Pregnancy and motherhood are a special time for every woman. Problems with work can be added to the mass of impressions and worries for a young mother. Having devoted all her free time to caring for her child, the mother should be calm about her financial situation.
In Russia, it has long been determined who pays for maternity leave - the employer or the state; if the employee and employer act in accordance with the law, the expectant mother has guarantees (financial and social).
New law
There is no concept of “maternity leave” in legal practice. This is how we talk about a vacation during which a woman is about to give birth. Any woman has the right to “go on maternity leave.” It means:
- maternity leave (Maternity leave);
- go on parental leave to care for your own child until he reaches the age of 1.5 years;
- leave to care for your own child until he reaches the age of 3 years.
Art. 255 and 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation guarantees every woman the right to maternity leave in 2019. Women are entitled to leave:
- officially employed;
- those who are in the status of unemployed;
- military personnel;
- female students;
- workers in military structures as civilian personnel.
A woman who works officially can count on receiving the required benefits for labor and employment, and then for caring for a newborn. An unemployed woman can receive such benefits through the social security authorities at her registration address.
In Art. 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates how many days such leave is paid:
- if pregnancy proceeds without complications - for 140 days;
- in case of difficult childbirth and caesarean section, the doctor of the maternity hospital has the right to extend the leave to 86 days, the total period will be 156 days;
- If a woman is expecting two or more children, then before giving birth she will receive 84 days of leave, and after - 110 days.
Results
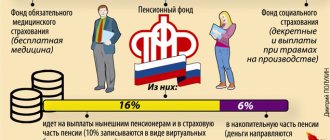
Maternity benefits are provided to all women insured in the compulsory social insurance system.
It is calculated based on data on earnings and hours worked for two calendar years preceding the insured event. By calculation, the maximum and minimum for this benefit are calculated for each year. Starting from 2021, maternity payments are made by the Social Insurance Fund, and the employer only provides it with the information and documents necessary for calculating and transferring benefits. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus.
Free trial access to the system for 2 days. https://youtu.be/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JXF0kOpiDNg
_
Maternity benefit
Women who are officially employed can receive it, since it is paid from the Social Insurance Fund. This fund is replenished exclusively from deductions from the official part of income. Categories of women to whom benefits will be paid:
- officially employed;
- dismissed within 12 months before such leave (from an enterprise that was liquidated;
- female students studying full-time and receiving a scholarship;
- contract military personnel;
- women who adopted children under 3 months of age.
Documents for issuing benefits:
- Sick leave. A pregnant woman receives it at a medical institution, where she must be registered.
- Statement. It is drawn up in the name of the employer in any form with a request to give leave under the BiR.
- Data for transferring benefits. You can get it in your hands, this is allowed by law.
- Certificate of income. Issued by the accounting department.
- Application for transfer of benefits. A request for assistance is made.
In what cases was payment for maternity leave until 2021 received directly from the Social Insurance Fund?
The fund itself also paid maternity benefits, but only in certain situations:
- The region participated in a pilot project, which implied direct interaction between the employee and the Social Insurance Fund regarding social benefits for disability. The employer's role in this process was limited to filling out the necessary information on the sick leave certificate.
- If the employer did not have enough funds to pay benefits. Read more here.
- Payments to women who voluntarily insured themselves in the fund. Such a step was possible for persons working under civil contracts and individual entrepreneurs who, by law, are not required to pay contributions for disability and maternity insurance on their income (subclause 2, clause 3, article 422, clause 6, art. 430 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accruals
The due amount is paid in the amount of 100% of the woman’s average income for the previous 2 years. The number of days worked in the last place of employment does not matter. For example, if an employee goes on maternity leave in 2021, then income for 2021 and 2021 is taken to make calculations.
When calculating, take into account:
- wages;
- vacation pay;
- travel allowances;
- bonuses;
- other payments specified in the 2-NDFL certificate.
To calculate the average daily income, take the total number of days for 2 years (730 or 731 days) . But from the total number of days they remove:
- number of days on sick leave;
- last vacation for employment and economics;
- last vacation when the woman was caring for a child;
- another vacation;
- other periods when there were no contributions to the Social Insurance Fund.
The due amount is received within 3 days after the woman has provided sick leave.
IMPORTANT! Foreign women working officially in Russia receive benefits according to Russian legislation, respectively, from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund.
Does the state return money to the enterprise?
The benefits accrued by the accounting department of the enterprise are issued to the recipient no later than 10 days from the date of transfer of the necessary documents. You can contact the Social Insurance Fund for reimbursement of the funds spent by the company. The statute of limitations established by law for the return of money spent on benefits from the state budget is 3 years.
Conditions for transferring funds from the insurance fund to the company’s accounts depending on the employee’s status:
- the recipient is an employee of the organization . Employment rules are followed, mandatory insurance premiums are paid;
- allowance for a woman individual entrepreneur . Creating a business and working in it complies with the law. Voluntary registration of an entrepreneur with the Social Insurance Fund. For the founding employee, mandatory contributions were paid for no less than 6 months.
To receive compensation, an application and a package of documents are prepared, sent to the insurance fund, and await the decision of the Social Insurance Fund. The review time depends on the accuracy and completeness of the information provided.
When there are no comments, the procedure is carried out within 5-10 days. Additional verification of the information provided will delay the decision on refund by 3 months.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
The state must return money to the enterprise for benefits paid if a document check does not reveal any violations. When a company has financial problems, the fund independently issues maternity money.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call: +7 Moscow and region.
+7 St. Petersburg and region. 8 Other regions of the Russian Federation You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of all your problems!
Payment amount
The minimum amount is:
- during childbirth without complications (140 days) – 43615.65 rubles;
- for difficult childbirth (156 days) – 48,600.33 rubles;
- if the pregnancy is multiple (194 days) – 60438.83 rubles.
The maximum benefit amount is limited to the amount of average earnings from which social insurance contributions are made at the time of temporary disability and in connection with childbirth.
This amount in 2021 is equal to 815,000 rubles, but when calculations are made, the insurance base is taken for 2021 and 2021. (this is 718,000 and 755,000 rubles). Therefore, the maximum payouts are:
- for normal childbirth - 282,106.70 rubles;
- for complex cases - 314,347.47 rubles;
- for multiple pregnancy - 390919.29 rubles.
To calculate benefits for subsequent maternity leave, the same periods will be taken as for the first time.
Why can the Social Insurance Fund refuse to reimburse an organization for payments?
The expenditure of state budget funds is controlled, including by the social insurance fund itself. All documents submitted for the return of money from the treasury are checked by FSS specialists to ensure the correctness of the sick leave certificate and the calculation of the amounts paid.
Depending on the severity and nature of the violations identified, the amount of funds due for refund is reduced or a decision is made to refuse the company to reimburse the money spent.
FSS employees pay attention to the following nuances:
- The position and education of the employee are not interconnected;
- the salary is disproportionately high for a place of work in similar conditions;
- the staffing position was entered into the schedule immediately before the employee joined the company, especially if she had no work experience in previous years;
- a significant increase in the earnings of a maternity leaver before she goes on vacation;
- inclusion in the calculation of periods when the employee did not work.
Such moments may be regarded as an attempt to unreasonably obtain inflated amounts of compensation from the state budget. Practice shows that such facts are identified by FSS employees and appropriate actions are taken on them. Any of the inconsistencies listed in the list may become a reason for denying compensation to a legal entity that has applied to the Social Insurance Fund for funds paid under maternity leave.
Monthly
If a pregnant woman is registered at a medical institution at a short period of time (up to 12 weeks), she has the right to receive one-time assistance.
Its value is 628.47 rubles. But to do this, you need to bring a certificate from a medical institution about early registration.
Additionally, at the birth of a child, one of the parents is entitled to a one-time benefit. From February 1, 2018, its value was 16,759.09 rubles.
At the end of maternity leave, the woman is credited with the amount that will be transferred to her during the period of leave to care for a newborn when he reaches one and a half years of age - 40% of average earnings, but not lower:
- 3788.33 for one child;
- 6284, 65 for the second and subsequent ones.
If several children are born at once, payments are made for each one. You must bring a birth certificate from the registry office to the accounting department at your place of work, and the second parent must also provide a certificate stating that you have not received a lump sum and do not receive a monthly allowance.
What should an employee’s employer do in an “interesting situation”?
Everyone says that in our country it is impossible to get a job while pregnant, and employers “don’t like” employees who go on maternity leave. Let's look at this issue through the eyes of the employer.
Firstly, pregnant women have guarantees and protection from the state. They cannot be fired or refused employment because they are pregnant, they can demand special working conditions and their job is kept for them.
Secondly, the employer wastes time and suffers losses when hiring a new employee. He trains her, waits for her to understand all the intricacies of production, and over time the employee leaves him, and he needs to find a temporary replacement for her and start all over again with new employees. One day the time will come, and it will be necessary to resolve the issue with the maternity leaver, return her, again give her time to devote herself to current affairs, or fire her.
Thirdly, submission of documents and financial settlements with the Social Insurance Fund and the employee. If the staff is small and there is only one accountant, his workload increases significantly with each maternity leave. Although in theory everything is not so complicated.
Taking into account the above, it can be assumed that employers do not like women on maternity leave, but the additional worries that they entail. It’s good if the employer is an adequate person and is humanly happy for his subordinate. A competent employer always takes care of himself and his subordinates. He promptly and accurately submits the necessary documents, complies with the law and hires a new employee for the position of the expectant mother in advance, so that she is the one who teaches him everything she can and does at the enterprise.
Who pays
Pregnancy, childbirth and child care is an insured event, so these expenses are borne by the state. It happens like this:
- The employer constantly makes deductions from the employee’s salary to the Social Insurance Fund, from the first and subsequent monthly income.
- After the employee provides the necessary documents, the employer makes the calculation and then submits the data to the Social Insurance Fund.
- The Social Insurance Fund transfers the required amount of money to the employer’s account.
- The employer issues or transfers the required amount to the employee.
If a woman receives payments untimely because the employer refers to the lack of transfers from the Social Insurance Fund, she should contact the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office. It is possible that the Social Insurance Fund is indeed delaying payments, but the employer must pay the employee from its own funds, and then compensate for them with revenues.
How to act if maternity payments are delayed by the company
At the same time, there is a situation where the company itself refuses to pay the employee adequate funds during maternity leave. In this situation, the employee (or her husband) must take the following actions:
- First of all, communicate directly with the employer, asking him to pay her the necessary funds and reminding her of her responsibility under the law. At the same time, it is necessary to clarify whether there has been a misunderstanding, for example, a typo in the bank account details.
- If the previous stage did not lead to the desired result, you can contact the Social Insurance Fund directly. This organization has mechanisms to influence companies that violate the rights of workers.
- Another option is to write an appeal to the prosecutor's office. Such paper can be transferred to this organization in person at the department at the place of residence of the applicant, or by registered mail with an inventory and acknowledgment of receipt. In addition, this can be done on the prosecutor’s office portal on the Internet.
- In addition, an employee may sue due to refusal to pay maternity benefits. This action can be taken immediately as soon as human rights have been violated.
It is not necessary to first contact the FSS or the prosecutor's office. After this, the court makes a decision in favor of the employee, after which the bailiffs collect the appropriate funds. They are guaranteed to receive the money, unless the company ceases to exist.
What to do if the company no longer exists
Of course, the situation when the company where the child’s mother worked before going on maternity ceased to exist is an extreme case, which is the least pleasant for her. In such a situation, it will not be legally possible to recover funds from this company.
For such cases, it is established that payments are made by the Social Insurance Fund. In such a situation, the applicant needs to come to the territorial office of this department. At the same time, she needs to take with her a package of documents with which she can confirm her own right to accrue maternity payments to her.
How many days does maternity leave last?
In accordance with the legislation and norms prescribed in the Labor Code, a woman has the right to maternity leave for the duration of:
- 70 days before and after the birth of the baby, if she is carrying one child.
- 70 days before and 86 days after birth in case of difficult births that were accompanied by complications.
- 84 days before giving birth and 110 days after if she is carrying two or more children.
For this period, a sick leave certificate is issued and funds are accrued, which are issued during pregnancy and after the birth of the baby.
Extension of leave is possible in the following cases:
- if they learn about a multiple pregnancy during childbirth, the maternity leave is extended for a period of 54 days;
- If the birth was complicated, the leave is extended by 16 days.
Return to the workforce. When is it possible to go to work?
Unfortunately, not all mothers have the opportunity to sit at home and take care of their beloved child. More and more often, mothers have to choose between a baby and a stable income.
The period of paid maternity leave is set to 1.5 years, and it cannot be extended. But a woman can extend her stay at home at her own expense. The workplace is assigned to a maternity leaver until her child reaches three years of age. It should be noted that these second year and a half are not included in the length of service.
A woman can go to work at any time without waiting for the end of maternity leave. But at the same time, if the child returns to work before the child is one and a half years old, the employee will lose the payments that are provided at this time. In other words, a woman can only receive one thing: a salary or an allowance.
We found out how much maternity leave is paid, let's figure out who has the right to take advantage of this leave.