In 2021 in the Russian Federation, the amount of maternity capital was 466,617 rubles. Parents often spend the certificate to improve their living conditions - they buy a mortgaged home using the funds as a down payment. But what happens to mortgages and maternity capital when an individual goes bankrupt?
Practice in similar cases has already been formed; the Arbitration Courts often consider situations when the case involves an apartment purchased partially with funds from maternal capital.
Alas, we have to admit the fact that maternity capital will not protect a mortgaged apartment and its buyers if they have financial difficulties and can no longer pay their fees. The apartment will be transferred to the bank that issued the loan, and it will sell it at auction.
The same thing will happen if a person with a mortgage in which maternal capital is invested files for bankruptcy. The family is left homeless.
In this article, we will provide the latest judicial practice for 2020, tell you how and in what order such bankruptcy cases are considered, and how to save mortgaged property when debts are written off.
Responsibility for misuse of family subsidies
Responsibility for using maternal capital for purposes other than its intended purpose is regulated by the second part of Article 159 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. This crime is punishable by up to two years of probation.
For someone accused of fraud, everything will depend on the scale of the criminal act and how many people were involved in the criminal scheme.
According to the Department of Economic Crimes, most of the economic crimes investigated in their department relate to fraud with family capital.
The verification of misuse is initiated by the Pension Fund , one of whose departments is responsible for monitoring such cases.
Expert opinion
Korolev Alexander Mikhailovich
Practitioner lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in protecting legal interests.
The fact that any unlawful actions with maternity capital is regarded by the Criminal Code as fraud with significant damage plays against potential fraudsters.
Significant damage, according to the Criminal Code, is equal to an amount of at least 10 thousand rubles. What responsibility for misuse can be incurred if fraud is proven in court?
- Correctional work.
- House arrest.
- Suspended prison sentence.
- Fine.
According to statistics from the same Department of Economic Crimes, suspended imprisonment is most often used.
But these cases are rare and are possible only with very large-scale fraud with cash subsidies.
Maternity capital fraud
There are many fraudulent schemes involving family capital. The most common motive that encourages people to join them by handing over a certificate is legal illiteracy and the desire for easy money.
There are companies that offer to cash out maternity capital for a small amount or even free of charge.
Sometimes real estate firms do this, offering to resell the apartment several times, cashing out the money as a result of several real estate transactions.
Sometimes fraud consists not only of an attempt to cash out or misuse the subsidy, but also of an illegal attempt to obtain a capital certificate.
If a person uses fake documents when applying for maternity capital, and then this is discovered, he will again be judged under Article 159.
Every year, methods for detecting fraud are improving. And although scammers assure young people that there will be no problems with the law, punishment cannot be avoided in most cases.
It is no coincidence that employees of the Pension Fund immediately inform those applying for a subsidy that fraud is very strictly punished by law.
Arbitrage practice
If you look at court decisions in cases related to the misuse of family capital, two interesting facts will emerge:
- Over the past four years, control over the use of MSC funds has increased.
- The Pension Fund, if it needs to win in court, will conduct all the necessary examinations and force them to pay compensation.
Having agreed with a third party to purchase a new home, she, firstly, received a loan for its purchase, and secondly, sent an application for maternity capital.
Expert opinion
Korolev Alexander Mikhailovich
Practitioner lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in protecting legal interests.
After the funds received from the loan were given to third parties, the transaction was closed, and the MSK certificate was used to repay the loan. A week later, citizen K.
I decided to cancel the deal to sell the apartment and get my money back. Thus, the maternity capital funds of citizen K.
were cashed out and then used to buy a car (can MK be used to buy a car?).
This scheme is typical for those wishing to cash out maternity capital. By colluding with third parties and promising them a cash kickback from the transaction, many hope to get easy money. The verdict passed by the court obliged citizen K. to compensate for the damage caused to the Federal Budget.
“Review of judicial practice in cases related to the implementation of the right to maternal (family) capital”; approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on June 22, 2016 (“Bulletin of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation”, No. 12, December 2016)
Approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on June 22, 2021.
REVIEW OF COURT PRACTICE ON CASES RELATED TO THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RIGHT TO MATERNITY (FAMILY) CAPITAL
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation has summarized the practice of consideration by courts in 2014 - 2015 of cases related to the exercise by citizens of the right to maternity (family) capital.
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 39 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation in the Russian Federation, everyone is guaranteed social security by age, in case of illness, disability, loss of a breadwinner, for raising children and in other cases established by law.
Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ “On additional measures of state support for families with children” (clauses 1 and 2 of Article 2) established additional measures of state support for families with children, implemented at the expense of maternal (family) capital and providing these families with the opportunity to improve their living conditions, receive education, social adaptation and integration of disabled children into society, and increase the level of pensions (hereinafter also referred to as additional measures of state support; maternal (family) capital).
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 2 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ “On additional measures of state support for families with children,” a document confirming the right to additional measures of state support is a state certificate for maternity (family) capital.
In 2014 - 2015, the courts resolved the following disputes related to the exercise by citizens of the right to maternity (family) capital:
— on recognizing the right to additional measures of state support and issuing a state certificate for maternity (family) capital;
— on invalidation of the state certificate for maternity (family) capital;
— on the disposal of maternal (family) capital;
- on the division between spouses of property acquired using maternal (family) capital;
— on determining the share of parents and children in the ownership of residential premises acquired using maternal (family) capital, as well as other disputes.
When considering these disputes, the courts, in particular, were guided by:
— the Constitution of the Russian Federation;
— Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ “On additional measures of state support for families with children” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ);
— Rules for filing an application for a state certificate for maternity (family) capital and issuing a state certificate for maternity (family) capital (its duplicate), approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated October 18, 2011 N 1180n;
— Rules for filing an application for the disposal of funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2008 N 779n;
— Rules for allocating funds (part of funds) of maternal (family) capital to improve housing conditions, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 12, 2007 N 862;
— Rules for the allocation of funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital for the education of a child (children) and other expenses related to the education of a child (children), approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 N 926.
A generalization of judicial practice showed that cases related to the exercise by citizens of the right to maternal (family) capital were considered by the courts in the manner of litigation.
Disputes regarding recognition of the right to additional measures of state support
Article 3 of Federal Law No. 256-FZ of December 29, 2006 defines the circle of persons entitled to additional measures of state support.
In accordance with this norm, the right to additional measures of state support arises upon the birth (adoption) of a child (children) who has citizenship of the Russian Federation:
- for women who are citizens of the Russian Federation, who gave birth to (adopted) a second child starting from January 1, 2007; those who gave birth (adopted) a third child or subsequent children starting from January 1, 2007, if they had not previously exercised the right to additional measures of state support;
- for male citizens of the Russian Federation who are the sole adoptive parents of a second, third child or subsequent children who have not previously exercised the right to additional measures of state support, if the court decision on adoption entered into legal force starting from January 1, 2007;
- for men (fathers or adoptive parents of children), regardless of their citizenship of the Russian Federation or the status of a stateless person, if the right of women to additional measures of state support has ceased;
- for minor children and (or) adult children studying full-time in an educational organization (except for the organization of additional education) until the end of such training, but no longer than until they reach the age of 23, if the right of the child’s mother, who is the only parent (adoptive parent) of the child, or the right of the father (adoptive parent) of the child to additional measures of state support has ceased, as well as if the father (adoptive parent) of the child did not have such a right after the termination of the right of the woman who gave birth (adopted) the child.
The right to additional measures of state support in the form of maternal (family) capital arises for the above persons once.
1. The right to additional measures of state support arises if both the woman who gave birth (adopted) the child and the child with whose birth (adoption) the law connects the emergence of this right have citizenship of the Russian Federation on the date of birth (adoption) of the child.
2. The basis for the emergence of the right to additional measures of state support is the birth of two or more children alive.
3. Children in respect of whom a woman was deprived of parental rights, as well as children who were her stepsons (stepdaughters) and subsequently adopted by her, are not taken into account when determining her right to maternal (family) capital.
Disputes regarding the disposal of maternal (family) capital funds
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ, the disposal of funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital is carried out by persons specified in Parts 1 and 3 of Article 3 of this Federal Law, who have received a certificate, by submitting to the territorial body of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation directly or through a multifunctional center for an application for the disposal of funds of maternal (family) capital (hereinafter referred to as the application for disposal), which indicates the direction of use of maternal (family) capital in accordance with the said Federal Law.
In cases where a child (children) has the right to additional measures of state support on the grounds provided for in parts 4 and 5 of Article 3 of Federal Law No. 256-FZ of December 29, 2006, the disposal of maternal (family) capital funds is carried out by adoptive parents and guardians (trustees) or adoptive parents of the child (children) with the prior permission of the guardianship and trusteeship authority or by the child (children) themselves upon reaching the age of majority or acquiring full legal capacity until reaching the age of majority (Part 2 of Article 7 of the Federal Law dated December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ).
An application for disposal may be submitted at any time after three years from the date of birth (adoption) of the second, third child or subsequent children, except for the case provided for in Part 6.1 of Article 7 (Part 6 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 256-FZ).
According to Part 6.1 of Article 7 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ, an application for disposal can be submitted at any time from the date of birth (adoption) of the second, third child or subsequent children if it is necessary to use the funds (part of the funds) of the maternal ( family) capital to pay the down payment and (or) repay the principal debt and pay interest on loans or borrowings for the purchase (construction) of residential premises, including mortgage loans provided to citizens under a loan agreement (loan agreement) concluded with an organization, including credit institution.
In accordance with subparagraph “a” of paragraph 13 of the Rules for directing funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital to improve housing conditions, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 12, 2007 N 862, in the case of sending funds (part of the funds) of maternal ( family) capital to repay the principal debt and pay interest on a credit (loan), including a mortgage, for the purchase or construction of housing, or on a credit (loan), including a mortgage, to repay a previously granted credit (loan) for the purchase or construction housing (with the exception of fines, commissions, penalties for late fulfillment of obligations under the specified credit (loan), the person who received the certificate, along with the documents specified in paragraph 6 of these Rules, submits a copy of the credit agreement (loan agreement). When sending funds (part of the funds ) maternal (family) capital to repay the principal debt and pay interest on a loan (loan), including a mortgage; to repay a previously granted loan (loan) for the purchase or construction of housing, a copy of the previously concluded credit agreement (loan agreement) for the purchase is additionally provided or housing construction.
4. The list of monetary obligations established by law, as well as types of contracts that mediate such obligations, for the repayment of which funds from maternal (family) capital can be used before the expiration of three years from the date of birth (adoption) of the second, third child or subsequent children, is exhaustive.
Directing maternal (family) capital funds to improve housing conditions
According to paragraph 1 of part 3 of article 7 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 256-FZ, persons who received the certificate (hereinafter referred to as the owner of the certificate) can dispose of maternity (family) capital funds in full or in parts, including using them to improve living conditions.
Clauses 1, 2 of part 1 and part 1.3 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 26, 2006 N 256-FZ establish that funds (part of the funds) of maternity (family) capital in accordance with the application for disposal can be sent to:
- for the acquisition (construction) of residential premises, carried out by citizens through any transactions that do not contradict the law and participation in obligations (including participation in housing, housing construction and housing savings cooperatives), by non-cash transfer of the specified funds to the organization carrying out the alienation (construction) of the acquired property (under construction) residential premises, or to an individual carrying out the alienation of the acquired residential premises, or to an organization, including a credit organization, which provided funds under a credit agreement (loan agreement) for the specified purposes;
- for the construction, reconstruction of an individual housing construction project, carried out by citizens without the involvement of an organization carrying out the construction (reconstruction) of an individual housing construction project, including under a construction contract, by transferring the specified funds to the bank account of the person who received the certificate;
— for compensation of costs for a constructed (reconstructed) individual housing construction project.
From the content of these norms it follows that the owner of the certificate has the right to dispose of the funds of maternal (family) capital (part of them) if his participation in obligations or the completion of any transactions that do not contradict the law or the construction (reconstruction) of an individual housing construction project is aimed at improving housing conditions.
Thus, legally significant circumstances for the correct resolution of disputes about the disposal of maternal (family) capital is the establishment of circumstances indicating an improvement in housing conditions, carried out through the acquisition of residential premises or the construction or reconstruction of an individual housing construction project.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 12, 2007 N 862 approved the Rules for the allocation of funds (part of the funds) of maternity (family) capital to improve housing conditions (hereinafter referred to as the Rules). The rules establish the types of expenses for which funds (part of the funds) of maternity (family) capital can be used to improve housing conditions, the procedure for filing an application for the disposal of these funds and the list of documents required for consideration of the application, as well as the procedure and timing for the transfer of these funds.
A generalization of judicial practice indicates that disputes most often arose between certificate holders and territorial bodies of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in connection with the refusal of the latter to allocate funds from maternity (family) capital to pay part of the cost of an apartment, house or share in the ownership of residential premises, acquired under purchase and sale agreements; to repay the principal debt, pay interest on loan agreements, credit agreements (including mortgages); for reimbursement of expenses incurred in connection with the construction and reconstruction of residential premises.
When resolving disputes regarding the direction by citizens of maternity (family) capital to improve housing conditions through the acquisition of residential premises, the courts established whether the premises acquired by the certificate holder met the requirements of housing legislation for residential premises, and also whether there was a actual improvement of living conditions.
5. The acquisition of a share in the ownership of residential premises, the size of which allows the allocation of an isolated residential premises for use, indicates an improvement in the living conditions of the family of the person who received the certificate for maternal (family) capital.
6. Residential premises purchased using maternal (family) capital must meet established sanitary and technical rules and regulations, as well as other legal requirements.
7. The absence of a decision of a local government body adopted in the established manner to recognize a residential premises as unfit for habitation cannot in itself serve as a basis for the court to satisfy a person’s request to direct funds from maternity (family) capital for the purchase of this residential premises, if the court has established that the residential premises the premises do not meet established sanitary and technical rules and regulations, as well as other legal requirements.
8. The requirement of the law for documentary confirmation of a citizen’s non-cash receipt of a loan for the purchase (construction) of residential premises applies to persons entitled to additional measures of state support and who entered into a loan agreement after June 7, 2013.
9. A person entitled to additional measures of state support and who has received a certificate, in the event of the return of previously transferred funds of maternal (family) capital to the relevant body of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, cannot be deprived of the right to dispose of funds of maternal (family) capital.
Disputes related to the determination of shares in the ownership of residential premises acquired (built, reconstructed) using maternal (family) capital funds
10. If the residential premises acquired using maternal (family) capital were not registered as the common property of parents and minor children, when resolving a dispute about the division of the common property of the spouses, the court should put this issue for discussion between the parties and determine the children’s shares in ownership for this residential property.
11. The presence of an encumbrance in the form of a mortgage on a real estate property (a residential building, an apartment) acquired at the expense of maternal (family) capital cannot serve as a basis for refusing to satisfy the spouses’ request to divide this property and determine the children’s shares in the ownership of this property.
12. A property acquired (built, reconstructed) using maternal (family) capital is in the common shared ownership of spouses and children.
13. Shares in the ownership of residential premises acquired using maternal (family) capital are determined based on the equality of shares of parents and children in maternal (family) capital, and not on all funds from which the residential premises were purchased.
14. The shares of parents and children in the ownership of a residential building acquired exclusively from maternal (family) capital are equal.
Direction of maternal (family) capital funds to pay for educational services
15. Maternity (family) capital funds can be used to pay for paid educational services provided by educational organizations under state accredited educational programs.
Can bailiffs arrest and take away social capital?
According to Federal Law No. 229 “On Enforcement Proceedings”, social subsidies are not included in the list of funds that can be seized by bailiffs. In addition, maternity capital funds are stored in pension fund accounts, so they cannot be seized or physically seized.
A maternity capital certificate is not money, but the right to dispose of the money received. Based on this, the actions of the bailiffs to confiscate maternity capital will be considered illegal.
How is the disbursement of funds controlled?
As a review of the practice of applying norms for the implementation of the right to MSK, approved by the Presidium of the RF Armed Forces in 2021, shows, the issuance of mat. capital is controlled primarily by the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation when making decisions on applications from citizens to issue appropriate orders.
But this does not deprive the owner of the certificate, if the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation makes a negative decision on his application, of the right to appeal in court.
What are the penalties for government subsidy scams?
It all depends on the scale of the crime.
The smallest punishment for fraud with maternity capital can be incurred if you alone try to illegally spend a government subsidy and mislead a certain circle of people.
Such a scam does not contain elements of conspiracy, since the criminal acted alone, and does not contain elements of bribery or intimidation of an official.
If they enter into a criminal conspiracy and deliberately create a criminal scheme, fraudsters can count on a real sentence of up to four years in prison.
In the best case, you can count on 480 hours of correctional labor and a fine equal to the salary of the convicted person for 2 years.
If you enter into an agreement with a corrupt official, the punishment can even reach 6 years in prison with a fine of 800 thousand rubles. If a scam involving maternity capital is discovered, the members of the criminal group will bear collective responsibility.
Review of judicial practice. Examples
Illustration of punishment for a fraudulent scheme with state payments using the example of a decision of the Nizhny Novgorod regional court:
Citizen M., accused of fraud with state payments, entered into a criminal conspiracy with citizen B, who promised to be the first to sell real estate at an inflated price.
The purchased house did not meet the formal requirements of the law. The price itself cannot be a reason for litigation.
According to the MSC law, the subsidy can be spent on repairs or purchase of real estate. But the condition of the house purchased by citizen M. was terrible: there were no basic means of communication, glass or frames on the windows, and dry leaves were scattered around the house. By all indications, the house can be considered abandoned.
The Supreme Court ruled to recognize the real estate sale transaction as illegal and ordered citizen M. to return the funds to the Pension Fund.
Let's consider the case of judicial practice with cashing out PF funds through a fictitious loan. In 2011, in the Kurgan region, citizen L., having forged documents and taken possession of a certificate for family capital, submitted an application to the Pension Fund for payment on a previously taken out loan.
The loan by citizen L. was taken from a shell company, which she herself managed through third parties. The application was approved by the Pension Fund, and the money ended up in the account of the shell company.
And at that moment, when L. finally intended to cash out money from the LLC’s account, the prosecutor’s office uncovered her criminal plan. Court decision: to deprive citizen L. of her liberty for a period of 1 year and 6 months with the obligation to reimburse the amount of the subsidy to the state.
As you can see, a lot of fraudulent schemes with maternity capital have been invented. People who do not have deep knowledge of jurisprudence cannot assess all the risks of participating in such schemes and become victims of scammers.
Punishment for such scams is a real prospect for lovers of easy money. Judicial practice only confirms this.
Useful video
You can learn more about how maternity capital fraud can turn out in the video below:
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
Practice in similar cases has already been formed; the Arbitration Courts often consider situations when the case involves an apartment purchased partially with funds from maternal capital.
In this article, we will provide the latest judicial practice for 2020, tell you how and in what order such bankruptcy cases are considered, and how to save mortgaged property when debts are written off.
Is bankruptcy right for you?
Limitation periods
A large number of cases regarding the invalidation of real estate transactions acquired with the help of maternal money indicates the imperfection of legislation in this area.
The statute of limitations in cases of this category is 3 years. Its course begins from the moment when the person became aware of the violation of his rights. In case of violation of the rights of a minor, the three-year limitation period begins only from the moment of his 18th birthday.
The consequences of declaring such transactions invalid will be their termination and the return of the parties to their original position that existed before registration. That is, the seller must return everything received under the contract to the buyer, and the latter, in turn, must return the property to the previous owner.
How is maternity capital involved in bankruptcy?
When a person has overdue debts and there are no sources to pay them off, the only normal way out of the situation is to declare the citizen’s bankruptcy. Accordingly, it is necessary to collect documents and apply to the Arbitration Court at your place of residence.
There are two possible procedures in bankruptcy:
- Debt restructuring is not a write-off, but an independent settlement with creditors on preferential terms. You can pay off your loans within 3 years without overpayments or excessive interest, under the control of a financial manager. In this case, no claims are made against the property.
- The sale of property is a procedure for declaring bankruptcy; debts are written off at the last court hearing. Creditors and collectors address their claims and demands to the financial manager and to the court from the first meeting.
The manager draws up a register of creditors' claims, and at the same time the formation of a bankruptcy estate is underway, which includes a person's property that can be sold to pay off debts (obligatory objects of collateral if the secured creditor has entered into the case). Next, auctions are held and the property is sold.
Now about maternity capital. In practice, young families more often use maternal capital to purchase housing and improve living conditions. That is, funds are deposited into a mortgage account as a down payment. In the future, the apartment is considered collateral until the mortgage loan is completely closed.
What property will be taken away from you during bankruptcy?
Particularly difficult cases
Registration of shares
Real estate acquired with the participation of MSC money must be registered as the property of all family members, divided into shares, including children. If the object was purchased under a mortgage agreement and is pledged to a credit institution, then until the said encumbrance is removed, it will not be possible to register the shares. To do this, the borrower draws up an obligation that he will register the right of common shared ownership of the housing after the encumbrance is removed from it. The specified obligation is certified by a notary and submitted to the Pension Fund.
If this requirement of the law is not fulfilled, the owner of the MSK certificate may be forced to take action to register shares through the court by the prosecutorial authorities supervising the implementation of legislation on family capital.
In addition, failure to include children among the co-owners of the residential premises will subsequently prevent the sale of the said property, since the registration service will be obliged to suspend any transaction in relation to the disputed property, notifying the guardianship authority, and they, in turn, will notify the prosecutor's office.
The sale of an apartment purchased with maternity capital is not prohibited by law, but has its own nuances. The rules for using maternity capital can be found here.
If this transaction is nevertheless carried out, then subsequently any interested party may recognize it as invalid (void by law), which will be fraught with consequences for both the seller and the buyers.
Stillborn
The right to capital funds arises for women who have given birth to their second and subsequent children. At the same time, the legislator recognizes the fact of a child’s birth alive as a legally significant circumstance.
Interesting in this regard is the judicial ruling of the Krasnodar Territory, from which it follows that the registration of the birth of a child who died in the first week of life may not be carried out. In this case, the mother can only obtain a death certificate.
Based on the above, the absence of a certificate of entry in the birth certificate with an existing birth certificate or death certificate is not a legal basis for refusing to issue a mat. capital for a second child.
Buying from relatives
Purchasing real estate from relatives using MSC funds in accordance with the law on family support is theoretically possible. However, there is a difficulty here - all shares of relatives must, according to the transaction, go to the owner of the certificate, and then in shares to all family members, including children, which is difficult to implement in practice.
This happens due to the fact that the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes a ban on transactions in which minors and their parents, guardians or close relatives are simultaneously parties. The exceptions are donation and gratuitous use. In other words, a child, together with a parent, cannot buy real estate in shares from an aunt, uncle, grandmother, or grandfather.
This prohibition can be easily circumvented by registering housing only in the name of the certificate holder with a written obligation to allocate shares after transferring funds to MSC.
This scheme is used in practice to cash out capital money. For example, a family lives in the apartment of a relative, with whom a purchase and sale agreement is concluded with the participation of family funds. After registering the transfer of rights, virtually nothing changes, everyone lives together as before, and the money allocated for the purchase is spent at their own discretion.
The Pension Fund of the Russian Federation often refuses to carry out such transactions, since there is no real improvement in living conditions, and the transaction, as defined by civil law, is called imaginary
Do they take away the apartment if there are debts?
Important!
In bankruptcy, the bankruptcy estate cannot include property protected by law, including:
- a plot of land where the only housing is located; - an apartment or house in which the debtor lives with his family, and which is recognized as the only residential property of the citizen.
But the problem is that collateral properties automatically lose their status as the only home, and they are subject to sale:
- Mortgage housing is included in the bankruptcy estate.
- Next comes the assessment. An expert is invited to evaluate the property and draw up an opinion on the value.
- Bankruptcy auctions are being organized. The procedure and terms of the auction are proposed by the pledge holder (bank) and approved by the Arbitration Court.
- If the housing was not sold at auction, it will be offered to the bank as compensation.
Are you in default on your mortgage? Find out how bankruptcy will work
What happens to the money from the sale of a mortgaged home?
Expert opinion
Korolev Alexander Mikhailovich
Practitioner lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in protecting legal interests.
At auction, property is sold at a reduced cost. That is, an apartment worth 2 million rubles will be sold at best for 1.75 million rubles.
The following persons participate in the distribution of proceeds:
- financial manager. 7% of the amount is allocated;
- secured creditor. 80% of the proceeds are sent to the bank, but not more than the amount of the debt;
- The proceeds can be used to pay legal expenses (if there is nothing else to cover).
- the remaining funds from the sale are sent to the debtor.
If the only apartment was sold for more than the mortgage debt, the money is transferred to the debtor and is not included in the bankruptcy estate.
In practice, such situations rarely arise; as a rule, there is still a debt on the loan, which is written off at the end of the bankruptcy procedure.
The participation of maternity capital does not play a role, and if after the sale of the apartment there was only enough money to cover the debt to the bank, the maternity capital is not reimbursed.
Therefore, it is important to contact lawyers before filing for bankruptcy in order to think about how to keep the mortgaged apartment or sell it yourself before the procedure at the market price.
Can a bankrupt sell an apartment?
There are 2 options for selling a mortgaged apartment:
- Before bankruptcy.
A person can contact the bank that issued the mortgage and request official permission to sell. It is impossible to conclude a deal without documents; approval from the secured creditor is required. If there are enough funds from the sale, the mortgage is closed, the person has the right to buy another single home or partially withdraw the money. - In bankruptcy proceedings.
Here, the debtor’s participation will be minimal - the apartment is included in the bankruptcy estate, and the financial manager is in charge of its sale. He also distributes the proceeds from the sale.
If we are talking about the only housing that is not encumbered with a mortgage, then it makes no difference when and how the debtor sells it. Lenders cannot claim such housing and the proceeds from its sale.
It is important not to miscalculate what the law considers the only housing
We have discussed in detail about single housing and its criteria in this article.
Selling an apartment with maternity capital during bankruptcy: how to save property?
In bankruptcy of individuals, 2 procedures are used, and in each you can save the mortgaged apartment.
Debt restructuring.
No claims are made against the property unless the bank goes into bankruptcy - for example, there is a co-borrower. The essence of the procedure is as follows: a plan is drawn up to repay the debt for a maximum period of 3 years, then the financial manager controls how the debtor copes with satisfying the claims of creditors.
Sale of property.
There are the following options for saving maternity capital and mortgages:
- Before bankruptcy, remove property from collateral.
Some debtors do the following: they take out a consumer loan, then deposit the funds into a mortgage account. The mortgage is closed, the apartment is no longer pledged.
You should be aware of the following nuances:
- After repaying the mortgage, you need to pay off the consumer loan for some time, otherwise there is a high risk that such actions will be considered unfair by the Arbitration Court. Reason: the loan was taken without the intention of repaying it;
- This method is suitable for those who have a short time left to pay off their mortgage and the amount is relatively small. It is possible to cover it with a consumer loan;
- within the framework of bankruptcy, a relative/spouse can participate in electronic auctions.
It is better to carry out such manipulations with legal support. The essence is as follows: a relative or other person becomes a potential buyer (you need to register on the electronic auction site and actively participate in the auction). Then he offers the best price and buys the mortgaged property. - need money for ransom. Considering that bankruptcy with bidding lasts about 1-2 years, you can collect a decent amount;
you need to navigate the procedure: know where and how the auction will be held. There are 3 stages, at each of which the price decreases. It is necessary to seize the favorable moment. Again, lawyers will help in this matter.
Looking for a financial manager?
Judicial practice: matkapital in bankruptcy of individuals
The arbitration court, having considered the circumstances of the case, refused to exclude it, indicating that the house was mortgaged on the basis of a mortgage agreement between the debtor and the bank. The debtor appealed the ruling, but the Court of Appeal agreed with the findings of the lower court and also refused to exclude the collateral housing from the bankruptcy estate.
Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of December 25, 2021 N 48
The courts take into account the provisions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated July 15, 2010 No. 978-О-О and dated October 19, 2010 No. 1341-О-О, that in bankruptcy cases where mortgaged housing is involved, it is necessary to rely on the provisions of the Federal Law “On Mortgage”
. That is, the creditor has the right to foreclose on the mortgage collateral, regardless of whether such housing is the only one for the debtor and his children.
Do you need to declare insolvency, but you don’t want to risk your apartment? Seek support from experienced lawyers - we will provide the necessary advice, instructions, and also provide legal support in the bankruptcy procedure and debt write-off while preserving property!
Maternity capital is one of the most popular ways for the state to support a number of families with children. The issuance of such assistance is strictly regulated by current Russian legislation, but various types of violations and fraudulent actions are often recorded.
Judicial practice on maternity capital is aimed at protecting the rights of minor children and assisting respectable citizens in the proper management of substantial sums of money.
- 1 What does judicial practice on maternity capital cover? 1.1 Fraud
- 1.2 Refusal to issue
- 1.3 Default
- 1.4 Refunds
- 1.5 Misuse
- 1.6 Registration of shares
- 1.7 Other
The right of citizens with children to use maternity capital to improve housing conditions
Our state has granted the right to families with children to use the amount of maternity capital on the basis of Federal Law No. 256-FZ of December 29, 2006 “On additional measures of state support for families with children” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 256) to improve housing conditions (Article 7 of Federal Law No. 256).
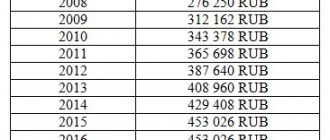
The amount of maternal (family) capital is specified in Article 6 of Federal Law No. 256 (as amended by Federal Law No. 35-FZ dated 01.03.2020):
Article 6. Amount of maternal (family) capital ConsultantPlus: note. Part 1 art. 6 (as amended by Federal Law No. 35-FZ dated March 1, 2020) applies to legal relations that arose from January 1, 2020. ConsultantPlus: note. For the current amount of maternal (family) capital, see the reference information. 1. Maternity (family) capital is established in the following amounts: 1) 466,617 rubles, provided that the right to additional measures of state support arose before December 31, 2021 inclusive
;
2) 466,617 rubles in the case of the birth (adoption) of the first child starting from January 1, 2021. In the case of the birth (adoption) of a second child starting from January 1, 2021, provided that the first child was born (adopted) also starting from January 1, 2021, the amount of maternal (family) capital increases by 150,000 rubles and amounts to a total of 616 617 rubles; 3) 616,617 rubles in the case of the birth (adoption) of a second child starting from January 1, 2021, provided that the first child was born (adopted) before January 1, 2021;
4)
616,617 rubles in the case of the birth (adoption) of a third child or subsequent children starting from January 1, 2021, provided that the right to additional measures of state support did not arise earlier
. (Part 1 as amended by Federal Law No. 35-FZ dated 01.03.2020) 2. The amount of maternal (family) capital is reviewed annually taking into account the rate of inflation and is established by the federal law on the federal budget for the corresponding financial year and for the planning period. The amount of the remaining amount of maternal (family) capital is reviewed in the same manner. (Part 2 as amended by Federal Law No. 241-FZ of July 28, 2010) 3. The amount of maternal (family) capital is reduced by the amount of funds used as a result of the disposal of this capital in the manner established by this Federal Law.
In addition to Federal Law No. 256, this issue is also regulated by the “Rules for allocating funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital to improve housing conditions,” approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 12, 2007 No. 862 (as amended by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 31, 2007) .2020 N 383)
, hereinafter – Rules No. 862.
According to Part 4 of Article 10 of Federal Law No. 256 (as amended by Federal Law No. 25-FZ dated March 1, 2020):
The person who received the certificate and his spouse are obliged to register the residential premises acquired (built, reconstructed) using funds (part of the funds) of maternal (family) capital as the common property of such person, his spouse, children (including including the first, second, third child and subsequent children) with the determination of the size of shares by agreement.
As numerous practice shows, including judicial practice, many citizens do not know the provisions of Federal Law No. 256 and the provisions of Rules No. 862, and some of the citizens, using various rumors and the well-known “maybe”, are trying to “cheat” the State when they use the amount of maternity capital to improve the family’s living conditions, thereby violating, first of all, the legal rights of their minor children to have a share of ownership in the purchased residential premises with an additional payment of the amount of maternity capital.
Prosecutors of many cities in Russia in 2019-2020 actively checked and are checking compliance by citizens of the Russian Federation with the provisions of Federal Law No. 256 and the provisions of Rules No. 862 when they use the amount of maternity capital to improve the living conditions of the family, incl. minor children.
Some citizens who use the amount of maternity capital to improve their living conditions try to violate the provisions of Federal Law No. 256 with various “machinations”, incl. Part 4 of Article 10 of Federal Law No. 256, and do not timely allocate ownership shares in purchased residential premises using the amount of maternity capital to their children, so that such housing can be sold without the permission of the Guardianship and Trusteeship Authority ( see Article 21 of Federal Law No. 48-FZ " About guardianship and trusteeship"
).
How this can end for such “cunning” people, see below in the section Judicial practice on claims by prosecutors to protect the housing rights of minor children.
What does judicial practice on maternity capital cover?
Litigation directly related to disputes about maternal capital most often have the following areas:
- prove the right to assistance from the state and obtain a certificate;
- invalidate the state certificate;
- obtaining the opportunity to manage maternity capital;
- division of residential premises for which state aid funds were spent;
- accurate determination of the size of the share of each family member in real estate acquired with family capital;
- other controversial issues.
What is important to know about state support for families with children:
- receiving funds is available only to Russian citizens - parents and their minor children;
- spending family capital before the child turns three years old is allowed only when receiving a mortgage loan and repaying the debt on it, or another type of loan;
- the basis for state support is two or more children born alive;
- parents and adoptive parents, who are deprived of their rights by law, cannot receive capital;
- housing purchased with the help of maternal capital must be in normal technical and sanitary condition and not be in disrepair;
- when receiving a non-cash loan for the construction or purchase of residential premises, it is necessary to confirm this fact with the help of documents in order to receive support from the state;
- each of the parents and their children is the full owner of the home purchased with maternal capital, each has their own share in it;
- state aid can be spent on education in accredited educational institutions.
Fraud
Despite the fact that maternity capital cannot be cashed out, thematic groups constantly appear on the Internet, promising to exchange the state certificate for “paper money” in the shortest possible time for a nominal fee.
From the outside, everything looks serious: an official agreement with an intermediary, who warns that there are scammers around, and you can cooperate with him. But in fact, the money was not cashed out - the interested parties did not receive it.
There have also been cases of fictitious home purchases, when parents provided the necessary documents for taking out a loan to improve their living conditions, but never bought new property. Crimes in this area were also committed by doctors in maternity hospitals who issued fake birth certificates for non-existent or stillborn children.
Refusal to issue
Since there are two stages in allocating funds for maternity capital (issuing a certificate and receiving financing for it), there are also two options for refusal. It happens that those who have the right to state assistance, the parent is issued a certificate, but he does not have the right to funding at the time of applying for money.
Main reasons for refusal:
- deprivation of parental rights;
- cancellation of adoption;
- death of a child or stillbirth;
- Not all necessary documents were submitted incorrectly or not collected;
- Inappropriate spending purposes are indicated;
- the desired amount exceeds the size of the capital.
Default
According to the law, when purchasing a home using funds from maternity capital, all family members receive equal shares in such real estate.
If this cannot be done before receiving government assistance, then a written commitment becomes a guarantee. When paying off a mortgage, participating in a savings cooperative, or other installment plans, the contract stipulates that the allocation of equal shares will be made after the last payment, the full repayment of the debt.
When carrying out reconstruction, participating in shared construction - after the “commissioning” of the house, its commissioning.
Refund
Expert opinion
Korolev Alexander Mikhailovich
Practitioner lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in protecting legal interests.
If less than two months have passed since the application for “mother’s capital” was submitted, then it can be canceled and a new one can be immediately submitted to the pension fund, indicating a different purpose for spending.
In another option, the contract with the construction company or the real estate seller is terminated, which returns all the money to the buyer, including swearing. capital that the recipient is obliged to return to the pension fund. Receiving state support is possible only through the court.
There is a third option: the money received from the developer is immediately invested in other housing, but documents confirming this must be kept for reporting to the pension fund.
Inappropriate use
Non-targeted ways of using state support funds include any other than improving the family’s living conditions, the child’s education or keeping him in one of the educational institutions, and the formation of a pension for the mother.
Any method of cashing out is considered a violation of the law; the owner of the certificate may also be recognized as an accomplice in criminal fraud.
Registration of shares
Each family member, including children born much later, receives their share in the common property. The allocation of shares or their donation is made no later than six months from the date of repayment of the mortgage.
If we are talking about a private house (its construction or reconstruction), then the shares of the land plot on which it stands are also distributed. When disagreements arise between parents on this issue, it is possible to resolve the problem in court.
general review
In its Resolution on disputes regarding maternity capital for 2021 and 2021, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation determined the following areas of judicial practice in cases of this category:
- the right to receive MSC funds arises only if both the parent and the minor have Russian citizenship;
- the basis for the emergence of the right to state support is the birth of 2 and subsequent children alive;
- children in respect of whom parents have been deprived of their rights, or in respect of whom adoption has been canceled, are not taken into account when determining whether they have the right to mat. capital;
- disposal of MSK funds until the child’s third birthday is possible only when receiving a loan or credit (including a mortgage);
- if the size of the share purchased in a residential building allows it to be allocated to a separate room, this is recognized as an improvement in housing;
- residential premises purchased with the participation of MSC funds must meet all requirements established by law, including sanitary and technical ones, while the absence of a decision from the local government to recognize such premises as unfit for living cannot serve as an unconditional basis for its automatic recognition as corresponding to the standards;
- persons who received a non-cash loan for the purchase (construction) of housing after June 2013 are required to confirm it with documents in order to receive government support measures related to the issuance of an MSC certificate;
- children and parents are equal owners of housing purchased with MSC money, such housing is in their common shared ownership;
- MSC funds can be paid to institutions with state accreditation for the educational programs provided.