into 3 categories:
- which you cannot do without;
- additional conditions;
- details and data of the parties (employer and employee).
Employment contracts
From 2021, it is planned to make another change to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, requiring the employer to include in the employment contract a condition for moving to seasonal work, if necessary to fulfill the employee’s job duties. The Ministry of Labor has prepared the corresponding changes to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The document was published on regulation.gov.ru.
Changes to Article 294 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation will affect employees who move for seasonal work to another area. They stipulate that the employment contract with a seasonal worker moving to work in another area must stipulate the conditions associated with such a move and return to the place of residence upon expiration of the contract and its early termination. If these conditions are included in the employment contract, the employer is obliged to reimburse the costs associated with the employee’s relocation from another area to the place of seasonal work and return to the place of residence. Specific amounts and procedures for reimbursement of expenses may be established by a collective agreement or local regulation, or by agreement of the parties.
Foreign workers: quotas reduced from 2021
The Government of the Russian Federation, by its Resolution No. 1467 dated December 4, 2021, approved quotas for foreign labor in organizations engaged in certain types of activities for 2021.
In particular, the quota for other land passenger transport (code 49.3), as well as road freight transport (code 49.41), was reduced from 30 to 28% of the total number of personnel. The remaining indicators remained at the 2021 level.
By January 1, employers whose number of foreign employees exceeds the new figures must correct this. Let us remind you that there is a special basis for dismissing workers in such a situation - paragraph 9 of Article 327.6 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For organizations, violating the permissible share of foreign workers can result in a fine of 800 thousand to 1 million rubles. or suspension of activities for a period of 14 to 90 days. Officials face a fine of 45 thousand to 50 thousand rubles.
It was allowed not to include provisions for issuing soap to employees in employment contracts
From June 12, 2021, Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated November 23, 2017 No. 805n comes into force. They made changes to the procedure for providing workers with flushing or neutralizing agents.
Let us remind you that the standard norms for issuing and the standard for providing workers with flushing and neutralizing agents were approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated December 17, 2010 No. 1122n. The new amendments stipulate that the standards for issuing flushing or neutralizing agents that correspond to the working conditions at the employee’s workplace are specified in the employee’s employment contract or in the employer’s local regulations. At the same time, they are brought to the attention of the employee in written or electronic form in a way that allows confirming the employee’s familiarity with these standards.
Previously, it was stipulated that the standards for issuing flushing and neutralizing agents were specified only in the employee’s employment contract.
How and by whom is an Employment Contract signed?
The document is prepared in two identical copies for both parties; this rule is enshrined in Art. 67 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The employment contract must be signed by the employee, as well as by the employer or an authorized person. Who can sign a document for an employer is listed in Part 6 of Art. 20 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Note! If the Charter stipulates the presence of a seal, then the agreement must be sealed with the seal of the enterprise. If the organization does not have a seal, then there is no need to put any seal on the contract.
The employee’s signature on the employer’s copy confirms that he took the second copy of the Employment Agreement for himself.
Occupational Safety and Health
Approved rules for the protection of objects and (or) property
By order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 28, 2017 No. 601n, it approved the rules for labor protection when carrying out security (protection) of objects and property. They apply from 17 February 2021.
The rules determine state regulatory requirements for labor protection when protecting objects and property by employees of legal entities with special statutory tasks, departmental security, as well as private security organizations.
The specified requirements are mandatory for implementation by employers - legal entities, regardless of their organizational and legal forms when they protect objects and property.
The employer is obliged to provide:
- carrying out work to protect objects in accordance with the requirements of the Rules, other regulatory legal acts containing state regulatory requirements for labor protection, and technical (operational) documentation of the manufacturing organization;
- conducting training of workers on labor protection and testing knowledge on labor protection;
- monitoring compliance by employees with labor safety instructions.
The order of the Russian Ministry of Labor approved:
- labor protection requirements when inspecting vehicles;
- labor protection requirements when inspecting trains, shunting convoys, locomotives, wagon couplings and cargo transported on them, as well as when escorting vehicles with protected cargo;
- labor protection requirements when implementing the protection of artificial structures.
Labor function of the employee
This clause of the contract specifies the employee’s profession and the position he will occupy. The position title is indicated exactly as it is written in the staffing table. If the enterprise has employees who have the right to professional compensation, benefits or restrictions, then the names of their positions, as well as professions or specialties, are indicated in strict accordance with the qualification directories of the EKS and EKSD. An employer cannot require his subordinates to perform duties that are not specified in the contract (Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Benefits
New rules for indexing child benefits have come into effect
In 2021 and subsequent years, child benefits must be indexed annually from February 1, the coefficient is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. A similar procedure was temporarily introduced for 2016 and 2021.
Indexation applies to the following benefits paid by the employer:
- a one-time benefit for women who registered in the early stages of pregnancy;
- lump sum benefit for the birth of a child;
- monthly child care allowance.
Permanent indexation rules were introduced by Federal Law No. 444-FZ of December 19, 2016.
From February 1, 2021, child benefits will be indexed by 1.025
From February 1, 2021, benefits will be indexed by a factor of 1.025 (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 26, 2018 No. 74 “On approval of the amount of indexation of payments, benefits and compensation in 2021”).
Payments are increased by the price growth index for the previous year (Federal Law dated December 19, 2016 No. 444-FZ). To calculate the benefit, the base amount is multiplied by the indexation coefficients for all years. Benefits will increase by 2.5 percent in 2021.
| Benefit | Size, rub | |
| Until February 1 | From February 1 | |
| One-time benefit for the birth of a child | 16 350,33 | RUR 16,759.09 |
| Minimum monthly allowance for caring for the first child | 3065.69 (including the minimum wage - 3120) | RUB 3,795.60 |
| Minimum monthly allowance for caring for the second and subsequent children | 6131,37 | 6284.65 rub. |
| One-time benefit for registration in the early stages of pregnancy | 613,14 | RUB 628.47 |
The amount of benefits in connection with a work injury has been established for 2018
Federal Law No. 417-FZ dated December 19, 2016 established the maximum amount of monthly benefits in connection with an industrial injury. In 2018, the amount was 75,182 rubles.
Introduced monthly payment for the birth of the first child
Russian President V. Putin decided, starting from 2021, to pay a monthly allowance for the first child until he reaches the age of 1.5 in the amount of 10,523 rubles. For more details, see “ Monthly payment for the birth of the first child .”
Annual report SZV-STAZH
The SZV-STAGE form is a report on the pension experience of employees, which is usually submitted to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation at the end of the year. The SZV-STAZH form is submitted by organizations and entrepreneurs who pay remuneration to individuals:
· under employment contracts;
· civil contracts for the performance of work or provision of services;
· copyright agreements and licensing agreements.
This is stated in paragraph 1.5 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Board of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation dated January 11, 2021 No. 3p. The SZV-STAZH form is submitted at the end of the year. The deadline is no later than March 1 of the following year. This form must be submitted for the first time for 2017, no later than March 1, 2021 (Clause 2, Article 11 of Law No. 27-FZ of April 1, 1996). Organizations submit SZV-STAZH to the territorial branches of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation at their place of registration. Entrepreneurs - at the place of residence (Clause 1, Article 11 of the Law of April 1, 1996 No. 27-FZ).
Notification of changes in the essential terms of the employment contract
If it is necessary to change some provisions of the employment document, it is important to notify the employee about this. The employer does not have the right to do this on his own. To draw up a notification according to all the rules, you need to know its features. The structure of the notice should include:
- Name of the company, personal data and position of the employee;
- Number of the working agreement, date of writing the notification;
- The reasons and essence of the changes and the date when they will become effective;
- It is obligatory to offer the subordinate other options in case of his disagreement.
It is important to pay attention to the notice period and the need for written confirmation from the subordinate.
ARTICLES 56-84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Insurance premiums
Increased income limits for calculating insurance premiums
In 2021, the base for calculating insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund (in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity) will be 815,000 rubles, and the base for calculating contributions to the Pension Fund at the “regular” rate is 1,021,000 rubles. This is provided for by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2017 No. 1378.
Let us remind you that for income exceeding the maximum base value, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are not charged, and contributions to the Pension Fund are paid at a rate of 10%, not 22%. As for “medical” contributions to the Federal Compulsory Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, a maximum base value is not established for them; therefore, these contributions are paid from all taxable payments. Those who have the right to apply reduced tariffs accrue pension contributions until in 2018 the amount of payments to an employee exceeds the maximum base value - 1,021,000 rubles.
Insurance premium rates have been retained until 2021
The tariffs for pension, medical and insurance contributions for temporary disability and in connection with maternity will not change in 2021 (Federal Law No. 361-FZ of November 27, 2017). So, if an organization does not have the right to use reduced tariffs, then in 2017 it must charge contributions at the basic tariffs. They are listed in the table:
| Type of contributions | Base in 2021 | Rate within the base | Rate over base |
| Pension | RUB 1,021,000 | 22% | 10% |
| For social insurance in case of temporary disability and maternity | 815,000 rub. | 2,9 % (1,8 %) | |
| Medical | Not installed | 5,1 % | |
The general contribution rate in 2021 is still 30% (Articles 425, 426 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 22% – for pension insurance;
- 5.1% – for health insurance;
- 2.9% - for social insurance. In this case, the amount of contributions to be paid depends on whether the income exceeded the established limit or not.
The 30% rate will be valid until 2021 inclusive (Articles 425, 426 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The extension of the tariff is provided for by Federal Law No. 361-FZ dated November 27, 2017.
Changes for microenterprises in 2018
Some changes also affected the employment contracts of those individual entrepreneurs who, according to the Federal Tax Service, were included in the state register of small and medium enterprises in the status of a micro-enterprise. It should be remembered that the Federal Tax Service enters information into the register independently, without notifying the individual entrepreneur, so it is recommended to periodically check the status of your enterprise in the register.
The law provides for the minimum maintenance of personnel records for microenterprises. At the same time, the main document regulating the legal relationship between the employer and the employee has become the employment contract, which provides for all aspects of the employee’s work activity - the amount of wages, the amount of compensation and bonuses, guarantees and insurance cases.
In 2021, due to widespread refusals to maintain internal business documentation in individual entrepreneurs and micro-enterprises, it became mandatory to draw up a standard agreement developed back in 2021. It is distinguished by the most complete compliance with the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and, in fact, replaces many acts of personnel documentation, which micro-enterprises, by virtue of a standard agreement, will be able to refuse. A template for a standard contract can be found freely available on the Internet. In particular, additional orders on wages, internal regulations, labor protection, shift work, etc. will become unnecessary. Also, the standard contract will replace many job descriptions that burdened the documentation of small businesses.
Important! The introduction of a standard contract at a micro-enterprise and the refusal to maintain personnel documentation is formalized by order of the manager.
Personal income tax
Changed personal income tax taxation of material benefits from savings on interest on loans
From January 1, 2021, situations have been established where personal income tax will be imposed on material benefits received by an individual from savings on interest for the use of borrowed (credit) funds:
Material benefits from savings on interest on loans (loans), as a general rule, will be subject to personal income tax if at least one of two conditions is met in relation to such savings:
| № | Condition |
| 1 | The loan (credit) was received from an organization or individual entrepreneur that is recognized as an interdependent person of the taxpayer or with which he has an employment relationship. |
| 2 | Savings are actually material assistance or a form of counter-fulfillment by an organization or individual entrepreneur of an obligation to the taxpayer, including payment (remuneration) for goods supplied by it (work performed, services rendered). |
According to the new rules, from 2021, benefits from savings will be subject to personal income tax if the borrower received money at an interest rate of less than 2/3 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Reason: Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 333-FZ. Until 2021, personal income tax had to be calculated if a company gave a loan (loan) at a low interest rate to any “physicist”, and not just to an interdependent one (clause 1 of Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From January 1, 2021, we recommend that you find out whether the borrower is dependent before issuing a loan. For example: a dependent company is a company and a founder who owns a share of more than 25% in the authorized capital (clause 5 of Article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The date of receipt of income upon debt forgiveness has been clarified
If an organization forgives a debt to an individual, then he receives income (economic benefit) in the form of the amount of the forgiven debt (Clause 1, Article 41 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Such income is recognized as an object of taxation and is taken into account when determining the tax base for personal income tax (clause 1 of article 209, clause 1 of article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of receipt of income upon debt forgiveness is the date the debt is written off from the organization’s balance sheet (subclause 5, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). From January 1, 2021, this norm is being clarified: it is necessary to determine income as of this date only if the company is interdependent in relation to the citizen. Reason: Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ. It turns out that if there is no fact of interdependence, then income for the purpose of paying personal income tax will not arise.
An organization as a tax agent is obliged to calculate, withhold from an individual and pay personal income tax to the budget on the amount of income received (clauses 1, 2 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Compensation to defrauded shareholders was exempted from personal income tax
From January 1, 2021, Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been supplemented with provisions that exempt from personal income tax the amount of compensation to participants in shared construction from the Fund for the Protection of the Rights of Citizens - Participants in Shared Construction, formed in accordance with Federal Law No. 218-FZ of July 29, 2017. Such compensations are also commonly referred to as payments in favor of “defrauded shareholders.” They are relied upon in case of bankruptcy of developers. Reason: Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 342-FZ.
We established a deflator coefficient for calculating the value of a patent for foreigners - 1.686
The personal income tax deflator coefficient increases the fixed personal income tax advance that a foreigner pays to obtain and renew a work patent. The basic fixed payment is 1200 rubles. It is multiplied by the deflator coefficient, as well as by the regional coefficient (clause 3 of Article 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Taking into account the new deflator coefficient, the fixed advance in 2018 will be 2032.2 rubles (1200 rubles × 1.686). However, the final amount depends on the coefficient of a particular subject of the Russian Federation.
In 2021, the minimum payment per month was 1816.8 rubles. (RUB 1,200 × 1,514).
In 2021, the employing company has the right to reduce personal income tax on a foreigner’s income by fixed payments if the employee writes an application and the Federal Tax Service issues a special notice to the organization (clause 6 of Article 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It has become clear to whom to submit 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL during reorganization
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has established provisions on who must submit 2-NDFL certificates and 6-NDFL calculations when reorganizing a company. From 2018, regardless of the form of reorganization, the successor will be required to file 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL for the reorganized legal entity, if it does not do so itself. If there are several legal successors, then the obligation of each of them will need to be determined based on the transfer deed or separation balance sheet (new paragraph 5 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Reason: Federal Law of November 27, 2017 No. 335-FZ.
Previously, experts disagreed: some believed that this responsibility lay with the reorganized company, while others believed that this responsibility lay with the legal successor.
A new certificate 2-NDFL is being introduced
The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation has developed a new form for a certificate of income of an individual (certificate 2-NDFL).
The current form of the 2-NDFL certificate was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/485. This form is subject to change. They are necessary to ensure that, during reorganization, the legal successors of the tax agent can provide information on the income of individuals. For these purposes, in section 1 “Data about the tax agent” of the certificate, a new field “Form of reorganization (liquidation)” was provided, where the corresponding code (from 0 to 6) will be indicated, as well as the field “TIN/KPP of the reorganized organization”.
Changes to the procedure for filling out the 2-NDFL certificate provide that the legal successor of the tax agent will indicate in the certificate the OKTMO code at the location of the reorganized organization or a separate division of the reorganized organization.
If 2-NDFL is submitted by the legal successor of a reorganized organization, in the “Tax Agent” field you will need to indicate the name of the reorganized organization or a separate division of the reorganized organization.
From Section 2 “Data about an individual – recipient of income”, fields related to the address of residence are excluded. Also, section 4 of the 2-NDFL certificate excludes investment deductions from tax deductions.
The new form 2-NDFL will need to be submitted to the Federal Tax Service starting with reporting for 2021.
There are now more income and deduction codes for 2-NDFL certificates
Since 2021, new income and deduction codes have appeared that need to be recorded in 2-NDFL certificates (Federal Tax Order No. MMV-7-11/820 dated October 24, 2017), namely:
| Revenue code | Decoding |
| 2013 | Amount of compensation for unused vacation |
| 2014 | The amount of payment in the form of severance pay, average monthly earnings for the period of employment, compensation to the manager, deputy managers and chief accountant of the organization in the part that generally exceeds three times the average monthly salary or six times the average monthly salary for dismissed workers from organizations in the Far North and similar areas |
| 2301 | The amounts of fines and penalties paid by an organization on the basis of a court decision for failure to comply with consumer requirements in accordance with the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300- |
| 2611 | The amount of bad debt written off from the organization’s balance sheet |
| 3021 | The amount of income in the form of interest (coupon) on circulating bonds of Russian organizations denominated in rubles |
Also, starting from 2021, a new deduction code “619” will appear. It will correspond to the amount of positive financial result that was obtained from transactions on an individual investment account (IIA).
Compensation, severance pay, fines and penalties previously did not have separate income codes. They were shown in 2-NDFL certificates with code 4800 “Other income” (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 19, 2016 No. BS-4-11/17537).
A new form 6-NDFL is being introduced
The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation has prepared a draft with amendments to the 6-NDFL calculation form, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 14, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/450. The text of the draft order was published on the Unified portal for posting draft legal acts.
The amendments change the cover page of the calculation form and also change the bar code “15201027” to the bar code “15202024”. Here's what else is changing:
- the largest taxpayers will indicate the TIN and KPP at the location of the organization as in the certificate of registration with the Federal Tax Service at the location (5th and 6th category of KPP - “01”);
- The successor organization will submit to the Federal Tax Service at its location 6-NDFL for the last submission period and updated 6-NDFL for the reorganized organization (in the form of affiliation, merger, division, transformation) with an indication on the title page in the column “at the location ( accounting) (code)" code "215". In this case, at the top of the title page it will be necessary to record the TIN and KPP of the successor organization;
- in the “tax agent” field you will need to show the name of the reorganized organization or a separate division of the reorganized company.
Registration of labor relations in 2018
From January 1, 2021, an employer who is a small business entity, which is classified as a micro-enterprise, has the right to conclude a standard employment contract with an employee, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation in August 2021 . However, it is not necessary to focus on it. At his discretion, the employer can use his own version of the document or approach the standard form creatively, taking from it only those provisions that are relevant to him, or setting out individual points in his own edition. In this case, an important condition relates to the listing of the parties to the agreement with the individual entrepreneur. Thus, in the employment contract between the individual entrepreneur and the individual entrepreneur there must be a mandatory indication that the agreement is concluded between two individuals with the status of an individual entrepreneur.
An important condition is a legislative ban on contractual clauses that could worsen the position of the parties in comparison with the norms of legislation in the labor sphere. This applies, in particular, to such issues as vacation and its duration, sick pay, frequency of salary payments (according to the law and the standard contract, strictly twice a month), etc.
The form in which the employment contract is concluded must only be written. There can be no talk of any verbal agreements - this is a gross violation of the law.
When applying for a job and concluding an employment contract, you must provide the employer with the following package of documents:
- passport or other identity document;
- certificate of assignment of TIN;
- work book, except for a part-time job;
- SNILS;
- military ID or other military registration document for those liable for military service;
- document confirming the required qualifications, if applicable;
- a certificate of no criminal record or termination of criminal prosecution on rehabilitative grounds for employment in positions for which current legislation requires applicants to have no criminal record;
- a certificate from a drug dispensary for employment in positions for which the law provides for appropriate restrictions.
If a candidate is applying for a job for the first time and has not yet acquired a TIN, the employer must help him obtain one. The same is true with SNILS and a work book during initial employment.
Presentation of a passport by an employee when concluding an employment contract is mandatory
The new employee can begin to perform his official duties even before signing the contract. There is no violation of this if the employer meets the three-day deadline during which he must draw up an employment contract with him. But the start date of the employment relationship in this case will be considered not the date of signing the document, but the actual date of admission to work. However, in practice, contracts in such situations are often concluded retroactively. However, experienced HR specialists recommend issuing a hiring order from the date the employee actually leaves.
If the terms of employment include a probationary period, this must be agreed upon with the candidate before he starts work and reflected in the employment contract and employment order. When an order is issued before the contract is signed, the probationary period provision in it becomes mandatory. Otherwise, it will not be possible to include it in the employment contract.
The following samples will help you cope with the task of drawing up an employment contract:
- standard employment contract (filling example);
- employment contract with a minor employee;
- unlimited contract for 0.5 rates;
- open-ended employment contract with a probationary period.