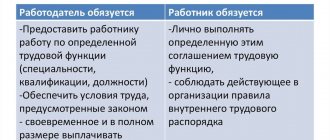
When hiring a new employee, the employer always stipulates the range of duties that he will have to perform, in other words, his job function. This promotes certainty and stability in labor relations. The employee knows all his duties and bears some responsibility for their implementation.
However, there are cases when, for one reason or another (organizational or economic), there is a need to formalize a change in the labor function. In this situation, it is important to comply with all legal requirements and document the process at the proper level. In the article we will discuss the professional standard, the labor function, as well as documentary support for its change.
Labor function: concept
This concept is legally enshrined in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Within the meaning of this legal norm, a labor function should be understood as work in a specific position in accordance with the staffing table, profession and specialty with a mandatory indication of qualifications, as well as the type of specific activity that is entrusted to the employee. Thus, the concept has two interpretation options according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The labor function is what is enshrined in the employment contract. The wording in it will depend on which interpretation of the concept you choose in each specific situation. So, in the first option, a clause must be included in the employment contract, for example, with the following content: “The employee undertakes to perform work in the position of a chief specialist (chief accountant, leading legal adviser, etc.).” The specific job duties that the newly hired employee will perform are the basis for creating a job description.
If the function of work activity is interpreted according to the second option, then the entry in the employment contract also changes. For example, it may sound like this: “This employee is entrusted with performing plumbing (installation, unloading and loading, etc.) work.
Experts are of the opinion that, within the meaning of Article 15, Part 2 of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the concepts of “position title” and “labor function” are not identical in content. In fact, the second is one of the characteristics of the first. The labor function is specified by certain job responsibilities.
Errors in drafting the text of the contract.
An employment contract must contain certain information, as well as a number of mandatory conditions. For clarity, we present them in a table.
| Information to be included in the employment contract | Mandatory terms of the contract | Additional terms of the agreement |
| Last name, first name, patronymic of the employee and the name of the employer who entered into the employment contract | Place of work | On clarification of the place of work (indicating the structural unit) or workplace |
| Information about documents proving the identity of the employee and the employer - an individual | Labor function | On non-disclosure of secrets protected by law (state, official, commercial and other) |
| Employer's TIN | Terms of payment | About the test |
| Information about the employer’s representative who signed the employment contract and the basis on which he is vested with the appropriate powers | Start date of work, duration and validity of a fixed-term contract and reasons for concluding such a contract | On the employee’s obligation to work after training for at least the period established by the contract |
| Place and date of conclusion of the employment contract | Working hours and rest hours | On the types and conditions of additional employee insurance |
| Guarantees and compensation for work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if the employee is hired for such work | On additional non-state pension provision for employees | |
| Conditions determining, where necessary, the nature of the work | On improving the social and living conditions of the employee and his family members | |
| Working conditions in the workplace | On clarifying the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer | |
| Condition for compulsory social insurance of an employee | ||
| Other conditions in cases provided for by labor legislation |
When providing information about an employee or employer, errors are the least common. Most often, this is a lack of information about the place where the contract was concluded, a document confirming the powers of the employer’s representative authorized to conclude an employment contract, or the registration address is indicated instead of the employee’s passport data.
If employment contracts do not contain any of the required information (check them against Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or the first column of our table), they must be added to the text. To do this, the missing information is added to both copies of the employment contract without drawing up additional agreements. The information entered is certified by the signatures of the parties to the agreement, and the date of entry must be indicated.
There are many more errors related to mandatory conditions.
Documentation of the labor function
It has already been said above that the labor function of an employee is work according to the position in accordance with the staffing table, profession and specialty. In this case, the qualifications and the specific type of work assigned to the new employee are separately indicated.
Analyzing this definition, we can conclude that the labor function should be documented. First of all, this is done in the staffing table, which indicates the profession and position. In addition, it is specified in the text of the concluded employment contract.
By signing it, the employee thereby expresses his consent to the specified labor function that the employer plans to assign to him. In order to change it in the future, mutual consent of both parties will be required. Even in the event of a change in technological or organizational conditions, labor legislation does not allow changes in the function of work activity only at the request of the employer, i.e. unilaterally.
As a rule, the scope of an employment contract is limited and does not allow describing in detail all the employee’s responsibilities related to a particular profession or position. In this case, a job description comes to the aid of the employer, which can be issued in the form of an appendix or a separate local regulation.
Not long ago, amendments were made to labor legislation regarding the so-called Professional Standard. It is understood as a characteristic of the qualifications that an employee requires to carry out professional activities of any particular type, including to perform any specific job function. Professional standards have been developed and applied in practice only in accordance with Articles 195.2, 195.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Signs of labor relations
Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a definition of the concept of “labor relations”.
This definition identifies features that allow us to distinguish labor relations from civil ones.
As explained by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the characteristic features of labor relations in accordance with Articles 15 and 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation include:
- the parties reach an agreement on the personal performance by the employee of a certain, predetermined labor function in the interests, under the control and management of the employer;
- the employee’s subordination to the employer’s internal labor regulations and work schedule (shift);
- provision of working conditions by the employer; performance by an employee of a labor function for pay (see for more details paragraph 17 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2018 N 15 “On the application by courts of legislation regulating the labor of employees working for employers - individuals and for employers - small businesses, which are classified to microenterprises").
What is an effective contract?
The Government of the Russian Federation issued an Order containing a program for improving conditions relating to remuneration. It reveals the concept of an effective contract. In essence, this is the same classic (employment) contract with an employee, but it details not only the terms of payment and job responsibilities, but also performance indicators, as well as criteria for assessing its effectiveness, which later form the basis for calculating incentive payments , social support measures. That is, the salary depends directly on the results of work and the quality of municipal (state) services provided by the employee.
So, an effective contract is a formalized employment relationship based on:
- the presence in the institution of a task (state or municipal) and target indicators characterizing the effectiveness of activities (they are approved by its founder);
- a system for assessing the effective performance by an employee of his labor function (actions), which consists of a set of indicators and criteria approved by the employer in the manner prescribed by law;
- a remuneration system that takes into account differences in the complexity of the work performed by employees, as well as the quality and quantity of labor expended (it must be approved in the prescribed manner by the employer);
- labor standardization system approved in accordance with the established procedure by the employer;
- detailed specification of the types of labor functions, taking into account the specifics inherent in each individual industry, in employment contracts and job responsibilities, criteria and indicators that allow assessing the effectiveness of labor, as well as the terms of its payment.
At the moment, some areas of activity have already developed their own methodological basis for the gradual introduction of an effective contract into practice: medical and educational institutions, the sphere of culture and social services.
If the employer is an individual
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 20 allows individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, to be employers along with organizations. These can be entrepreneurs without obtaining the status of a legal entity, private legal professionals (lawyers, notaries), and specialists who have passed state registration and have a license. They have the right to joint activities with employees as individual entrepreneurs.
Responsibilities of an individual acting as an employer
The second group of employers is represented by individuals who cooperate with employees as service personnel and to provide assistance in organizing household chores. This area of activity does not relate to individual entrepreneurship and has special specifics of labor relations and legal regulation.
Important! An individual employer independently exercises his labor rights and obligations and is responsible for their implementation.
The ability to work based on age and volitional qualities is the main criterion. For 18-year-old persons with independent income, with judicial restrictions on their legal capacity, the law provides for the right to conclude employment agreements (with the written consent of their supervisors) for service and economic work.
By law, an individual employer can develop local legal documents, which he independently approves.
There are examples of actions when individual employers transfer their work to the level of business to generate income. In such circumstances, they must obey the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and fulfill the duties assigned to the individual entrepreneur.
Drawing up an employment contract: how to use the professional standard?
It doesn’t matter what you choose - an employment contract in its classic version or an effective contract - in any case, it specifies the employee’s labor functions - this is not a wish, but a necessity. To do everything right, you should be guided by professional standards.
It is considered a mistake to indicate only the position in the employment contract, because it is not a labor function. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Article 57 regulates its content. It is separately emphasized that it is necessary to reflect in the text “work according to the position”, and not just its title. Often, employers violate the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, not suspecting that the fine for this offense can be a very significant amount - from 50 to 100 thousand rubles. Moreover, they can be summed up if the inspector finds a violation in several employment contracts.
So, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the labor function must be prescribed, but how to do this correctly? By simply rewriting a job description into a standard employment contract, the employer is essentially tying his own hands. Professional standards are designed to help in this matter.
We cancel the agreement
The employer has the legal right to cancel the agreement. Yes, Art. 61 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that if a new employee does not start work on the appointed day, the employer can cancel the concluded contract. A canceled employment contract is considered not concluded (Part 4 of Article 61 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In case of cancellation of the contract, the employer does not bear any obligations to the employee. At the same time, the employee retains the right to receive social insurance if, during the period from the date of conclusion of the contract to the day of its cancellation, an insured event occurs to him.
Contract – separately, job description – separately
You can often encounter a situation where an employee’s job description is simply rewritten into an employment contract. The employer is reinsured and complies with Art. 57 of labor legislation, but this is not entirely correct.
With this approach, the instruction is part of the employment contract, which means that changes to it can only be made with the consent of the employee (it is given in writing), since they will directly relate to a change in the labor function - this is confirmed by Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. When an employee does not agree, nothing can be changed and it is also not possible to fire him.
In order to reserve the opportunity to make adjustments to the employee’s duties and at the same time comply with the requirements of labor legislation, the employer can reflect in the contract only general labor functions, which can be found in the professional standard. They are indicated depending on the level of qualification of the specialist. But in the job description, drawn up in a separate document, the employer already indicates the algorithm of actions for a specific employee.
How to distinguish a function from an action? It's actually simple. A labor function is a task, and actions are specific operations, which together constitute an algorithm for its implementation.
Place of work.
The Labor Code does not define the concept of “place of work”; therefore, in practice, employers either do not indicate the place of work at all, or indicate it incorrectly - they specify the place of work in detail, indicating the address of the organization, or too abstractly.
We emphasize: the name of the employer must be indicated as the place of work in the employment contract. The Review of the practice of consideration by courts of cases related to the implementation of labor activities by citizens in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, approved by the Presidium of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation on February 26, 2014, states that in the theory of labor law, a place of work is understood as located in a certain locality (settlement). ) a specific organization, its representative office, branch, or other separate structural unit.
If you specify the place of work too specifically, the employer risks the following: if the organization moves, the employee will refuse to move and will need to pay him compensation. Moreover, this is possible not only if you move to another area, but also simply if you change the location of your office or production. After all, the company address indicated in the employment contract is an essential condition and the employer cannot change it unilaterally. Accordingly, even if the location of the office is changed, it will be necessary to comply with the requirements of Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with all the ensuing consequences.
If the place of work is vague, for example, only the name of the company is given, the employer may have problems dismissing the employee for absenteeism. In this case, the employee will say that the workplace named by the employer during the trial and the workplace at which the dismissed person was supposed to be present (and was present) are significantly different. For example, if an organization has several sites where the main economic activities are carried out (several sites where repair work is carried out, several points of distribution of goods, etc.), then the employee has a real opportunity in the event that the employer indicates his absence at one such facility, talk about your work at another.
We propose the following wording of the place of work in the employment contract, which inspectors do not find fault with.
“Place of work of the employee: Pravda LLC, Nizhny Novgorod.”
If an employee is accepted into a separate structural unit, the condition can be formulated as follows:
“Place of work of the employee: Pravda LLC, Arzamas branch, Arzamas.”
Transformation of the employment contract
The general procedure for amending employment contracts is established by Article 74 of the labor legislation. At the initiative of the employer (in other words, unilaterally), this can happen in the event of a change in working conditions of an organizational and technological nature. It is this provision that should be followed when implementing an effective contract.
When introduced, key changes will affect the terms of the employment contract relating to remuneration and employee responsibilities. In this case, the employer is obliged to indicate the reasons for the adjustment and justify them as inevitable. It is necessary to refer to changes in the conditions regarding remuneration and the Program approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, which established clear criteria and performance indicators.
How to change a job description?
Can an employer change his job description without the employee’s consent? The answer is yes. It is a local normative act. It is not the employee’s labor function that is subject to adjustment, but his actions. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not prohibit this. In this case, there is no need to notify the employee 2 months in advance and obtain his consent to this procedure. It is enough just to familiarize him with the updated job description. However, it is important to remember that when adding new labor actions to it, it is necessary to ensure that they do not contradict and comply with the general labor functions specified in the contract. In practice, it often happens when, for example, a cleaner is given the duties of a janitor, as they say, “as a burden.” In this form, this situation is unacceptable.
If an employer wants to assign any new job functions to an employee that are not part of his professional standard, this will have to be done in a different way. The algorithm of actions is as follows. First, with the consent of the employee, he adds a general labor function from the second professional standard to the employment contract, and only then begins to develop a new job description. In this case, the employee will already have to meet the requirements of two professional standards.
The legislation allows for changes in the labor function; this right of the employer and employee is enshrined in Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This action is formalized by transfer to another job, and it can be either temporary or permanent.
Before regulatory authorities
Law N 294-FZ and the Regulations impose responsibilities on the employer when carrying out an inspection:
- The head of a company or enterprise must, in accordance with Article 12 Part 5 of Law No. 294, provide documents for verification only if the documentation has not been verified before.
Providing documents to regulatory authorities is one of the employer’s responsibilities
Accordingly, it is necessary to formalize in writing (an inventory or acceptance certificate) the issuance of documents for verification with a list, details, and number of sheets. The inventory in 2 copies is signed by the head or authorized executor of the company, indicating the position, deciphering the signature, and indicating the date and time of delivery.
The act is signed by the person carrying out the inspection. The document stipulates that the information should be used only for control activities. One copy of the inventory remains with the company or organization, the second is attached to the package of documents. This procedure confirms the necessary fulfillment of duties (Article 88 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- During the inspection, the presence of the head of the organization or an authorized person is required.
- The employer ensures free entry of inspectors into the area of his organization, to all structures that are used in the course of business work, to equipment and vehicles (paragraph 8, clause 8 of the Regulations).
- The employer, in a standard log where inspections are taken into account, reflects the fact and progress of the procedure in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated April 30, 2009 N 141.
The commission familiarizes the owner of the organization with the order appointing this event (Article 12, Part 4 of Federal Law No. 294), which indicates the full name of the legal entity. It is not allowed to make corrections or additions to the acts. If the names do not correspond with the order, the manager has the right not to provide documentation.
Change of work function for a while
The work function can be changed for a certain period of time. Thus, Article 72.2 of the labor legislation establishes that an employee can be transferred for a period of up to one year, or until the absent employee returns to another job.
In this case, mutual written consent to change the job function is required. There may not be any (additional) training for the new position. In any case, all aspects of such a translation are negotiated by the parties, and their consent is always required. The exception is situations where there has been an industrial accident, man-made or natural disaster and other exceptional cases that put the life and health of the population at risk. In this situation, a transfer can be completed without the employee’s consent, but the period should not exceed one month.
Is it necessary to conclude an employment contract with an employee, and when?
When applying for a job, an employment contract must be concluded; in a small business, it is optional, but recommended.
Before signing the document, the employer familiarizes the future employee with the regulations of the organization, the collective labor agreement, the provision on trade secrets, other official documents, as well as the norms and working conditions, the rights and responsibilities of employees.
This requirement is fixed in Art. 68 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
If for some reason an employee refuses to sign an act of familiarization and agreement with the documents presented to him, then there is no point in signing an employment contract with him.
An employment contract should be drawn up within three working days from the date on which the employee began his duties specified in the contract.
This provision is enshrined in Art. 67 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The employment contract must be kept in the organization for 75 years, in accordance with clauses 656, 657 of the List of standard documents approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation No. 558 of August 25, 2010, or until the liquidation of the enterprise.
Changing the employee’s job function on a permanent basis
Not a temporary, but a permanent change in the job function is also possible and can be caused by various kinds of circumstances: the initiative of the employee or employer, other objective reasons. Partly the same principles apply as in the previous case.
If the employer initiates a permanent transfer, he will have to obtain the employee’s consent. Registration is carried out according to Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The exception is emergency situations.
The initiative can also come from the employee; moreover, in certain cases he can demand a transfer, then the parties must document this.
In addition, a change in labor function in this form may be caused by such an objective factor as a medical report. In all of the above cases, changes must be made to the employment contract.
Responsibility.
If, after reading the article, you realized that the company most likely made mistakes when concluding employment contracts, it is necessary to correct the shortcomings. If you leave everything as it is, then the inspectors from the State Tax Inspectorate, when they come with an inspection, will definitely issue a fine:
- according to Part 4 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - evasion of execution or improper execution of an employment contract, for example, failure to include any mandatory conditions. This may entail the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles, on individual entrepreneurs - from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles, on legal entities - from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles;
- according to Part 1 of Art. 5.27 – violation of labor laws. This provision will be applied if an error is detected when concluding an agreement - refusal to conclude, failure to draw up an agreement in two copies, etc. Punishment includes a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine on officials, as well as individual entrepreneurs in the amount of 1,000 to 5 000 rubles, for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
If such errors are detected again, the company may be fined up to RUB 200,000.
Does the transfer formalize the renaming of a position?
In practice, you can often encounter a situation where, for one reason or another, the title of a position changes. For example, there was an “OT engineer”, but became an “OT specialist” or “forwarding driver” - just “driver”.
As a rule, not only the title of the position is changed, but also the range of job responsibilities along the way. In this case, we are talking about the transfer of an employee.
If there is a change in position without changing the job function, the transfer to another job is not formalized. Nevertheless, even partial renaming should be regarded as an adjustment to the employment contract. Therefore, it is important to document everything. First of all, changes are made to the existing staffing table, then to the employment contract with the employee and his work book.
Is it necessary to bring the job title in accordance with the professional standard?
There is no direct indication that it is the employer's responsibility to rename all existing positions in its staffing table in accordance with appropriate professional standards. However, if the organization plans to implement them one way or another, it would be advisable to do so. It is necessary to issue an order of appropriate content. All employees who are directly affected by them should be made aware of the upcoming changes. Please note that the law does not oblige the employer to immediately implement professional standards for all employees. The transition can be planned or gradual.
Conditions on compulsory social insurance.
Employers forget to indicate this condition, mainly because they do not know how to formulate it. However, if the employment contract does not contain a clause on employee insurance, then even if the company actually transfers contributions to all necessary funds, the employer may be fined for the absence of this clause. This condition can be formulated as follows:
“The employee is subject to all types of compulsory social insurance in connection with work activities. The types and conditions of compulsory social insurance of an employee in connection with work activities are carried out by the Employer in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.”